
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 14, 2007
Registration No. 333-139572
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Amendment No. 2
to
Form S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 2813 | 20-5913059 | ||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
717 Texas Avenue, Suite 3100
Houston, Texas 77002
(713) 659-1361
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of registrant’s principal executive offices)
Don A. Turkleson
Chief Financial Officer
717 Texas Avenue, Suite 3100
Houston, Texas 77002
(713) 659-1361
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
| Geoffrey K. Walker Andrews Kurth LLP 600 Travis, Suite 4200 Houston, Texas 77002 (713) 220-4200 |
Joshua Davidson Sean T. Wheeler Baker Botts L.L.P. One Shell Plaza 910 Louisiana Street Houston, Texas 77002 (713) 229-1234 |
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public: As soon as practicable after this Registration Statement becomes effective.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. ¨
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
The Registrant hereby amends this Registration Statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the Registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this Registration Statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or until the Registration Statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
The information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
SUBJECT TO COMPLETION, DATED FEBRUARY 14, 2007
P R O S P E C T U S

12,500,000 Common Units
Representing Limited Partner Interests
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
$ per unit
We are a limited partnership recently formed by Cheniere Energy, Inc., or Cheniere. This is the initial public offering of our common units. This prospectus relates to an estimated 5,210,331 common units to be offered by us and an estimated 7,289,669 common units to be offered by Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC, an affiliate of Cheniere. The allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder will vary based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund a distribution reserve. We expect the initial public offering price to be between $ and $ per unit. The selling unitholder has granted the underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to an additional 1,875,000 common units to cover over-allotments. We will not receive any proceeds from any common units sold by the selling unitholder. We have applied to list our common units on the American Stock Exchange under the symbol “CQP.”
We will establish a distribution reserve with the net proceeds that we receive from this offering, which will be used to fund the payment of the initial quarterly distribution of $0.425 per unit on all common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, through the quarter ending June 30, 2009.
Investing in our common units involves risks. Please read “ Risk Factors” beginning on page 18.
These risks include the following:
| • | We are a development stage company without any revenues, operating cash flows or operating history. If our efforts to complete construction of the Sabine Pass liquefied natural gas, or LNG, receiving terminal are unsuccessful or substantially delayed for any reason, you may lose all or a portion of your investment. |
| • | We are dependent on three customers for all of our revenue. If any of these customers fails to perform under its terminal use agreement, or TUA, for any reason, our business will be materially and adversely affected and you may lose all or a portion of your investment. |
| • | Until we begin to receive significant cash flows under our TUAs, which we expect to occur in 2009, our distributions to you will come from the distribution reserve and will be a return of your investment. |
| • | Half of our contracted TUA revenue is from an affiliate of our general partner, Cheniere Marketing, which has a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy. |
| • | If Cheniere Marketing is unable to enter into commercial arrangements for the use of its contracted capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or otherwise generate funds, it will be unable to make its TUA payments without financial support from Cheniere, which has guaranteed Cheniere Marketing’s obligations under its TUA. Cheniere has a non-investment grade corporate rating of B. |
| • | Cheniere Marketing’s ability to satisfy its obligations under its TUA is dependent on favorable industry conditions, including increased demand for LNG in the United States. |
| • | The indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes issued to fund construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal prohibits cash distributions to us unless specified conditions have been satisfied, including a fixed charge coverage ratio test. Because payments under the other two customers’ TUAs will not provide sufficient coverage, substantial additional revenues from the Cheniere Marketing TUA or from other sources will be required after March 31, 2009 to satisfy the indenture test. If these additional payments are not received from the Cheniere Marketing TUA or from other sources, or if Cheniere Marketing makes the payments but those payments are not considered revenue under generally accepted accounting principles, the indenture will prevent Sabine Pass LNG from making distributions to us. As a result, we would be unable to make any distributions on our common units. |
| • | Cheniere is not restricted from competing with us and is free to develop, operate and dispose of, and is currently developing, LNG receiving terminals, pipelines and other assets without any obligation to offer us the opportunity to develop or acquire those assets. |
| • | Our general partner and its affiliates have conflicts of interest and limited fiduciary duties, which may permit them to favor their own interests to your detriment. |
| • | Holders of our common units are not entitled to elect our general partner or its directors. |
| • | You may be required to pay taxes on income from us even if you do not receive any cash distributions from us. |
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or passed upon the adequacy or accuracy of this prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
| Per Common Unit |
Total | |||||
| Initial public offering price |
$ | $ | ||||
| Underwriting discount(1) |
$ | $ | ||||
| Proceeds to Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. |
$ | $ | ||||
| Proceeds to selling unitholder (before expenses) |
$ | $ | ||||
| (1) | Includes a structuring fee equal to 0.50% of the gross proceeds of this offering, or approximately $ million, payable to Citigroup Global Markets Inc. |
The underwriters expect to deliver the common units on or about , 2007.
| Citigroup | Merrill Lynch & Co. | Credit Suisse |
, 2007

You should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus. We have not, and the underwriters and selling unitholder have not, authorized anyone to provide you with different information. If anyone provides you with different or inconsistent information, you should not rely on it. We are not, and the underwriters and selling unitholder are not, making an offer to sell these securities in any jurisdiction where an offer or sale is not permitted. You should assume that the information appearing in this prospectus is accurate only as of the date on the front cover of this prospectus. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may have changed since that date.
| Page | ||
| 1 | ||
| 1 | ||
| 6 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 14 | ||
| Selected Financial Data of Our Combined Predecessor Entities |
17 | |
| 18 | ||
| 18 | ||
| Risks Relating to Completion of the Sabine Pass LNG Receiving Terminal |
19 | |
| 23 | ||
| 28 | ||
| 36 | ||
| 41 | ||
| 44 | ||
| 45 | ||
| 46 | ||
| 47 | ||
| 47 | ||
| 49 | ||
| 58 | ||
| 58 | ||
| 59 | ||
| 61 | ||
| 62 | ||
i
| Page | ||
| 84 | ||
| 84 | ||
| 87 | ||
| 87 | ||
| 87 | ||
| 87 | ||
| 89 | ||
| 90 | ||
| 92 | ||
| 98 | ||
| 99 | ||
| 100 | ||
| 101 | ||
| 102 | ||
| 102 | ||
| 103 | ||
| 103 | ||
| 106 | ||
| 108 | ||
| 112 | ||
| 116 | ||
| 116 | ||
| 121 | ||
| 121 | ||
| 122 | ||
| 122 | ||
| 123 | ||
| 123 | ||
| 124 | ||
| 126 | ||
| 126 | ||
| 127 | ||
| 128 | ||
| Page | ||
| Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and the Selling Unitholder |
129 | |
| 131 | ||
| Distributions and Payments to Our General Partner and Its Affiliates |
131 | |
| 133 | ||
| 133 | ||
| 133 | ||
| 133 | ||
| 134 | ||
| Sabine Pass LNG General Partner Management Services Agreement |
134 | |
| 134 | ||
| 134 | ||
| 135 | ||
| 135 | ||
| 136 | ||
| 136 | ||
| 140 | ||
| 143 | ||
| 143 | ||
| 143 | ||
| 143 | ||
| 145 | ||
| 145 | ||
| 145 | ||
| 145 | ||
| 145 | ||
| 145 | ||
| 147 | ||
| 147 | ||
| 148 | ||
| 149 | ||
| 151 | ||
| 151 | ||
ii
| Page | ||
| 152 | ||
| 152 | ||
| 153 | ||
| 154 | ||
| 154 | ||
| 154 | ||
| 155 | ||
| 156 | ||
| 156 | ||
| 156 | ||
| 157 | ||
| 157 | ||
| 158 | ||
| 158 | ||
| 158 | ||
| 159 | ||
| 160 | ||
| 161 | ||
| 161 | ||
| 163 | ||
| Page | ||
| 163 | ||
| 168 | ||
| 169 | ||
| 171 | ||
| 171 | ||
| 172 | ||
| 174 | ||
| Investment in Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. by Employee Benefit Plans |
176 | |
| 177 | ||
| 180 | ||
| 180 | ||
| 180 | ||
| 180 | ||
| 181 | ||
| 181 | ||
| F-1 | ||
| A-1 | ||
| B-1 | ||
References in this prospectus to “Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.,” “we,” “our,” “us” or like terms when used in a historical context refer to the business conducted by Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and its general partner and limited partner, the equity interests of which are being contributed to Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. in connection with this offering. When used in the present tense or prospectively, those terms refer to Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. and its subsidiaries. References to “Cheniere” with respect to periods prior to the closing of this offering mean Cheniere Energy, Inc., together with its subsidiaries, as the historical owner and operator of our business, while those references with respect to periods from and after the closing of this offering mean Cheniere Energy, Inc., together with its subsidiaries, as the indirect owner of our general partner. References to “Sabine Pass LNG” refer to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., our indirect wholly-owned subsidiary. References to the “selling unitholder” and “Cheniere Holdings” refer to Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC, an indirect subsidiary of Cheniere and our sole limited partner prior to the closing of this offering.
iii
This summary highlights information contained elsewhere in this prospectus. It does not contain all of the information that you should consider before investing in the common units. You should read the entire prospectus carefully, including the historical financial statements and the notes to those financial statements. You should read “Risk Factors” for information about important risks to consider before buying our common units. Unless otherwise indicated, the information presented in this prospectus assumes an initial offering price per common unit of $20.00 and that the underwriters’ option to purchase additional units is not exercised.
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
Overview
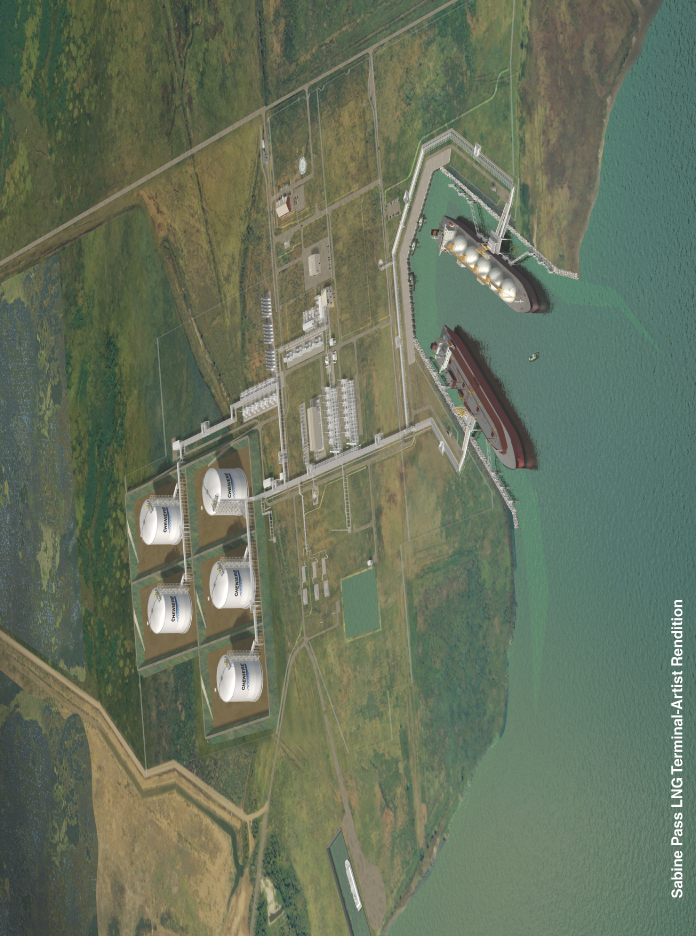
We are a Delaware limited partnership recently formed by Cheniere Energy, Inc. Through our wholly-owned subsidiary, Sabine Pass LNG, we will develop, own and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal currently under construction in western Cameron Parish, Louisiana on the Sabine Pass Channel.
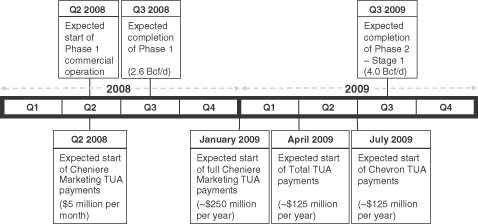
Construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal began in March 2005. Upon completion of construction, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be the largest LNG receiving terminal in North America with approximately 4.0 billion cubic feet per day, or Bcf/d, of regasification capacity and approximately 16.8 Bcf of LNG storage capacity. All of this capacity has been contracted for under three 20-year, firm commitment terminal use agreements, or TUAs. Each customer must make payments on a “take-or-pay” basis, which means that the customer will be obligated to pay the full contracted amount of monthly fees whether or not it uses any of its reserved capacity. Provided the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal has achieved the required level of commercial operation, which we expect will occur in the third quarter of 2008, these “take-or-pay” TUA payments will be made as follows:
| • | Total LNG USA, Inc., or Total, has reserved approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $125 million per year for 20 years commencing April 1, 2009. Total, S.A. has guaranteed Total’s obligations under its TUA up to $2.5 billion. Total, S.A. has Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s corporate ratings of Aa1 and AA, respectively. |
| • | Chevron U.S.A., Inc., or Chevron, has reserved approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $125 million per year for 20 years commencing not later than July 1, 2009. Chevron Corporation has guaranteed up to 80% of the fees payable by Chevron under its TUA. Chevron Corporation has Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s corporate ratings of Aa2 and AA, respectively. |
| • | Cheniere Marketing, Inc., or Cheniere Marketing, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere, has reserved approximately 2.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity, is entitled to use any capacity not utilized by Total and Chevron and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $250 million per year for at least 19 years commencing January 1, 2009. In addition, Cheniere Marketing has agreed to make payments of $5 million per month during an initial commercial operations ramp-up period in 2008. Cheniere has guaranteed Cheniere Marketing’s obligations under its TUA. Cheniere has no Moody’s rating and a Standard & Poor’s corporate rating of B. |
The Sabine Pass LNG Receiving Terminal
The initial phase, or Phase 1, of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal was designed, and permitted by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, or the FERC, with a regasification capacity of 2.6 Bcf/d, three LNG storage tanks with an aggregate LNG storage capacity of 10.1 billion cubic feet, or Bcf, and two unloading docks capable of handling the largest LNG carriers currently being operated or built. In July 2006, Sabine Pass LNG
1
received approval from the FERC to increase the regasification capacity of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal from 2.6 Bcf/d to 4.0 Bcf/d by adding up to three additional LNG storage tanks, additional vaporizers and related facilities. We refer to the entire FERC-approved expansion as Phase 2. The first stage of the Phase 2 expansion will include two additional LNG storage tanks, additional vaporizers and related facilities, and will achieve a full operability at approximately 4.0 Bcf/d and an aggregate storage capacity of approximately 16.8 Bcf. We refer to this expansion as Phase 2 – Stage 1. We will conduct further Phase 2 expansion, if any, including construction of a potential sixth LNG storage tank, in one or more subsequent stages.
The timeline below sets forth the anticipated timing for completing construction of Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and the timing of payments to Sabine Pass LNG under the TUAs.
We estimate that the cost to construct Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be approximately $900 million to $950 million, before financing costs. We estimate that the cost to construct Phase 2 – Stage 1 will be approximately $500 million to $550 million, before financing costs. These cost estimates are subject to change due to such items as cost overruns, change orders, delays in construction, increased component and material costs, escalation of labor costs and increased spending to maintain the construction schedule. As of December 31, 2006, Sabine Pass LNG had paid $564.2 million and $44.0 million of Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 construction costs, respectively. The remaining construction expenditures will be funded by Sabine Pass LNG from a construction account established in November 2006 with $886.7 million of the proceeds from the issuance of $2,032 million of its senior secured notes, which we refer to as the Sabine Pass LNG notes. Please read “Indebtedness” for more information about the Sabine Pass LNG notes and, among other things, the restricted payment requirements imposed on Sabine Pass LNG by the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes.
Business Objectives
Our primary business objectives are to complete construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and, thereafter, to generate stable cash flows sufficient to pay the initial quarterly distribution to our unitholders and, over time and upon satisfaction of these objectives, to increase our quarterly cash distribution.
Competitive Strengths
We believe that we have several strengths in pursuing our business objectives and strategies, including:
| • | three long-term TUAs providing for contracted and stable cash flows; |
2
| • | solid arrangements with Bechtel Corporation, or Bechtel, for the construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | what we believe is one of the best available North American sites for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | ample access, currently under development, to natural gas transmission pipelines |
| • | economies of scale in operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | an environmentally sound and community friendly approach in developing the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; and |
| • | an experienced management team. |
Our Relationship with Cheniere
Cheniere is the indirect owner of our general partner, as well as of our common and subordinated units that will represent a 90.4% limited partner interest in us upon completion of this offering. Cheniere is engaged primarily in the business of developing onshore LNG receiving terminals, and related natural gas pipelines, along the Gulf Coast of the United States. Cheniere is also developing a business to market LNG and natural gas, primarily through Cheniere Marketing. To a limited extent, Cheniere is also engaged in oil and natural gas exploration and development activities in the Gulf of Mexico.
Cheniere Marketing has entered into a TUA for all of the regasification capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal not reserved and utilized by Total and Chevron. As a result, approximately 50% of our anticipated combined revenues will be attributable to fees paid by Cheniere Marketing under its TUA with Sabine Pass LNG, which will be guaranteed by Cheniere. Cheniere Marketing is a small, development stage company, with a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy. Cheniere Marketing’s business plan is to purchase LNG on a short-term and long-term basis, to regasify the LNG at Sabine Pass LNG or other LNG receiving terminals, and to trade natural gas and market regasified LNG in North America and other worldwide natural gas markets. It intends to earn a profit on the purchase of LNG and sale of natural gas after paying its TUA and pipeline fees and other operating expenses. Cheniere Marketing has no agreements or arrangements for supplies of LNG, a limited history of trading natural gas and no unconditional commitments from customers for the purchase of natural gas.
In addition to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Cheniere has two other LNG receiving terminals that are currently in early stages of development: the Corpus Christi LNG receiving terminal near Corpus Christi, Texas, and the Creole Trail LNG receiving terminal at the mouth of the Calcasieu Channel in central Cameron Parish, Louisiana. If constructed in accordance with the permits that have been issued by the FERC, these two terminals would have an aggregate designed regasification capacity of approximately 5.9 Bcf/d. Cheniere is also developing, and anticipates constructing, natural gas pipelines to connect each of the three LNG receiving terminals to North American natural gas markets.
In the future, we may have opportunities to acquire some or all of these assets from Cheniere at an appropriate stage of commercialization and development, although we cannot predict whether any acquisitions will be made available to us or whether we will pursue or complete any future acquisitions. Our relationship with Cheniere also provides us with access to Cheniere’s management talent, market insights and significant industry relationships. Although we believe that our relationship with Cheniere is a strength, it is also a source of conflicts of interest. Cheniere is not restricted from competing with us and is free to develop, operate and dispose of, and is currently developing, LNG receiving terminals, pipelines and other assets without any obligation to offer us the opportunity to develop or acquire those assets. Please read “Conflicts of Interest and Fiduciary Duties.”
3
Independent Engineer’s Report
This prospectus contains a report by Stone & Webster Management Consultants, Inc., or the Independent Engineer. The Independent Engineer is a leading consulting and engineering firm that devotes a substantial portion of its resources to providing services related to the technical, environmental and economic aspects of industrial facilities. The Independent Engineer’s report analyzes certain construction, technical, environmental and economic aspects of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. This report includes, among other things, discussions of the technology used at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, engineering and construction execution issues and costs, operating plans, timing matters, environmental permitting status, and a technical review of the construction and related documents pertaining to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. A copy of the report is attached as Appendix B to this prospectus and should be read in its entirety.
In the preparation of its report, the Independent Engineer has relied on assumptions regarding circumstances beyond the control of us or any other person. By their nature, these assumptions are subject to significant uncertainties, and actual results will differ, perhaps materially, from those stated in the report. We cannot give any assurance that these assumptions will prove to be correct. If our actual results are materially less favorable than those shown in the Independent Engineer’s report, or if the assumptions prove to be incorrect, Sabine Pass LNG’s ability to pay distributions to us, and our ability to pay distributions to our unitholders, may be adversely affected.
Summary of Risk Factors
An investment in our common units involves risks associated with our business, our partnership structure and the tax characteristics of our common units. Those risks are described under the caption “Risk Factors” and include:
Risks Relating to Our Business in General
| • | We are a development stage company without any revenues, operating cash flows, operating history or experience constructing, operating or maintaining an LNG facility, and if we are unable to complete construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or if our customers fail to perform under their contracts for whatever reason, our business will be materially and adversely affected and you could lose all or a significant portion of your investment. |
| • | Until we begin to receive cash flows under all three of our TUAs in 2009, all or a portion of our distributions to you will be a return of your investment. |
| • | Our substantial indebtedness could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and to pay or increase distributions to you. |
Risks Relating to Completion of the Sabine Pass LNG Receiving Terminal
| • | Sabine Pass LNG’s inability to timely construct and commission the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal would prevent it from commencing operations when anticipated and would delay or prevent it, and consequently us, from realizing anticipated cash flows. Factors that might delay or prevent completion of construction include failure of the contractors to fulfill their contractual obligations, failure to enter additional agreements with contractors, shortages of materials, difficulty in financing any cost overruns, difficulties in obtaining LNG for commissioning activities, failure to obtain necessary governmental and third-party permits, weather conditions and other catastrophes, labor shortages or disputes, and local community resistance. |
| • | We are dependent on Bechtel and other contractors for the successful completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
4
| • | We may experience cost overruns. |
Risks Relating to Our Cash Distributions
| • | We may not have sufficient cash from operations to enable us to fund the initial quarterly distribution following establishment of cash reserves and payment of fees and expenses, including payments to our general partner and funding of capital expenditures. |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG may be restricted under the terms of the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes from making distributions to us and from incurring additional indebtedness under certain circumstances, which may limit our ability to pay or increase distributions to you. |
| • | Cost reimbursements and management fees due to our general partner and its affiliates will reduce cash available to pay distributions to you. |
| • | Our financial estimates, including our forecast of cash available for distribution, and our Independent Engineer’s conclusions are based on certain assumptions that may not materialize. |
Risks Relating to Development and Operation of Our Business
| • | We will be dependent for substantially all of our revenues and cash flows on the TUA counterparties, including Cheniere Marketing, which has a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy. |
| • | After the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is placed in service, its business will involve significant operational risks. |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG may be required to purchase more natural gas than anticipated to provide fuel at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which would increase operating costs and could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. |
| • | The inability to import LNG into the U.S. could materially adversely affect our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, and our business plans and results of operations if Sabine Pass LNG has to replace TUAs that terminate or expire. |
| • | Failure of sufficient LNG liquefaction capacity to be constructed worldwide could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions. |
| • | A shortage of LNG tankers worldwide could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions. |
| • | Failure of imported LNG to become a competitive source of energy in North America could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions. |
| • | Decreases in the price of natural gas could lead to reduced development of LNG projects worldwide, which could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions. |
| • | Cyclical changes in the demand for LNG regasification capacity may adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions. |
5
| • | We may face competition from competitors with far greater resources, as well as potential overcapacity in the LNG receiving terminal marketplace. |
Risks Relating to an Investment in Us and Our Common Units
| • | Our general partner and its affiliates have conflicts of interest and limited fiduciary duties, which may permit them to favor their own interests to the detriment of us and our unitholders. |
| • | Cheniere is not restricted from competing with us and is free to develop, operate and dispose of, and is currently developing, LNG receiving terminals, pipelines and other assets without any obligation to offer us the opportunity to develop or acquire those assets. |
| • | Our partnership agreement limits our general partner’s fiduciary duties to unitholders and restricts the remedies available to unitholders for actions taken by our general partner that might otherwise constitute breaches of fiduciary duty. |
| • | Even if unitholders are dissatisfied, they cannot initially remove our general partner without its consent. |
| • | Our general partner has a limited call right that may require you to sell your common units at an undesirable time or price. |
| • | You will experience immediate and substantial dilution of $20.95 per common unit. |
Risks Relating to Tax Matters
| • | Our tax treatment depends on our status as a partnership for federal income tax purposes, as well as our not being subject to a material amount of entity level taxation by individual states. If the Internal Revenue Service, or IRS, were to treat us as a corporation or if we were to become subject to a material amount of entity level taxation for state tax purposes, then our cash available for distribution to you would be substantially reduced. |
| • | A successful IRS contest of the federal income tax positions that we take may adversely impact the market for our common units, and the costs of any contests will be borne by our unitholders and our general partner. |
| • | You may be required to pay taxes on your share of our taxable income even if you do not receive any cash distributions from us. |
| • | Tax gain or loss on the disposition of our common units could be different than expected. |
Formation Transactions and Partnership Structure
General
We are a Delaware limited partnership formed in November 2006. At the closing of this offering, the following transactions will occur:
| • | Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC, which we refer to as Cheniere Holdings, will contribute through us to our wholly-owned subsidiary, Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC, all of its equity interests in Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC, which own all of the equity interests in Sabine Pass LNG; |
| • | we will issue to Cheniere Holdings 21,206,026 common units and 135,383,831 subordinated units; |
| • | we will issue to our general partner, a direct wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere Holdings, 3,302,045 general partner units representing a 2% general partner interest in us and all of our incentive distribution rights, which will entitle our general partner to increasing percentages of the cash that we distribute in excess of $0.489 per unit per quarter; |
6
| • | we will issue an estimated 5,210,331 common units to the public in this offering; |
| • | we will use our net proceeds from this offering to deposit approximately $96.7 million into a distribution reserve account as described in “—The Offering;” |
| • | Cheniere Holdings will sell an estimated 7,289,669 common units to the public in this offering, after which Cheniere Holdings and the public will have an estimated aggregate 90.4% and 7.6% limited partner interest in us, respectively; |
| • | our general partner will enter into a services agreement with an affiliate of Cheniere under which it will provide various general and administrative services following the closing of this offering for an annual administrative fee of $10 million (adjusted for inflation after January 1, 2007), with payment commencing January 1, 2009; and |
| • | our general partner will enter into a services and secondment agreement pursuant to which we anticipate that certain employees of a Cheniere affiliate will be seconded to our general partner to provide operating and routine maintenance services with respect to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
The allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder will vary based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund the distribution reserve at the time we price the offering, which we currently believe will be approximately $96.7 million. Any net proceeds that we receive in excess of the amount necessary to fund the distribution reserve will be distributed to the selling unitholder, and any shortfall in that amount will be contributed to us by the selling unitholder.
As is common with publicly traded limited partnerships and in order to maximize operational flexibility, we will conduct our operations through subsidiaries.
7
Organizational Structure
The following table and diagram depict our ownership and organizational structure, after giving effect to this offering and the related transactions, and our relationship with Cheniere and Cheniere Marketing.
| Public Common Units(1) |
7.6 | % | |
| Cheniere Affiliate Common Units(1) |
8.4 | % | |
| Cheniere Affiliate Subordinated Units |
82.0 | % | |
| General Partner Units |
2.0 | % | |
| Total |
100.0 | % | |
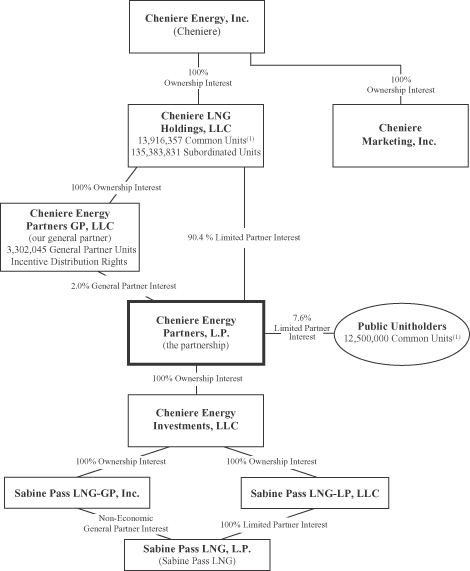
| (1) | The allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder (and the corresponding limited partner interest of the selling unitholder and the public) will vary based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund the distribution reserve at the time that we price the offering, which we currently believe will be approximately $96.7 million. |
8
Management of Our Partnership
Our general partner, Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC, will manage our operations and activities. Cheniere indirectly owns and controls our general partner. An affiliate of Cheniere will receive an annual administrative fee of $10 million (adjusted for inflation after January 1, 2007), with payment commencing January 1, 2009, for the provision of various general and administrative services to us. Such affiliate will also be entitled to reimbursement of all direct expenses incurred on our behalf following the closing of this offering. Our general partner will also be entitled to distributions on its general partner units and, if specified requirements are met, on its incentive distribution rights. Please read “Cash Distribution Policy and Restrictions on Distributions” and “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions.” Unlike stockholders in a publicly traded corporation, our unitholders will not be entitled to elect our general partner or its directors.
Principal Executive Offices and Internet Address
Our principal executive offices are located at 717 Texas Avenue, Suite 3100, Houston, Texas 77002, and our telephone number is (713) 659-1361. Our website is http://www.cheniereenergypartners.com. We will make our periodic reports and other information filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, available, free of charge, through our website, as soon as reasonably practicable after those reports and other information are electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. Information on our website or any other website is not incorporated by reference into this prospectus and does not constitute a part of this prospectus.
Summary of Conflicts of Interest and Fiduciary Duties
Our general partner has a fiduciary duty to manage us in a manner beneficial to our unitholders. However, because our general partner is indirectly wholly-owned by Cheniere, the officers and directors of our general partner also have fiduciary duties to manage the business of our general partner in a manner beneficial to Cheniere. Certain of the executive officers and non-independent directors of our general partner also serve as executive officers and directors of Cheniere. As a result of these relationships, conflicts of interest exist and may arise in the future between us and our unitholders, on the one hand, and our general partner and its affiliates, on the other hand. Cheniere and its affiliates may compete directly with us and do not have an obligation to present business opportunities to us. For more detailed descriptions of the conflicts of interest of our general partner, please read “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to an Investment in Us and Our Common Units” and “Conflicts of Interest and Fiduciary Duties—Conflicts of Interest.”
Our partnership agreement limits the liability and reduces the fiduciary duties of our general partner to our unitholders. Our partnership agreement also restricts the remedies available to unitholders for actions that might otherwise constitute a breach of our general partner’s fiduciary duties owed to our unitholders. By purchasing a common unit, you are treated as having consented to various actions contemplated in the partnership agreement and to conflicts of interest that might otherwise be considered a breach of fiduciary or other duties under applicable state law. Please read “Conflicts of Interest and Fiduciary Duties—Fiduciary Duties” for a description of the fiduciary duties imposed on our general partner by Delaware law, the material modifications of these duties contained in our partnership agreement and certain legal rights and remedies available to our unitholders.
For a description of our other relationships with our affiliates, especially Cheniere Marketing, please read “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions.”
9
| Common units offered by us |
An estimated 5,210,331 common units. |
| Common units offered by the selling unitholder |
An estimated 7,289,669 common units, or 9,164,669 common units if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional units in full. |
The allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder will vary based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund a distribution reserve.
| Units outstanding after this offering |
26,416,357 common units, representing a 16% limited partner interest, 135,383,831 subordinated units, representing an 82% limited partner interest, and 3,302,045 general partner units, representing a 2% general partner interest. |
| Use of proceeds |
We estimate that we will receive net proceeds of approximately $96.7 million from the sale of our common units in this offering, after deducting the underwriting discount and structuring fee on each unit sold, assuming an initial public offering price of $20.00 per common unit. We will use all of our net proceeds to purchase U.S. treasury securities to fund a distribution reserve to pay the $0.425 initial quarterly distribution on all common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. Any net proceeds that we receive in excess of the amount necessary to fund the distribution reserve will be distributed to the selling unitholder, and any shortfall in that amount will be contributed to us by the selling unitholder. |
| The selling unitholder will pay the same underwriting discount and structuring fee on each unit sold, as well as all offering costs. The selling unitholder has granted the underwriters an option to purchase additional common units to cover over-allotments, if any, in connection with this offering. We will not receive any proceeds from any common units sold by the selling unitholder, including proceeds received from any exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional common units. |
| Distribution reserve |
We will deposit all of the net proceeds that we receive from this offering as a distribution reserve in a separate account. The deposited amount will be invested in U.S. treasury securities maturing as to principal and interest at such times and in such amounts as will be sufficient to pay the $0.425 initial quarterly distribution per common unit for all common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. In the event that we issue additional common units prior to June 30, 2009, we will use a portion of the net proceeds from such issuance to increase the distribution reserve by an amount that our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines is required to fund the initial quarterly distribution for such additional common units and related general partner units from their date of issuance through the |
10
| distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. Any amount remaining in the distribution reserve on August 15, 2009 will be distributed to Cheniere Holdings. We may distribute amounts in the distribution reserve to Cheniere Holdings prior to August 15, 2009 if our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee, determines that such reserves are not necessary to provide for distributions on all of our common units and general partner units for any quarter ending on or prior to June 30, 2009. |
| Anticipated cash distributions |
We must distribute all of our cash on hand at the end of each quarter, less any reserves established by our general partner. We refer to this as available cash, and we define its meaning in our partnership agreement. We expect that we will not have sufficient operating cash flow under the TUAs to pay the full initial quarterly distribution on all the common and general partner units until the third quarter of 2009. Therefore, we will use the distribution reserve to fund the initial quarterly distribution on the common units and general partner units through the quarter ending June 30, 2009. |
| For each calendar quarter, we intend to pay the initial quarterly distribution on all of our outstanding units to the extent that we have sufficient cash in the distribution reserve and from operations, after establishment of cash reserves and payment of fees and expenses, including payments to our general partner and its affiliates. Our ability to pay the initial quarterly distribution is subject to various restrictions and other factors described in more detail under the caption “Cash Distribution Policy and Restrictions on Distributions.” In general, we will pay any cash distributions that we make with respect to each such quarter in the following manner: |
| • | first, 98% to the common units and 2% to our general partner, until each common unit has received the initial quarterly distribution of $0.425 plus any arrearages from prior quarters; |
| • | second, 98% to the subordinated units and 2% to our general partner, until each subordinated unit has received the initial quarterly distribution of $0.425; and |
| • | third, 98% to all units, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until each unit has received an aggregate distribution equal to $0.489; |
| • | fourth, 85% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 15% to our general partner, until each unitholder receives a total of $0.531 per unit for that quarter; |
| • | fifth, 75% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 25% to our general partner, until each unitholder receives a total of $0.638 per unit for that quarter; and |
| • | thereafter, 50% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 50% to our general partner. |
| We refer to distributions to our general partner in excess of 2% as incentive distributions. |
11
| Cash distributions on the common units will generally be made within 45 days after the end of each quarter. The initial quarterly distribution for the period from the closing of this offering through the end of the quarter in which the closing occurs will be adjusted based on the actual length of the period. |
| Subordination period |
During the subordination period, the subordinated units will not be entitled to receive any distributions until the common units have received the initial quarterly distribution plus any arrearages on the initial quarterly distribution from prior quarters. Subordinated units will not accrue arrearages. |
| The subordination period generally will end if: |
| • | we have earned and paid at least $0.425 on each outstanding common unit, subordinated unit and general partner unit for each of the three consecutive, non-overlapping four-quarter periods ending on or after June 30, 2010; or |
| • | if we have earned and paid at least $0.638 (150% of the initial quarterly distribution) on each outstanding common unit, subordinated unit and general partner unit for any four- consecutive quarters ending on or after June 30, 2008. |
| The subordination period will also end upon the removal of our general partner other than for cause if the units held by our general partner and its affiliates are not voted in favor of such removal. Please read “How We Make Cash Distributions—Subordination Period.” |
| When the subordination period ends, all subordinated units will convert into common units on a one-for-one basis, the common units will no longer be entitled to any arrearages and the converted units will then participate pro rata with the other common units in distributions of available cash. |
| Issuance of additional units |
During the subordination period, we may not issue any additional common units or units on a parity with or senior to our common units without the approval of the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner. For any additional common units that we issue prior to June 30, 2009, we must increase the distribution reserve by an amount that our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines is required to fund the initial quarterly distribution on such additional common units and related general partner units from their date of issuance through the distribution in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. After the subordination period, we can issue an unlimited number of additional partnership securities for the consideration and on the terms and conditions determined by our general partner without the approval of the conflicts committee. Please read “Units Eligible for Future Sale” and “The Partnership Agreement—Issuance of Additional Securities.” |
12
| Limited voting rights |
Our general partner will manage and operate us. Unlike the holders of common stock in a corporation, you will have only limited voting rights on matters affecting our business. You will have no right to elect our general partner or the directors of our general partner. Our general partner may not be removed except by a vote of the holders of at least 66 2/3% of the outstanding units, including any units owned by our general partner and its affiliates, voting together as a single class. Upon consummation of this offering, our general partner and its affiliates will own an aggregate of 92.3% of our common and subordinated units (approximately 91.1% if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional common units in full). This will give our general partner the practical ability to prevent its involuntary removal. Please read “The Partnership Agreement—Voting Rights.” |
| Limited call right |
If at any time our general partner and its affiliates own more than 80% of our outstanding common units, our general partner has the right, but not the obligation, to purchase all, but not less than all, of our remaining common units at a price not less than the current market price, as defined in our partnership agreement, of our common units. Please read “The Partnership Agreement—Limited Call Right.” |
| Estimated ratio of taxable income to distributions |
We estimate that if you own the common units you purchase in this offering through the record date for distributions for the period ending December 31, 2009, you will be allocated, on a cumulative basis, an amount of federal taxable income for that period that will be less than % of the cash distributed to you with respect to that period. Please read “Material Tax Consequences—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership” for the basis of this estimate. |
| Material tax consequences |
For a discussion of other material federal income tax consequences that may be relevant to prospective unitholders who are individual citizens or residents of the United States, please read “Material Tax Consequences.” |
| Exchange listing |
We have applied to list our common units on the American Stock Exchange under the symbol “CQP.” |
13
Forecast of Cash Available to Pay Distributions
The following table summarizes our forecast of the expected revenues, EBITDA and cash available to pay the initial quarterly distribution of $0.425 on all of our outstanding common units, subordinated units and general partner units for each of the four quarters in the twelve-month period ending June 30, 2010. Prior to June 30, 2009, we will use funds from the distribution reserve to pay the initial quarterly distribution of $0.425 on all of our outstanding common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner. This information should be read in conjunction with the more detailed information presented in the table illustrating our forecast of cash available for distribution for the period from March 31, 2007 through June 30, 2010, including the accompanying footnotes, explanations and descriptions of assumptions relating thereto, set forth under “Cash Distribution Policy and Restrictions on Distributions.”
The information set forth below summarizes our anticipated results of operations, including the projected revenues under our 20-year TUAs with Total, Chevron and Cheniere Marketing, for the first four consecutive quarters in which we expect to receive operating revenues under all three TUAs. In preparing this information, we have relied on assumptions regarding circumstances beyond the control of us or any other person. By their nature, the assumptions are subject to significant uncertainties, and actual results will differ, perhaps materially, from those forecasted. We cannot give any assurance that these assumptions are correct or that this information will reflect actual results. Accordingly, this forecast is not intended to be a prediction of future results. If our actual results are materially less favorable than those shown, or if the assumptions used in preparing this information prove to be incorrect, our ability to make distributions to our unitholders may be adversely affected. For additional information relating to our financial forecast, please read “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Our Cash Distributions—Our financial estimates, including our forecast of cash available for distribution, and our Independent Engineer’s conclusions are based on certain assumptions that may not materialize.” For information about risks relating to Cheniere Marketing’s business as a development stage company, please read “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Development and Operation of Our Business—We will be dependent for substantially all of our revenues and cash flows on the TUA counterparties, including Cheniere Marketing, which has a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy.”
The operating expenses set forth in the table below for the four quarters ending June 30, 2010 may be higher in later years due to numerous factors, such as increased maintenance costs of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal as the facility ages. As a result, the Sabine Pass LNG EBITDA forecast for the fourth quarter ending June 30, 2010 is not indicative of the Sabine Pass LNG EBITDA that may be achieved in the future. Furthermore, Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA does not include capital expenditures and other non-operating items that require cash expenditures, which over time may be material to our business and may have a significant negative impact on our cash available for payment of interest on, and the principal of, the Sabine Pass LNG notes.
Approximately one-half of our forecast revenues are attributable to Cheniere Marketing, which is a small, development stage company with virtually no operating history. See “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Development and Operation of Our Business—We will be dependent for substantially all of our revenues and cash flows on the TUA counterparties. Cheniere Marketing has a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy and may not be able to make payments to us under its TUA.” We do not expect to generate sufficient cash flow from operations to repay the Sabine Pass LNG notes upon maturity without additional refinancing, which may not be available on terms reasonably acceptable to us or at all. See “Risk Factors—Risk Relating to Our Business in General—Our substantial indebtedness could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and to pay or increase distributions to you.”
14
Forecast of Cash Available for Distribution
Four Quarters Ending June 30, 2010
(in millions)
| TUA revenues(1) |
||||
| Total TUA(2) |
$ | 125.5 | ||
| Chevron TUA(2) |
129.9 | |||
| Cheniere Marketing TUA |
255.7 | |||
| Aggregate TUA revenues |
511.1 | |||
| Deferred revenues(2) |
(4.0 | ) | ||
| Operating expenses of Sabine Pass LNG(3) |
(36.7 | ) | ||
| Assumed commissioning costs(4) |
— | |||
| State and local taxes |
(9.9 | ) | ||
| Sabine Pass LNG EBITDA(5) |
460.5 | |||
| Maintenance capital expenditures(3) |
(1.5 | ) | ||
| Interest on Sabine Pass LNG Notes(6) |
(151.0 | ) | ||
| General and administrative expenses of our partnership(7) |
(13.3 | ) | ||
| Cash available for distribution |
294.7 | |||
| Annual distributions to:(8) |
||||
| Publicly held common units |
(21.3 | ) | ||
| Common units held by affiliates of our general partner |
(23.7 | ) | ||
| Subordinated units held by affiliates of our general partner |
(230.1 | ) | ||
| General partner units held by our general partner |
(5.6 | ) | ||
| Total annual distributions |
(280.7 | ) | ||
| Surplus |
$ | 14.0 | ||
| (1) | Fixed capacity reservation fees, including an operating fee component subject to adjustment for annual consumer price index inflation (assumed to be 2.5% annually). |
| (2) | TUA revenues include $2 million of annual non-cash deferred revenues during the first ten years under each of the Total and Chevron TUAs related to $20 million of advance capacity reservation fees previously received from each of Total and Chevron. |
| (3) | Combined Sabine Pass LNG operating expenses and maintenance capital expenditures are as estimated by us and the Independent Engineer. See the report of the Independent Engineer, attached as Appendix B to this prospectus. Maintenance capital expenditures estimated by us at $1.5 million per year beginning in 2009, escalating with inflation at 2.5% annually thereafter, are presented separately in this table. |
| (4) | We anticipate that these commissioning costs will be paid before the third quarter of 2009. |
| (5) | Calculated as Sabine Pass LNG’s aggregate TUA revenues less non-cash deferred revenues, operating expenses, assumed commissioning costs and state and local taxes. See “—Non-GAAP Financial Measure” below for more information. |
| (6) | Assumes total debt consists solely of the $2,032 million of the Sabine Pass LNG notes, which have a weighted-average fixed interest rate of 7.432% paid semi-annually. |
| (7) | Estimated tax compliance and publicly traded partnership tax reporting, accounting, SEC reporting and other costs of operating as a publicly traded partnership of $2.5 million per year and, commencing January 1, 2009, annual payments of $10 million per year to a Cheniere affiliate for providing general and administrative services to us following the closing of this offering, in each case as adjusted for assumed inflation at 2.5% per year after January 1, 2007. |
15
| (8) | The allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder (and the corresponding distributions to the public and affiliates of the general partner) will vary based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund the distribution reserve at the time that we price the offering, which we currently estimate will be approximately $96.7 million. |
Non-GAAP Financial Measure
Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA is computed as total revenues less non-cash deferred revenues, operating expenses, assumed commissioning costs and state and local taxes. It does not include depreciation expenses and certain non-operating items. Because we have not forecasted such depreciation expense and non-operating items, we have not made any forecast of net income, which would be the most directly comparable financial measure under generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP. As a result, we are unable to reconcile differences between forecasts of EBITDA and net income. EBITDA is used as a supplemental financial measure by management and by external users of our financial statements, such as commercial banks, to assess:
| • | the anticipated financial performance of our assets without regard to financing methods, capital structure or historical cost basis; |
| • | the ability of our assets to generate cash sufficient to pay interest on our indebtedness; and |
| • | our anticipated operating performance and return on invested capital compared to other comparable companies, without regard to their financing methods and capital structure. |
Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA should not be considered an alternative to net income, operating income, cash flows from operating activities or any other measure of financial performance or liquidity presented in accordance with GAAP. Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA excludes some, but not all, items that affect net income and operating income, and these measures may vary among companies. Therefore, Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA may not be comparable to similarly titled measures of other companies.
16
Selected Financial Data of Our Combined Predecessor Entities
The following tables set forth the selected financial data of our combined predecessor entities for the periods and at the dates indicated. Our combined predecessor entities refer to Cheniere Energy Partners and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, including Sabine Pass LNG.
The combined statement of operations data for the period from October 20, 2003 (inception) through December 31, 2006, for the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006, and the combined balance sheet information at December 31, 2005 and 2006 are derived from our audited combined financial statements, which are included elsewhere in this prospectus. The summary combined statement of operations data for the period from October 20, 2003 (inception) through December 31, 2003 and the summary combined balance sheet information at December 31, 2003 and 2004 have been derived from our audited combined financial statements, which are not included in this prospectus. Our past financial or operating performance is not a reliable indicator of our future performance (particularly anticipated revenues, debt costs and expenses), and you should not use our historical performance to anticipate results or future period trends.
We derived the information in the following table from, and that information should be read together with and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, the combined financial statements and the accompanying notes included in this prospectus. The table should also be read together with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
| Combined Predecessor Entities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Period from October 20, 2003 (inception) to December 31, 2003 |
Year ended December 31, |
Period from October 20, 2003 (inception) to December 31, 2006 |
||||||||||||||||||
| 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Operations Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Expenses |
2,763 | 4,682 | 4,719 | 10,277 | 22,441 | |||||||||||||||
| Loss from operations |
(2,763 | ) | (4,682 | ) | (4,719 | ) | (10,277 | ) | (22,441 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other income (expense)(1) |
— | 28 | 456 | (50,495 | ) | (50,011 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (2,763 | ) | $ | (4,654 | ) | $ | (4,263 | ) | $ | (60,772 | ) | $ | (72,452 | ) | |||||
| Cash Flow Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows provided by (used in) operating activities |
$ | 101 | $ | 23,192 | $ | 6,319 | $ | (27,912 | ) | $ | 1,699 | |||||||||
| Cash flows used in investing activities |
(101 | ) | (124 | ) | (246,337 | ) | (1,544,408 | ) | (1,790,968 | ) | ||||||||||
| Cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities |
— | (1,246 | ) | 218,201 | 1,572,322 | 1,789,276 | ||||||||||||||
| Combined Predecessor Entities | ||||||||||||
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | |||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | — | $ | 21,822 | $ | 5 | $ | 7 | ||||
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents (current) |
— | — | 8,871 | 355,327 | ||||||||
| Non-current restricted cash and cash equivalents |
— | — | — | 803,610 | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment |
96 | 212 | 270,740 | 651,676 | ||||||||
| Total assets |
101 | 23,316 | 309,139 | 1,858,114 | ||||||||
| Long-term debt |
— | — | 72,485 | 2,032,000 | ||||||||
| Deferred revenues |
— | 22,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 | ||||||||
| Total other long-term liabilities |
2,864 | 17,418 | 120 | 1,149 | ||||||||
| (1) | The year ended 2006 includes a $23.8 million loss related to the expensing of debt issuance costs and a $20.6 million derivative loss as a result of terminating interest rate swaps, both related to the termination of the Sabine Pass credit facility in November 2006. |
17
Limited partner interests are inherently different from the capital stock of a corporation, although many of the business risks to which we are subject are similar to those that would be faced by a corporation engaged in a similar business. You should carefully consider the following risk factors together with all of the other information included in this prospectus when evaluating an investment in our common units. If any of the following risks were to occur, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be materially adversely affected. In that case, we might not be able to pay distributions on our common units, the trading price of our common units could decline, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
The risk factors in this section are grouped into the following categories:
| • | Risks Relating to Our Business in General, beginning on this page 18; |
| • | Risks Relating to Completion of the Sabine Pass LNG Receiving Terminal, beginning on page 19; |
| • | Risks Relating to Our Cash Distributions, beginning on page 23; |
| • | Risks Relating to Development and Operation of Our Business, beginning on page 27; |
| • | Risks Relating to an Investment in Us and Our Common Units, beginning on page 35; and |
| • | Risks Relating to Tax Matters, beginning on page 41. |
Risks Relating to Our Business in General
We are a development stage company without any revenues, operating cash flows, operating history or experience constructing, operating or maintaining an LNG facility, and if we are unable to complete construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or if our customers fail to perform under their contracts for whatever reason, our business will be materially and adversely affected and you could lose all or a significant portion of your investment.
We are a newly-formed development stage company with no revenues, operating cash flows or operating history. We had net losses of $72.5 million for the period from inception through December 31, 2006. We expect to continue to incur losses and experience negative operating cash flow through 2008 and to incur significant capital expenditures through completion of development of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Any delays beyond the expected development periods for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal would prolong, and could increase the level of, our operating losses and negative operating cash flows. Neither we nor Cheniere and its affiliates have ever managed the construction, operation or maintenance of an LNG facility.
As more fully discussed in subsequent risk factors, our ability to generate sufficient cash flow to pay the initial quarterly distribution on all units is dependent on the successful and timely completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and on the ability of our three customers, Chevron, Total and Cheniere Marketing, to perform their obligations under their TUAs. Cheniere Marketing has a limited operating history, and Cheniere has a non-investment grade corporate rating. As a result, Cheniere Marketing and Cheniere have a higher risk of being financially unable to perform on the Cheniere Marketing TUA than either Chevron or Total under their TUAs.
Until we begin to receive cash flows under all three of our TUAs in 2009, all or a portion of our distributions to you will be a return of your investment.
Except to the extent that we receive revenues under TUAs, all distributions on our common units will be made from the distribution reserve through the distribution in respect of the second quarter of 2009 and will be a return of your investment. We do not expect to receive any TUA revenues until 2008, and we do not expect to receive sufficient revenues under our TUAs to make all other required cash expenditures and cover all distributions to you until the third quarter of 2009.
18
Our substantial indebtedness could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and to pay or increase distributions to you.
As of December 31, 2006, we had $2,032 million of indebtedness, consisting entirely of the Sabine Pass LNG notes. Our substantial indebtedness could have important consequences, including:
| • | limiting our ability to pay distributions to our unitholders; |
| • | limiting our ability to obtain additional financing to fund our capital expenditures, working capital, acquisitions, debt service requirements or liquidity needs for general business or other purposes; |
| • | limiting our ability to use operating cash flow in other areas of our business because we must dedicate a substantial portion of these funds to service debt, including indebtedness that we may incur in the future; |
| • | limiting our ability to compete with other companies who are not as highly leveraged; |
| • | limiting our ability to react to changing market conditions in our industry and in our customers’ industries and to economic downturns; |
| • | limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and future business opportunities; |
| • | making us more vulnerable than a less leveraged company to a downturn in our business or in the economy; |
| • | limiting our ability to attract customers; and |
| • | resulting in a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition if we are unable to service our indebtedness or obtain additional financing, as needed. |
Under some circumstances, our substantial indebtedness and the restrictive covenants contained in our debt agreements may not allow us the flexibility that we need to operate our business in an effective and efficient manner and may prevent us from taking advantage of strategic and financial opportunities that would benefit our business. See also “—Risks Relating to Our Cash Distributions—Sabine Pass LNG may be restricted under the terms of the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes from making distributions to us and from incurring additional indebtedness under certain circumstances, which may limit our ability to pay or increase distributions to you.”
Our ability to satisfy our obligations will depend upon our future operating performance. Prevailing economic conditions and financial, business and other factors, many of which are beyond our control, will affect our ability to make payments on our debt obligations. We do not expect to receive full contracted revenues under the Cheniere Marketing TUA until the first quarter of 2009 and under the Total and Chevron TUAs until the second and third quarters of 2009, respectively. If we cannot thereafter generate sufficient cash from operations to meet our other obligations, we may need to refinance all or a portion of our indebtedness, including the Sabine Pass LNG notes, on or before maturity. We may not be able to refinance any of our indebtedness on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
Risks Relating to Completion of the Sabine Pass LNG Receiving Terminal
Sabine Pass LNG’s inability to timely construct and commission the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal would prevent it from commencing operations when anticipated and would delay or prevent it, and consequently us, from realizing anticipated cash flows.
Sabine Pass LNG may not complete Phase 1 or Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal in a timely manner, or at all, due to numerous factors, some of which are beyond our control. Factors that could adversely affect our planned completion include:
| • | failure by Bechtel or the other contractors to fulfill their obligations under their construction contracts, or disagreements with them over their contractual obligations; |
19
| • | failure by Sabine Pass LNG to enter into satisfactory additional agreements with contractors for the rest of Phase 2 – Stage 1; |
| • | shortages of materials or delays in delivery of materials; |
| • | cost overruns and difficulty in obtaining sufficient debt or equity financing to pay for such additional costs; |
| • | difficulties or delays in obtaining LNG for commissioning activities necessary to achieve commercial operability of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | failure to obtain all necessary governmental and third-party permits, licenses and approvals for the construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | weather conditions, such as hurricanes, and other catastrophes, such as explosions, fires, floods and accidents; |
| • | difficulties in attracting a sufficient skilled and unskilled workforce, increases in the level of labor costs and the existence of any labor disputes; |
| • | resistance in the local community to the development of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal due to safety, environmental or security concerns; and |
| • | local and general economic and infrastructure conditions. |
Sabine Pass LNG’s inability to timely complete the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, including as a result of any of the foregoing factors, could prevent it from commencing operations when anticipated, which could delay payments under the TUAs. As a result, we may not receive our anticipated cash flows on time or at all.
We are dependent on Bechtel and other contractors for the successful completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
We have no experience constructing LNG receiving terminals and limited experience working with EPC contractors, including Bechtel, and with other construction contractors. Timely and cost-effective completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal in compliance with agreed specifications is central to our business strategy and is highly dependent on our contractors’ performance under their agreements with Sabine Pass LNG. Our contractors’ ability to perform successfully under their contracts is dependent on a number of factors, including their ability to:
| • | design and engineer the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal to operate in accordance with specifications; |
| • | engage and retain third-party subcontractors and procure equipment and supplies; |
| • | respond to difficulties such as equipment failure, delivery delays, schedule changes and failure to perform by subcontractors, some of which are beyond their control; |
| • | attract, develop and retain skilled personnel, including engineers; |
| • | post required construction bonds and comply with the terms thereof; |
| • | manage the construction process generally, including coordinating with other contractors and regulatory agencies; and |
| • | maintain their own financial condition, including adequate working capital. |
These risks are heightened for Phase 2 – Stage 1, which is still in the contracting phase. A substantial number of contracts, such as for performing portions of or supplying materials for Phase 2 – Stage 1, remain to be negotiated for Phase 2 – Stage 1, and we may be unable to reach satisfactory arrangements for these contracts. As a result, the scope, design, timing and cost for Phase 2 – Stage 1 construction are not as well defined as they
20
are for Phase 1, and therefore the risk of delays, cost overruns or non-completion is greater for Phase 2 – Stage 1 than for Phase 1.
Although some of our EPC contracts provide for liquidated damages, if the contractor fails to perform in the manner required with respect to certain of its obligations, the events that trigger a requirement to pay liquidated damages may delay or impair the operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and any liquidated damages that we receive may not be sufficient to cover the damages that we suffer as a result of any such delay or impairment. In addition, each contractor’s liability for liquidated damages is subject to a cap. Each of our material agreements with contractors is also subject to termination by the contractor prior to completion of construction under certain circumstances, including extended delays (of 100 days or more) caused by force majeure events and our insolvency, breach of material obligations not subject to adjustment by change order, or failure to pay undisputed amounts. Please read “Description of Principal Construction Agreements” for further information.
Furthermore, we may have disagreements with our contractors about different elements of the construction process, which could lead to the assertion of rights and remedies under their contracts and increase the cost of the project or result in a contractor’s unwillingness to perform further work on the project. If any contractor is unable or unwilling to perform according to the negotiated terms and timetable of its respective agreement for any reason or terminates its agreement, Sabine Pass LNG would be required to engage a substitute contractor. This would likely result in significant project delays and increased costs.
The failure of our contractors to perform under their contracts for any of the reasons described above may extend the date on which our TUA customers are required to begin making payments to us. This delay in payments could have a material adverse effect on our cash flows and results of operations and on our ability to make distributions to you in a timely manner, or at all.
We may experience cost overruns and delays in the completion of Phase 1 or Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal as well as difficulties in obtaining funding for any additional costs, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and ability to make cash distributions to our unitholders.
Our construction costs for Phase 1 and for Phase 2 – Stage 1 may be significantly higher than our current estimates as a result of cost overruns, change orders under existing or future construction contracts, increased component and material costs, escalating labor costs, limited availability of labor, delays in construction and increased spending to maintain construction schedules. As of January 17, 2007, change orders for $119.5 million have been approved under the Phase 1 EPC agreement with Bechtel. We do not have any prior experience in constructing LNG receiving terminals, and no LNG receiving terminal has been constructed and placed in service in the United States in almost 25 years, as a result of which there are limited benchmarks against which to compare our estimates. If our construction costs are higher than estimated, our cash available for distribution to unitholders may be reduced.
Furthermore, in order to cover not only increased costs but also the cost of a sixth LNG storage tank that we may be required to construct if requested by Cheniere Marketing under its TUA, we may need to obtain additional funding. If we fail to obtain sufficient funding and Sabine Pass LNG fails to complete Phase 1, our business plan could fail. If Phase 1 is satisfactorily completed but funding is not sufficient for completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1, Sabine Pass LNG will be entitled to receive payments under the TUAs, including the Cheniere Marketing TUA, but Cheniere Marketing may not have access to regasification capacity or other resources or business opportunities sufficient to generate cash flow to fund its required payments to Sabine Pass LNG under the Cheniere Marketing TUA. This could cause Cheniere Marketing to default on its obligations, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
Our ability to obtain debt or equity financing that may be needed to provide additional funding to cover increased costs will depend, in part, on factors beyond our control, such as the status of various capital and
21
industry markets at the time financing is sought. Accordingly, we may not be able to obtain financing on terms that are acceptable to us, if at all. Even if we are able to obtain financing, we may have to accept terms that are disadvantageous to us or that may have a material adverse effect on our current or future business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
To commission the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Sabine Pass LNG must purchase and process LNG. Sabine Pass LNG has not previously purchased or processed any LNG.
The Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal must undergo a commissioning process for its storage tanks and other equipment before commencement of commercial operation. The commissioning process will require a substantial quantity of LNG as well as access to adequate LNG tankers to deliver the LNG.
Our construction cost estimates do not include the costs of acquiring this LNG (other than a minor portion we refer to as “heel” LNG) at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which we have projected will be approximately $157.5 million for purposes of calculating forecasted cash available for distribution to unitholders in this prospectus. Please read “Cash Distribution Policy and Restrictions on Distributions—Forecast of Cash Available for Distribution.” Our actual cost to obtain LNG for the commissioning process could exceed our estimates, and the overrun could be significant.
Sabine Pass LNG faces several principal risks associated with this required purchase of LNG, including the following:
| • | Sabine Pass LNG may be unable to enter into a contract for the purchase of the LNG needed for commissioning and may be unable to obtain tankers to deliver such LNG on terms reasonably acceptable to it or at all. Although Sabine Pass LNG expects to contract with Cheniere Marketing to provide the LNG and the tankers, it has not negotiated any such contract at this time with Cheniere Marketing or any other third party; |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG will bear the commodity price risk associated with purchasing the LNG, holding it in inventory for a period of time and selling the regasified LNG; and |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG may be unable to obtain financing for the purchase and shipment of the LNG on terms that are reasonably acceptable to it or at all. |
The failure of Sabine Pass LNG to obtain LNG, tankers or both, or its inability to finance the purchase of LNG needed for commissioning, would impede commencement of commercial operation at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which could delay the date on which our TUA customers are required to begin making payments to us. This delay in payments could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
To commission the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Sabine Pass LNG must obtain natural gas pipeline transportation access. The required pipeline infrastructure is under development by a Cheniere entity but has not yet been constructed.
The commissioning process for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is dependent upon completion of pipeline infrastructure to supply natural gas fuel for power generation units prior to delivery of cool down LNG and to take away natural gas produced in the commissioning process. We expect to obtain access to the pipeline infrastructure required for the commissioning process from Cheniere Sabine Pass Pipeline, L.P., a subsidiary of Cheniere, either directly or through Cheniere Marketing, but we have no existing contract or other arrangements for access. This pipeline infrastructure has not been constructed, and its timely completion is subject to numerous risks, such as weather delays, accidents and inability to obtain governmental approvals.
22
Failure to obtain and maintain approvals and permits from governmental and regulatory agencies with respect to the development of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or related pipeline infrastructure could impede completion and have a material adverse effect on us.
The design, construction and operation of LNG receiving terminals are all highly regulated activities. The FERC’s approval under Section 3 of the Natural Gas Act of 1938, as well as several other material governmental and regulatory approvals and permits, are required in order to construct and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Although Sabine Pass LNG has obtained Section 3 authorization to construct and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, such authorization is subject to ongoing conditions imposed by the FERC. Sabine Pass LNG also has not obtained several other material governmental and regulatory approvals and permits required in order to construct and operate Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and third parties have not obtained approvals and permits to develop related pipeline infrastructure, including several under the Clean Air Act and the Clean Water Act from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and the Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality. We have no control over the outcome of the review and approval process. We do not know whether or when any such approvals or permits can be obtained, or whether or not any existing or potential interventions or other actions by third parties will interfere with Sabine Pass LNG’s ability to obtain and maintain such permits or approvals. Failure to obtain and maintain any of these approvals and permits could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
Hurricanes or other disasters could result in a delay in the completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, higher construction costs and the deferral of the dates on which our TUA counterparties are obligated to begin making payments to us.
In August and September of 2005, Hurricanes Katrina and Rita and related storm activity, including windstorms, storm surges, floods and tornadoes, caused extensive and catastrophic damage to coastal and inland areas located in the Gulf Coast region of the U.S. (parts of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama) and certain other parts of the southeastern U.S. Construction at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal site was temporarily suspended in connection with Hurricane Katrina, as a precautionary measure. Approximately three weeks after the occurrence of Hurricane Katrina, the terminal site was again secured and evacuated in anticipation of Hurricane Rita, the eye of which made landfall to the east of the site. As a result of these 2005 storms and related matters, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal experienced construction delays and increased costs totaling approximately $30.6 million.
Future similar storms and related storm activity and collateral effects, or other disasters such as explosions, fires, floods or accidents, could result in damage to, delays or cost increases in construction of, or interruption of operations at, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or related infrastructure.
Risks Relating to Our Cash Distributions
We may not have sufficient cash from operations to enable us to fund the initial quarterly distribution following establishment of cash reserves and payment of fees and expenses, including payments to our general partner and funding of capital expenditures.
We plan to retain cash in a distribution reserve sufficient to fund the initial quarterly distribution only through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. After that time, we may not have sufficient available cash each quarter to pay the initial quarterly distribution. The amount of cash that we can distribute on our common units principally will depend upon the amount of cash that we generate from our operations, which will be based on, among other things:
| • | Sabine Pass LNG’s success in completing Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and the timing and cost of completion; |
| • | performance by counterparties of their obligations under the TUAs; |
| • | performance by Sabine Pass LNG of its obligations under the TUAs; |
23
| • | the adequacy of Sabine Pass LNG’s 2% retainage to cover fuel requirements and natural gas losses; and |
| • | the level of our operating costs, including payments to our general partner and its affiliates. |
In addition, the actual amount of cash that we will have available for distribution will depend on other factors such as:
| • | the level of capital expenditures that we make, including those for a sixth LNG storage tank that we may be required to construct, which we have internally estimated could cost in the range of $120 million to $140 million. Sabine Pass LNG will not receive additional revenues in exchange for constructing a sixth LNG storage tank under the Cheniere Marketing TUA; |
| • | the restrictions contained in our debt agreements and our debt service requirements, including the ability of Sabine Pass LNG to pay distributions to us under the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes as a result of requirements for a $75 million debt service reserve account, a debt payment account and satisfaction of a fixed charge coverage ratio. See “Indebtedness—Indenture—Covenants—Restricted Payments;” |
| • | the costs and capital requirements of acquisitions, if any; |
| • | fluctuations in our working capital needs; |
| • | our ability to borrow for working capital or other purposes; and |
| • | the amount, if any, of cash reserves established by our general partner. |
Sabine Pass LNG may be restricted under the terms of the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes from making distributions to us and from incurring additional indebtedness under certain circumstances, which may limit our ability to pay or increase distributions to you.
The indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes restricts payments that Sabine Pass LNG can make to us in certain events and limits the indebtedness that Sabine Pass LNG can incur. Please read “Indebtedness.” Prior to Phase 1 Target Completion, as defined in the indenture, which we anticipate will not occur until the second quarter of 2008, Sabine Pass LNG will not be permitted to pay any distributions to us. Following Phase 1 Target Completion, Sabine Pass LNG will be permitted to pay distributions to us only after the following payments have been made:
| • | an operating account has been funded with amounts sufficient to cover the succeeding 45 days of operating and maintenance expenses, maintenance capital expenditures and obligations, if any, under an assumption agreement and a state tax sharing agreement; |
| • |
1/6th of the amount of interest due on the Sabine Pass LNG notes on the next interest payment date (plus any shortfall from any such month subsequent to the preceding interest payment date) has been transferred to a debt payment account; |
| • | outstanding principal on the Sabine Pass LNG notes then due and payable has been paid; |
| • | taxes payable by Sabine Pass LNG and permitted payments in respect of taxes have been paid; and |
| • | the debt service reserve account has been replenished with the amount (or acceptable letters of credit or acceptable guarantees in respect of such amount) required to make the next interest payment on the Sabine Pass LNG notes. |
In addition, Sabine Pass LNG will only be able to make distributions to us in the event that it could, among other things, incur at least $1.00 of additional indebtedness under the fixed charge coverage ratio test of 2.0 to 1.0 at the time of payment and after giving pro forma effect to the distribution. Please read “Indebtedness—Indenture—Covenants” for the method of calculating the fixed charge coverage ratio.
24
Sabine Pass LNG will also be prohibited under the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes from paying distributions to us or incurring additional indebtedness upon the occurrence of any of the following events, among others:
| • | a default for 30 days in the payment of interest on, or additional interest, if any, with respect to, the Sabine Pass LNG notes; |
| • | a failure to pay any principal of, or premium, if any, on the Sabine Pass LNG notes; |
| • | a failure by Sabine Pass LNG to comply with various covenants in the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes; |
| • | a failure to observe any other agreement in the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes beyond any specified cure periods; |
| • | a default under any mortgage, indenture or instrument governing any indebtedness for borrowed money by Sabine Pass LNG in excess of $25 million if such default results from a failure to pay principal or interest on, or results in the acceleration of, such indebtedness; |
| • | a final money judgment or decree (not covered by insurance) in excess of $25 million is not discharged or stayed within 60 days following entry; |
| • | a failure of any material representation or warranty in the security documents entered into in connection with the indenture to be correct; |
| • | the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal project is abandoned; or |
| • | certain events of bankruptcy or insolvency. |
Sabine Pass LNG’s inability to pay distributions to us or to incur additional indebtedness as a result of the foregoing restrictions in the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes may inhibit our ability to pay or increase distributions to you.
After March 31, 2009, the fixed charge coverage ratio test contained in the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes could prevent Sabine Pass LNG from making cash distributions to us. As a result, we may be prevented from making distributions to our unitholders, which could materially and adversely affect the market price of our common units.
After March 31, 2009, Sabine Pass LNG will not be permitted to make cash distributions to us if its consolidated cash flow is not at least twice its fixed charges, calculated as required in the indenture. See “Indebtedness—Indenture—Covenants” for more detail regarding this calculation. In order to satisfy this fixed charge coverage ratio test after March 31, 2009, we estimate that Sabine Pass LNG’s revenues under its TUAs must aggregate at least approximately $350 million per year. Accordingly, we will not receive cash distributions from Sabine Pass LNG if Sabine Pass LNG does not receive, in addition to the approximately $250 million per year of contracted annual revenues from the Total and Chevron TUAs, substantial revenues under the Cheniere Marketing TUA or from one or more substitute customers.
Cheniere Marketing is a development stage company with a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy. It may never develop its business, assets or revenues sufficiently to pay its fees under its TUA. Cheniere has guaranteed 100% of the obligations of Cheniere Marketing under its TUA. Cheniere has a non-investment grade corporate rating of B from Standard & Poor’s. If Cheniere does not receive sufficient future cash flows from businesses that Cheniere is developing, Cheniere may be unable to perform its guarantee of the Cheniere Marketing TUA.
In addition, even if Sabine Pass LNG receives the contracted payments under the Cheniere Marketing TUA, the fixed charge coverage test will not be satisfied if those payments do not constitute revenues under GAAP as then in effect and as provided in the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes. Because the Cheniere
25
Marketing TUA is an agreement between related parties, payments under the Cheniere Marketing TUA may not constitute revenues under GAAP as currently in effect if Cheniere Marketing is determined to lack economic substance apart from Sabine Pass LNG. We believe Cheniere Marketing could be determined to lack economic substance apart from Sabine Pass LNG if, for example, Cheniere Marketing has no substantive business and is not pursuing, and has no prospect of developing, any substantive business apart from its TUA with Sabine Pass LNG.
If we do not receive distributions from Sabine Pass LNG, we may not be able to continue to make distributions to our unitholders, which could have a material and adverse effect on the perceived value of our partnership and the market price of our common units.
The indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes may prevent Sabine Pass LNG from engaging in certain beneficial transactions.
In addition to restrictions on the ability of Sabine Pass LNG to make distributions or incur additional indebtedness, the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes also contains various other covenants that may prevent it from engaging in beneficial transactions, including limitations on Sabine Pass LNG’s ability to:
| • | sell or transfer assets; |
| • | incur liens; |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; |
| • | consolidate, merge, sell or lease all or substantially all of its assets; and |
| • | enter into sale and leaseback transactions. |
Management fees and cost reimbursements due to our general partner and its affiliates will reduce cash available to pay distributions to you.
We will pay significant management fees to our general partner and its affiliates and reimburse them for expenses incurred on our behalf, which will reduce our cash available for distribution to you. These fees and expenses are payable as follows:
| • | under a services agreement, we will pay an affiliate of Cheniere an administrative fee of $10 million per year (as adjusted for inflation after January 1, 2007), commencing January 1, 2009, for general and administrative services for our benefit following the closing of this offering. This fee does not include reimbursements by us of direct expenses that the affiliate incurs on our behalf, such as salaries of operational personnel performing services on-site at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and the cost of their employee benefits, including 401(k) plan, pension and health insurance benefits; |
| • | under an operation and maintenance agreement that an affiliate of Cheniere will assign to our general partner at or near the closing of the offering, Sabine Pass LNG will pay our general partner a fixed monthly fee of $95,000 (indexed for inflation) and reimburse our general partner for its operating expenses, which consist of labor, maintenance, land lease and insurance expenses, and for maintenance capital expenditures. The fixed monthly fee will increase to $130,000 (indexed for inflation) upon substantial completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Thereafter, our general partner will, under certain circumstances, be entitled to a bonus equal to 50% of the salary component of labor costs; |
| • | under a management services agreement, Sabine Pass LNG will pay its general partner a monthly fixed fee of $340,000 (indexed for inflation) prior to substantial completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; thereafter, the monthly fixed fee will increase to $520,000 (indexed for inflation). The general partner of Sabine Pass LNG will, in turn, pay an affiliate of Cheniere all amounts that it receives from Sabine Pass LNG under the management services agreement; and |
| • | through 2008, we will fund costs of approximately $2.5 million per year, adjusted for inflation at 2.5% per year after January 1, 2007, with funds advanced to us from Cheniere for tax compliance and publicly traded partnership tax reporting, accounting, SEC reporting and other costs of operating as a publicly traded partnership. |
26
Our general partner and its affiliates will also be entitled to reimbursement for all other direct expenses that they incur on our behalf. The payment of fees to our general partner and its affiliates and the reimbursement of expenses could adversely affect our ability to pay cash distributions to you. Please read “Conflicts of Interest and Fiduciary Duties—Conflicts of Interest.”
The amount of cash that we have available for distributions to you will depend primarily on our cash flow and not solely on profitability.
The amount of cash that we will have available for distributions will depend primarily on our cash flow, including cash reserves and working capital or other borrowings, and not solely on profitability, which will be affected by non-cash items. As a result, we may make cash distributions during periods when we record losses, and we may not make cash distributions during periods when we record net income.
We will not be able to increase the distributions on our common units unless we are able to make accretive acquisitions.
We will not be able to increase distributions on our common units by generating additional cash flows from Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal because the entire capacity of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal has already been reserved under fixed fee TUAs with three customers. As a result, we must make accretive acquisitions of additional cash-generating assets and operations in order to increase the quarterly distributions on our common units.
Our financial estimates, including our forecast of cash available for distribution, and our Independent Engineer’s conclusions are based on certain assumptions that may not materialize.
The financial estimates that we have included in this prospectus, including under “Summary—Forecast of Cash Available to Pay Distributions” and “Cash Distribution Policy and Restrictions on Distributions—Cash Distributions” are based upon assumptions and information that we believe are reliable as of today. However, these estimates and assumptions are inherently subject to significant business, economic and other uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control. Financial estimates are necessarily speculative in nature, and you should expect that some or all of the assumptions will not materialize. Actual results will probably vary from the estimates, and the variations will likely be material and are likely to increase over time. Consequently, the inclusion of estimates in this prospectus should not be regarded as a representation by us or the underwriters or any other person that the estimated results will actually be achieved. Moreover, we do not intend to update or otherwise revise the estimates to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this prospectus or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. Undue reliance should not be placed on the estimates contained in this prospectus. Our estimates were not prepared with a view toward compliance with the guidelines of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants. Moreover, no independent accountants compiled or examined the estimates, and, accordingly, our independent registered public accounting firm does not express an opinion or any other form of assurance with respect to our estimates and assume no responsibility for, and disclaim any association with, the estimates.
In the preparation of its report, the Independent Engineer relied on assumptions regarding circumstances beyond the control of us or any other person. By their nature, these assumptions are subject to significant uncertainties, and actual results will differ, perhaps materially, from those stated in the Independent Engineer’s report. We cannot give any assurance that these assumptions will prove to be correct. If our actual results are materially less favorable than those shown in the Independent Engineer’s report, or if the assumptions in the Independent Engineer’s report on which we rely for certain of our financial estimates, prove to be incorrect, Sabine Pass LNG’s ability to pay distributions to us, and our ability to pay distributions to our unitholders, may be adversely affected.
27
Risks Relating to Development and Operation of Our Business
We will be dependent for substantially all of our revenues and cash flows on the TUA counterparties. Cheniere Marketing has a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy, and may not be able to make payments to us under its TUA.
We will be dependent on the Chevron, Total and Cheniere Marketing TUAs for substantially all of our operating revenues and cash flows. Each of Chevron and Total will pay approximately $125 million annually when payments under those contracts commence, and Cheniere Marketing will pay approximately $250 million annually commencing in 2009. In order for us to pay the initial quarterly distribution on all of our units, our TUA counterparties must pay these amounts in full. We are also exposed to the credit risk of the guarantors of our customers’ obligations under the TUAs in the event that Sabine Pass LNG must seek recourse under a guaranty, and any nonpayment or nonperformance by the guarantors could reduce the ability of Sabine Pass LNG to pay distributions to us and, in turn, our ability to pay distributions to our unitholders.
Cheniere Marketing has a limited operating history, limited capital and an unproven business strategy. Cheniere Marketing has no credit rating, and Cheniere has a non-investment grade corporate rating of B from Standard and Poor’s, indicating that Cheniere Marketing and Cheniere have a higher risk of being financially unable to perform on the Cheniere Marketing TUA than either Chevron or Total have with respect to their TUAs. Although each of our TUA counterparties faces a risk that it will not be able to enter into commercial arrangements for the use of its capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal to support the payment of its obligations under its TUA, due to negative developments in the LNG industry or for other reasons, that risk is greater for Cheniere Marketing than for Total and Chevron. The principal risks attendant to Cheniere Marketing’s future ability to generate operating cash flow to support its TUA obligations include the following:
| • | Cheniere Marketing has no agreements or arrangements for any supplies of LNG, for any vessels to transport LNG or for the utilization of the capacity that it has contracted for under its TUA with Sabine Pass LNG and may not be able to obtain such agreements or arrangements on economical terms, or at all; |
| • | Cheniere Marketing does not have unconditional commitments from customers for the purchase of the natural gas it proposes to sell from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and it may not be able to obtain commitments or other arrangements on economical terms, or at all; |
| • | the pipeline infrastructure on which Cheniere Marketing will rely to transport gas from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal to interconnections with other pipelines has not been constructed, and its timely construction is subject to numerous risks, such as weather delays, accidents, difficulty in obtaining construction financing and inability to obtain required rights-of-way or governmental approvals. In addition, Cheniere Marketing has no existing arrangements with other pipelines for transportation of natural gas to customers from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | even if Cheniere Marketing is able to arrange for supplies and transportation of LNG to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and for transportation and sales of natural gas to customers, it may experience negative cash flows and adverse liquidity effects due to fluctuations in supply, demand and price for LNG, for transportation of LNG, for natural gas and for storage and transportation of natural gas; and |
| • | Cheniere Marketing engages in trading and hedging activities involving both physical natural gas and natural gas derivatives, which requires posting of collateral with trade counterparties and imposes other liquidity requirements and constraints that may be difficult for Cheniere Marketing to satisfy because it has no credit rating and limited access to capital. In pursuing this business, Cheniere Marketing will be exposed to losses from fluctuations in commodity prices and could also result in negative cash flows and adverse liquidity effects for Cheniere Marketing. |
In pursuing each aspect of its planned business, Cheniere Marketing will encounter intense competition, including competition from major oil companies and other competitors with significantly greater resources.
28
Cheniere Marketing will also compete with our other customers and may compete with Cheniere and its other subsidiaries that are developing or operating other LNG receiving terminals and related infrastructure, which may include vessels, pipelines and storage. Cheniere Marketing’s regasification capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, in particular, will be marketed in competition with existing capacity and additional future capacity offered by other terminals that currently exist or that may be completed or expanded in the future by Cheniere affiliates or others.
Any or all of these factors, as well as other risk factors that we or Cheniere Marketing may not be able to anticipate, control or mitigate, could materially and adversely affect the business, results of operations, financial condition, prospects and liquidity of Cheniere Marketing, which in turn could have a material adverse effect upon us.
Sabine Pass LNG may be required to purchase natural gas to provide fuel at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which would increase operating costs and could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Sabine Pass LNG’s three TUAs provide for an in-kind deduction of 2% of the LNG delivered to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which it will use primarily as fuel for revaporization and self-generated power and to cover natural gas unavoidably lost at the facility. There is a risk that this 2% in-kind deduction will be insufficient for these needs and that Sabine Pass LNG will have to purchase additional natural gas from third parties. Sabine Pass LNG has no arrangements in place to obtain any such natural gas and will bear the risk of changing prices with respect to additional natural gas that it may need to purchase for fuel.
The inability to import LNG into the U.S. could materially adversely affect our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, and our business plans and results of operations if Sabine Pass LNG has to replace TUAs that terminate or expire.
Upon completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, our business will be dependent upon the ability of our customers to import LNG supplies into the U.S. Political instability in foreign countries that have supplies of natural gas, or strained relations between such countries and the U.S., may impede the willingness or ability of LNG suppliers in such countries to export LNG to the U.S. Such foreign suppliers may also be able to negotiate more favorable prices with other LNG customers around the world than with customers in the U.S., thereby reducing the supply of LNG available to be imported into the U.S. market. Any significant impediment to the ability to import LNG into the U.S. could have a material adverse affect on Sabine Pass LNG’s customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, and on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. In addition, the quality of LNG available for importation may not meet the quality specifications of the pipelines interconnected with or downstream of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and the terminal and its customers do not have plans or equipment in place to condition such LNG to meet the pipeline specifications. The inability to import LNG into the U.S. may also limit the LNG assets being constructed, and therefore, our potential acquisition opportunities, which may limit our ability to increase distributions to you.
Failure of sufficient LNG liquefaction capacity to be constructed worldwide could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions.
Commercial development of an LNG liquefaction facility can take a number of years and requires a very substantial capital investment. Many factors could negatively affect continued development of LNG liquefaction facilities, including:
| • | increases in interest rates or other events that may affect the availability of sufficient financing for LNG projects on commercially reasonable terms; |
| • | decreases in the price of LNG and natural gas, which might decrease the expected returns relating to investments in LNG projects; |
29
| • | the inability of project owners or operators to obtain governmental approvals to construct or operate LNG facilities; |
| • | political unrest in exporting countries or local community resistance in such countries to the siting of LNG facilities due to safety, environmental or security concerns; and |
| • | any significant explosion, spill or similar incident involving an LNG liquefaction facility or LNG vessel. |
If sufficient LNG liquefaction capacity is not constructed, our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, may find it difficult to obtain sufficient utilization of their capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal to support their obligations under their TUAs. A lack of growth in liquefaction capacity may also limit the LNG assets being constructed and therefore, our potential acquisition opportunities, which may limit our ability to increase distributions to you.
A shortage of LNG tankers worldwide could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions.
We believe that the existing fleet of tankers that is available to transport LNG is inadequate, and the failure to expand LNG tanker capacity would impede our customers’ ability to import LNG into the U.S. The construction and delivery of additional LNG vessels require significant capital, and the availability of the vessels could be delayed to the detriment of our customers because of:
| • | an inadequate number of shipyards constructing LNG vessels and a backlog of orders at these shipyards; |
| • | political or economic disturbances in the countries where the vessels are being constructed; |
| • | changes in governmental regulations or maritime self-regulatory organizations; |
| • | work stoppages or other labor disturbances at the shipyards; |
| • | bankruptcy or other financial crisis of shipbuilders; |
| • | quality or engineering problems; |
| • | weather interference or a catastrophic event, such as a major earthquake, tsunami or fire; and |
| • | shortages of or delays in the receipt of necessary construction materials. |
Failure of imported LNG to become a competitive source of energy in North America could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions.
In North America, due mainly to an historically abundant supply of natural gas, imported LNG has not been a major energy source in the past. Cheniere Marketing’s business plan is based, in part, on the belief that LNG can be produced and delivered at a lower cost than the cost to produce some domestic supplies of natural gas, or other alternative energy sources. Through the use of improved exploration technologies, additional sources of natural gas may be discovered in North America, which could further increase the available supply of natural gas at a lower cost than LNG. In addition to natural gas, LNG also competes with other sources of energy, including coal, oil, nuclear, hydroelectric, wind and solar energy. As a result, LNG may not become a competitive source of energy in North America. The failure of LNG to become a competitive supply alternative to domestic natural gas, oil and other import alternatives could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions. In addition, other continents have a longer history of importing LNG and, due to their geographic proximity to LNG producers and limited domestic natural gas supplies, may be willing and able to pay more for LNG, thereby limiting the supply of LNG available in North American markets. The failure of LNG to become a competitive supply alternative may impede the ability of our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, to obtain customers for regasified LNG, which may decrease their revenues and ability to make payments under their TUAs and result in a default of their payment obligations thereunder.
30
Decreases in the price of natural gas could lead to reduced development of LNG projects worldwide, which could adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions.
The development of domestic LNG receiving terminals and LNG projects generally is based on assumptions about the future price of natural gas and the availability of imported LNG. Natural gas prices have been, and are likely to continue to be, volatile and subject to wide fluctuations in response to any of the following factors:
| • | relatively minor changes in the supply of, and demand for, natural gas; |
| • | political conditions in international natural gas producing regions; |
| • | the extent of domestic production and importation of natural gas in relevant markets; |
| • | the level of consumer demand; |
| • | weather conditions; |
| • | the competitive position of natural gas as a source of energy compared with other energy sources; and |
| • | the effect of federal and state regulation on the production, transportation and sale of natural gas. |
The willingness of potential customers to contract for regasification capacity would be negatively impacted and, once facilities are in operation, LNG throughput volumes would likely decline if the price of natural gas in North America is, or is forecast to be, lower than the cost to produce and deliver LNG to North American markets. Any significant decline in the price of natural gas could cause the cost of natural gas produced from imported LNG to be higher than domestically produced natural gas. As a result, our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, may not be able to procure supplies of LNG or customers for regasified LNG, which may decrease their revenues and ability to make payments under the TUAs and result in a default of their payments obligations thereunder. Such payment defaults may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. In addition, a decline in the price of natural gas may result in fewer LNG assets being constructed or available for acquisition by us at a given time and, therefore, limit our ability to increase distributions to you.
Cyclical changes in the demand for LNG regasification capacity may adversely affect the performance by our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, of their obligations under the TUAs and could reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions.
The economics of Sabine Pass LNG terminal operations could be subject to cyclical swings, reflecting alternating periods of under-supply and over-supply of LNG importation capacity and available natural gas, principally due to the combined impact of several factors, including:
| • | significant additions in regasification capacity in North America, Europe, Asia and other markets, which could divert LNG from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | reduced demand for natural gas, which could suppress demand for LNG; |
| • | increased natural gas production deliverable by pipelines, which could suppress demand for LNG; |
| • | insufficient LNG production worldwide, which may limit the LNG traded worldwide, including at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | cost improvements that allow competitors to offer LNG regasification services at reduced prices; |
| • | changes in supplies of, and prices for, alternative energy sources such as coal, oil, nuclear, hydroelectric, wind and solar energy, which may reduce the demand for natural gas; and |
| • | cyclical trends in general business and economic conditions that cause changes in the demand for natural gas. |
31
These changes in the economics of LNG terminal operations could materially adversely affect the ability of our customers, including Cheniere Marketing, to procure supplies of LNG to be imported into North America and to procure customers for regasified LNG at economical prices, or at all. If and when the TUAs terminate or expire, unfavorable economic conditions that affect our customers could, in turn, for similar reasons, reduce our operating revenues, cause us operating losses and adversely affect our ability to make or increase distributions. In addition, these cyclical changes may result in fewer LNG assets being constructed or available for acquisition by us at a given time and, therefore, limit our ability to increase distributions to you.
We may experience increased labor costs, and the unavailability of skilled workers or our failure to retain key personnel could hurt our ability to construct and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
Companies in our industry, including us, are dependent upon the available labor pool of skilled employees. We compete with other energy companies and other employers to attract and retain qualified personnel with the technical skills and experience required to construct the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and, upon commencement of commercial operation, to provide our customers with the highest quality service. A shortage in the labor pool of skilled workers or other general inflationary pressures or changes in applicable laws and regulations could make it more difficult to attract and retain personnel and could require an increase in the wage and benefits packages that we offer, thereby increasing our operating costs and reducing cash available for distribution. For example, in the aftermaths of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita, Bechtel and certain subcontractors temporarily experienced a shortage of available skilled labor necessary to meet the requirements of the Phase 1 construction plan. As a result, Sabine Pass LNG agreed to change orders with Bechtel concerning additional activities and expenditures to mitigate the hurricanes’ effects on the completion of Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Any increase in our operating costs could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
We may face competition from competitors with far greater resources, as well as potential overcapacity in the LNG receiving terminal marketplace.
Many companies are considering or pursuing the development of infrastructure in the domestic LNG market, including major oil and natural gas companies such as Chevron Corporation, ConocoPhillips, ExxonMobil, Royal Dutch/Shell and Total. Other energy companies such as AES, Dominion, El Paso Corporation, Excelerate Energy, McMoRan Exploration, Occidental Petroleum, Sempra, Suez and other public and private companies have also proposed developing or expanding LNG receiving facilities in North America, both onshore and offshore. Almost all of these competitors have longer operating histories, more development experience, greater name recognition, larger staffs and substantially greater financial, technical and marketing resources and access to LNG supply than we and our affiliates do. The superior resources that these competitors have available for deployment could allow them to compete successfully against us, if and when Sabine Pass LNG’s TUAs terminate or expire, and/or against Cheniere Marketing, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
Industry analysts have predicted that if a substantial number of the proposed LNG receiving terminals in North America that have been announced by developers were actually built, there would likely be substantial excess capacity available from such terminals in the future. In addition, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will likely continue to face competition when and if it is completed, including competition from North American sources of natural gas and onshore, offshore and shipboard LNG regasification facilities. The Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will also compete with the Corpus Christi and Creole Trail LNG receiving terminals that Cheniere is proposing to develop and the Freeport LNG receiving terminal that is currently under construction and in which Cheniere owns a minority interest. If the number of LNG receiving terminals built outstrips demand for natural gas from those terminals, the excess capacity could have a material adverse effect on Cheniere Marketing, or on us in the event Sabine Pass LNG has to replace its TUAs, and on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
32
Each of the three TUAs that Sabine Pass LNG has entered into is subject to termination by the contractual counterparty under certain circumstances, and Sabine Pass LNG is dependent on the performance of those counterparties under the TUAs.
Sabine Pass LNG has entered into long-term TUAs with Total, Chevron and Cheniere Marketing. Each of the TUAs contains various termination rights. For example, each counterparty may terminate its TUA if the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal experiences a force majeure delay for longer than 18 months, fails to deliver a specified amount of natural gas redelivery nominations or fails to receive or unload a specified number of LNG cargoes. Please read “Business—Customers.” Sabine Pass LNG may not be able to replace these TUAs on desirable terms, or at all, if they are terminated. In the case of each of these TUAs, Sabine Pass LNG is dependent on the respective counterparty’s continued willingness and ability to perform its obligations under the TUAs. If any of these counterparties fails to perform its obligations under its respective TUA, our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects could be materially adversely affected, even if Sabine Pass LNG was to be ultimately successful in seeking damages from that counterparty or its guarantor for a breach of the TUA.
We will be entirely dependent on Cheniere, including employees of Cheniere and its subsidiaries, for key personnel, and a loss of key personnel could have a material adverse effect on our business.
As of December 31, 2006, Cheniere and its subsidiaries had approximately 238 full-time employees, who, for the most part, were focused on the development of three LNG receiving terminals and other complementary businesses. As construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal progresses, we will have to hire or otherwise arrange with Cheniere affiliates for new onsite employees to manage the facility. Before the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal commences operations, we will also have to hire or otherwise arrange for an entire staff to operate the facility, which will increase the personnel needed to operate the facility from 12 as of December 31, 2006 to 65 in the first quarter of 2008, at an estimated annual cost of approximately $5.3 million. We will rely to a significant extent on the new personnel that we hire or otherwise arrange to perform these functions. As our operations expand, our general partner, Sabine Pass LNG’s general partner and other Cheniere subsidiaries will also have to expand their administrative staffs. If we or those other entities are not able to successfully manage the expansion, our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects could be materially adversely affected.
Our general partner’s executive officers are also officers of Cheniere and its affiliates. Please read “Management—Directors and Executive Officers of Our General Partner.” We do not maintain key person life insurance policies on any personnel. Although Cheniere has arranged agreements relating to compensation and benefits with certain of our general partner’s executive officers, our general partner does not have any employment contracts or other agreements with key personnel binding them to provide services for any particular term. The loss of the services of any of these individuals, including Messrs. Souki, Horton and Turkleson, could have a material adverse effect on our business. In addition, our future success will depend in part on our general partner’s ability to engage, and Cheniere’s ability to attract and retain, additional qualified personnel.
If we do not make acquisitions on economically acceptable terms, our future growth and our ability to increase distributions to you will be limited.
Our ability to grow depends on our ability to make accretive acquisitions. We may be unable to make accretive acquisitions for any of the following reasons:
| • | we are unable to identify attractive acquisition candidates or negotiate acceptable purchase contracts with them; |
| • | we are unable to obtain necessary governmental approvals; |
| • | we are unable to obtain financing for the acquisitions on economically acceptable terms, or at all; |
| • | we are unable to secure adequate customer commitments to use the acquired facilities; or |
| • | we are outbid by competitors. |
33
If we are unable to make accretive acquisitions, then our future growth and ability to increase distributions to you will be limited.
We intend to pursue acquisitions of additional LNG receiving terminals, natural gas pipelines and related assets in the future, either directly from Cheniere or from third parties. However, Cheniere is not obligated to offer us any of these assets. If Cheniere does offer us the opportunity to purchase assets, we may not be able to successfully negotiate a purchase and sale agreement and related agreements, we may not be able to obtain any required financing for such purchase and we may not be able to obtain any required governmental and third-party consents. The decision whether or not to accept such offer, and to negotiate the terms of such offer, will be made by the conflicts committee of our general partner, which may decline the opportunity to accept such offer for a variety of reasons, including a determination that the acquisition of the assets at the proposed purchase price would not result in an increase, or a sufficient increase, in our adjusted operating surplus per unit within an appropriate timeframe.
Acquisitions involve risks that may adversely affect our business and ability to make distributions to you.
Any acquisition involves potential risks, including:
| • | an inability to integrate successfully the businesses that we acquire with our existing business; |
| • | a decrease in our liquidity by using a significant portion of our available cash or borrowing capacity to finance the acquisition; |
| • | the assumption of unknown liabilities; |
| • | limitations on rights to indemnity from the seller; |
| • | mistaken assumptions about the cash generated, or to be generated, by the business acquired or the overall costs of equity or debt; |
| • | the diversion of management’s and employees’ attention from other business concerns; and |
| • | unforeseen difficulties encountered in operating new business segments or in new geographic areas. |
If we consummate any future acquisitions, our capitalization and results of operations may change significantly, and you will not have the opportunity to evaluate the economic, financial and other relevant information that we will consider in determining the application of our future funds and other resources. In addition, if we issue additional units in connection with future growth, your interest in us will be diluted, and distributions to you may be reduced.
We are subject to significant operating hazards and uninsured risks, one or more of which may create significant liabilities for us.
The construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be subject to the inherent risks often associated with this type of operation, including explosions, pollution, release of toxic substances, fires, hurricanes and adverse weather conditions and other hazards, each of which could result in a significant delay in the timing of commencement of operations and/or in damage to or destruction of the facility or damage to persons and property. In addition, operations at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and the facilities and tankers of third parties on which our operations are dependent face possible risks associated with acts of aggression or terrorism.
We do not maintain and intend to maintain insurance against some of these risks and losses. See “Business—Insurance.” We may not be able to maintain desired or required insurance in the future at rates that we consider reasonable. The occurrence of a significant event not fully insured or indemnified against could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
34
Existing and future U.S. governmental regulation could result in increased compliance costs or additional operating costs and restrictions.
Our business is and will be subject to extensive federal, state and local laws and regulations that regulate the discharge of natural gas, hazardous substances, materials and other compounds into the environment or otherwise relate to the protection of the environment. Many of these laws and regulations, such as the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act, the Clean Air Act, the Oil Pollution Act and the Clean Water Act, and analogous state laws and regulations, restrict or prohibit the types, quantities and concentration of substances that can be released into the environment in connection with the construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Releases in violation of these regulations can lead to substantial liabilities for non-compliance or for pollution or releases of hazardous substances, materials or compounds or otherwise require additional costs or changes in operations that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may also result in substantial civil and criminal fines and penalties.
Existing environmental laws and regulations may be revised or reinterpreted or new laws and regulations may be adopted or become applicable to us. For example, the adoption of frequently proposed legislation implementing a carbon tax on energy sources that emit carbon dioxide into the atmosphere may have a material adverse effect on the ability of our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing: (i) to import LNG, if imposed on them as importers of potential emission sources, or (ii) to sell regasified LNG, if imposed on them or their customers as natural gas suppliers or consumers. In addition, as Sabine Pass LNG consumes retainage gas at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, this carbon tax may also be imposed on Sabine Pass LNG directly. Other future legislation and regulations, such as those relating to the transportation and security of LNG imported to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal through the Sabine Pass Channel, could cause additional expenditures, restrictions and delays in our business and to our planned construction, the extent of which cannot be predicted and which may require us to limit substantially, delay or cease operations in some circumstances. Revised, reinterpreted or additional laws and regulations that result in increased compliance costs or additional operating costs and restrictions could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
Our lack of diversification could have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
All of our revenue is derived from payments under TUAs relating to one asset, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Due to our lack of asset and geographic diversification, an adverse development at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or in the LNG industry would have a significantly greater impact on our financial condition and results of operations than if we maintained more diverse assets and operating areas.
Terrorist attacks or military campaigns may adversely impact our business.
A terrorist incident involving an LNG facility or LNG carrier may result in delays in, or cancellation of, construction of new LNG facilities, including the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which would increase our costs and decrease our cash flows and could delay commencement of commercial operations. A terrorist incident may also result in temporary or permanent closure of existing LNG facilities, which, after commencement of commercial operations at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, could increase our costs and decrease our cash flows, depending on the duration of the closure. Operations at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal could also become subject to increased governmental scrutiny that may result in additional security measures at a significant incremental cost to us. In addition, the threat of terrorism and the impact of military campaigns may lead to continued volatility in prices for natural gas that could adversely affect our customers, particularly Cheniere Marketing, including their ability to satisfy their obligations to us under their TUAs.
35
Risks Relating to an Investment in Us and Our Common Units
Our general partner and its affiliates have conflicts of interest and limited fiduciary duties, which may permit them to favor their own interests to the detriment of us and our unitholders.
Following this offering, Cheniere will control our general partner, which has sole responsibility for conducting our business and managing our operations. Some of our general partner’s directors are also directors of Cheniere, and certain of our general partner’s officers are officers of Cheniere. Therefore, conflicts of interest may arise between Cheniere and its affiliates, including our general partner, on the one hand, and us and our unitholders, on the other hand. In resolving these conflicts, our general partner may favor its own interests and the interests of its affiliates over the interests of us and our unitholders. These conflicts include, among others, the following situations:
| • | neither our partnership agreement nor any other agreement requires Cheniere to pursue a business strategy that favors us. Cheniere’s directors and officers have a fiduciary duty to make these decisions in favor of the owners of Cheniere, which may be contrary to our interests; |
| • | our general partner controls the interpretation and enforcement of contractual obligations between us, on one hand, and Cheniere, on the other hand, including provisions governing administrative services and acquisitions; |
| • | our general partner is allowed to take into account the interests of parties other than us, such as Cheniere and its affiliates, in resolving conflicts of interest, which has the effect of limiting its fiduciary duty to us and our unitholders; |
| • | our general partner has limited its liability and reduced its fiduciary duties under the partnership agreement, while also restricting the remedies available to our unitholders for actions that, without these limitations, might constitute breaches of fiduciary duty; |
| • | Cheniere is not limited in its ability to compete with us. Please read “—Cheniere is not restricted from competing with us and is free to develop, operate and dispose of, and is currently developing, LNG receiving terminals, pipelines and other assets without any obligation to offer us the opportunity to develop or acquire those assets;” |
| • | our general partner determines the amount and timing of asset purchases and sales, capital expenditures, borrowings, issuances of additional partnership securities, and the establishment, increase or decrease in the amounts of reserves, each of which can affect the amount of cash that is distributed to our unitholders; |
| • | our general partner determines the amount and timing of any capital expenditures and whether a capital expenditure is a maintenance capital expenditure, which reduces operating surplus, or an expansion capital expenditure, which does not reduce operating surplus. This determination can affect the amount of cash that is distributed to our unitholders and the ability of the subordinated units to convert to common units; |
| • | Cheniere Marketing may exercise an option, free of any fiduciary duty to us, for us to construct, at our cost, a sixth LNG tank at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, although we will not receive any additional revenue from this tank. We estimate the cost to construct this tank to be in the range of $120 million to $140 million. |
| • | our partnership agreement does not restrict our general partner from causing us to pay it or its affiliates for any services rendered on terms that are fair and reasonable to us or entering into additional contractual arrangements with any of these entities on our behalf; |
| • | our general partner intends to limit its liability regarding our contractual and other obligations and, in some circumstances, is entitled to be indemnified by us; |
| • | our general partner may exercise its limited right to call and purchase common units if it and its affiliates own more than 80% of the common units; and |
| • | our general partner decides whether to retain separate counsel, accountants or others to perform services for us. |
We expect that there will be additional agreements or arrangements with Cheniere and its affiliates, including future interconnection, natural gas balancing and storage agreements with one or more Cheniere-
36
affiliated natural gas pipelines as well as other agreements and arrangements that cannot now be anticipated. In those circumstances where additional contracts with Cheniere and its affiliates may be necessary or desirable, additional conflicts of interest will be involved.
Cheniere is not restricted from competing with us and is free to develop, operate and dispose of, and is currently developing, LNG receiving terminals, pipelines and other assets without any obligation to offer us the opportunity to develop or acquire those assets.
Cheniere and its affiliates are not prohibited from owning assets or engaging in businesses that compete directly or indirectly with us. Cheniere may acquire, construct or dispose of its planned Corpus Christi or Creole Trail LNG receiving terminals, its planned pipelines or any other assets without any obligation to offer us the opportunity to purchase or construct any of those assets. In addition, under our partnership agreement, the doctrine of corporate opportunity, or any analogous doctrine, will not apply to Cheniere and its affiliates. As a result, neither Cheniere nor any of its affiliates will have any obligation to present new business opportunities to us, and they may take advantage of such opportunities themselves. Cheniere also has significantly greater resources and experience than we have, which may make it more difficult for us to compete with Cheniere and its affiliates with respect to commercial activities or acquisition candidates.
Our partnership agreement limits our general partner’s fiduciary duties to unitholders and restricts the remedies available to unitholders for actions taken by our general partner that might otherwise constitute breaches of fiduciary duty.
Our partnership agreement contains provisions that reduce the standards to which our general partner would otherwise be held by state fiduciary duty law. For example, our partnership agreement:
| • | permits our general partner to make a number of decisions in its individual capacity, as opposed to in its capacity as our general partner. This entitles our general partner to consider only the interests and factors that it desires, and it has no duty or obligation to give any consideration to any interest of, or factors affecting, us, our affiliates or any limited partner. Examples include the exercise of its limited call right, the exercise of its rights to transfer or vote the units it owns, the exercise of its registration rights and its determination whether or not to consent to any merger or consolidation of the partnership or amendment to the partnership agreement; |
| • | provides that our general partner will not have any liability to us or our unitholders for decisions made in its capacity as general partner, as long as it acted in good faith, meaning that it believed the decision was in the best interests of our partnership; |
| • | generally provides that affiliated transactions and resolutions of conflicts of interest not approved by the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner and not involving a vote of unitholders must be on terms no less favorable to us than those generally being provided to or available from unrelated third parties or be “fair and reasonable” to us and that, in determining whether a transaction or resolution is “fair and reasonable,” our general partner may consider the totality of the relationships between the parties involved, including other transactions that may be particularly favorable or advantageous to us; |
| • | provides that our general partner, its affiliates and their officers and directors will not be liable for monetary damages to us or our limited partners for any acts or omissions unless there has been a final and non-appealable judgment entered by a court of competent jurisdiction determining that our general partner or those other persons acted in bad faith or engaged in fraud, willful misconduct or, in the case of a criminal matter, acted with knowledge that such conduct was criminal; and |
| • | provides that in resolving conflicts of interest, it will be presumed that in making its decision the conflicts committee or the general partner acted in good faith, and in any proceeding brought by or on behalf of any limited partner or us, the person bringing or prosecuting such proceeding will have the burden of overcoming such presumption. |
By purchasing a common unit, a unitholder will become bound by the provisions of our partnership agreement, including the provisions described above. Please read “Description of the Common Units—Transfer of Common Units.”
37
Holders of our common units have limited voting rights and are not entitled to elect our general partner or its directors, which could reduce the price at which the common units trade.
Unlike the holders of common stock in a corporation, unitholders have only limited voting rights on matters affecting our business and, therefore, limited ability to influence management’s decisions regarding our business. Unitholders will have no right to elect our general partner or its board of directors on an annual or other continuing basis. The board of directors of our general partner is chosen entirely by Cheniere Holdings, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere. As a result, the price at which the common units will trade could be diminished because of the absence or reduction of a control premium in the trading price.
Even if unitholders are dissatisfied, they cannot initially remove our general partner without its consent.
If our unitholders will be unable initially to remove our general partner. Our unitholders will be unable to remove our general partner without the consent of Cheniere Holdings because Cheniere Holdings will own a sufficient number of common and subordinated units upon completion of this offering to be able to prevent removal of our general partner. The vote of the holders of at least 66 2/3% of all outstanding common and subordinated units (including any units owned by our general partner and its affiliates) voting together as a single class is required to remove our general partner. Following the closing of this offering, Cheniere Holdings will own approximately 92.3% of our common and subordinated units (approximately 91.1% if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional common units in full). In addition, if our general partner is removed without cause during the subordination period and units held by our general partner and its affiliates are not voted in favor of that removal, all remaining subordinated units will automatically be converted into common units and any existing arrearages on the common units will be extinguished. A removal of our general partner under these circumstances would adversely affect the common units by prematurely eliminating their distribution and liquidation preference over the subordinated units, which would otherwise have continued until we had met certain distribution and performance tests.
Cause is narrowly defined in our partnership agreement to mean that a court of competent jurisdiction has entered a final, non-appealable judgment finding our general partner liable for actual fraud or willful misconduct in its capacity as our general partner. Cause does not include most cases of poor management of the business, so the removal of the general partner because of the unitholder’s dissatisfaction with our general partner’s performance in managing our partnership will most likely result in the termination of the subordination period and conversion of all subordinated units to common units.
Control of our general partner may be transferred to a third party without unitholder consent.
Our general partner may transfer its general partner interest to a third party in a merger or in a sale of all or substantially all of its assets without the consent of the unitholders. Furthermore, our partnership agreement does not restrict the ability of the owners of our general partner from transferring all or a portion of their respective ownership interest in our general partner to a third party. The new owners of our general partner would then be in a position to replace the board of directors and officers of our general partner with its own choices and thereby influence the decisions taken by the board of directors and officers.
We will incur significant costs as a result of being a publicly traded company.
We have no history operating as a publicly traded company. As a publicly traded company, we will incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we would not incur as a private company. In addition, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as well as rules subsequently implemented by the SEC and the American Stock Exchange, have required changes in corporate governance practices of publicly traded companies. We expect these rules and regulations to increase our legal and financial compliance costs and to make activities more time-consuming and costly. For example, as a result of becoming a publicly traded company, we are required to have at least three independent directors, create additional board committees and adopt policies regarding internal controls and disclosure controls and procedures, including the preparation of reports on internal controls over
38
financial reporting. In addition, we will incur additional costs associated with our publicly traded company reporting requirements. We also expect these new rules and regulations to make it more difficult and more expensive for our general partner to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and it may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the same or similar coverage. As a result, it may be more difficult for our general partner to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on its board of directors or as executive officers.
Our general partner has a limited call right that may require you to sell your common units at an undesirable time or price.
At the completion of this offering, and assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional units, an affiliate of our general partner will own 52.7% of our total common units. If the subordinated units convert into common units, an affiliate of our general partner will own approximately 92.3% of the common units (approximately 91.1% if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional common units in full). If at any time more than 80% of our outstanding common units are owned by our general partner and its affiliates, our general partner will have the right, but not the obligation, which it may assign to any of its affiliates or to us, to acquire all, but not less than all, of our common units held by unaffiliated persons at a price not less than their then-current market price, as defined in our partnership agreement. As a result, you may be required to sell your common units at an undesirable time or price and may not receive any return on your investment. You may also incur a tax liability upon a sale of your common units. Our general partner is not obligated to obtain a fairness opinion regarding the value of the common units to be repurchased by it upon exercise of the limited call right. There is no restriction in our partnership agreement that prevents our general partner from issuing additional common units or other equity securities and exercising its call right. If our general partner exercised its limited call right, the effect would be to take us private and, if the common units were subsequently deregistered, we would no longer be subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act. For additional information about the limited call right, please read “The Partnership Agreement—Limited Call Right.”
Our partnership agreement restricts the voting rights of unitholders (other than our general partner and its affiliates) owning 20% or more of any class of our units.
Our partnership agreement restricts unitholders’ voting rights by providing that any units held by a person that owns 20% or more of any class of units then outstanding, other than our general partner and its affiliates, their transferees and persons who acquired such units with the prior approval of the board of directors of our general partner, cannot vote on any matter. The partnership agreement also contains provisions limiting the ability of unitholders to call meetings or to acquire information about our operations, as well as other provisions limiting the unitholders’ ability to influence the manner or direction of management.
Our partnership agreement prohibits a unitholder (other than our general partner and its affiliates) who acquires 15% or more of our limited partner units without the approval of the board of directors of our general partner from engaging in a business combination with us for three years unless certain approvals are obtained. This provision could discourage a change of control that our unitholders may favor, which could negatively affect the price of our common units.
Our partnership agreement effectively adopts Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, or the DGCL. Section 203 of the DGCL as it applies to us prevents an interested unitholder, defined as a person who owns 15% or more of our outstanding limited partner units, from engaging in business combinations with us for three years following the time such person becomes an interested unitholder unless certain approvals are obtained. Section 203 broadly defines “business combination” to encompass a wide variety of transactions with or caused by an interested unitholder, including mergers, asset sales and other transactions in which the interested unitholder receives a benefit on other than a pro rata basis with other unitholders. This provision of our partnership agreement could have an anti-takeover effect with respect to transactions not approved in advance by the board of directors of our general partner, including discouraging takeover attempts that might result in a premium over the market price for our common units.
39
You will experience immediate and substantial dilution of $20.95 per common unit.
The assumed initial public offering price of $20.00 per common unit exceeds the pro forma net tangible book value of $(0.95) per common unit as of December 31, 2006. You will incur immediate and substantial dilution of $20.95 per common unit. This dilution results primarily because the assets contributed by our general partner and its affiliates are recorded at their historical cost, and not their fair value, in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP. Please read “Dilution.”
You may not have limited liability if a court finds that unitholder action constitutes control of our business.
A general partner of a partnership generally has unlimited liability for the obligations of the partnership, except for contractual obligations of the partnership that are expressly made without recourse to the general partner. We are organized under Delaware law, and we conduct business in other states. As a limited partner in a partnership organized under Delaware law, you could be held liable for our obligations to the same extent as a general partner if a court determined that the right or the exercise of the right by our unitholders as a group to remove or replace our general partner, to approve some amendments to the partnership agreement or to take other action under our partnership agreement constituted participation in the “control” of our business. In addition, limitations on the liability of holders of limited partner interests for the obligations of a limited partnership have not been clearly established in many jurisdictions. Please read “The Partnership Agreement—Limited Liability.”
You may have liability to repay distributions wrongfully made.
Under certain circumstances, our unitholders may have to repay amounts wrongfully distributed to them. Under Section 17-607 of the Delaware Revised Uniform Limited Partnership Act, we may not make a distribution to our unitholders if the distribution would cause our liabilities to exceed the fair value of our assets. Delaware law provides that, for a period of three years from the date of the impermissible distribution, partners who received such a distribution and who knew at the time of the distribution that it violated Delaware law will be liable to the partnership for the distribution amount. Liabilities to partners on account of their partner interests and liabilities that are non-recourse to the partnership are not counted for purposes of determining whether a distribution is permitted.
We may issue additional units without your approval, which would dilute your ownership interest.
At any time during the subordination period, with the approval of the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner, we may issue an unlimited number of limited partner interests of any type without the approval of our unitholders. After the subordination period, we may issue an unlimited number of limited partner interests of any type without limitation of any kind. The issuance by us of additional common units or other equity securities of equal or senior rank will have the following effects:
| • | our unitholders’ proportionate ownership interest in us will decrease; |
| • | the amount of cash available per unit to pay distributions may decrease; |
| • | because a lower percentage of total outstanding units will be subordinated units, the risk will increase that a shortfall in the payment of the initial quarterly distribution will be borne by our common unitholders; |
| • | the ratio of taxable income to distributions may increase; |
| • | the relative voting strength of each previously outstanding unit may be diminished; and |
| • | the market price of the common units may decline. |
There is no existing market for our common units, and a trading market that will provide you with adequate liquidity may not develop.
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for the common units, and our common units have not previously traded on any exchange or market. After this offering, there will be only 12,500,000 publicly traded
40
common units, assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional common units. We do not know the extent to which investor interest will lead to the development of a trading market or how liquid that market might be. Unitholders may not be able to resell their common units at or above the initial public offering price. In addition, the lack of liquidity may result in wide bid-ask spreads, contribute to significant fluctuations in the market price of the common units and limit the number of investors who are able to buy the common units. We cannot assure you as to:
| • | the likelihood that an active market will develop for our common units; |
| • | the liquidity of any such market; |
| • | the ability for you to sell your common units; or |
| • | the price that you may obtain for your common units. |
The price of our common units may fluctuate significantly, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
The initial public offering price for our common units will be determined by negotiations between us and the representatives of the underwriters and may not be indicative of the market price of our common units that will prevail in the trading market. The market price of our common units may decline below the initial public offering price. The market price of our common units may also be influenced by many factors, some of which are beyond our control, including:
| • | our quarterly distributions; |
| • | our quarterly or annual earnings or those of other companies in our industry; |
| • | actual or potential non-performance by any customer under a TUA; |
| • | announcements by us or our competitors of significant contracts; |
| • | changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance, interpretations or principles; |
| • | general economic conditions; |
| • | the failure of securities analysts to cover our common units after this offering or changes in financial or other estimates by analysts; |
| • | future sales of our common units; and |
| • | other factors described in these “Risk Factors.” |
Our tax treatment depends on our status as a partnership for federal income tax purposes, as well as our not being subject to a material amount of entity level taxation by individual states. If the IRS were to treat us as a corporation or if we were to become subject to a material amount of entity level taxation for state tax purposes, then our cash available for distribution to you would be substantially reduced.
The anticipated after-tax economic benefit of an investment in our common units depends largely on our being treated as a partnership for federal income tax purposes. We have not requested, and do not plan to request, a ruling from the IRS on this matter.
If we were treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes, we would pay federal income tax on our taxable income at the corporate tax rate, which is currently a maximum of 35%, and we likely would pay state taxes as well. Distributions to you would generally be taxed again as corporate distributions, and no income, gains, losses or deductions would flow through to you. Because a tax would be imposed upon us as a corporation, the cash available for distributions to you would be substantially reduced. Therefore, treatment of us as a corporation would result in a material reduction in the anticipated cash flow and after-tax return to you, likely causing a substantial reduction in the value of our common units.
41
Current law may change, causing us to be treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes or otherwise subjecting us to a material amount of entity level taxation for federal, state or local income tax purposes. In addition, several states are evaluating ways to subject partnerships to entity level taxation through the imposition of state income, franchise or other forms of taxation. For example, we will be subject to a new entity level tax on the portion of our revenue generated in Texas beginning for tax reports due on or after January 1, 2008. Specifically, the Texas margin tax will be imposed at a maximum effective rate of 0.7% of our gross income apportioned to Texas. Imposition of such tax on us by the State of Texas, or any other state, will reduce the cash available for distribution to you.
A successful IRS contest of the federal income tax positions that we take may adversely impact the market for our common units, and the costs of any contests will be borne by our unitholders and our general partner.
The IRS may adopt positions that differ from the positions that we take, even positions taken with advice of counsel. It may be necessary to resort to administrative or court proceedings to sustain some or all of the positions that we take. A court may not agree with some or all of the positions that we take. Any contest with the IRS may materially and adversely impact the market for our common units. In addition, the costs of any contest with the IRS, principally legal, accounting and related fees, will be borne indirectly by our unitholders and our general partner.
You may be required to pay taxes on your share of our taxable income even if you do not receive any cash distributions from us.
Because our unitholders will be treated as partners to whom we will allocate taxable income, which could be different in amount from the cash that we distribute, you will be required to pay federal income taxes and, in some cases, state and local income taxes on your share of our taxable income even if you do not receive any cash distributions from us. You may not receive cash distributions from us equal to your share of our taxable income or even equal to the actual tax liability which results from your share of our taxable income.
We intend to allocate items of income, gain, loss and deduction among the holders of our common units and subordinated units on or after the date that the subordination period ends to ensure that common units issued in exchange for our subordinated units have the same economic and federal income tax characteristics as our other common units. Any such allocation of items of our income or gain to unitholders, which may include allocations to holders of our common units, would not be accompanied by a distribution of cash to such unitholders. In addition, any such allocation of items of deduction or loss to specific unitholders (for example, to the holder of the subordinated units) would effectively reduce the amount of items of deduction or loss that will be allocated to other unitholders.
You may receive a smaller distribution per unit than our general partner and its affiliates if we were to liquidate.
If we were to liquidate, we would make liquidating distributions to our unitholders, including our general partner and its affiliates, in accordance with the balances in their “capital accounts.” The capital accounts of common units purchased in this offering will likely decrease each quarter, as compared to the capital accounts of the subordinated units held by our general partner and its affiliates, during the period that distributions on our common units and general partner units are funded from the distribution reserve established in connection with this offering. Under some circumstances, including upon our liquidation, items of our income, gain, loss and deduction will be allocated in a manner that eliminates part or all of this disparity. If we were to liquidate at a time when the capital accounts of the subordinated units held by the general partner and its affiliates exceeded (on a per unit basis) the capital accounts of the common units purchased in this offering, and if there were not sufficient items of income, gain, loss and deduction in connection with our liquidation to eliminate that excess, holders of common units purchased in this offering would receive a smaller liquidating distribution (on a per unit basis) than our general partner and its affiliates.
42
Tax gain or loss on the disposition of our common units could be different than expected.
If you sell common units, you will recognize gain or loss equal to the difference between the amount realized and your tax basis in those common units. Prior distributions to you in excess of the total net taxable income a unitholder is allocated for a common unit, which decreased your tax basis in that common unit, will, in effect, become taxable income to you if the common unit is sold at a price greater than your tax basis in that common unit, even if the price you receive is less than your original cost. A substantial portion of the amount realized, whether or not representing gain, may be ordinary income to you.
Tax-exempt entities and foreign persons face unique tax issues from owning common units that may result in adverse tax consequences to them.
Investments in common units by tax-exempt entities, such as individual retirement accounts (known as IRAs) and foreign persons raises issues unique to them. For example, virtually all of our income allocated to unitholders who are organizations exempt from federal income tax, including individual retirement accounts and other retirement plans, will be unrelated business taxable income and will be taxable to them. Distributions to non-U.S. persons will be reduced by withholding taxes at the highest applicable effective tax rate, and non-U.S. persons will be required to file United States federal income tax returns and pay tax on their share of our taxable income.
We will treat each holder of our common units as having the same tax benefits without regard to the actual common units held. The IRS may challenge this treatment, which could adversely affect the value of our common units.
Because we cannot match transferors and transferees of common units, we adopt depreciation and amortization positions that may not conform with all aspects of applicable Treasury regulations. A successful IRS challenge to those positions could adversely affect the amount of tax benefits available to a common unitholder. It also could affect the timing of these tax benefits or the amount of gain from a sale of common units and could have a negative impact on the value of our common units or result in audit adjustments to the common unitholders’ tax returns.
You will likely be subject to state and local taxes and return filing requirements as a result of an investment in our common units.
In addition to federal income taxes, you will likely be subject to other taxes, including state and local income taxes, unincorporated business taxes and estate, inheritance or intangible taxes that are imposed by the various jurisdictions in which we do business or own property. We will initially own property or do business in Louisiana and Texas. You will likely be required to file state and local income tax returns and pay state and local income taxes in some or all of these various jurisdictions. Furthermore, you may be subject to penalties for failure to comply with those requirements. We may own property or conduct business in other states or foreign countries in the future. It is your responsibility to file all United States federal, state and local tax returns. Our counsel has not rendered an opinion on the state and local tax consequences of an investment in our common units.
The sale or exchange of 50% or more of our capital and profits interests during any twelve-month period will result in the termination of our partnership for federal income tax purposes.
We will be considered to have terminated for federal income tax purposes if there is a sale or exchange of 50% or more of the total interests in our capital and profits within a twelve-month period. Our termination would, among other things, result in the closing of our taxable year for all unitholders and could result in a deferral of depreciation deductions allowable in computing our taxable income. Please read “Material Tax Consequences—Disposition of Common Units—Constructive Termination” for a discussion of the consequences of our termination for federal income tax purposes.
43
We will sell in this offering a number of common units that will generate net proceeds to us of approximately $96.7 million, after deducting the underwriting discount of approximately $7.0 million and the structuring fee of approximately $521,000 that we will pay on the sale of our common units. We will use all of our net proceeds to purchase U.S. treasury securities maturing as to principal and interest at such times and in such amounts as will be sufficient to pay the $0.425 initial quarterly distribution on all common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. These U.S. treasury securities will be held as a distribution reserve under our partnership agreement.
The allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder (and the corresponding net proceeds to be received by us and the selling unitholder) will vary based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund the distribution reserve at the time that we price the offering. We currently estimate that the public offering price will be $20.00 per common unit and that the cost of the U.S. treasury securities needed to fund the distribution reserve will be approximately $96.7 million. Any net proceeds that we receive in excess of the amount necessary to fund the distribution reserve will be distributed to the selling unitholder, and any shortfall in that amount will be contributed to us by the selling unitholder.
We estimate that the selling unitholder will receive approximately $132.0 million in net proceeds from this offering, after deducting the underwriting discount of approximately $9.8 million on the units that it sells, the structuring fee of approximately $729,000 that it will pay and all other costs of this offering, which we estimate will be $3.3 million. The selling unitholder has granted the underwriters an option to purchase additional common units to cover over-allotments, if any, in connection with this offering. We will not receive any proceeds from any common units sold by the selling unitholder, including proceeds received from any exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional common units.
44
The following table shows:
| • | our combined historical capitalization as of December 31, 2006; and |
| • | our combined capitalization as of December 31, 2006, on a pro forma basis to reflect: |
| • | the issuance of our common units, subordinated units and general partner units to our general partner and its affiliate; and |
| • | the issuance and sale of additional common units in this offering and application of the net proceeds that we receive. |
This table is derived from and should be read together with and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, our historical and unaudited combined financial statements and the accompanying notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. You should also read this table in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
| As of December 31, 2006 | ||||||||
| Combined Actual |
Combined Pro Forma |
|||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Long-term debt: |
||||||||
| Sabine Pass LNG notes due 2013 |
$ | 550,000 | $ | 550,000 | ||||
| Sabine Pass LNG notes due 2016 |
1,482,000 | 1,482,000 | ||||||
| Total long-term debt |
2,032,000 | 2,032,000 | ||||||
| Equity: |
||||||||
| Owners’ deficit |
(253,338 | ) | — | |||||
| Held by public: |
||||||||
| Common units |
— | 96,652 | ||||||
| Held by the general partner and its affiliate: |
||||||||
| Common units |
— | (23,104 | ) | |||||
| Subordinated units |
— | (224,762 | ) | |||||
| General partner units |
— | (5,472 | ) | |||||
| Total deficit |
(253,338 | ) | (156,686 | ) | ||||
| Total capitalization |
$ | 1,778,662 | $ | 1,875,314 | ||||
45
Dilution is the amount by which the offering price paid by purchasers of common units sold in this offering will exceed the net tangible book value per common unit after the offering. Based on the assumed initial public offering price of $20.00 per common unit, on a pro forma basis as of December 31, 2006, after giving effect to the offering of common units and the related transactions, our net tangible book value was negative $156.7 million, or negative $0.95 per common unit. Purchasers of common units in this offering will experience substantial and immediate dilution in net tangible book value per common unit, as illustrated in the following table.
| Assumed initial public offering price per common unit |
$ | 20.00 | ||||||
| Pro forma net tangible book value per common unit before the offering(1) |
$ | (1.58 | ) | |||||
| Increase in net tangible book value per common unit attributable to purchasers in the offering |
0.63 | |||||||
| Less: Pro forma net tangible book value per common unit after the offering(2) |
(0.95 | ) | ||||||
| Immediate dilution in net tangible book value per common unit to purchasers in the offering |
$ | 20.95 | ||||||
| (1) | Determined by dividing the total number of units (21,206,026 common units, 135,383,831 subordinated units, and 3,302,045 general partner units) to be issued to our general partner and its affiliate for the contribution of the equity interests in the limited partner and general partner of Sabine Pass LNG into the net tangible book value of the contributed assets. |
| (2) | Determined by dividing the total number of units (26,416,357 common units, 135,383,831 subordinated units, and 3,302,045 general partner units) to be outstanding after the offering into our pro forma net tangible book value, after giving effect to the application of the expected net proceeds of the offering. |
The following table sets forth the number of units that we will issue and the total consideration contributed to us by our general partner and its affiliate and by the purchasers of common units in this offering upon consummation of the transactions contemplated by this prospectus.
| Units Acquired | Total Consideration |
|||||||||||
| Number | Percent | Amount | Percent | |||||||||
| (in millions, other than percentages) | ||||||||||||
| General partner and its affiliate(1)(2) |
152.6 | 92.4 | % | $ | (253.3 | ) | 7,676 | % | ||||
| New investors |
12.5 | 7.6 | % | 250.0 | (7,576 | )% | ||||||
| Total |
165.1 | 100.0 | % | $ | (3.3 | ) | 100.0 | % | ||||
| (1) | Upon consummation of the transactions contemplated by this prospectus, our general partner and its affiliate are expected to own 13,916,357 common units, 135,383,831 subordinated units and 3,302,045 general partner units. The actual number of common units owned by our general partner and its affiliates (and its corresponding limited partner interest in us) will vary based on the allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder, which will be based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund the distribution reserve at the time of this offering (which we currently believe will be approximately $96.7 million). |
| (2) | The assets contributed by our general partner and its affiliate were recorded at historical cost in accordance with GAAP. Book value of the consideration provided by our general partner and its affiliate, as of December 31, 2006, was negative $253.3 million. |
46
CASH DISTRIBUTION POLICY AND RESTRICTIONS ON DISTRIBUTIONS
You should read the following discussion of our cash distribution policy in conjunction with the specific assumptions included in this section. For more detailed information regarding the factors and assumptions upon which our cash distribution policy is based, please read “—Assumptions and Considerations” below. In addition, you should read “Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and “Risk Factors” for information regarding statements that do not relate strictly to historical or current facts and certain risks inherent in our business.
Rationale for Our Cash Distribution Policy
For the Period Through June 30, 2009
We are a development stage company without any revenues, operating cash flows or operating history. We do not expect that revenues from our TUAs with Total and Chevron will begin until the second and third quarter of 2009, respectively. Therefore, we do not expect to generate sufficient cash from operations to fund distributions to our unitholders until the third quarter of 2009. As a result, we will use all of the net proceeds that we receive from this offering to purchase an amount of U.S. treasury securities sufficient to fund a distribution reserve to pay the $0.425 initial quarterly distribution per common unit for all common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. Any net proceeds that we receive in excess of the amount necessary to fund the distribution reserve will be distributed to the selling unitholder, and any shortfall in that amount will be contributed to us by the selling unitholder. Distributions to our unitholders from the distribution reserve will be a return of your investment.
In the event that we issue additional common units prior to June 30, 2009, we will use a portion of the net proceeds to increase the distribution reserve by an amount that our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines is required to fund the initial quarterly distribution for such additional common units, as well as related distributions on the general partner units, from their date of issuance through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. Any amount remaining in the distribution reserve on August 15, 2009 will be distributed to Cheniere Holdings. We may distribute amounts in the distribution reserve to Cheniere Holdings prior to August 15, 2009 if our general partner, with the concurrence of its conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines that such reserves are not necessary to provide for distributions on all of our common units and general partner units for any quarter ending on or prior to June 30, 2009. If we generate cash from operations during the period from the closing of this offering to June 30, 2009, we will make quarterly distributions on our common units and general partner units from such cash generated from operations and, if the amount of such cash is insufficient to make the full quarterly distribution, from amounts in the distribution reserve.
For the Period After June 30, 2009
Beginning in the third quarter of 2009, the combined cash flow received from the Total and Chevron TUAs is expected to be sufficient to cover all annual debt service on the Sabine Pass LNG notes, which will be approximately $151 million, and all other annual operating costs of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which will be approximately $48 million for the four consecutive quarters ending June 30, 2010. The remaining funds from Total and Chevron will be sufficient for us to pay the operating expenses of our partnership and the initial quarterly distribution on all of our common units and general partner units so long as these funds are distributable under the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes, which would require us to be receiving substantial revenues under the Cheniere Marketing TUA or from one or more substitute customers.
We are entitled to receive $5 million per month under the Cheniere Marketing TUA commencing with Phase 1 commercial operation, which we expect will occur during the second quarter of 2008. We will not
47
receive the full contracted payments from Cheniere Marketing of approximately $21 million per month until the first quarter of 2009. These payments from Cheniere Marketing are expected to be sufficient to cover the initial quarterly distribution on the subordinated units beginning in the third quarter of 2009 but will not be sufficient to permit an increase in the common unit distribution above the initial quarterly distribution.
Our cash distribution policy beginning in the third quarter of 2009 will reflect a basic judgment that our unitholders will be better served by our distributing our cash available after expenses and reserves rather than retaining it. Because we are not subject to entity level federal income tax, we will have more cash to distribute to you than would be the case were we subject to tax. Our cash distribution policy is consistent with the terms of our partnership agreement, which requires that we distribute all of our available cash quarterly.
Limitations on Our Ability to Pay Quarterly Distributions After June 30, 2009
There is no guarantee that unitholders will receive quarterly distributions from us for the period after June 30, 2009. Our distribution policy may be changed at any time and is subject to certain restrictions and uncertainties, including:
| • | Our ability to pay distributions to our unitholders will depend on the performance of Sabine Pass LNG and its ability to distribute funds to us. In general, Sabine Pass LNG may make distributions under its indenture if: |
| • | no default or event of default under the indenture has occurred and is continuing or would occur as a consequence of such distribution; and |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG has successfully completed Phase 1 Target Completion (as defined in the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes), which we currently expect to occur during the second quarter of 2008; and |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG would, at the time of such distribution and after giving pro forma effect thereto as if such distribution had been made at the beginning of the applicable four-quarter period (or if fewer than four fiscal quarters have elapsed since the achievement of Phase 1 Target Completion, the number of full fiscal quarters that have elapsed), have been permitted to incur at least $1.00 of additional indebtedness pursuant to the 2.0 to 1.0 fixed charge coverage ratio test described in the indenture; and |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG has on deposit in a debt payment account an amount equal to (i) the aggregate amount of interest on the Sabine Pass LNG notes due on the immediately succeeding interest payment date, multiplied by (ii) the number of months passed since the preceding interest payment date, divided by (iii) six; and |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG has on deposit in a debt service reserve account an amount no less than the amount required to make the interest payments on the Sabine Pass LNG notes on the next succeeding interest payment date. |
For more information on the Sabine Pass LNG indenture, please read “Indebtedness–Indenture.”
| • | We may lack sufficient cash to pay distributions to our unitholders due to a number of factors that could adversely affect us. Please read “Risk Factors” for more information regarding these factors. |
| • | Our general partner has broad discretion to establish reserves for the prudent conduct of our business, and the establishment of those reserves could result in a reduction of our cash distributions to you from levels we currently anticipate pursuant to our stated distribution policy. |
| • | Even if our cash distribution policy is not modified, the amount of distributions that we pay under our cash distribution policy and the decision to pay any distribution is determined by our general partner, taking into consideration the terms of our partnership agreement. |
48
| • | Although our partnership agreement requires us to distribute our available cash, our partnership agreement may be amended. During the subordination period, with certain exceptions, our partnership agreement may not be amended without the approval of nonaffiliated common unitholders. However, our partnership agreement can be amended with the consent of our general partner and the approval of a majority of the outstanding common units after the subordination period has ended. At the closing of this offering, our general partner and its affiliates will own approximately 52.7% of the outstanding common units (45.6% if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional common units) and 100% of the outstanding subordinated units. |
| • | Under Section 17-607 of the Delaware Revised Uniform Limited Partnership Act, we may not make a distribution to you if the distribution would cause our liabilities to exceed the fair value of our assets. |
Our Cash Distribution Policy May Limit Our Ability to Grow
We will distribute all of our available cash to our unitholders. As a result, we expect to rely primarily upon external financing sources, including commercial borrowings and issuances of debt or equity securities, to fund our acquisition and capital investment expenditures. The incurrence of additional commercial borrowings or other debt to finance our operations would result in increased interest expense, which in turn may impact the available cash that we have to distribute to our unitholders. If we are unable to finance growth externally, our cash distribution policy could significantly impair our ability to grow.
After the subordination period, there are no limitations in our partnership agreement on our ability to issue additional units, including units ranking senior to the common units. In the event that we issue additional common units prior to June 30, 2009, we will use a portion of the net proceeds to increase the distribution reserve by an amount that our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines is required to fund the initial quarterly distribution for such additional common units and related general partner units from their date of issuance through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. To the extent we issue additional units after June 30, 2009, the payment of distributions on those additional units may increase the risk that we will be unable to maintain or increase our per unit distribution level, which in turn may impact the available cash that we have to distribute on each unit.
Overview
The amount of the initial quarterly distribution on our common units is $0.425 per unit, or $1.70 per year. The amount of cash needed to pay the initial quarterly distribution on all of the common units, subordinated units and general partner units to be outstanding immediately after this offering for one quarter and for four quarters ending June 30, 2010 will be approximately:
| Number of Units |
One Quarter |
Four Quarters | ||||||
| Public Common Units |
12,500,000 | $ | 5,312,500 | $ | 21,250,000 | |||
| Cheniere Affiliate Common Units |
13,916,357 | 5,914,452 | 23,657,807 | |||||
| Cheniere Affiliate Subordinated Units |
135,383,831 | 57,538,128 | 230,152,513 | |||||
| General Partner Units |
3,302,045 | 1,403,369 | 5,613,476 | |||||
| Total |
165,102,233 | $ | 70,168,449 | $ | 280,673,796 | |||
Our Initial Distribution Rate
For each calendar quarter through the quarter ending June 30, 2009, we will make cash distributions of $0.425 per unit, or $1.70 per year, on all outstanding common units using cash from the distribution reserve that will be funded with the proceeds we receive from this offering. We will make these quarterly cash distributions
49
within 45 days after the end of each quarter, beginning with the quarter ending March 31, 2007, to unitholders of record on the applicable record date. We will adjust the initial quarterly distribution for the period from the closing of this offering through March 31, 2007 based on the actual length of the period. We believe that following the completion of the offering, we will have sufficient available cash in the distribution reserve to allow us to pay the full initial quarterly distribution on all of our outstanding common units, as well as the related distributions on the general partner units, for each quarter through the quarter ending June 30, 2009.
Until the end of the subordination period, before we make any quarterly distributions to subordinated unitholders, our common unitholders are entitled to receive payment of the full initial quarterly distribution plus any arrearages from prior quarters. Please read “How We Make Cash Distributions—Subordination Period.”
As of the date of this offering, our general partner will be entitled to 2% of all distributions that we make prior to our liquidation. The general partner’s initial 2% interest in these distributions may be reduced if we issue additional units in the future and our general partner does not contribute a proportionate amount of capital to us to maintain its initial 2% general partner interest. Our general partner has the right, but not the obligation, to contribute a proportionate amount of capital to us to maintain its current general partner interest.
In the sections that follow, we present in detail the basis for our belief that we will be able:
| • | to pay the initial quarterly distribution on all of our outstanding common units, as well as the related distributions on the general partner units, for each quarter through the quarter ending June 30, 2009; and |
| • | to pay the initial quarterly distribution on all outstanding common units and subordinated units, as well as related distributions on the general partner units, for each of the four consecutive quarters ending June 30, 2010. |
Financial Forecast for the Period from the Closing of this Offering Through June 30, 2010
Set forth below is a financial forecast of the expected revenues, EBITDA and cash available for distribution for Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. for the period from the closing of this offering through June 30, 2010. Our financial forecast presents, to the best of our knowledge and belief, the expected revenues, EBITDA and cash available for distribution for Cheniere Energy Partners L.P. for the forecast period. EBITDA is calculated as Sabine Pass LNG’s aggregate TUA revenues less Sabine Pass LNG’s non-cash deferred revenues, operating expenses, assumed commissioning costs and state and local taxes.
Our financial forecast reflects our judgment as of the date of this prospectus of conditions we expect to exist and the course of action we expect to take during the period from the closing of this offering through June 30, 2010. The footnotes to the financial forecast below describe numerous assumptions and considerations that we believe are significant to our financial forecast. We believe our actual revenues and cash flows will approximate those reflected in our financial forecast; however, we can give you no assurance that our forecast results will be achieved. There will likely be differences between our forecast and the actual results and those differences could be material. If the forecast is not achieved, we may not be able to pay cash distributions on our common units at the initial distribution rate stated in our cash distribution policy or at all. For all quarters ending on or before June 30, 2009, we will use funds from our distribution reserve to pay the initial quarterly distribution of $0.425 per unit on all of our outstanding common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner. In order to fund distributions to our unitholders at our initial quarterly rate of $0.425 per common unit for the twelve months ending June 30, 2010, our cash available for distribution for the twelve months ending June 30, 2010 must be at least $280.7 million. As set forth in the table on the following pages, we estimate that our cash available for distribution for the twelve months ending June 30, 2010 will be approximately $294.7 million.
After this offering, we do not intend to make public projections as to future sales, earnings or other results. The accompanying prospective financial information was not prepared with a view toward complying with the
50
guidelines established by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants with respect to prospective financial information, but, in the view of our management, was prepared on a reasonable basis, and presents, to the best of management’s knowledge and belief, our expected course of action and our expected future financial performance. However, this information is not fact and should not be relied upon as being necessarily indicative of future results, and readers of this prospectus are cautioned not to place undue reliance on the prospective financial information.
Neither our independent registered public accounting firm, nor any other registered public accounting firm, has compiled, examined or performed any procedures with respect to the prospective financial information contained below, nor have they expressed any opinion or any other form of assurance on such information or its achievability, and assume no responsibility for, and disclaim any association with, the prospective financial information.
Please read the footnotes below for a discussion of the material assumptions underlying our belief that we will be able to generate sufficient cash available to pay distributions for the forecast period. Our belief is based on those assumptions and reflects our judgment, as of the date of this prospectus, regarding the conditions that we expect to exist and the course of action that we expect to take over the estimation period. The assumptions that we disclose below are those that we believe are significant to our ability to generate sufficient cash available to pay distributions for the forecast period. If our estimates prove to be materially incorrect, we may not be able to pay the full initial quarterly distribution or any amount on our outstanding common and subordinated units.
When considering this forecast, you should keep in mind the risk factors and other cautionary statements under the heading “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. Any of these risk factors or the other risks discussed in this prospectus could cause our financial condition and consolidated results of operations to vary significantly from those set forth in the table below. In addition, we do not undertake any obligation to release publicly the results of any future revisions that we may make to these estimates or to update these estimates to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this prospectus. Therefore, we caution you not to place undue reliance on this information.
51
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
Forecast of Cash Available for Distribution
(in millions, except per unit amounts)
| Line |
Closing Until Phase 1 Commercial Operation |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1. | Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.: |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | TUA Revenues(6) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 3. | Total TUA(7) |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| 4. | Chevron TUA(7) |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 5. | Cheniere Marketing TUA(8) |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 6. | Aggregate TUA Revenues |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| 7. | Deferred Revenues(9) |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 8. | Operating Expenses(10) |
(3.8 | ) | (2.4 | ) | (3.3 | ) | (3.0 | ) | (8.7 | ) | |||||||||||
| 9. | Assumed Commissioning Costs(11) |
— | — | — | — | (0.5 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| 10. | State and Local Taxes(12) |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 11. | Sabine Pass LNG EBITDA(13) |
$ | (3.8 | ) | $ | (2.4 | ) | $ | (3.3 | ) | $ | (3.0 | ) | $ | (9.2 | ) | ||||||
| 12. | Capital Expenditures |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 13. | Construction Capital Expenditures(14) |
$ | (155.7 | ) | $ | (121.0 | ) | $ | (100.5 | ) | $ | (90.6 | ) | $ | (63.9 | ) | ||||||
| 14. | Construction Account Disbursements (Construction Capital)(15) |
155.7 | 121.0 | 100.5 | 90.6 | 63.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| 15. | Construction Account Disbursements (Operating Expenses)(15) |
3.8 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 3.0 | 9.2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 16. | (Interest Earned on Construction Account)(15) |
— | 4.2 | 5.9 | 4.8 | 3.6 | ||||||||||||||||
| 17. | (Ending Balance in Construction Account)(15) |
607.4 | 488.3 | 390.4 | 301.5 | 232.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 18. | Maintenance Capital Expenditures(16) |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 19. | Debt Service |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 20. | Interest on Notes |
$ | — | $ | (75.5 | ) | $ | — | $ | (75.5 | ) | $ | — | |||||||||
| 21. | Debt Payment Account Funding (17) |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 22. | Interest Payments Funded from Debt Payment Account |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 23. | Interest Payments Funded from Const. Period Debt Service Reserve Account |
— | 75.5 | — | 75.5 | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 24. | (Interest Earned on Construction Period Debt Service Reserve Account)(18) |
4.6 | 4.4 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 2.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| 25. | (Ending Balance in Construction Period Debt Service Reserve Account) |
359.4 | 291.5 | 295.3 | 223.4 | 226.3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 26. | Permanent Debt Service Reserve Funding (17) |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 27. | Cash Distributable to Us |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| 28. | Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 29. | Cash Received from Sabine Pass LNG |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||
| 30. | Operating Expenses(19) |
— | (0.6 | ) | (0.6 | ) | (0.6 | ) | (0.6 | ) | ||||||||||||
| 31. | Advance from Cheniere Energy, Inc.(19) |
— | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | ||||||||||||||||
| 32. | Distribution Reserve |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 33. | (Beginning Balance in Distribution Reserve)(20) |
$ | — | $ | 96.7 | $ | 86.5 | $ | 76.1 | $ | 65.7 | |||||||||||
| 34. | (Interest Earned on Distribution Reserve)(20) |
— | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| 35. | Common Unit Distribution |
— | (11.2 | ) | (11.2 | ) | (11.2 | ) | (11.2 | ) | ||||||||||||
| 36. | General Partner Distribution |
— | (0.2 | ) | (0.2 | ) | (0.2 | ) | (0.2 | ) | ||||||||||||
| 37. | Ending Balance in Distribution Reserve |
96.7 | 86.5 | 76.1 | 65.7 | 55.1 | ||||||||||||||||
| 38. | Cash Available to Pay Distributions |
$ | — | $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | |||||||||||
| 39. | Anticipated Cash Distributions |
$ | — | $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | |||||||||||
| 40. | Anticipated Cash Distributions Per Unit: |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 41. | Common Units |
$ | — | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | |||||||||||
| 42. | Subordinated Units |
— | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| 43. | General Partner Units |
— | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.069 | ||||||||||||||||
| Note: | Italicized amounts are provided for informational purposes. They do not affect the total and subtotals of amounts not in italics. |
52
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
Forecast of Cash Available for Distribution
(in millions, except per unit amounts)
| Phase 1 Commercial Operation through Phase 1 Completion (2.6 Bcf/d) |
Phase 1 Completion through Phase 2 – Stage 1 Completion (4.0 Bcf/d) |
Phase 2 – Stage 1 Completion (4.0 Bcf/d) |
Line Item | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 |
2009 |
2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q2(1) | Q3(2) | Q4 | Q1(3) | Q2(4) | Q3(5) | Q4 | Q1 | Q2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 31.3 | $ | 31.6 | $ | 31.6 | $ | 31.0 | $ | 31.3 | 3. | ||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | 32.8 | 32.8 | 32.0 | 32.4 | 4. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15.8 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 63.0 | 63.7 | 64.4 | 64.4 | 63.1 | 63.8 | 5. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 15.8 | $ | 16.0 | $ | 16.0 | $ | 63.0 | $ | 95.0 | $ | 128.8 | $ | 128.8 | $ | 126.1 | $ | 127.5 | 6. | ||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | (0.5 | ) | (1.0 | ) | (1.0 | ) | (1.0 | ) | (1.0 | ) | 7. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (8.7 | ) | (8.7 | ) | (8.7 | ) | (8.6 | ) | (9.1 | ) | (9.1 | ) | (9.1 | ) | (9.3 | ) | (9.3 | ) | 8. | ||||||||||||||||||
| (0.4 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 9. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (0.9 | ) | (0.9 | ) | (0.9 | ) | (1.3 | ) | (2.4 | ) | (2.4 | ) | (2.4 | ) | (2.5 | ) | (2.5 | ) | 10. | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 5.8 | $ | 6.4 | $ | 6.4 | $ | 53.1 | $ | 83.0 | $ | 116.3 | $ | 116.3 | $ | 113.3 | $ | 114.7 | 11. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 12. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | (60.5 | ) | $ | (34.9 | ) | $ | (33.9 | ) | $ | (23.1 | ) | $ | (20.1 | ) | $ | (10.2 | ) | $ | (6.6 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | 13. | |||||||||||
| 60.5 | 34.9 | 33.9 | 23.1 | 20.1 | 10.2 | 6.6 | — | — | 14. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9.1 | 8.7 | 8.7 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 15. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.7 | 2.0 | 1.4 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 16. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 165.0 | 123.4 | 82.2 | 59.9 | 40.6 | 30.9 | 24.7 | 25.0 | 25.3 | 17. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | (0.4 | ) | (0.4 | ) | (0.4 | ) | (0.4 | ) | (0.4 | ) | (0.4 | ) | 18. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 19. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | (75.5 | ) | $ | — | $ | (75.5 | ) | $ | — | $ | (75.5 | ) | $ | — | $ | (75.5 | ) | $ | — | $ | (75.5 | ) | 20. | |||||||||||||
| (14.9 | ) | (15.1 | ) | (15.1 | ) | (45.3 | ) | (37.8 | ) | (37.8 | ) | (37.8 | ) | (37.8 | ) | (37.8 | ) | 21. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 9.9 | — | 30.1 | — | 75.5 | — | 75.5 | — | 75.5 | 22. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 65.6 | — | 45.5 | 123.7 | — | — | — | — | — | 23. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2.7 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 1.6 | — | — | — | — | — | 24. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 163.4 | 165.6 | 122.1 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 25. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | (75.5 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | 26. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 55.6 | $ | 44.8 | $ | 78.1 | $ | 78.1 | $ | 75.2 | $ | 76.6 | 27. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 28. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 55.6 | $ | 44.8 | $ | 78.1 | $ | 78.1 | $ | 75.2 | $ | 76.6 | 29. | ||||||||||||||||||
| (0.6 | ) | (0.6 | ) | (0.6 | ) | (3.3 | ) | (3.3 | ) | (3.3 | ) | (3.3 | ) | (3.4 | ) | (3.4 | ) | 30. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 31. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 55.1 | $ | 44.4 | $ | 33.5 | $ | 22.5 | $ | 11.3 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | 33. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.1 | — | — | — | — | 34. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (11.2 | ) | (11.2 | ) | (11.2 | ) | (11.2 | ) | (11.2 | ) | — | — | — | — | 35. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (0.2 | ) | (0.2 | ) | (0.2 | ) | (0.2 | ) | (0.2 | ) | — | — | — | — | 36. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 44.4 | 33.5 | 22.5 | 11.3 | — | — | — | — | — | 37. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | $ | 63.8 | $ | 53.0 | $ | 74.8 | $ | 74.8 | $ | 71.8 | $ | 73.2 | 38. | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | $ | 11.5 | $ | 63.8 | $ | 53.0 | $ | 70.2 | $ | 70.2 | $ | 70.2 | $ | 70.2 | 39. | ||||||||||||||||||
| 40. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | $ | 0.425 | 41. | ||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | 0.379 | 0.301 | 0.425 | 0.425 | 0.425 | 0.425 | 42. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.069 | 0.386 | 0.321 | 0.425 | 0.425 | 0.425 | 0.425 | 43. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
53
| (1) | We expect to achieve Phase 1 commercial operation during the second quarter of 2008. For purposes of this forecast, we have assumed that Phase 1 commercial operation will commence in April 2008. From the date that we achieve Phase 1 commercial operation through December 2008, Cheniere Marketing will pay $5 million per month plus tax reimbursements under its TUA with Sabine Pass LNG. |
| (2) | We expect to complete Phase 1 with three LNG storage tanks and a sendout rate of 2.6 Bcf/d, which we refer to as Phase 1 completion, during the third quarter of 2008. Under its EPC contract with Sabine Pass LNG, Bechtel has guaranteed Phase 1 substantial completion by December 20, 2008. |
| (3) | Provided we have achieved Phase 1 commercial operation, Cheniere Marketing will be required under its TUA with Sabine Pass LNG to pay monthly capacity reservation fees aggregating approximately $255.5 million per year, starting January 2009. These monthly payments will be required on what is referred to as a “take or pay” basis, which means that the customer will be obligated to pay the full contracted amount of monthly fees whether or not it uses its capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
| (4) | Provided we have achieved the level of commercial operability required under Total’s TUA, which we expect will occur during the third quarter of 2008, Total will be required under its TUA with Sabine Pass LNG to pay monthly capacity reservation fees aggregating approximately $125.5 million per year, starting April 2009. These monthly payments will be required on a “take or pay” basis. |
| (5) | Provided we have achieved the level of commercial operability required under Chevron’s TUA, which we expect will occur during the third quarter of 2008, Chevron will be required under its TUA with Sabine Pass LNG to pay monthly capacity reservation fees aggregating approximately $129.9 million per year, starting not later than July 2009. These monthly payments will be required on a “take or pay” basis. |
| (6) | Monthly capacity reservation fees under the TUAs are based on the aggregate million British thermal units, or MMbtu, receipt capacity reserved by each customer and will include a fixed fee component equivalent to approximately $0.28 per MMbtu and an additional fee component equivalent to approximately $0.04 per MMbtu that is adjusted annually for consumer price index inflation, which we assume will be 2.5% annually. This adjustment will commence one year after the commercial start date for Total, on January 1, 2010 for Chevron and on January 1, 2009 for Cheniere Marketing. The aggregate MMbtu reserved capacity is equivalent to approximately 1.0 Bcf/d for each of Total and Chevron from inception of payments under its TUA and is equivalent to approximately 2.0 Bcf/d for Cheniere Marketing when we achieve Phase 2 – Stage 1 completion. We will achieve Phase 2 – Stage 1 completion when we complete two additional LNG storage tanks and achieving full operability of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal at approximately 4.0 Bcf/d. We expect to achieve Phase 2 – Stage 1 completion in the third quarter of 2009. Also included in TUA revenues are reimbursements by TUA customers of state and local taxes paid by Sabine Pass LNG (see footnote (12)). In addition, under each customer’s TUA, Sabine Pass LNG is entitled to take an in-kind “retainage” equal to 2% of the LNG delivered for the customer’s account, which Sabine Pass LNG will use primarily as fuel for revaporization and self-generated power and to cover natural gas unavoidably lost at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. We have assumed that Sabine Pass LNG will not have any revenue from retainage LNG and will not incur any cost to provide fuel to revaporize LNG for sendout, to provide self-generated power and to cover natural gas unavoidably lost at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
| (7) | Each of Total and Chevron has previously paid $20 million of advance capacity reservation fees to Sabine Pass LNG. These payments will be recognized as deferred revenues and will reduce cash payments by each customer by $2 million per year in each of the first ten years under its TUA. TUA revenues from each of Total and Chevron include $2 million per year of non-cash deferred revenues. |
| (8) | Cheniere Marketing has agreed to relinquish up to 200 million cubic feet per day, or MMcf/d, of its reserved capacity (and proportionately reduce the monthly fee) under its TUA if required to allow Sabine Pass LNG to satisfy its obligations under a TUA that it may potentially enter into with J&S Cheniere, S.A., as more fully discussed in “Business—Customers—Cheniere Marketing TUA.” We have assumed that any assignment to J&S Cheniere will not affect our forecast. |
| (9) | Non-cash deferred revenues of $2 million per year are deducted from TUA revenues from each of Total and Chevron in calculating EBITDA. |
54
| (10) | Sabine Pass LNG’s combined operating expenses and maintenance capital expenditures have been estimated by us and the Independent Engineer at approximately $36.6 million for the calendar year 2010 in order to support receiving terminal operations at 2.0 Bcf/d, the minimum level required to perform Sabine Pass LNG’s obligations under both the Total TUA and the Chevron TUA. We and the Independent |
| Engineer have also estimated that Sabine Pass LNG’s combined operating expenses and maintenance capital expenditures will increase by approximately $2.1 million to approximately $38.7 million for the calendar year 2010 in order to support receiving terminal operations at 4.0 Bcf/d. Each of these estimates includes $8.3 million of fees and expenses payable under agreements with Cheniere affiliates for services necessary to operate and maintain the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. In preparing our forecast, we have assumed operating expenses and maintenance capital expenditures as estimated to support operations at the 2.0 Bcf/d level beginning January 1, 2008 and at the 4.0 Bcf/d level beginning April 1, 2009 upon commencement of the Total TUA. We have separated out $1.5 million per year from operating expenses and classified that amount as maintenance capital expenditures (see footnote (16)). We have assumed Sabine Pass LNG operating expenses (net of the $1.5 million of maintenance capital expenditures) of $37.2 million for the calendar year 2010. We have assumed inflation of 2.5% in 2008 and 2009 in estimating operating expenses for those years. Please read the report of the Independent Engineer attached as Appendix B to this prospectus for more information. |
| (11) | Sabine Pass LNG must obtain LNG in order to commission its receiving terminal. We have assumed that Sabine Pass LNG will obtain three 3.0 Bcf cargoes of LNG in the first quarter of 2008 at an aggregate cost of $85.5 million ($9.50 per MMbtu, which was the average NYMEX price on November 28, 2006 for contracts to purchase natural gas in the first quarter of 2008) and three additional 3.0 Bcf cargoes of LNG in the second quarter of 2008 at an aggregate cost of $72.0 million ($8.00 per MMbtu, which was the average NYMEX price on November 28, 2006 for contracts to purchase natural gas in the second quarter of 2008). We have assumed that we will not make any profit or incur any loss in reselling the natural gas produced from these six cargoes of LNG. Our assumed commissioning costs shown in the table consist solely of interest costs to finance purchases of these six LNG cargoes and assumes an interest rate of 7.0% per annum. In calculating interest cost, we have further assumed that we are in possession of, on average, one cargo on each day in the first and second quarters of 2009. |
| (12) | Sabine Pass LNG will pay a 4% usage tax on LNG consumed in plant operations. We have estimated the amount of this tax assuming that Sabine Pass LNG’s full 2% “retainage” of LNG will be consumed in plant operations. Sabine Pass LNG will also pay ordinary ad valorem taxes on its plant assets. Sabine Pass LNG has obtained a 100% deferral of those ad valorem taxes through 2018. In order to assist the taxing authorities to fund reconstruction of infrastructure that was damaged by hurricanes in 2005 and that supports development and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Sabine Pass LNG has offered to make payments in lieu of taxes to the extent of approximately $2.5 million annually for ten years. We have assumed that this offer will be accepted and that payments will begin in 2009. The TUA customers are obligated to reimburse Sabine Pass LNG for all usage and ad valorem taxes (see footnote (6)), provided that Sabine Pass LNG will assume half of Total’s ad valorem tax obligation subject to a cap of $3.9 million. |
| (13) | Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA is calculated as aggregate TUA revenues less non-cash deferred revenues, operating expenses, assumed commissioning costs and state and local taxes. See “—Non-GAAP Financial Measure” below for more information. |
| (14) | Construction capital expenditures represent our current estimates of the amounts and timing of the capital expenditures that will be required to achieve Phase 1 commercial operation, Phase 1 completion and full Phase 2 – Stage 1 operability on the schedules specified in footnotes (1), (2) and (6). The base amount of LNG, referred to as “heel” LNG, that must be retained in the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal in order to maintain requisite cryogenic temperatures after commissioning of all of Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 has been included in the construction budget and will be funded from the construction account described in footnote (15). Sabine Pass LNG may also be required to construct a sixth LNG storage tank for the benefit of Cheniere Marketing within four years after notification from Cheniere Marketing. We have assumed that no funds are required to be expended prior to July 1, 2010 in respect of this potential sixth tank. We have internally estimated that the cost of the sixth tank could be in the range of $120 to $140 million. Sabine Pass LNG will not receive any additional revenue from this tank. |
55
| (15) | In connection with its issuance of $2,032 million of notes in November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG deposited approximately $886.7 million into a construction account to fund completion and commissioning costs of Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 of its receiving terminal, as well as other incidental expenses, including taxes and operating fees and expenses. We estimate that approximately $24.7 million of interest earned on amounts in the construction account will have been transferred from the construction account and be unexpended funds available for distribution when we have completed Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. We have assumed that funds on deposit in the construction account will earn interest at 5.25% per year. Under the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes, the first $20 million of such interest earnings must be transferred to a construction period debt service reserve account described in footnote (18). |
| (16) | Maintenance capital expenditures estimated by us at $1.5 million per year beginning in 2009, escalating with inflation at 2.5% annually thereafter. This amount does not include natural gas turbine generator maintenance costs, which are covered by a third-party contract fee included in operating expenses. Maintenance capital expenditures in the forecast period are low because the receiving terminal will be brand new, will require little maintenance and will initially be protected by warranties. These maintenance capital costs have been separated out from the Independent Engineer’s estimates and reclassified as described in footnote (10). |
| (17) | Under the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes, Sabine Pass LNG may not make distributions to us until certain conditions are satisfied. The indenture requires that Sabine Pass LNG apply its net operating cash flow (i) first, to fund with monthly deposits its next semiannual payment of approximately $75.5 million of interest on its notes, and (ii) second, to fund a one-time, permanent debt service reserve fund equal to one semiannual interest payment of approximately $75.5 million on its notes. Distributions to us from Sabine Pass LNG will be permitted only after Phase 1 Target Completion, as defined in the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes, or such earlier date as project revenues are received by Sabine Pass LNG, upon satisfaction of the foregoing funding requirements and after satisfaction of a fixed charge coverage ratio test and other conditions specified in the indenture. Please read “Indebtedness—Indenture” for more information. We will not receive the full contracted payments from the Cheniere Marketing TUA until the first quarter of 2009 and, accordingly, do not expect that Sabine Pass LNG will make distributions to us until the first quarter of 2009. |
| (18) | In connection with its issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes in November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG also deposited $335 million into a construction period debt service reserve account. This account, together with $20 million of interest earned on amounts on deposit in the construction account that will be transferred to the construction period debt service reserve account as described in footnote (17), and together with interest earned on amounts on deposit in the construction period debt service reserve account, is intended to be sufficient to pay all scheduled semiannual payments of interest on the Sabine Pass LNG notes through the payment due May 30, 2009. We have assumed that funds on deposit in the construction period debt service reserve account will earn interest at 5.25% per year. |
| (19) | We have estimated that our partnership will incur costs of approximately $2.5 million per year, adjusted for inflation at 2.5% per year after January 1, 2007, for tax compliance and publicly traded partnership tax reporting, accounting, SEC reporting and other costs of operating as a publicly traded partnership. Through 2008, we will fund these costs with funds advanced to us from Cheniere, after which time we will use available cash to pay such expenses and, after payment of the initial quarterly distribution on all units, to reimburse Cheniere. In addition, commencing January 1, 2009, we will pay a Cheniere affiliate a fixed amount of $10 million per year, adjusted for inflation at 2.5% per year after January 1, 2007, for providing general and administrative services to our partnership following the closing of this offering. |
| (20) | At completion of this offering, our partnership will fund a distribution reserve of approximately $96.7 million, which will be invested in U.S. treasury securities. The distribution reserve, together with interest earned on funds on deposit in the distribution reserve and operating cash flows, will be used to pay the $0.425 initial quarterly distribution per common unit for all common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, through the distribution in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. We have assumed that unexpended funds in the distribution reserve will earn interest at 5.00% per year. |
56
Assumptions and Considerations
The footnotes to the financial forecast set forth above describe the numerous assumptions and considerations that we believe are significant to our financial forecast. While we believe that these assumptions are reasonable based upon management’s current expectations concerning future events, they are inherently uncertain and are subject to significant risks and uncertainties, including those described in “Risk Factors” or in the footnotes to the financial forecast included above, that could cause actual results to differ materially from those we anticipate. We cannot give any assurance these assumptions or assessments are correct. If any of our assumptions are not correct, or if we inaccurately assess any of these considerations, the actual available cash that we generate could be substantially less than that currently expected and could, therefore, be insufficient to permit us to pay distributions to our unitholders, in which event the market price of the common units may decline materially.
In the preparation of its report attached to this prospectus as Appendix B, the Independent Engineer has relied on assumptions regarding circumstances beyond the control of us or any other person. By their nature, these assumptions are subject to significant uncertainties, and actual results will differ, perhaps materially, from those stated in the report. We cannot give any assurance that these assumptions will prove to be correct. If our actual results are materially less favorable than those shown in the Independent Engineer’s report, or if the assumptions in the Independent Engineer’s report on which we rely for certain of our financial estimates, prove to be incorrect, Sabine Pass LNG’s ability to pay distributions to us, and our ability to pay distributions to our unitholders, may be adversely affected.
Non-GAAP Financial Measure
Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA is computed as total revenues less non-cash deferred revenues, operating expenses, assumed commissioning costs and state and local taxes. It does not include depreciation expense and certain non-operating items. Because we have not forecasted such depreciation expense and non-operating items, we have not made any forecast of net income, which would be the most directly comparable financial measure under GAAP. As a result, we are unable to reconcile differences between forecasts of EBITDA and net income. EBITDA is used as a supplemental financial measure by management and by external users of our financial statements, such as commercial banks, to assess:
| • | the anticipated financial performance of our assets without regard to financing methods, capital structure or historical cost basis; |
| • | the ability of our assets to generate cash sufficient to pay interest on our indebtedness; and |
| • | our anticipated operating performance and return on invested capital compared to other comparable companies, without regard to their financing methods and capital structure. |
Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA should not be considered an alternative to net income, operating income, cash flows from operating activities or any other measure of financial performance or liquidity presented in accordance with GAAP. Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA excludes some, but not all, items that affect net income and operating income, and these measures may vary among companies. Therefore, Sabine Pass LNG’s EBITDA may not be comparable to similarly titled measures of other companies.
57
HOW WE MAKE CASH DISTRIBUTIONS
Distributions of Available Cash
General
Our partnership agreement requires that, within 45 days after the end of each quarter, beginning with the quarter ending March 31, 2007, we distribute all of our available cash to unitholders of record on the applicable record date.
Definition of Available Cash
We define available cash in the partnership agreement, and it generally means, for each fiscal quarter, the sum of all cash and cash equivalents on hand at the end of the quarter, including cash released from the distribution reserve as available cash in accordance with our partnership agreement:
| • | less the amount of cash reserves established by our general partner to: |
| • | provide for the proper conduct of our business; |
| • | comply with applicable law, any of our debt instruments, or other agreements; and |
| • | provide funds for distributions to our unitholders and to our general partner for any one or more of the next four quarters; |
| • | plus all additional cash and cash equivalents on hand on the date of determination of available cash for the quarter resulting from working capital borrowings made after the end of the quarter. Working capital borrowings are generally borrowings that are made under a credit facility, commercial paper facility or similar financing arrangement, and in all cases are used solely for working capital purposes or to pay distributions to partners and with the intent of the borrower to repay such borrowings within 12 months. |
Minimum Quarterly Distribution
We will distribute to the holders of common units and subordinated units on a quarterly basis at least the minimum quarterly distribution of $0.425 per unit, or $1.70 per year, to the extent that we have sufficient cash from our operations after establishment of cash reserves and payment of fees and expenses, including payments to our general partner. However, there is no guarantee that we will pay the minimum quarterly distribution on the units in any quarter. Even if our cash distribution policy is not modified or revoked, the amount of distributions paid under our policy and the decision to make any distribution is determined by our general partner, taking into consideration the terms of our partnership agreement. Please see “Cash Distribution Policy and Restrictions on Distributions” for a discussion of the restrictions that may restrict our ability to make distributions.
General Partner Interest and Incentive Distribution Rights.
Initially, our general partner will be entitled to 2% of all quarterly distributions since inception that we make prior to our liquidation. This general partner interest will be represented by 3,302,045 general partner units. Our general partner has the right, but not the obligation, to contribute a proportionate amount of capital to us to maintain its current general partner interest. The general partner’s initial 2% interest in these distributions may be reduced if we issue additional units in the future and our general partner does not contribute a proportionate amount of capital to us to maintain its 2% general partner interest.
Our general partner also currently holds incentive distribution rights that entitle it to receive increasing percentages, up to a maximum of 50%, of the cash that we distribute from operating surplus (as defined below) in excess of $0.638 per unit per quarter. The maximum distribution of 50% includes distributions paid to our
58
general partner on its 2% general partner interest and assumes that our general partner maintains its general partner interest at 2%. The maximum distribution of 50% does not include any distributions that our general partner may receive on subordinated units that it owns. Please see “—Incentive Distribution Rights” for additional information.
Operating Surplus and Capital Surplus
Overview
All cash distributed to unitholders will be characterized as either “operating surplus” or “capital surplus.” We treat distributions of available cash from operating surplus differently than distributions of available cash from capital surplus.
Definition of Operating Surplus
We define operating surplus in the partnership agreement, and for any period it generally means:
| • | $30 million (as described below); plus |
| • | all of our cash receipts after the closing of this offering, excluding cash from: |
| • | borrowings that are not working capital borrowings, |
| • | sales of equity securities and debt securities, |
| • | sales or other dispositions of assets outside the ordinary course of business, |
| • | the termination of commodity hedge contracts or interest rate swap agreements prior to the termination date specified therein, |
| • | capital contributions received, and |
| • | corporate reorganizations or restructurings; plus |
| • | working capital borrowings made after the end of a quarter but on or before the date of determination of operating surplus for the quarter; plus |
| • | all cash released from the distribution reserve; plus |
| • | cash distributions paid on equity issued in connection with the construction or development of a capital improvement or replacement asset during the period beginning on the date that we enter into a binding commitment to commence the construction or development of such capital improvement or replacement asset and ending on the earlier to occur of the date the capital improvement or replacement asset is placed into service and the date that it is abandoned or disposed of; less |
| • | all of our operating expenditures (as defined below) after the closing of this offering; less |
| • | the amount of cash reserves established by our general partner to provide funds for future operating expenditures; less |
| • | all working capital borrowings not repaid within twelve months after having been incurred or repaid within such twelve-month period with the proceeds of additional working capital borrowings. |
If a working capital borrowing, which increases operating surplus, is not repaid during the twelve month period following the borrowing, it will be deemed repaid at the end of such period, thus decreasing operating surplus at such time. When such working capital is in fact repaid, it will not be treated as a reduction in operating surplus because operating surplus will have been previously reduced by the deemed repayment.
We define operating expenditures in the partnership agreement, and it generally means all of our expenditures, including, but not limited to, taxes, payments to our general partner, reimbursements of expenses
59
incurred by our general partner on our behalf, non-pro rata repurchases of units, repayment of working capital borrowings, debt service payments, interest payments, payments made in the ordinary course of business under commodity hedge contracts and maintenance capital expenditures, provided that operating expenditures will not include:
| • | repayment of working capital borrowings deducted from operating surplus pursuant to the last bullet point of the definition of operating surplus above when such repayment actually occurs; |
| • | payments (including prepayments) of principal of and premium on indebtedness other than working capital borrowings; |
| • | expansion capital expenditures; |
| • | investment capital expenditures; |
| • | payment of transaction expenses (including taxes) relating to interim capital transactions; |
| • | distributions to our partners; and |
| • | non-pro rata repurchases of units of any class made with the proceeds of an interim capital transaction (as defined below). |
Capital Expenditures
Maintenance capital expenditures are those capital expenditures required to maintain, including over the long-term, our operating capacity or asset base. Maintenance capital expenditures include interest (and related fees) on debt incurred and distributions on equity issued to finance the construction or development of a replacement asset during the period from such financing until the earlier to occur of the date any such replacement asset is placed into service and the date that it is abandoned or disposed.
Expansion capital expenditures are those capital expenditures that we expect will increase our operating capacity or asset base over the long term. Expansion capital expenditures include interest (and related fees) on debt incurred and distributions on equity issued to finance the construction or development of a capital improvement during the period from such financing until the earlier to occur of the date any such capital improvement is placed into service and the date that it is abandoned or disposed.
Investment capital expenditures are those capital expenditures that are neither maintenance capital expenditures nor expansion capital expenditures. Examples of investment capital expenditures include traditional capital expenditures for investment purposes, such as purchases of securities, as well as other capital expenditures that might be made in lieu of such traditional investment capital expenditures, such as the acquisition of a capital asset for investment purposes, but which is not expected to expand our asset base for more than the short-term.
Neither investment capital expenditures nor expansion capital expenditures are subtracted from operating surplus. Because investment capital expenditures and expansion capital expenditures include interest payments (and related fees) on debt incurred and distributions on equity issued to finance the construction or development of a capital improvement or replacement asset during the period from such financing until the earlier to occur of the date any such capital improvement or replacement asset is placed into service or the date that it is abandoned or disposed, such interest payments and equity distributions are also not subtracted from operating surplus (except, in the case of maintenance capital expenditures, to the extent such interest payments and distributions are included in maintenance capital expenditures).
Capital expenditures that are made in part for maintenance capital purposes and in part for investment capital or expansion capital purposes will be allocated as maintenance capital expenditures, investment capital expenditures or expansion capital expenditure by the board of directors of our general partner, based upon its good faith determination, subject to approval by our conflicts committee.
60
Definition of Capital Surplus
We also define capital surplus in the partnership agreement and in “—Characterization of Cash Distributions” below, and it will generally be generated only by the following, which we call “interim capital transactions:”
| • | borrowings other than working capital borrowings; |
| • | sales of debt and equity securities; |
| • | sales or other dispositions of assets for cash, other than inventory, accounts receivable and other assets sold in the ordinary course of business or as part of normal retirements or replacements of assets; |
| • | the termination of commodity hedge contracts or interest rate swap agreements prior to the termination date specified therein; |
| • | capital contributions received; and |
| • | corporate reorganizations or restructurings. |
Characterization of Cash Distributions
Our partnership agreement requires that we treat all available cash distributed as coming from operating surplus until the sum of all available cash distributed since we began operations equals the operating surplus as of the most recent date of determination of available cash. We will treat any amount distributed in excess of operating surplus, regardless of its source, as capital surplus. As reflected above, operating surplus includes $30 million in addition to cash on hand at the closing of this offering. This amount does not reflect actual cash on hand at closing that is available for distribution to our unitholders. It is instead a provision that will enable us, if we choose, to distribute as operating surplus up to $30 million of cash that we receive in the future from interim capital transactions, that would otherwise be distributed as capital surplus. We do not anticipate that we will make any distributions from capital surplus.
We will deposit all of the net proceeds that we receive from this offering as a distribution reserve in a separate account. The deposited amount will be invested in U.S. treasury securities maturing as to principal and interest at such times and in such amounts as will be sufficient to pay the $0.425 initial quarterly distribution per common unit for all common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. Any net proceeds that we receive in excess of the amount necessary to fund the distribution reserve will be distributed to the selling unitholder, and any shortfall in that amount will be contributed to us by the selling unitholder. In the event that we issue additional common units prior to June 30, 2009, we will use a portion of the net proceeds from such issuance to increase the distribution reserve by an amount that our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines is required to fund the initial quarterly distribution for such additional common units and related general partner units from their date of issuance through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. Any amount remaining in the distribution reserve on August 15, 2009 will be distributed to Cheniere Holdings. We may distribute amounts in the distribution reserve to Cheniere Holdings prior to August 15, 2009 if our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines that such reserves are not required to provide for distributions on all of our common units and general partner units for any quarter ending on or prior to June 30, 2009. If we generate cash from operations during the period from the closing of this offering to June 30, 2009, we will make quarterly distributions for our common units from such cash generated from operations and, if the amount of such cash is insufficient to make the full quarterly distribution, from amounts in the distribution reserve.
61
General
During the subordination period, which will commence upon the closing of this offering, the common units will have the right to receive distributions of available cash from operating surplus in an amount equal to the initial quarterly distribution of $0.425 per quarter, plus any arrearages in the payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units from prior quarters, before any distributions of available cash from operating surplus may be made on the subordinated units. Cheniere Holdings will own all of the 135,383,831 subordinated units, representing 83.7% of the limited partner interests in us. These units are deemed “subordinated” because for a period of time, referred to as the subordination period, the subordinated units will not be entitled to receive any distributions until after the common units have received the initial quarterly distribution plus any arrearages from prior quarters. Furthermore, no arrearages will be paid on the subordinated units. The practical effect of the subordination period is to increase the likelihood that during this period there will be sufficient available cash to pay the initial quarterly distribution on the common units.
Definition of Subordination Period
Subordination Period
The subordination period will extend until the first business day following the distribution of available cash to partners in respect of any quarter ending on or after June 30, 2010 that each of the following occurs:
| • | distributions of available cash from operating surplus on each of the outstanding common units, subordinated units and general partner units equaled or exceeded the initial quarterly distribution for each of the three consecutive, non-overlapping four-quarter periods immediately preceding that date; |
| • | the “adjusted operating surplus” (as defined below) generated during each of the three consecutive, non-overlapping four-quarter periods immediately preceding that date equaled or exceeded the sum of the initial quarterly distributions on all of the outstanding common units, subordinated units and general partner units during those periods on a fully diluted basis; and |
| • | there are no arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units. |
Expiration of the Subordination Period
When the subordination period expires, each outstanding subordinated unit will convert into one common unit and will then participate pro rata with the other common units in distributions of available cash. In addition, if the unitholders remove our general partner other than for cause and units held by the general partner and its affiliates are not voted in favor of such removal:
| • | the subordination period will end and each subordinated unit will immediately convert into one common unit; |
| • | any existing arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units will be extinguished; and |
| • | the general partner will have the right to convert its general partner units and its incentive distribution rights into common units or to receive cash in exchange for those interests. |
Early Conversion of Subordinated Units
The subordination period will automatically terminate and all of the subordinated units will convert into common units on a one-for-one basis on the first business day following the distribution of available cash to partners in respect of any quarter ending on or after June 30, 2008 that each of the following occurs:
| • | distributions of available cash from operating surplus on each outstanding common unit and subordinated unit equaled or exceeded $2.55 (150% of the annualized initial quarterly distribution) for any four-quarter period immediately preceding that date; |
| • | the “adjusted operating surplus” (as defined below) generated during any four-quarter period immediately preceding that date equaled or exceeded the sum of a distribution of $2.55 (150% of the annualized initial quarterly distribution) on all of the outstanding common units and subordinated units and general partner units on a fully diluted basis; and |
62
| • | there are no arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units. |
Definition of Adjusted Operating Surplus
We define adjusted operating surplus in the partnership agreement, and for any period, it generally means:
| • | operating surplus generated with respect to that period (other than amounts released from the distribution reserve); less |
| • | any net increase in working capital borrowings with respect to that period; less |
| • | any net reduction in cash reserves for operating expenditures with respect to that period not relating to an operating expenditure made with respect to that period; plus |
| • | any net decrease in working capital borrowings with respect to that period; plus |
| • | any net increase in cash reserves for operating expenditures with respect to that period required by any debt instrument for the repayment of principal, interest or premium. |
Adjusted operating surplus is intended to reflect the cash generated from operations during a particular period and therefore excludes cash on hand at the closing of this offering, the $30 million operating surplus “basket,” net increases in working capital borrowings, net drawdowns of reserves of cash generated in prior periods and amounts held in the distribution reserve or amounts released therefrom to pay distributions.
Distributions of Available Cash from Operating Surplus During the Subordination Period
We will make distributions of available cash from operating surplus for any quarter during the subordination period in the following manner:
| • | First, 98% to the common unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until we distribute for each outstanding common unit an amount equal to the initial quarterly distribution for that quarter; |
| • | Second, 98% to the common unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until we distribute for each outstanding common unit an amount equal to any arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units for any prior quarters during the subordination period; |
| • | Third, 98% to the subordinated unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until we distribute for each outstanding subordinated unit an amount equal to the initial quarterly distribution for that quarter; and |
| • | Thereafter, in the manner described in “—Incentive Distribution Rights” below. |
The preceding discussion is based on the assumptions that our general partner maintains its 2% general partner interest and that we do not issue additional classes of equity securities.
Distributions of Available Cash from Operating Surplus After the Subordination Period
We will make distributions of available cash from operating surplus for any quarter after the subordination period in the following manner:
| • | First, 98% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to the general partner, until we distribute for each outstanding unit an amount equal to the initial quarterly distribution for that quarter; and |
| • | Thereafter, in the manner described in “—Incentive Distribution Rights” below. |
The preceding discussion is based on the assumptions that our general partner maintains its 2% general partner interest and that we do not issue additional classes of equity securities.
Incentive distribution rights represent the right to receive an increasing percentage (13%, 23% and 48%) of quarterly distributions of available cash from operating surplus after the initial quarterly distribution and that the target distribution levels have been achieved. Our general partner currently holds the incentive distribution rights but may transfer these rights separately from its general partner interest, subject to restrictions in our partnership agreement.
63
If for any quarter:
| • | we have distributed available cash from operating surplus to the unitholders in an amount equal to the initial quarterly distribution; and |
| • | we have distributed available cash from operating surplus on outstanding common units in an amount necessary to eliminate any cumulative arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution to the common units; |
then we will distribute any additional available cash from operating surplus for that quarter among the unitholders and our general partner in the following manner:
| • | First, 98% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until each unitholder receives a total of $0.489 per unit for that quarter (the “first target distribution”); |
| • | Second, 85% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 15% to our general partner, until each unitholder receives a total of $0.531 per unit for that quarter (the “second target distribution”); |
| • | Third, 75% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 25% to our general partner, until each unitholder receives a total of $0.638 per unit for that quarter (the “third target distribution”); and |
| • | Thereafter, 50% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 50% to our general partner. |
In each case, the amount of the target distribution set forth above is exclusive of any distributions to common unitholders to eliminate any cumulative arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution to the common unitholders. The preceding discussion is based on the assumptions that our general partner maintains its 2% general partner interest and has not transferred its incentive distribution rights and that we do not issue additional classes of equity securities.
Percentage Allocations of Available Cash from Operating Surplus
The following table illustrates the percentage allocations of the additional available cash from operating surplus between the unitholders and our general partner up to the various target distribution levels. The amounts set forth under “Marginal Percentage Interest in Distributions” are the percentage interests of our general partner and the unitholders in any available cash from operating surplus that we distribute up to and including the corresponding amount in the column “Total Quarterly Distribution,” until available cash from operating surplus that we distribute reaches the next target distribution level, if any. The percentage interests shown for the unitholders and our general partner for the initial quarterly distribution are also applicable to quarterly distribution amounts that are less than the initial quarterly distribution. The percentage interests set forth below for our general partner include its 2% general partner interest and assume that our general partner maintains its 2% general partner interest and has not transferred its incentive distribution rights.
| Total Quarterly Distribution |
Marginal Percentage Interest in Distributions |
|||||||
| Common and Subordinated Unitholders |
General Partner |
|||||||
| Target Amount |
||||||||
| Initial quarterly distribution |
$0.425 | 98 | % | 2 | % | |||
| First Target Distribution |
above $0.425 up to $0.489 | 98 | % | 2 | % | |||
| Second Target Distribution |
above $0.489 up to $0.531 | 85 | % | 15 | % | |||
| Third Target Distribution |
above $0.531 up to $0.638 | 75 | % | 25 | % | |||
| Thereafter |
above $0.638 | 50 | % | 50 | % | |||
64
Distributions from Capital Surplus
How Distributions from Capital Surplus Will Be Made
We will make distributions of available cash from capital surplus, if any, in the following manner:
| • | First, 98% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until we distribute for each common unit that was issued in this offering an amount of available cash from capital surplus equal to the initial public offering price; |
| • | Second, 98% to the common unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until we distribute for each common unit an amount of available cash from capital surplus equal to any unpaid arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units; and |
| • | Thereafter, we will make all distributions of available cash from capital surplus as if they were from operating surplus. |
The preceding discussion is based on the assumptions that our general partner maintains its 2% general partner interest and that we do not issue additional classes of equity securities.
Effect of a Distribution from Capital Surplus
Our partnership agreement treats a distribution of capital surplus as the repayment of the initial unit price from this initial public offering, which is a return of capital. The initial public offering price less any distributions of capital surplus per unit is referred to as the “unrecovered initial unit price.” Each time a distribution of capital surplus is made, the initial quarterly distribution and the target distribution levels will be reduced in the same proportion as the corresponding reduction in the unrecovered initial unit price. Because distributions of capital surplus will reduce the initial quarterly distribution, after any of these distributions are made, it may be easier for our general partner to receive incentive distributions and for the subordinated units to convert into common units. However, any distribution of capital surplus before the unrecovered initial unit price is reduced to zero cannot be applied to the payment of the initial quarterly distribution or any arrearages.
Once we distribute capital surplus on a unit issued in this offering in an amount equal to the initial unit price, we will reduce the initial quarterly distribution and the target distribution levels to zero. We will then make all future distributions from operating surplus, with 50% being paid to the unitholders, pro rata, and 50% to our general partner. The percentage interests shown for our general partner include its 2% general partner interest and assume that our general partner maintains its 2% general partner interest and has not transferred its incentive distribution rights.
Adjustment to the Initial Quarterly Distribution and Target Distribution Levels
In addition to adjusting the initial quarterly distribution and target distribution levels to reflect a distribution of capital surplus, if we combine our units into fewer units or subdivide our units into a greater number of units, we will proportionately adjust:
| • | the initial quarterly distribution; |
| • | the target distribution levels; |
| • | the unrecovered initial unit price; and |
| • | the number of common units into which a subordinated unit is convertible. |
For example, if a two-for-one split of the common units should occur, the initial quarterly distribution, the target distribution levels and the unrecovered initial unit price would each be reduced to 50% of its initial level and each subordinated unit would be convertible into two common units. We will not make any adjustment by reason of the issuance of additional units for cash or property.
In addition, if legislation is enacted or if existing law is modified or interpreted by a court of competent jurisdiction so that we become taxable as a corporation or otherwise subjecting us to a material amount of entity
65
level taxation for federal, state or local income tax purposes, our general partner may reduce the initial quarterly distribution and the target distribution levels for each quarter by multiplying each distribution level by a fraction, the numerator of which is available cash for that quarter (after deducting our general partner’s estimate of our aggregate liability for the quarter for such income taxes payable by reason of such legislation or interpretation) and the denominator of which is the sum of available cash for that quarter plus our general partner’s estimate of our aggregate liability for the quarter for such income taxes payable by reason of such legislation or interpretation. To the extent that the actual tax liability differs from the estimated tax liability for any quarter, the difference will be accounted for in subsequent quarters.
Distributions of Cash Upon Liquidation
General
If we dissolve in accordance with our partnership agreement, we will sell or otherwise dispose of our assets in a process called liquidation. We will first apply the proceeds of liquidation to the payment of our creditors. We will distribute any remaining proceeds to the unitholders and our general partner, in accordance with their capital account balances, as adjusted to reflect any gain or loss upon the sale or other disposition of our assets in liquidation.
The allocations of gain and loss upon liquidation are intended, to the extent possible, to entitle the holders of outstanding common units to a preference over the holders of outstanding subordinated units upon our liquidation, to the extent required to permit common unitholders to receive their unrecovered initial unit price plus the initial quarterly distribution for the quarter during which liquidation occurs plus any unpaid arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units. However, there may not be sufficient gain upon our liquidation to enable the holders of common units to fully recover all of these amounts, although there may be cash available for distribution to the holders of subordinated units. Any further net gain recognized upon liquidation will be allocated in a manner that takes into account the incentive distribution rights currently owned by our general partner.
Manner of Adjustments for Gain
The manner of the adjustment for gain is set forth in our partnership agreement. If our liquidation occurs before the end of the subordination period, we will allocate any gain to the partners in the following manner:
| • | First, to the general partner and the holders of units who have negative balances in their capital accounts to the extent of and in proportion to those negative balances; |
| • | Second, 98% to the common unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until the capital account for each common unit is equal to the sum of: |
| (1) | the unrecovered initial unit price; |
| (2) | the amount of the initial quarterly distribution for the quarter during which our liquidation occurs; and |
| (3) | any unpaid arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution; |
| • | Third, 98% to the subordinated unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until the capital account for each subordinated unit is equal to the sum of: |
| (1) | the unrecovered initial unit price; and |
| (2) | the amount of the initial quarterly distribution for the quarter during which our liquidation occurs; |
| • | Fourth, 98% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, until we allocate under this paragraph an amount per unit equal to: |
| (1) | the sum of the excess of the first target distribution per unit over the initial quarterly distribution per unit for each quarter of our existence; less |
| (2) | the cumulative amount per unit of any distributions of available cash from operating surplus in excess of the initial quarterly distribution per unit that we distributed 98% to the unitholders, pro rata, and 2% to our general partner, for each quarter of our existence; |
66
| • | Fifth, 85% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 15% to our general partner, until we allocate under this paragraph an amount per unit equal to: |
| (1) | the sum of the excess of the second target distribution per unit over the first target distribution per unit for each quarter of our existence; less |
| (2) | the cumulative amount per unit of any distributions of available cash from operating surplus in excess of the first target distribution per unit that we distributed 85% to the unitholders, pro rata, and 15% to our general partner for each quarter of our existence; |
| • | Sixth, 75% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 25% to our general partner, until we allocate under this paragraph an amount per unit equal to: |
| (1) | the sum of the excess of the third target distribution per unit over the second target distribution per unit for each quarter of our existence; less |
| (2) | the cumulative amount per unit of any distributions of available cash from operating surplus in excess of the second target distribution per unit that we distributed 75% to the unitholders, pro rata, and 25% to our general partner for each quarter of our existence; and |
| • | Thereafter, 50% to all unitholders, pro rata, and 50% to our general partner. |
The percentages set forth above are based on the assumptions that our general partner maintains its 2% general partner interest and has not transferred its incentive distribution rights and that we do not issue additional classes of equity securities.
If the liquidation occurs after the end of the subordination period, the distinction between common units and subordinated units will disappear, so that clause (3) of the second bullet point above and all of the third bullet point above will no longer be applicable.
Manner of Adjustments for Losses
If our liquidation occurs before the end of the subordination period, we will generally allocate any loss to our general partner and the unitholders in the following manner:
| • | First, 98% to holders of subordinated units in proportion to the positive balances in their capital accounts and 2% to our general partner, until the capital accounts of the subordinated unitholders have been reduced to zero; |
| • | Second, 98% to the holders of common units in proportion to the positive balances in their capital accounts and 2% to our general partner, until the capital accounts of the common unitholders have been reduced to zero; and |
| • | Thereafter, 100% to our general partner. |
The 2% interests set forth in the first and second bullet points above for our general partner are based on the assumptions that our general partner maintains its 2% general partner interest and that we do not issue additional classes of equity securities.
If the liquidation occurs after the end of the subordination period, the distinction between common units and subordinated units will disappear, so that all of the first bullet point above will no longer be applicable.
Adjustments to Capital Accounts
We will make adjustments to capital accounts upon the issuance of additional units. In doing so, we will allocate any unrealized and, for tax purposes, unrecognized gain or loss resulting from the adjustments to the unitholders and our general partner in the same manner as we allocate gain or loss upon liquidation. In the event that we make positive adjustments to the capital accounts upon the issuance of additional units, we will allocate any later negative adjustments to the capital accounts resulting from the issuance of additional units or upon our liquidation in a manner which results, to the extent possible, in our general partner’s capital account balances equaling the amount which they would have been if no earlier positive adjustments to the capital accounts had been made.
67
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA OF OUR COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
The following tables set forth the selected financial data of our combined predecessor entities for the periods and at the dates indicated. Our combined predecessor entities refer to Cheniere Energy Partners and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, including Sabine Pass LNG.
The combined statement of operations data for the period from October 20, 2003 (inception) through December 31, 2006, for the years ended December 31, 2004, 2005 and 2006, and the combined balance sheet information at December 31, 2005 and 2006 are derived from our audited combined financial statements, which are included elsewhere in this prospectus. The summary combined statement of operations data for the period from October 20, 2003 (inception) through December 31, 2003 and the summary combined balance sheet information at December 31, 2003 and 2004 have been derived from our audited combined financial statements, which are not included in this prospectus. Our past financial or operating performance is not a reliable indicator of our future performance (particularly anticipated revenues, debt costs and expenses), and you should not use our historical performance to anticipate results or future period trends.
We derived the information in the following table from, and that information should be read together with and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, the combined financial statements and the accompanying notes included in this prospectus. The table should also be read together with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
| Combined Predecessor Entities | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Period from October 20, 2003 (inception) to December 31, 2003 |
Year ended December 31, |
Period from October 20, 2003 (inception) to December 31, 2006 |
||||||||||||||||||
| 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Operations Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Expenses |
2,763 | 4,682 | 4,719 | 10,277 | 22,441 | |||||||||||||||
| Loss from operations |
(2,763 | ) | (4,682 | ) | (4,719 | ) | (10,277 | ) | (22,441 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other income (expense)(1) |
— | 28 | 456 | (50,495 | ) | (50,011 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (2,763 | ) | $ | (4,654 | ) | $ | (4,263 | ) | $ | (60,772 | ) | $ | (72,452 | ) | |||||
| Cash Flow Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows provided by (used in) operating activities |
$ | 101 | $ | 23,192 | $ | 6,319 | $ | (27,912 | ) | $ | 1,699 | |||||||||
| Cash flows used in investing activities |
(101 | ) | (124 | ) | (246,337 | ) | (1,544,408 | ) | (1,790,968 | ) | ||||||||||
| Cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities |
— | (1,246 | ) | 218,201 | 1,572,322 | 1,789,276 | ||||||||||||||
| Combined Predecessor Entities | ||||||||||||
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | |||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | — | $ | 21,822 | $ | 5 | $ | 7 | ||||
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents (current) |
— | — | 8,871 | 355,327 | ||||||||
| Non-current restricted cash and cash equivalents |
— | — | — | 803,610 | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment |
96 | 212 | 270,740 | 651,676 | ||||||||
| Total assets |
101 | 23,316 | 309,139 | 1,858,114 | ||||||||
| Long-term debt |
— | — | 72,485 | 2,032,000 | ||||||||
| Deferred revenues |
— | 22,000 | 40,000 | 40,000 | ||||||||
| Total other long-term liabilities |
2,864 | 17,418 | 120 | 1,149 | ||||||||
| (1) | The year ended 2006 includes a $23.8 million loss related to the expensing of debt issuance costs and a $20.6 million derivative loss as a result of terminating interest rate swaps, both related to the termination of the Sabine Pass credit facility in November 2006. |
68
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The combined financial statements included in this prospectus reflect the combined business and financial results of Sabine Pass LNG and its general partner and limited partner to be contributed to us by Cheniere in connection with this offering. The following discussion analyzes the financial condition and results of operations of these combined predecessor entities. You should read the following discussion of the financial condition and results of operations for these combined predecessor entities in conjunction with the historical combined financial statements and notes included elsewhere in this prospectus.
In addition to historical information, the following discussion contains forward-looking statements that are subject to significant risks and uncertainties. Our actual results may differ materially from those discussed in the forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including the factors set forth under the captions “Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus.
We are a Delaware limited partnership recently formed by Cheniere to develop, own and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal currently under construction in western Cameron Parish, Louisiana on the Sabine Pass Channel. The Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is being constructed in two phases:
| • | Phase 1. The initial phase of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal was designed with an initial regasification capacity of 2.6 Bcf/d and three LNG storage tanks with an aggregate LNG storage capacity of 10.1 Bcf, along with two unloading docks capable of handling the largest LNG carriers currently being built. Construction of Phase 1 began in March 2005, commercial operation is expected to commence during the second quarter of 2008 and construction is expected to be completed during the third quarter of 2008. We estimate the cost to construct Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be approximately $900 million to $950 million, before financing costs. As of December 31, 2006, Sabine Pass LNG had paid $564.2 million of Phase 1 construction costs. |
| • | Phase 2. The first stage of the second phase of the development of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is expected to increase the regasification capacity from 2.6 Bcf/d to 4.0 Bcf/d by adding two LNG storage tanks, additional vaporizers and related facilities. We estimate the cost to construct Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be approximately $500 million to $550 million, before financing costs. As of December 31, 2006, Sabine Pass LNG had paid $44.0 million of Phase 2 – Stage 1 construction costs. |
We are a development stage company without any revenues, operating cash flows or operating history. We currently do not expect that we will begin receiving any revenues from operations until the second quarter of 2008, at the earliest.
Upon completion of construction, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will have approximately 4.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity and approximately 16.8 Bcf of storage capacity. All of this capacity has been contracted for under three 20-year, firm commitment terminal use agreements, or TUAs. Each customer must make payments on a “take-or-pay” basis, which means that the customer will be obligated to pay the full contracted amount of monthly fees whether or not it uses any of its reserved capacity. Provided the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal has achieved commercial operation at 2.0 Bcf/d, which we expect will occur during the second quarter of 2008, these “take-or-pay” TUA payments will be made as follows:
| • | Total has reserved approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $125 million per year for 20 years commencing April 1, |
69
| 2009. Total, S.A. has guaranteed Total’s obligations under its TUA up to $2.5 billion, subject to certain exceptions. |
| • | Chevron has reserved approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $125 million per year for 20 years commencing not later than July 1, 2009. Chevron Corporation has guaranteed Chevron’s obligations under its TUA up to 80% of the fees payable by Chevron. |
| • | Cheniere Marketing has reserved approximately 2.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity, is entitled to use any capacity not utilized by Total and Chevron and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $250 million per year for at least 19 years commencing January 1, 2009, plus payments of $5 million per month during an initial commercial operations ramp-up period in 2008. Cheniere has guaranteed Cheniere Marketing’s obligations under its TUA. |
Cheniere Marketing is a development stage company with a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy. It may never develop its business, assets or revenues sufficiently to make payments under its TUA. Cheniere has guaranteed 100% of the obligations of Cheniere Marketing under its TUA. Cheniere has a non-investment grade corporate rating of B from Standard & Poor’s. If Cheniere does not receive sufficient future cash flows from businesses that Cheniere is developing, Cheniere may be unable to perform its guarantee of the Cheniere Marketing TUA. Without sufficient revenue from the Cheniere Marketing TUA, Sabine Pass LNG would fail to meet the fixed charge coverage ratio test under the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes, which would prevent Sabine Pass LNG from being able to distribute cash to us. If we do not receive distributions from Sabine Pass LNG, we may not be able to continue to make distributions to our unitholders, which could have a material and adverse effect on the perceived value of our partnership and the market price of our common units.
Each of Total and Chevron has paid us $20 million in nonrefundable advance capacity reservation fees, which are being amortized over a 10-year period as a reduction of each customer’s regasification capacity fees payable under its TUA.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
General
We estimate that the aggregate total cost to complete construction of Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be approximately $1.4 billion to $1.5 billion, before financing costs. Our cost estimates are subject to change due to such items as cost overruns, change orders, increased component and material costs, escalation of labor costs and increased spending to maintain our construction schedule.
We will fund our construction period capital resource requirements from a portion of the $2,032 million in net proceeds received from Sabine Pass LNG’s issuance of senior secured notes in November 2006. We placed $335 million of the net proceeds in a reserve account to fund scheduled interest payments on the Sabine Pass LNG notes through May 2009. We also placed approximately $887 million in a construction account, which, until satisfaction of construction completion milestones, will only be applied to pay construction and startup costs of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and to pay other expenses incidental for us to complete construction of the project. We used the remaining net proceeds received from the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes to repay indebtedness, to make a distribution to Cheniere Holdings for the repayment of its outstanding term loan and to pay fees and expenses related to the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes.
We believe that we have adequate financial resources to complete Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and to meet our anticipated operating, maintenance and debt service requirements and all of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units through the first half of 2009. Furthermore, we anticipate that:
| • | cash flows from operations will commence in the second quarter of 2008, when Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is anticipated to commence commercial operation; and |
70
| • | beginning in the third quarter of 2009, cash flows from operations will be sufficient to cover all debt service on the Sabine Pass LNG notes, all other costs of operating Sabine Pass LNG and all of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units, subordinated units and general partner units. |
Any delays in construction could prevent us from commencing operations when we anticipate and could prevent us from realizing anticipated cash flows. Our future liquidity may also be affected by the timing of construction financing availability in relation to our incurrence of construction costs and other outflows and by the timing of our receipt of cash flows under the TUAs in relation to our incurrence of project and operating expenses. Moreover, many factors (including factors beyond our control) could result in a disparity between our liquidity sources and cash needs, including factors such as construction delays and breaches of construction agreements. After the construction period, our business may not generate sufficient cash flow from operations, currently anticipated costs may increase or future borrowings may not be available to us in amounts sufficient to enable us to pay our indebtedness or to fund our other liquidity needs, including operating expenses and distributions to our unitholders. The operation of our business is subject to many risks (many of which are beyond our control), including general economic, financial, competitive, legislative, regulatory and other developments.
Uses of Capital
Phase 1 EPC Agreement
In December 2004, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a lump-sum turnkey EPC agreement with Bechtel for Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Except for certain third-party work specified in the EPC agreement, the work to be performed by Bechtel includes all of the work required to achieve substantial completion and final completion of Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal in accordance with the requirements of the EPC agreement.
Pursuant to the EPC agreement, Sabine Pass LNG agreed to pay Bechtel a contract price of $646.9 million plus certain reimbursable costs for the work performed under the EPC agreement. This contract price is subject to adjustment for certain costs of materials, contingencies, change orders and other items. As of January 17, 2007, change orders for $119.5 million were approved, primarily for design changes, increases in costs of materials, insurance costs and costs related to the 2005 hurricanes, increasing the total contract price to $766.4 million.
Phase 2 Construction Agreements
In July 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into three construction agreements to facilitate construction of the Phase 2 – Stage 1 expansion, as follows:
| • | EPCM agreement. Sabine Pass LNG entered into an engineering, procurement, construction and management, or EPCM, agreement with Bechtel pursuant to which Bechtel will provide: design and engineering services for Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal project, except for such portions to be designed by other contractors and suppliers that Sabine Pass LNG contracts with directly; construction management services to manage the construction of the LNG receiving terminal; and a portion of the construction services. Under the terms of the EPCM agreement, Bechtel will be paid on a cost reimbursable basis, plus a fixed fee in the amount of $18.5 million. A discretionary bonus may be paid to Bechtel at Sabine Pass LNG’s sole discretion upon completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1. For more information, please read “Description of Principal Construction Agreements—Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPCM Agreement.” |
| • | EPC Tank Contract. Sabine Pass LNG entered into an EPC LNG tank contract, or tank contract, with Zachry Construction Corporation, or Zachry, and Diamond LNG LLC, or Diamond, under which Zachry and Diamond will furnish all plant, labor, materials, tools, supplies, equipment, transportation, supervision, technical, professional and other services, and perform all operations necessary and required to satisfactorily engineer, procure materials for and construct the two Phase 2 – Stage 1 LNG storage tanks. In addition, Sabine Pass LNG has the option (to be elected on or before March 31, 2007) |
71
| for Zachry and Diamond to engineer, procure and construct a sixth LNG storage tank, with the cost and completion date to be agreed upon if the option is exercised. The tank contract provides that Zachry and Diamond will receive a lump-sum, total fixed price payment for the two Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks of approximately $140.9 million, which is subject to adjustment based on fluctuations in the cost of labor and certain materials, including the steel used in the Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks, and change orders. For more information, please read “Description of Principal Construction Agreements—Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPC LNG Tank Contract.” |
| • | EPC LNG Unit Rate Soil Contract. Sabine Pass LNG entered into an EPC LNG unit rate soil contract, or soil contract, with Remedial Construction Services, L.P., or Recon. Under the soil contract, Recon is required to furnish all plant, labor, materials, tools, supplies, equipment, transportation, supervision, technical, professional and other services, and perform all operations necessary and required to satisfactorily conduct soil remediation and improvement on the Phase 2 site, unless otherwise set forth in the soil contract. Upon issuing a final notice to proceed in August 2006, Sabine Pass LNG paid Recon an initial payment of approximately $2.9 million. The soil contract price is based on unit rates. Payments under the soil contract will be made based on quantities of work performed at unit rates. For more information, please read “Description of Principal Construction Agreements—Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPC LNG Soil Contract.” |
Cheniere Marketing’s Option for a Sixth LNG Storage Tank
The Cheniere Marketing TUA provides that, at Cheniere Marketing’s request, Sabine Pass LNG must construct a sixth LNG storage tank with a working capacity of approximately 160,000 cubic meters of LNG as soon as possible but not later than four years after notification from Cheniere Marketing. Our obligation to construct the additional LNG storage tank will be subject to receipt of all FERC and other required governmental permits and approvals and obtaining financing that we consider reasonably acceptable in form and content.
If Cheniere Marketing exercises its option to require us to construct the sixth LNG storage tank, we may have to incur additional debt. Our internal estimate of the cost to construct the sixth tank is in the range of $120 million to $140 million. As described above, we have an option, exercisable on or before March 31, 2007, to require Zachry and Diamond to engineer, procure and construct the sixth LNG storage tank, with the cost and completion date to be agreed upon if the option is exercised. If Cheniere Marketing exercises its option after March 31, 2007, we may have to negotiate one or more new construction agreements with one or more new contractors. Sabine Pass LNG will not receive additional revenues in exchange for constructing a sixth LNG storage tank under the Cheniere Marketing TUA.
Cash Distributions to Unitholders
For each calendar quarter through June 30, 2009, we will make quarterly cash distributions of $0.425 per unit on all outstanding common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, using cash from a distribution reserve that will be funded with proceeds from this offering. We believe that the amount of the distribution reserve, together with interest expected to be earned on that amount and cash from operations, if any, will be sufficient to allow us to pay the full initial quarterly distribution on all our outstanding common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, for each quarter through June 30, 2009. After the quarter ended June 30, 2009, we intend to pay distributions to our unitholders primarily with operating cash flows.
Services Agreements
Operation and Maintenance Agreement. In February 2005, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an Operation and Maintenance Agreement, or O&M Agreement, with Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P., or O&M Services, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere. Pursuant to the O&M Agreement, O&M Services agreed to provide all necessary services required to construct, operate and maintain the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. The O&M Agreement will remain in effect until 20 years after substantial completion of the facility.
72
Prior to substantial completion of the facility, Sabine Pass LNG is required to pay a fixed monthly fee of $95,000 (indexed for inflation). The fixed monthly fee will increase to $130,000 (indexed for inflation) upon substantial completion of the facility, and O&M Services will thereafter be entitled to a bonus equal to 50% of the salary component of labor costs in certain circumstances to be agreed upon between Sabine Pass LNG and O&M Services at the beginning of each operating year. In addition, Sabine Pass LNG is required to reimburse O&M Services for its operating expenses, which are comprised of labor, maintenance, land lease and insurance expenses and for maintenance capital expenditures.
At or near the closing of this offering, O&M Services will assign the O&M Agreement to our general partner, and O&M Services and our general partner will enter into a services and secondment agreement pursuant to which we anticipate that certain employees of O&M Services will be seconded to our general partner to provide operating and routine maintenance services with respect to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal under the direction, supervision and control of our general partner. Under this agreement, our general partner will pay O&M Services amounts that it receives from Sabine Pass LNG under the O&M Agreement.
Management Services Agreements. In February 2005, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a Management Services Agreement, or the Sabine Pass LNG MSA, with its general partner, Sabine Pass LNG–GP, Inc., which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of us. Pursuant to the Sabine Pass LNG MSA, Sabine Pass LNG appointed its general partner to manage the construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, excluding those matters provided for under the O&M Agreement. The Sabine Pass LNG MSA terminates 20 years after the commercial start date set forth in the Total TUA. Prior to substantial completion of construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Sabine Pass LNG is required to pay its general partner a monthly fixed fee of $340,000 (indexed for inflation); thereafter, the monthly fixed fee will increase to $520,000 (indexed for inflation).
In September 2006, the general partner of Sabine Pass LNG entered into a Management Services Agreement with Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc., or Cheniere Terminals, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere. Pursuant to this agreement, Cheniere Terminals provides the general partner with technical, financial, staffing and related support necessary to allow it to meet its obligations to Sabine Pass LNG under the Sabine Pass LNG MSA. Under this agreement with Cheniere Terminals, the general partner of Sabine Pass LNG pays Cheniere Terminals amounts that it receives from Sabine Pass LNG for management of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
Services Agreement. Our general partner anticipates entering into a services agreement with Cheniere Terminals upon the closing of this offering. Under this agreement, we will pay Cheniere Terminals an annual administrative fee of $10 million (adjusted for inflation after January 1, 2007) commencing January 1, 2009 for the provision of various general and administrative services for our benefit following the closing of this offering and will reimburse Cheniere Terminals for its services in an amount equal to the sum of all out-of-pocket costs and expenses incurred by Cheniere Terminals that are directly related to our business or activities, such as salaries of operational personnel performing services on-site at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and the cost of their employee benefits, including 401(k) plan, pension and health insurance benefits. The annual administrative fee includes expenses incurred by Cheniere Terminals to perform all technical, commercial, regulatory, financial, accounting, treasury, tax and legal staffing and related support and all management and other services necessary or reasonably requested on behalf of our partnership by our general partner in order to conduct our business as contemplated by our partnership agreement.
Our general partner will also be entitled to a special annual bonus, which is payable in the in the sole discretion of Sabine Pass LNG. These fees and bonus payments do not include substantial reimbursements that we will make to our general partner and its affiliates on an annual basis for expenses incurred on our behalf. For more information on these agreements, please read “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions.”
Public Company Expenses
Following this offering, our general and administrative expenses will increase as a result of becoming a publicly traded partnership. In addition, Sabine Pass LNG will also become a reporting entity under the Exchange Act once its registration statement relating to the Sabine Pass LNG notes is declared effective. As a
73
result, we anticipate that our combined total annual general and administrative expenses following the completion of this offering will increase by approximately $2.5 million. This increase is expected to result from the cost of additional accounting and support services to be incurred after this offering, including costs related to compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, filing annual and quarterly reports with the SEC, increased audit fees, tax compliance and publicly traded partnership tax reporting, investor relations, director compensation, directors’ and officers’ insurance, legal fees, registrar and transfer agent fees and stock exchange fees. Cheniere will advance us funds to pay public company expenses associated with being a publicly traded partnership through 2008, after which time we will use available cash to pay such expenses directly and, after payment of the initial quarterly distribution on all units, to reimburse Cheniere.
Maintenance Capital Expenditures
Beginning in 2009, Sabine Pass LNG expects to incur approximately $1.5 million per year in maintenance capital expenditures, which are generally capital expenditures to maintain the operating capacity or asset base of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and extend its useful life.
State Tax Sharing Agreement
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a state tax sharing agreement with Cheniere. Under this agreement, Cheniere has agreed to prepare and file all Texas franchise tax returns which it and Sabine Pass LNG are required to file on a combined basis and to timely pay the combined tax liability. If Cheniere, in its sole discretion, demands payment, Sabine Pass LNG will pay to Cheniere an amount equal to the Texas franchise tax that Sabine Pass LNG would be required to pay if its Texas franchise tax liability were computed on a separate company basis. This agreement contains similar provisions for other state and local taxes that Cheniere and Sabine Pass LNG are required to file on a combined, consolidated or unitary basis. The agreement is effective for tax returns first due on or after January 1, 2008. For more information on this agreement, please read “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions—Arrangement Regarding Taxes.”
Debt Agreements
Sabine Pass LNG Notes
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG issued $550 million aggregate principal amount of 7.25% Senior Secured Notes due 2013 and $1,482 million aggregate principal amount of 7.50% Senior Secured Notes due 2016 in a private placement. For more information regarding these notes, please read “Indebtedness.”
Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility
In February 2005, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an $822 million credit agreement with HSBC Bank, USA and Société Générale and a syndicate of financial institutions, and related interest rate swap agreements with HSBC Bank, USA and Société Générale. This original credit facility was subsequently amended and restated in July 2006. The amended credit facility increased the amount of loans available to Sabine Pass LNG from $822 million under the original credit facility to $1.5 billion to finance Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 expansion construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. In connection with the closing of the credit facility and subsequent amendment, Sabine Pass LNG entered into interest rate swap agreements with HSBC Bank, USA and Société Générale. In connection with the issuance of the notes in November 2006, the amended credit facility and related interest rate swaps were paid in full and terminated.
74
Historical Cash Flows
The following table summarizes the changes in our cash and cash equivalents from 2004 to 2006. Additional discussion of the key elements contributing to these changes follow the table (in thousands).
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
| Cash provided by (used in): |
||||||||||||
| Operating activities |
$ | (27,912 | ) | $ | 6,319 | $ | 23,192 | |||||
| Investing activities |
(1,544,408 | ) | (246,337 | ) | (124 | ) | ||||||
| Financing activities |
1,572,322 | 218,201 | (1,246 | ) | ||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 2 | $ | (21,817 | ) | $ | 21,822 | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
$ | 7 | $ | 5 | $ | 21,822 | ||||||
Operating Activities—Net cash used in operating activities was $27.9 million during 2006 compared to $6.3 million net cash provided by operating activities in 2005. Net cash used in operating activities during 2006 was primarily the result of the $20.6 million derivative loss incurred upon the termination of interest rate swaps related to the termination of the amended credit facility. Absent this non-cash loss, we would have had recorded net cash used in operating activities of $7.4 million. Net cash provided by operating activities during 2005 was primarily the result of our receipt of $18.0 million in advance terminal capacity reservation fees partially offset by a $7.4 million reimbursement of expenses paid to an affiliate. Absent these items, we would have recorded net cash used in operating activities of $4.3 million for 2005. Net cash provided by operating activities during 2004 was primarily the result of our receipt of $22.0 million in advance terminal capacity reservation fees.
Investing Activities—Net cash used in investing activities was $1.5 billion during 2006 compared to net cash used in investing activities of $246.3 million during 2005. During 2006, we funded $1.2 billion related to restricted cash balances as required by the Sabine Pass LNG notes, and we recorded $387.7 million to construction-in-progress related to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Our investment activities during 2005 included $229.1 million recorded to construction-in-progress related to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, $8.9 million related to the funding of restricted cash balances, and $8.1 million of advances to our EPC contractor.
Financing Activates—Net cash provided by financing activities during 2006 was $1.6 billion compared to net cash provided by financing activities of $218.2 million during 2005. During 2006, we received proceeds from borrowings under the amended credit facility and Sabine Pass LNG notes totaling $383.4 million and $2.0 billion, respectively. These proceeds were partially offset by repayments of the amended credit facility of $383.4 million and a subordinated note to an affiliate of $37.4 million. We also paid debt issuance costs during 2006 of $44.0 million as a result of amending our credit facility and the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes, and we made a $378.3 million distribution to our limited partner. During 2005, we received $161.6 million in limited partner capital contributions from an affiliate, $37.4 million in proceeds from a subordinated note issued to an affiliate and $35.1 million related to an affiliate payable, which were partially reduced by $15.8 million in debt issuance costs related to the original Sabine Pass LNG credit facility.
Our cash and cash equivalent ending balances were $7,000 and $5,000 as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, as most cash and cash equivalents were restricted under the terms of the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes and the amended credit facility.
75
Contractual Obligations
We are committed to make cash payments in the future pursuant to certain of our contracts. We have no off-balance sheet debt or other such unrecorded obligations, and we have not guaranteed the debt of any other party. The following table summarizes certain contractual obligations in place as of December 31, 2006 (in thousands).
| Payments Due for Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| Total | 2007 | 2008-2009 | 2010-2011 | Thereafter | |||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations— |
|||||||||||||||
| LNG site rental (1) |
$ | 132,104 | $ | 1,507 | $ | 3,012 | $ | 3,002 | $ | 124,583 | |||||
| Long-term debt (2) |
2,032,000 | — | — | — | 2,032,000 | ||||||||||
| Service contracts — |
|||||||||||||||
| Affiliate O&M agreement (1) |
33,480 | 1,140 | 2,700 | 3,120 | 26,520 | ||||||||||
| Affiliate Sabine Pass LNG MSA (1) |
134,320 | 4,080 | 9,600 | 12,480 | 108,160 | ||||||||||
| Construction and purchase obligations (1)(3) |
706,092 | 405,469 | 300,623 | — | — | ||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 3,037,996 | $ | 412,196 | $ | 315,935 | $ | 18,602 | $ | 2,291,263 | |||||
| (1) | A discussion of these obligations can be found in Note 14 to our combined financial statements. |
| (2) | A discussion of these obligations can be found in Note 11 to our combined financial statements and in the section of this prospectus titled “Indebtedness.” |
| (3) | Represents construction contracts and obligations to purchase long lead equipment and materials for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
LNG Receiving Terminal Construction Contracts
As more fully described in note 14 to our combined financial statements, we have entered into construction contracts with various third parties to construct Phase 1 and Phase 2—Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. We estimate that the cost to construct Phase 1 and Phase 2—Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be approximately $1.4 billion to $1.5 billion, before financing costs.
Inflation
We have experienced escalating steel prices relating to the construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and increasing labor costs in connection with the collateral effects of the 2005 hurricanes, which we believe have been fully reflected in our estimated costs to construct the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
Comparison of the Fiscal Years Ended December 31, 2006 and 2005
Overview
Our financial results for the year ended December 31, 2006 reflected a net loss of $60.8 million, compared to a net loss of $4.3 million in 2005. Because we are a development stage company and our operations consist solely of constructing the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, we have not generated any operating revenues since inception.
Expenses
Total expenses increased $5.6 million, or 119.1%, to $10.3 million in 2006 compared to $4.7 million in 2005. This increase was primarily attributable to the reimbursement of development expenses related to Phase 2—Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and land site rental costs.
Prior to the execution of the amended credit facility in July 2006, an affiliate spent $4.5 million related to technical, consulting, legal and other professional fees associated with front-end engineering and design work, obtaining an order from the FERC authorizing construction of Phase 2—Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG
76
receiving terminal and other required permitting. Concurrently with the execution of the amended credit facility in July 2006, such development expenses became our obligation, and we reimbursed the affiliate for such expenses in August 2006. During 2005, land site rental payments were capitalized as part of the construction cost of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; however, beginning in January 2006, these rental payments ($1.5 million) have been expensed as required by FSP FAS No. 13-1, Accounting for Rental Costs Incurred during a Construction Period.
Other Income (Expense)
Total other expense, net of interest income, for the year ended December 31, 2006 was $50.5 million compared to other income of $0.5 million in 2005. In connection with the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes in November 2006, we terminated the amended credit facility. As a result, we recorded a $23.8 million non-cash loss on the early extinguishment of debt related to debt issuance costs and a $20.6 million derivative loss primarily as a result of terminating related interest rate swaps. In 2006, we also recorded interest expense of $15.5 million, net of $22.3 million capitalized interest. These expenses were partially offset by interest income in 2006 of $9.3 million as a result of the increase in restricted cash from the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes.
Other income for the year ended December 31, 2005 was $0.5 million. We recorded a derivative gain of $0.3 million in 2005 related to the ineffective portion of our interest rate swap gain associated with the original credit facility entered into in February 2005.
Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2005 compared to Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2004
Overview
Our financial results for the year ended December 31, 2005 reflected a net loss of $4.3 million compared to a net loss of $4.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2004.
Expenses
Total expenses for each of the years ended December 31, 2004 and 2005 were $4.7 million. During 2004, primarily all of our expenses related to technical, consulting, legal and other professional fees associated with front-end engineering and design work, obtaining an order from FERC authorizing construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and other required permitting. In March 2005, we received the order from FERC authorizing construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and other required permitting. In March 2005, we received an order from the FERC authorizing construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and, accordingly, began construction. In mid-February 2005, we began paying overhead charges to affiliates related to services required to construct the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. These charges totaled $4.1 million in 2005 (net of $0.3 million capitalized).
Other Income
Other income for the year ended December 31, 2005 was $0.5 million compared to $28,000 for 2004. We recorded a derivative gain of $0.3 million in 2005 compared to none in 2004. The derivative gain was related to the ineffective portion of our interest rate swap gain associated with the original Sabine Pass LNG credit facility entered into in February 2005.
Period from October 20, 2003 (Inception) to December 31, 2003
We recorded a net loss of $2.8 million for the period from October 20, 2003 (inception) to December 31, 2003. The net loss related to expenses incurred for technical, consulting, legal and other professional fees associated with front-end engineering and design work, obtaining an order from FERC authorizing construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and other required permitting.
77
Critical Accounting Estimates and Policies
The selection and application of accounting policies is an important process that has developed as our business activities have evolved and as the accounting rules have developed. Accounting rules generally do not involve a selection among alternatives but involve an implementation and interpretation of existing rules, and the use of judgment, to the specific set of circumstances existing in our business. We make every effort to comply properly with all applicable rules on or before their adoption, and we believe that the proper implementation and consistent application of the accounting rules are critical. However, not all situations are specifically addressed in the accounting literature. In these cases, we must use our best judgment to adopt a policy for accounting for these situations. We accomplish this by analogizing to similar situations and the accounting guidance governing them.
Accounting for LNG Activities
Generally, expenditures for direct construction activities, major renewals and betterments are capitalized, while expenditures for maintenance and repairs and general and administrative activities are charged to expense as incurred. Beginning in 2006, site rental costs are expensed as required by FSP 13-1, Accounting for Rental Costs Incurred During a Construction Period.
During the construction period of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, we capitalize interest and other related debt costs in accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards, or SFAS, No. 34, Capitalization of Interest Cost, as amended by SFAS No. 58, Capitalization of Interest Cost in Financial Statements That Include Investments Accounted for by the Equity Method (an Amendment of FASB Statement No. 34). Upon commencement of operations, capitalized interest, as a component of the total cost, will be amortized over the estimated useful life of the asset.
Revenue Recognition
LNG receiving terminal capacity reservation fees are recognized as revenue over the term of the respective TUAs. Advance capacity reservation fees are deferred initially. For information regarding revenue from related parties, please read notes 13 and 14 to our combined financial statements.
Cash Flow Hedges
As defined in SFAS No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, cash flow hedge transactions hedge the exposure to variability in expected future cash flows (i.e., in our case, the variability of floating interest rate exposure). In the case of cash flow hedges, the hedged item (the underlying risk) is generally unrecognized (i.e., not recorded on the balance sheet prior to settlement), and any changes in the fair value, therefore, will not be recorded within earnings. Conceptually, if a cash flow hedge is effective, this means that a variable, such as a movement in interest rates, has been effectively fixed so that any fluctuations will have no net result on either cash flows or earnings. Therefore, if the changes in fair value of the hedged item are not recorded in earnings, then the changes in fair value of the hedging instrument (the derivative) must also be excluded from the income statement or else a one-sided net impact on earnings will be reported, despite the fact that the establishment of the effective hedge results in no net economic impact. To prevent such a scenario from occurring, SFAS No. 133 requires that the fair value of a derivative instrument designated as a cash flow hedge be recorded as an asset or liability on the balance sheet, but with the offset reported as part of other comprehensive income, to the extent that the hedge is effective. We assess, both at the inception of each hedge and on an on-going basis, whether the derivatives that are used in our hedging transactions are highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows of the hedged items. On an on-going basis, we monitor the actual dollar offset of the hedges’ market values compared to hypothetical cash flow hedges. Any ineffective portion will be reflected in earnings. Ineffectiveness is the amount of gains or losses from derivative instruments that are not offset by corresponding and opposite gains or losses on the expected future transaction.
78
In February 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 155, Accounting for Certain Hybrid Financial Instruments. SFAS No. 155 provides entities with relief from having to separately determine the fair value of an embedded derivative that would otherwise be required to be bifurcated from its host contract in accordance with SFAS No. 133. SFAS No. 155 allows an entity to make an irrevocable election to measure such a hybrid financial instrument at fair value in its entirety, with changes in fair value recognized in earnings. SFAS No. 155 is effective for all financial instruments acquired, issued or subject to a remeasurement event occurring after the beginning of an entity’s first fiscal year that begins after September 15, 2006. We believe that the adoption of SFAS No. 155 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In March 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 156, Accounting for Servicing of Financial Assets – An Amendment to FASB Statement No. 140. SFAS No. 156 requires entities to recognize a servicing asset or liability each time they undertake an obligation to service a financial asset by entering into a servicing contract in certain situations. This statement also requires all separately recognized servicing assets and servicing liabilities to be initially measured at fair value and permits a choice of either the amortization or fair value measurement method for subsequent measurement. The effective date of this statement is for annual periods beginning after September 15, 2006, with earlier adoption permitted as of the beginning of an entity’s fiscal year provided the entity has not issued any financial statements for that year. We believe that the adoption of SFAS No. 155 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In July 2006, the FASB issued FASB Interpretation, or FIN, No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—An Interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109. FIN No. 48 clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in an enterprise’s financial statements in accordance with SFAS No. 109, Accounting for Income Taxes. It prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. This new standard also provides guidance on derecognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosure, and transition. The provisions of FIN No. 48 are to be applied to all tax positions upon initial adoption of this standard. Only tax positions that meet the more likely-than-not recognition threshold at the effective date may be recognized or continue to be recognized upon adoption of FIN No. 48. The cumulative effect of applying the provisions of FIN No. 48 should be reported as an adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings (or other appropriate components of equity or net assets in the statement of financial position) for that fiscal year. The provisions of FIN No. 48 are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2006. Earlier application is permitted as long as the enterprise has not yet issued financial statements, including interim financial statements, in the period of adoption. We believe that the adoption of FIN No. 48 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In September 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 157, Fair Value Measurements. SFAS No. 157 clarifies the principle that fair value should be based on the assumptions market participants would use when pricing an asset or liability and establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the information used to develop those assumptions. Under the standard, fair value measurements would be separately disclosed by level within the fair value hierarchy. SFAS No. 157 is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007, and interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted. We are currently determining the effect, if any, the adoption of SFAS No. 157 will have on our financial statements.
In September 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 158, Employers’ Accounting for Defined Benefit Pension and Other Postretirement Plan—an amendment of FASB Statement No. 87, 88, 106 and 132(R). SFAS No. 158 requires an employer to recognize the overfunded or underfunded status of a defined benefit postretirement plan as an asset or liability in its statement of financial position and recognize changes in the funded status in the year in which the changes occur. SFAS No. 158 is effective for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2006. We believe that the adoption of SFAS No. 158 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
79
In September 2006, the FASB issued FSP No. AUG AIR-1, Accounting for Planned Major Maintenance Activities. FSP No. AUG AIR-1 prohibits the use of the accrue-in-advance method for accounting for major maintenance activities and confirms the acceptable methods of accounting for planned major maintenance activities. FSP No. AUG AIR-1 is effective the first fiscal year beginning after December 15, 2006. We believe that the adoption of FSP No. AUG AIR-1 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We have cash investments that we manage based on internal investment guidelines that emphasize liquidity and preservation of capital. Such cash investments are stated at historical cost, which approximates fair market value on our balance sheet.
80
We obtained the information in this prospectus about the LNG industry from several independent outside sources, including: the Energy Information Administration, or EIA, an independent statistical and analytical agency within the U.S. Department of Energy; Groupe International des Importateurs de Gaz Naturel Liquéfié, or GIIGNL, an industry organization representing LNG importers; the BP Statistical Review of World Energy, June 2006; Wood Mackenzie Limited, a consulting company; and the FERC. Much of the most recent government data available regarding the LNG industry is for 2004 and 2005.
LNG is an effective means to transport natural gas from remote areas to demand centers. In 2005, natural gas satisfied more than 23% of worldwide, and 25% of North American, primary energy consumption according to the 2006 BP Statistical Review. The EIA expects global demand for natural gas to grow by 0.7% per year, on average, from 2005 to 2030. This growth will be driven by economic growth, the clean-burning nature of natural gas and the widespread applicability of natural gas as a fuel source. Furthermore, according to the EIA, demand for natural gas has increased at a faster rate than supply since 2004 and is forecast to continue doing so through 2030.
Substantial natural gas reserves are located in countries that have low energy consumption and are far from major energy demand centers. Natural gas supplies close to some major consuming markets are facing declining production. To transport natural gas effectively from remote locations to major energy demand centers, natural gas is liquefied to condense its volume and permit efficient transportation by sea. Liquefying natural gas is, therefore, becoming an increasingly significant alternative for distributing natural gas produced in remote areas to key centers of natural gas consumption.
Global LNG export capability is expanding. LNG provides a cost-effective means for transporting natural gas overseas because it is supercooled to a liquid form, which reduces its volume to approximately 1/600th of its volume in a gaseous state. The EIA reports that between 1995 and 2005, annual LNG exports increased by an 8% compound annual growth rate, from 9 Bcf/d to 19 Bcf/d, as a result of increasing worldwide energy demand and achievement of economies of scale in liquefaction, shipping and regasification. Historically, the LNG trade was led by large utilities in Europe, Japan, South Korea and Taiwan, which lack adequate indigenous supplies of natural gas. LNG export facilities in Algeria, Indonesia, Malaysia, Australia and Alaska served these markets. Today, European utilities seek to diversify their supply sources to meet peak winter demand, and North American producers seek to support growing demand. This has encouraged more liquefaction development globally, including in the Americas (Trinidad, Venezuela and Peru), Africa (Egypt, Algeria, Nigeria, Equatorial Guinea, Angola and Libya), the Middle East (Qatar, Oman and Iran), Asia (Indonesia, Malaysia and Papua New Guinea), Australia and Russia.
North America, the largest natural gas market in the world, needs new natural gas supplies, including LNG. North America has the largest interconnected natural gas market in the world, consuming approximately 76 Bcf/d in 2004, according to the EIA. LNG’s contribution to the North American market has historically been minimal, due mainly to abundant, indigenous supplies of low cost natural gas. The average wellhead price of natural gas produced in the United States has increased significantly from 2002 to 2006, which is an indication of a depleted resource base. LNG imports are expected to gain market share as a competitive source of supply to meet growing natural gas demand. According to the EIA, LNG imports accounted for less than 1% of total U.S. consumption in 2000 and grew to 3.2% of total U.S. consumption in 2005, and it forecasts that LNG imports will grow to 16.2% of U.S. consumption by 2030.
North America’s LNG receiving capability is expanding, and LNG’s share of the North American natural gas market is increasing. According to the EIA, in 2005, North American LNG imports were sourced from Trinidad and Tobago, Algeria, Egypt, Nigeria, Oman, Qatar and Malaysia. Currently, there are five onshore receiving terminals in continental North America with a combined natural gas sendout capacity of approximately
81
4.75 Bcf/d, or about 6% of total North American natural gas consumption. As of December 2006, six additional LNG receiving terminals with an aggregate send-out capacity of 11 Bcf/d were under construction in North America.
The LNG supply chain can be divided into five major phases:
Production: Natural gas is produced and transported via pipeline to natural gas liquefaction facilities located along the coast of the producing country.
Liquefaction: Once delivered to the liquefaction facility, the natural gas is supercooled to a temperature of -260 degrees Fahrenheit, transforming the gas into a liquid 1/600th the volume of its gaseous state.
Shipping: LNG is loaded onto specially designed, double-hulled LNG carriers and transported overseas from the liquefaction facility to the receiving terminal.
Regasification: In receiving terminals (either onshore or aboard specialized LNG carriers), the LNG is returned to its gaseous state, or regasified.
Storage, Transportation and Marketing: Once regasified, the natural gas is stored in specially designed facilities or transported to natural gas consumers via pipelines.
The following diagram illustrates the flow of natural gas and LNG from production to end use marketing.
Worldwide Natural Gas Reserves
Worldwide proved natural gas reserves as of January 1, 2007 were estimated to be 6,183 trillion cubic feet, or Tcf, according to the EIA. The following chart displays the natural gas reserves of countries with more than 25 Tcf of proved reserves as estimated by the EIA. The chart also highlights the current and potential future LNG exporters. Current LNG exporters hold 33% of total proved natural gas reserves. Russia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Venezuela, Iraq and Norway have 52% of total proved natural gas reserves and access to coastline such that they could become LNG exporters under appropriate economic and political conditions.
82
Source: EIA and Wood Mackenzie. Proved reserves as of January 1, 2007.
According to GIIGNL, as of 2005, there were 76 “trains,” or production units, in 13 countries capable of producing approximately 23.4 Bcf/d of LNG. LNG production capacity grew by over 40% during the 2000 to 2005 period. Liquefaction capacity will reach approximately 37 Bcf/d in 2010 according to Wood Mackenzie Limited. A country’s ability to export LNG depends on its access to natural gas reserves and on its capacity to liquefy natural gas.
As of 1995, the Asia Pacific region, including Indonesia, Malaysia, Australia, Brunei and the United States via Alaska, represented approximately 73% of LNG exports. By 2005, these countries only accounted for 46% of global exports, with the Middle East Gulf increasing its share of global LNG trade from 7% to 23% and the Atlantic Basin increasing its share from 20% to 31%. In 2005, Qatar became the third largest exporting country, with 14% of total LNG exports. The following table lists the LNG exporting countries.
| Country |
1995 Exports | 2005 Exports |
|||||
| (Bcf/d) |
(Bcf/d) | % of Total | |||||
| Indonesia |
3.3 | 3.1 | 17 | % | |||
| Malaysia |
1.3 | 2.8 | 15 | % | |||
| Qatar |
— | 2.7 | 14 | % | |||
| Algeria |
1.7 | 2.4 | 13 | % | |||
| Australia |
1.0 | 1.6 | 9 | % | |||
| Trinidad and Tobago |
— | 1.3 | 7 | % | |||
| Nigeria |
— | 1.2 | 6 | % | |||
| Oman |
— | 0.9 | 5 | % | |||
| Brunei |
0.8 | 0.9 | 5 | % | |||
| United Arab Emirates |
0.6 | 0.7 | 4 | % | |||
| Egypt |
— | 0.7 | 4 | % | |||
| United States |
0.2 | 0.2 | 1 | % | |||
| Libya |
0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | % | |||
| Total |
9.0 | 18.6 | 100 | % | |||
Source: EIA.
83
Historically, regasification capacity has significantly exceeded liquefaction capacity, as Asian and European markets constructed regasification capacity for peak winter needs in highly fragmented markets. As the global LNG trade continues to expand, capacity in the U.S. Gulf Coast will become increasingly important to balancing worldwide seasonal demand variations with baseload LNG production. According to GIIGNL, at the end of 2005, there were 51 regasification plants in 15 countries with a total capacity of 46.3 Bcf/d. Of this regasification capacity, 71% of capacity was in the Asia Pacific region, 17% in Europe and 12% in North America. Global regasification capacity grew by 42% during the 2001 to 2005 period.
As of 1995, the Asia Pacific region, including Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, and India, imported 78% of worldwide LNG. By 2005, these countries accounted for only 66% of global imports, with Europe increasing its share of global LNG trade from 21% to 24% and North America increasing its share from less than 1% to 10%. From 1995 to 2005, worldwide LNG imports also grew at an 8% compound annual growth rate. From 1995 to 2005, U.S. LNG imports grew at a 43% compound annual growth rate, and in 2005 the U.S. became the fourth largest LNG importing country, with 9% of total imports. The following table lists the LNG importing countries.
| Country |
1995 Imports | 2005 Imports |
|||||
| (Bcf/d) | (Bcf/d) |
% of Total | |||||
| Japan |
5.8 | 7.8 | 42 | % | |||
| South Korea |
0.9 | 2.9 | 16 | % | |||
| Spain |
0.7 | 2.1 | 11 | % | |||
| United States |
0.0 | 1.7 | 9 | % | |||
| France |
0.7 | 1.2 | 7 | % | |||
| Taiwan |
0.3 | 0.9 | 5 | % | |||
| India |
— | 0.6 | 3 | % | |||
| Turkey |
0.1 | 0.5 | 3 | % | |||
| Belgium |
0.5 | 0.3 | 2 | % | |||
| Italy |
— | 0.2 | 1 | % | |||
| Portugal |
— | 0.2 | 1 | % | |||
| Puerto Rico |
— | 0.1 | 0 | % | |||
| United Kingdom |
— | 0.0 | 0 | % | |||
| Greece |
— | 0.0 | 0 | % | |||
| Dominican Republic |
— | 0.0 | 0 | % | |||
| Total |
9.0 | 18.7 | 100 | % | |||
Source: EIA.
North American Natural Gas Market
Currently, natural gas demand in North America is primarily supplied by domestic production from the Gulf of Mexico, Texas, Oklahoma, Louisiana, Appalachia, the Rocky Mountains and Western Canada.
According to the EIA estimates, the U.S. produced 18.6 Tcf of natural gas in 2006 and had proved natural gas reserves totaling 204 Tcf as of January 1, 2006. Within the U.S., Texas is the largest natural gas producing state, representing 29.4% of total production in 2005. The Gulf Coast, both onshore and offshore, has historically been the most prolific natural gas producing region in the U.S., but it is currently experiencing declining production levels. The EIA expects the Rocky Mountain region and Alaska to partially offset declining Gulf Coast production, with these two areas projected to provide the largest increases in domestic production between 2004 and 2020.
According to EIA estimates, Canada produced 6.5 Tcf of natural gas in 2004 and had 56.6 Tcf of proven gas reserves as of January 1, 2006. Canada’s natural gas production is concentrated in the Western Canada
84
Sedimentary Basin, and it is believed that natural gas production in that area has reached its zenith and will likely decline in the coming years.
According to EIA estimates, Mexico produced 1.46 Tcf of natural gas in 2004 and had 16.0 Tcf of proven natural gas reserves as of January 1, 2006. Recently, natural gas consumption has increased in Mexico, driven mostly by the electricity sector, whose share of total natural gas consumption increased from 16% in 1994 to 33% in 2004. Pemex is the single largest consumer of natural gas, representing 43% of domestic consumption in 2004.
Demand for natural gas in North America has increased over the years and is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. As shown in the table below, the strong demand for natural gas and the limited domestic supply has caused natural gas prices to trend higher, with the average price per MMbtu of natural gas more than tripling since 1999.
The EIA estimates that natural gas consumption will increase from 27.4 Tcf for North America in 2003 to 36.6 Tcf in 2030. With such a growing demand for natural gas, LNG is a resource that can help to meet such demand.
85
North American Regasification Facilities
As illustrated in the following map, as of December 2006, there were five operational onshore LNG regasification facilities in continental North America with an aggregate sendout capacity of 4.75 Bcf/d and the capability to satisfy approximately 6% of natural gas consumption in North America. There is also one offshore receiving system not shown, which regasifies LNG on-board specialized LNG vessels that can interconnect with an offshore pipeline in the Gulf of Mexico and potentially the U.S. East Coast. In December 2006, six additional LNG receiving terminals with an aggregate sendout capacity of 11 Bcf/d were under construction: one in Eastern Canada, four in the Gulf Coast, and one in Baja California, Mexico. With the exception of Cameron LNG, the owners of North American LNG receiving terminals, both existing and under construction, have sold all of their available capacity under long term contracts. According to the FERC, as of January 18, 2007, there were another 36 terminals and expansion projects in various stages of permitting, proposals and planning in the U.S. Most of these projects were sited in the U.S. Gulf or East Coasts. If constructed, these LNG receiving terminals would interconnect with natural gas pipelines that could transport natural gas to market areas in the U.S., Canada and Mexico.
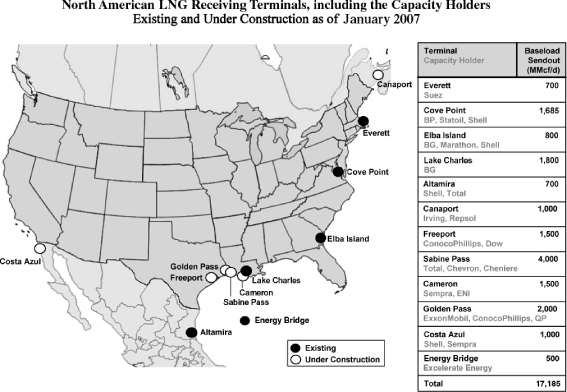
| Source: | Websites of Capacity Holders; Wood Mackenzie Limited; Poten & Partners, Inc. |
86
We are a Delaware limited partnership recently formed by Cheniere. Through our wholly-owned subsidiary, Sabine Pass LNG, we will develop, own and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal currently under construction in western Cameron Parish, Louisiana on the Sabine Pass Channel.
Construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal began in March 2005. Upon completion of construction, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be the largest LNG receiving terminal in North America with approximately 4.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity and approximately 16.8 Bcf of LNG storage capacity. All of this capacity has been contracted for under three 20-year, firm commitment terminal use agreements, or TUAs. Each customer must make payments on a “take-or-pay” basis, which means that the customer will be obligated to pay the full contracted amount of monthly fees whether or not it uses any of its reserved capacity. Provided the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal has achieved the required level of commercial operation, which we expect will occur in the third quarter of 2008, these “take-or-pay” TUA payments will be made as follows:
| • | Total has reserved approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $125 million per year for 20 years commencing April 1, 2009. Total, S.A. has guaranteed Total’s obligations under its TUA up to $2.5 billion. Total, S.A. has Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s corporate ratings of Aa1 and AA, respectively. |
| • | Chevron has reserved approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $125 million per year for 20 years commencing not later than July 1, 2009. Chevron Corporation has guaranteed up to 80% of the fees payable by Chevron under its TUA. Chevron Corporation has Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s corporate ratings of Aa2 and AA, respectively. |
| • | Cheniere Marketing has reserved approximately 2.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity, is entitled to use any capacity not utilized by Total and Chevron and has agreed to make monthly payments to us aggregating approximately $250 million per year for at least 19 years commencing January 1, 2009. In addition, Cheniere Marketing has agreed to make payments of $5 million per month during an initial commercial operations ramp-up period in 2008. Cheniere has guaranteed Cheniere Marketing’s obligations under its TUA. Cheniere has no Moody’s rating and a Standard & Poor’s corporate rating of B. |
Our primary business objectives are to complete construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and, thereafter, to generate stable cash flows sufficient to pay the initial quarterly distribution to our unitholders and, over time and upon satisfaction of these objectives, to increase our quarterly cash distribution. We intend to achieve these objectives by executing the following strategies:
| • | manage the development and construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal to achieve completion, commissioning and commercial operation in a timely manner and on budget; |
| • | after construction and commissioning, operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal safely, at a low cost and in an efficient manner, utilizing proven, conventional regasification technology; and |
| • | expand our existing asset base through acquisitions from Cheniere or third parties of complementary businesses or assets, such as pipelines, other LNG receiving terminals and natural gas storage assets. |
We believe that we have several strengths in pursuing our business strategies.
87
Contracted and Stable Long-Term Cash Flows. All of the regasification capacity that will be available at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal upon completion of Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 is reserved under long-term TUAs. The TUAs are structured to provide Sabine Pass LNG with stable cash flows as a result of the following:
| • | $250 Million of Revenues Annually from Total and Chevron. Total and Chevron have each agreed to pay Sabine Pass LNG on a “take-or-pay” basis a monthly fixed capacity reservation fee plus a monthly operating fee in a fixed amount that is adjusted annually for inflation. The Total and Chevron TUAs are supported by guarantees from Total, S.A. and Chevron Corporation, respectively, which have Moody’s and Standard & Poor’s corporate ratings of Aa1/AA and Aa2/AA, respectively. Contracted cash revenues of approximately $250 million per year under the Total and Chevron TUAs, which are expected to begin in the third quarter of 2009, should be sufficient by themselves to cover: |
| • | all annual debt service on the Sabine Pass LNG notes, which will be approximately $151 million; and |
| • | all other annual costs of operating Sabine Pass LNG, which we estimate will be approximately $48 million for the four consecutive quarters ending June 30, 2010. |
| The remaining funds from Total and Chevron are expected to be sufficient for us to pay the operating expenses of our partnership and the initial quarterly distribution on all of our common units and the related distribution or our general partner units so long as those funds are distributable to us under the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes. |
| • | No Direct LNG Supply Risk or Direct Commodity Price Risk under the TUAs. Our customers, rather than Sabine Pass LNG, bear all direct risks associated with obtaining supplies of LNG, transporting LNG to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, arranging for pipelines to transport regasified LNG from the receiving terminal to natural gas markets, and assuring that the regasified LNG satisfies downstream natural gas pipeline quality specifications. Under the TUAs, the amount of the cash payments Sabine Pass LNG is entitled to receive from its customers will not be affected by changes in demand for, or the price of, LNG or natural gas. Marketing and direct commodity price risks are borne by Sabine Pass LNG’s customers. |
| • | Long-term Commitments. Under the TUAs, Sabine Pass LNG’s customers have committed to make monthly payments for 20-year terms. Sabine Pass LNG’s customers have options to extend their TUAs for one or more additional 10-year terms. Sabine Pass LNG’s customers are able to terminate their TUAs before 20 years only in limited circumstances, such as a force majeure delay that extends for 18 months or more, and are required to continue to make monthly payments for up to 18 months even if terminal services are unavailable due to a force majeure event. |
Please read “Risk Factors” for information regarding Sabine Pass LNG’s dependence upon contractual revenues under the Cheniere Marketing TUA and the risk that Sabine Pass LNG may not be able to distribute any cash to us, including cash received from Total and Chevron, in the event that it does not receive the contracted revenues under the Cheniere Marketing TUA.
Solid Construction Arrangements. Bechtel Corporation, or Bechtel, is our EPC contractor under a lump-sum turnkey EPC agreement for Phase 1 and is providing design and engineering services and acting as construction manager for Phase 2 – Stage 1. Our construction agreements with Bechtel provide bonuses for early completion, and the EPC agreement for Phase 1 obligates Bechtel to pay liquidated damages for delayed completion. We believe these provisions mitigate the potential for delays. In addition, Sabine Pass LNG has fixed the costs for a substantial majority of the materials used to construct the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which minimizes the risk posed by escalation of those prices.
Early Mover Advantage. Cheniere established its LNG business plan in 1999 at a time when the construction of new LNG import capacity in North America was being seriously considered for the first time since completion of the last domestic LNG import terminal in the early 1980s. As a result, Cheniere secured what
88
we believe is one of the best available North American sites for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Located at the Texas/Louisiana border only 3.7 miles from open waters near the Gulf of Mexico, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal site is easily accessible by the largest LNG transport vessels currently operating or being built. The Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is located in close proximity to interconnection points with numerous existing natural gas pipelines.
Ample Pipeline Access. We anticipate that the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will have ample access to natural gas markets. Kinder Morgan Energy Partners, L.P. has announced that it is building a 3.2 Bcf/d take-away pipeline system from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal to interconnection points that will transport natural gas to the interstate pipeline network. Total and Chevron have both announced agreements with Kinder Morgan securing 100% of the initial capacity on this pipeline for 20 years. In addition, Cheniere Sabine Pass Pipeline, L.P., a subsidiary of Cheniere, is developing a 16-mile natural gas pipeline from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal that is designed to transport 2.6 Bcf/d to interconnection points with existing natural gas transmission pipelines. Cheniere Marketing has contracted to use this pipeline, and construction is expected to commence in the second quarter of 2007.
Economies of Scale. With approximately 4.0 Bcf/d of sendout capacity and approximately 16.8 Bcf of storage capacity upon completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be the largest LNG receiving terminal in North America, designed to have more than two times the capacity of any other terminal operating in North America. With this capacity, we believe that the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will benefit from economies of scale in operating expenses. After completing Phase 1, we expect that the annual operating expenses of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be approximately $35 million to support 2.6 Bcf/d of sendout capacity. We expect annual operating expenses will only increase by approximately $2 million to support the full 4.0 Bcf/d of sendout capacity upon completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1.
Environmentally Sound and Community Friendly Approach. We are committed to an environmentally sound and community friendly approach in developing and operating the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. We consider investing time and effort into developing strong community relationships a key factor in ensuring the success of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Sabine Pass LNG began the application process for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal only after it was convinced that the local community understood the process and was willing to support the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal project.
Experienced Management Team. Cheniere has assembled a team of professionals with extensive experience in the LNG industry to pursue its business, including construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Through tenure with major oil companies, operators of LNG receiving terminals, pipelines, and engineering and construction companies, Cheniere’s senior management team has substantial experience in the areas of LNG project development, operation, engineering, technology, transportation and marketing. Because of our relationship with Cheniere, we will continue to have access to these professionals not only for the operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal but also for any future growth opportunities.
Our Relationship with Cheniere
Cheniere is the indirect owner of our general partner, as well as of our common and subordinated units that will represent a 90.4% limited partner interest in us upon completion of this offering. Cheniere is engaged primarily in the business of developing onshore LNG receiving terminals, and related natural gas pipelines, along the Gulf Coast of the United States. Cheniere is also developing a business to market LNG and natural gas, primarily through Cheniere Marketing. To a limited extent, Cheniere is also engaged in oil and natural gas exploration and development activities in the Gulf of Mexico.
Cheniere Marketing has entered into a TUA for all of the regasification capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal not reserved and utilized by Total and Chevron. As a result, approximately 50% of our anticipated combined revenues will be attributable to fees paid by Cheniere Marketing under its TUA with
89
Sabine Pass LNG, which will be guaranteed by Cheniere. Cheniere Marketing is a small, development stage company, with a limited operating history, limited capital, no credit rating and an unproven business strategy. Cheniere Marketing’s business plan is to purchase LNG on a short-term and long term-basis, to regasify the LNG at Sabine Pass LNG or other LNG receiving terminals, and to trade natural gas and market its regasified LNG in North America and other worldwide natural gas markets. It intends to earn a profit on the purchase of LNG and sale of natural gas after paying its TUA and pipeline fees and other operating expenses. Cheniere Marketing has no agreements or arrangements for supplies of LNG, a limited history of trading natural gas and no unconditional commitments from customers for the purchase of natural gas.
In addition to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Cheniere has two other LNG receiving terminals that are currently in early stages of development: the Corpus Christi LNG receiving terminal near Corpus Christi, Texas, and the Creole Trail LNG receiving terminal at the mouth of the Calcasieu Channel in central Cameron Parish, Louisiana. If constructed in accordance with the permits that have been issued by the FERC, these two terminals would have an aggregate designed regasification capacity of approximately 5.9 Bcf/d. Cheniere is also developing, and anticipates constructing, natural gas pipelines to connect each of the three LNG receiving terminals to North American natural gas markets.
In the future, we may have opportunities to acquire some or all of these assets from Cheniere at an appropriate stage of commercialization and development, although we cannot predict whether any acquisitions will be made available to us or whether we will pursue or complete any future acquisitions. Our relationship with Cheniere also provides us with access to Cheniere’s management talent, market insights and significant industry relationships. Although we believe that our relationship with Cheniere is a strength, it is also a source of conflicts of interest. Cheniere is not restricted from competing with us and is free to develop, operate and dispose of, and is currently developing, LNG receiving terminals, pipelines and other assets without any obligation to offer us the opportunity to develop or acquire those assets. Please read “Conflicts of Interest and Fiduciary Duties.”
LNG Receiving Terminal Development
In 2003, Sabine Pass LNG was formed by Cheniere as the entity to own, develop and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal in western Cameron Parish, Louisiana, on the Sabine Pass Channel. Sabine Pass LNG has entered into leases for three tracts of land comprising 853 acres in Cameron Parish, Louisiana for the project site. Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal was designed, and permitted by the FERC, with an initial regasification capacity of 2.6 Bcf/d and three LNG storage tanks with an aggregate LNG storage capacity of 10.1 Bcf and two unloading docks capable of handling the largest LNG carriers currently being built. In July 2006, Sabine Pass LNG received approval from the FERC to increase the regasification capacity of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal from 2.6 Bcf/d to 4.0 Bcf/d by adding up to three additional LNG storage tanks, additional vaporizers and related facilities. This expansion is referred to as Phase 2.
Phase 1
In March 2005, the FERC issued an order authorizing Sabine Pass LNG to commence construction of Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, subject to certain ongoing conditions. Construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal began in March 2005. During the second quarter of 2008, Sabine Pass LNG expects to complete construction and cool down of the first two tanks, to complete related equipment installation and specified checks and tests, and to achieve a sustained revaporized natural gas sendout at a significant rate for a preagreed period of time (currently provided to be a rate of at least 2.0 Bcf/d for a minimum sustained test period of at least 24 hours). Sabine Pass LNG expects to complete construction and commissioning of the third tank and the rest of Phase 1, and to achieve the full 2.6 Bcf/d of Phase 1 regasification capacity, during the third quarter of 2008.
The cost to construct Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is currently estimated to be approximately $900 million to $950 million, before financing costs, but including the change orders discussed
90
below. In December 2004, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a lump-sum turnkey agreement with Bechtel, a major international EPC contractor, which currently requires Sabine Pass LNG to pay Bechtel $766.4 million, including change orders agreed through January 17, 2007. Our cost estimates are subject to change due to such items as cost overruns, change orders, delays in construction, increased component and material costs, escalation of labor costs and increased spending to maintain our construction schedules.
In August 2005, construction at Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal site was temporarily suspended in connection with Hurricane Katrina, as a precautionary measure. In September 2005, the terminal site was again secured and evacuated in anticipation of Hurricane Rita. Construction activities were remobilized at the site and returned to pre-hurricane levels by mid-November 2005. While no significant damage occurred to the site, equipment or materials at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving facility, as a residual effect of the hurricanes, Bechtel and certain subcontractors temporarily experienced a shortage of available skilled labor necessary to meet the requirements of the Phase 1 construction plan. As a result, Sabine Pass LNG agreed to change orders with Bechtel concerning additional activities and expenditures to mitigate the hurricanes’ effects on the completion of Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. See “Description of Principal Construction Agreements—Phase 1 EPC Agreement—Force Majeure.”
Phase 2
In July 2006, Sabine Pass LNG received authorization from the FERC to commence site preparation construction activities for the Phase 2 expansion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, subject to certain ongoing conditions. The first stage of the Phase 2 expansion will include the addition of the fourth and fifth LNG storage tanks, additional vaporizers and related facilities, thereby increasing the total regasification capacity of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal to 4.0 Bcf/d. This expansion is referred to as Phase 2 – Stage 1. LNG regasification operations relating to the Phase 2 – Stage 1 expansion are expected to commence by April 2009. Sabine Pass LNG expects to complete all of Phase 2 – Stage 1, including construction and commissioning of the fourth and fifth tanks, and to achieve full operability at 4.0 Bcf/d and aggregate storage capacity of approximately 16.8 Bcf during the third quarter of 2009.
In July 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into three construction agreements to facilitate construction of the Phase 2 – Stage 1 expansion, as follows:
Sabine Pass LNG entered into an EPCM agreement with Bechtel pursuant to which Bechtel will provide: design and engineering services for Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal project, except for such portions to be designed by other contractors and suppliers that Sabine Pass LNG contracts with directly; construction management services to manage the construction of the LNG receiving terminal; and a portion of the construction services. Under the terms of the EPCM agreement, Bechtel will be paid on a cost reimbursable basis, plus a fixed fee in the amount of $18.5 million. A discretionary bonus may be paid to Bechtel at Sabine Pass LNG’s sole discretion upon completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1. See “Description of Principal Construction Agreements—Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPCM Agreement.”
Sabine Pass LNG entered into an EPC LNG tank contract with Zachry and Diamond pursuant to which Zachry and Diamond will furnish all plant, labor, materials, tools, supplies, equipment, transportation, supervision, technical, professional and other services, and perform all operations necessary and required to satisfactorily engineer, procure and construct the two Phase 2 – Stage 1 LNG storage tanks. In addition, Sabine Pass LNG has the option (to be elected on or before March 31, 2007) for Zachry and Diamond to engineer, procure materials for and construct a sixth LNG storage tank, with the cost and completion date to be agreed upon if the option is exercised. The tank contract provides that Zachry and Diamond will receive a lump-sum, total fixed price payment for the two Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks of approximately $140.9 million, which is subject to adjustment based on fluctuations in the cost of labor and certain materials, including the steel used in the Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks, and change orders. See “Description of Principal Construction Agreements—Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPC LNG Tank Contract.”
91
Sabine Pass LNG entered into an EPC LNG unit rate soil contract with Recon. Under the soil contract, Recon is required to furnish all plant, labor, materials, tools, supplies, equipment, transportation, supervision, technical, professional and other services, and perform all operations necessary and required to satisfactorily conduct soil remediation and improvement on the Phase 2 site, unless otherwise set forth in the soil contract. Upon issuing a final notice to proceed in August 2006, Sabine Pass LNG paid Recon an initial payment of approximately $2.9 million. The soil contract price is based on unit rates. Payments under the soil contract will be made based on quantities of work performed at unit rates. See “Description of Principal Construction Agreements—Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPC LNG Soil Contract.”
Phase 2 – Stage 1 is estimated to cost approximately $500 million to $550 million, before financing costs. Operations relating to the Phase 2 – Stage 1 expansion are expected to commence before April 2009, and all of Phase 2 – Stage 1 is expected to be completed during the third quarter of 2009.
Sabine Pass LNG has entered into three TUAs, through which Total, Chevron and Cheniere Marketing have reserved, in the aggregate, the entire approximately 4.0 Bcf/d of LNG regasification capacity that will be available upon completion of Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. The Total TUA and the Chevron TUA reserve a combined annual LNG regasification capacity of approximately 2.0 Bcf/d. Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal (2.6 Bcf/d) will be sufficient to cover Sabine Pass LNG’s obligations under the Total and Chevron TUAs. Cheniere Marketing has reserved the entire 2.0 Bcf/d of capacity that will be available beyond the Total and Chevron TUA capacity reservations, upon completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1, as well as any Phase 1 capacity that is available prior to the commencement of the Total and Chevron TUAs and after Sabine Pass LNG has fulfilled its obligations under the Total and Chevron TUAs.
Total TUA
In September 2004, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a TUA with Total to provide berthing for LNG vessels and for the unloading, storage and regasification of LNG at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Sabine Pass LNG has no obligation to provide Total with certain services such as (i) harbor, mooring and escort services for LNG vessels, including the provision of tugboats, (ii) the transportation of natural gas downstream from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or the construction of any pipelines to provide such transportation or (iii) the marketing of natural gas.
Under the TUA, Total has reserved 390,915,000 MMBtu of annual LNG receipt capacity, which is equivalent to approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity, assuming an energy content of 1.05 MMBtu per thousand cubic feet and retainage of 2%. Total’s fees under the TUA are payable monthly in advance, commencing with the commercial start date of April 1, 2009 (subject to achieving commercial operations completion by that date, and subject to delay by events of force majeure) and will continue for a term of 20 years subject to six additional 10-year extension terms. Commercial operations completion will be achieved when the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is ready to be used for its intended purpose to provide the services called for under the Total TUA, with Bechtel as contractor for the Phase 1 EPC agreement having achieved all minimum acceptance requirements under the Phase 1 EPC agreement sufficient to provide the services called for under the Total TUA and contracts with other customers purchasing LNG terminalling services from Sabine Pass LNG similar to the services called for under the Total TUA. Under the Total TUA, Total will pay a monthly fixed capacity reservation fee of $9.1 million; a monthly operating fee of $1.3 million, which is adjusted annually for changes in the U.S. Consumer Price Index (All Urban Consumers); and certain other incremental costs and governmental authority taxes and costs. These monthly payment amounts, which are due on the 20th of the month prior to the month in which Sabine Pass LNG provides services under the Total TUA, are equivalent to payments of $0.28 per MMBtu for capacity and $0.04 per MMBtu (subject to adjustment for inflation) for operating fees, respectively, of reserved monthly LNG receipt capacity. In addition, each month Sabine Pass LNG is entitled to
92
receive a “retainage” equal to 2% of the LNG delivered for Total’s account, which Sabine Pass LNG will use primarily as fuel for revaporization and self-generated power and to cover natural gas unavoidably lost at the facility.
If any governmental authority (i) imposes any taxes on Sabine Pass LNG (excluding taxes on revenue or income) with respect to the services provided under the TUA, or the LNG receiving terminal or (ii) enacts any safety or security related regulation which materially increases Sabine Pass LNG’s costs in relation to the services provided or the LNG receiving terminal, Total will bear 40% of such taxes or increased regulatory costs. When LNG regasification capacity exceeds 3.0 Bcf/d, Total will thereafter bear a proportionate share of such taxes or increased regulatory costs, not to exceed 40%. After the Chevron and Total TUAs commence, Sabine Pass LNG expects that Total’s proportionate share of such taxes and increased regulatory costs will be 25%. To the extent any ad valorem taxes are imposed and not abated, Sabine Pass LNG will reimburse Total for up to one-half of such amount, not to exceed $3.9 million per year.
Sabine Pass LNG is obligated to pay liquidated damages to Total in the event of certain types of docking and unloading delays.
Either party may assign its interests under the TUA to affiliates, and, as permitted by the TUA, Sabine Pass LNG has pledged its interest under the TUA to the collateral trustee of the Sabine Pass LNG notes to secure its obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes. In addition, Total may make a partial assignment of its total reserved regasification capacity to nonaffiliates provided that (i) the assignee agrees to be bound by the TUA, (ii) the parent guarantee continues to apply to all assigned obligations and (iii) Total and the assignee designate a representative and jointly exercise all rights under the TUA.
An assignment under the TUA will extinguish Total’s or Sabine Pass LNG’s obligations only if (i) the assignment constitutes all of such party’s rights and obligations under the TUA, (ii) the assignee agrees to be bound by the TUA and (iii) the assignee demonstrates creditworthiness at the time of the assignment that is the same as or better than the guarantor, in the case of Total, or Sabine Pass LNG.
Total may terminate the TUA if Sabine Pass LNG has declared force majeure with respect to a period that has extended, or is projected to extend, for 18 months, or for reasons not excused by force majeure or Total’s actions, if Sabine Pass LNG:
| • | fails to deliver at least 191,625,000 MMBtu of Total’s total natural gas nominations in a 12-month period; |
| • | fails entirely to receive at least 15 cargoes nominated by Total over a period of 90 consecutive days; or |
| • | fails to unload 50 cargoes or more scheduled for delivery by Total for a 12-month period. |
Sabine Pass LNG may terminate the TUA if:
| • | the parent guarantee ceases to be in full force and effect; |
| • | for a period exceeding 15 days, two of the parent guarantor’s credit ratings fall below investment grade; or |
| • | the parent guarantor commences bankruptcy or liquidation proceedings, or has such proceedings commenced against it, and such proceedings are not stayed within 60 days of service. |
Either party may terminate the TUA with 30 days’ written notice if (i) a party has failed to pay when due an amount to the other party owed that causes its cumulative delinquency to exceed three times the monthly capacity reservation fee, (ii) the cumulative delinquency has not been paid within 60 days of such notice and (iii) the other party has subsequently given 30 days’ written notice to terminate the TUA.
93
In November 2004, Total exercised its option to proceed with the transaction by delivering to Sabine Pass LNG an advance capacity reservation fee payment of $10 million and an irrevocable guarantee for an amount up to $2.5 billion by its parent entity, Total S.A., of Total’s payment obligations under the TUA, except for claims arising in tort or strict liability or claims for damages to property or personal injury. Because Total elected to proceed with the transaction and Bechtel accepted the final notice to proceed in April 2005, Total paid Sabine Pass LNG an additional advance capacity reservation fee payment of $10 million.
Sabine Pass LNG also entered into an omnibus agreement with Total in September 2004, under which the TUA remains subject to certain conditions. Under the omnibus agreement, if Sabine Pass LNG enters into a new TUA with a third party, other than its affiliates, for capacity of 50 MMcf/d or more, with a term of five years or more, prior to the commercial start date under the TUA, Total will have the option, exercisable within 30 days of the receipt of notice of such transaction, to adopt the pricing terms contained in such new TUA for the remainder of the term of the Total TUA. In addition, the omnibus agreement provides Total with an option to increase its reserved capacity in the event that either party provided notice of a plan to expand the Sabine Pass LNG facility. During 2005, Sabine Pass LNG provided such notice to Total, and Total’s option to increase its reserved capacity expired.
Chevron TUA
In November 2004, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a TUA with Chevron to provide berthing for LNG vessels and for the unloading, storage and regasification of LNG at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Sabine Pass LNG has no obligation to provide certain services such as (i) harbor, mooring and escort services for LNG vessels, including the provision of tugboats, (ii) the transportation of natural gas downstream from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or the construction of any pipelines to provide such transportation or (iii) the marketing of natural gas.
In December 2005, Chevron exercised its option under its omnibus agreement to increase its regasification capacity by 300 MMcf/d for a total of 1.0 Bcf/d and paid Sabine Pass LNG an additional $3 million advance capacity reservation fee. As a result of Chevron exercising its option, the TUA was amended to reflect the increased reservation of regasification capacity. Under the amended TUA, Chevron has reserved 403,945,500 MMBtu of annual LNG receipt capacity, which is equal to approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity, assuming an energy content of 1.085 MMBtu per thousand cubic feet and retainage of 2%.
Although Chevron could select a date as early as February 1, 2009, it is expected that payments of fees under the Chevron TUA will commence on July 1, 2009 (subject to achieving commercial operations completion by that date, and subject to delay caused by events of force majeure). Chevron’s fees under the Chevron TUA are payable monthly in advance and will continue for a term of 20 years subject to two additional 10-year extensions. Under the Chevron TUA, Chevron is required to pay Sabine Pass LNG a fixed monthly fee for this regasification capacity that consists of (i) a reservation fee of $9.4 million, (ii) an operating fee of $1.3 million and (iii) certain taxes and regulatory costs. The operating fee is adjusted annually for changes in the U.S. Consumer Price Index (All Urban Consumers). In addition, each month Sabine Pass LNG is entitled to receive a “retainage” equal to 2% of the LNG delivered for Chevron’s account, which Sabine Pass LNG will use primarily as fuel for revaporization and self-generated power and to cover natural gas unavoidably lost at the facility. Chevron’s payments under the Chevron TUA are due on the 25th of the month prior to the month in which Sabine Pass LNG provides services under the Chevron TUA. Chevron Corporation has guaranteed Chevron’s payment obligations under the TUA in an amount up to a maximum of 80% of the fees payable under the TUA.
If any governmental authority (i) imposes any taxes on Sabine Pass LNG (excluding taxes on revenue or income) with respect to the services provided under the TUA, or the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or (ii) enacts any safety or security related regulation which materially increases Sabine Pass LNG’s costs in relation to the services provided at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Chevron will bear a proportionate share of such taxes or increased regulatory costs, not to exceed 28%. After the Chevron and Total TUAs
94
commence, Sabine Pass LNG expects that Chevron’s proportionate share of such taxes and increased regulatory costs will be 25%.
Sabine Pass LNG is obligated to pay liquidated damages to Chevron in the event of certain types of docking and unloading delays.
Both parties may assign their interests under the TUA to affiliates, and, as permitted by the TUA, Sabine Pass LNG has pledged its interest under the TUA to the collateral trustee of the Sabine Pass LNG notes to secure its obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes. In addition, Chevron may make a partial assignment of its total reserved regasification capacity to non-affiliates provided (i) the assignee agrees to be bound by the TUA, (ii) the parent guarantee continues to apply to all assigned obligations, (iii) Chevron remains liable for payments owed and (iv) the respective responsibilities of the parties under the TUA are not increased or decreased.
An assignment under the TUA will extinguish Chevron’s or Sabine Pass LNG’s obligations only if (i) the assignment constitutes all of such party’s rights and obligations under the TUA, (ii) the assignee agrees to be bound by the TUA and (iii) the assignee demonstrates creditworthiness at the time of the assignment that is the same as or better than the guarantor, in the case of Chevron, or Sabine Pass LNG.
Chevron may terminate the TUA if Sabine Pass LNG has declared force majeure with respect to a period that has extended, or is projected to extend, for 18 months, or for reasons not excused by force majeure or Chevron’s actions, if Sabine Pass LNG:
| • | fails to deliver at least 191,625,000 MMBtu of Chevron’s total natural gas nominations in a 12-month period; |
| • | fails entirely to receive 15 cargoes or more nominated by Chevron over a period of 90 days; or |
| • | fails to unload, or notify Chevron that Sabine Pass LNG would be unable to unload, 50 cargoes or more scheduled for delivery by Chevron for a 12-month period. |
Sabine Pass LNG may terminate the TUA if the parent guarantee ceases to be in full force and effect or if Chevron or its parent guarantor, Chevron Corporation, commences bankruptcy, insolvency or liquidation proceedings, or has such proceedings commenced against it, that are not stayed within 60 days.
Either party may terminate the TUA with 30 days written notice if (i) a party has failed to pay when due an amount owed to the other party that causes its cumulative delinquency to exceed three times the monthly capacity reservation fee, (ii) the cumulative delinquency has not been paid within 60 days after issuance of a delinquency notice and (iii) the other party has subsequently given 30 days written notice to terminate the TUA.
Sabine Pass LNG simultaneously entered into an omnibus agreement with Chevron, under which Chevron agreed to make advance capacity reservation fee payments. Under the omnibus agreement, Chevron exercised an option in December 2005, at the same fee, to increase its reserved capacity to 1.0 Bcf/d. As a result, Chevron paid Sabine Pass LNG a total of $20 million of advance capacity reservation fee payments under the omnibus agreement. In addition, the omnibus agreement provided Chevron with an option to increase its reserved capacity in the event that either party provided notice of a plan to expand the Sabine Pass LNG facility. During 2005, Sabine Pass LNG provided such notice to Chevron and its option expired.
Cheniere Marketing TUA
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an amended and restated TUA with Cheniere Marketing, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere, to provide berthing for LNG vessels and for the unloading, storage and regasification of LNG at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Sabine Pass LNG has no obligation to provide Cheniere Marketing with certain services such as (i) harbor, mooring and escort services for LNG vessels, including the provision of tugboats, (ii) the transportation of natural gas downstream from the Sabine Pass LNG
95
receiving terminal or the construction of any pipelines to provide such transportation or (iii) the marketing of natural gas.
Under the Cheniere Marketing TUA, Cheniere Marketing will pay fees to Sabine Pass LNG based on 781,830,000 MMBtu of stipulated maximum annual LNG reception quantity, which is equivalent to approximately 2.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity assuming an energy content of 1.05 MMBtu per Mcf and retainage of 2%.
Cheniere Marketing’s fees under the Cheniere Marketing TUA are payable monthly in advance commencing on the commercial start date (which will be the later of January 1, 2008 or the date when commercial operations completion is achieved), and will continue for a term of 20 years subject to four additional 10-year extension terms. Commercial operations completion will be achieved when the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is ready to be used for its intended purpose to provide the services called for under the Cheniere Marketing TUA, with Bechtel as contractor for the Phase 1 EPC agreement having achieved all minimum acceptance requirements under the Phase 1 EPC agreement sufficient to provide the services called for under the Cheniere Marketing TUA. Under the Cheniere Marketing TUA, Cheniere Marketing is required to pay Sabine Pass LNG a fixed monthly fee for this regasification capacity that is comprised of: (i) a reservation fee of $0.28 per MMBtu times 1/12 of the stipulated maximum annual LNG reception quantity; (ii) an operating fee of $0.04 per MMBtu times 1/12 of the stipulated maximum annual LNG reception quantity, which operating fee is adjusted annually for changes in the U.S. Consumer Price Index (All Urban Consumers); and (iii) certain other taxes and regulatory costs. Notwithstanding the foregoing, Cheniere Marketing is required to pay a flat fee of $5 million per month from the commercial start date under the Cheniere Marketing TUA through December 31, 2008. Cheniere Marketing’s payments under the Cheniere Marketing TUA are due on the 25th of the month prior to the month in which Sabine Pass LNG provides services under the Cheniere Marketing TUA.
The stipulated maximum LNG reception quantity allocated to Cheniere Marketing is reduced to the extent that the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is unable to provide services up to such amount as a result of the timing of start dates under existing customer agreements (including the Total and Chevron TUAs) or delays in commencing commercial operation of the Phase 2 – Stage 1 expansion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; however, the fees to be paid by Cheniere Marketing under the Cheniere Marketing TUA will not be accordingly adjusted. In addition, each month, Sabine Pass LNG is entitled to receive a “retainage” equal to 2% of the LNG delivered for Cheniere Marketing’s account, which Sabine Pass LNG will use primarily as fuel for revaporization and self-generated power and to cover natural gas unavoidably lost at the facility. All of Cheniere Marketing’s obligations during the initial 20-year term of the TUA are supported by an irrevocable guaranty in favor of Sabine Pass LNG by Cheniere.
If any governmental authority (i) imposes any taxes on Sabine Pass LNG (excluding taxes on revenue or income) with respect to the services provided under the Cheniere Marketing TUA, or the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or (ii) enacts any safety or security related regulation which materially increases Sabine Pass LNG’s costs in relation to the services provided at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Cheniere Marketing will bear such taxes or increased regulatory costs at a rate proportional to its percentage of the right to use of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal’s total capacity.
Both Sabine Pass LNG and Cheniere Marketing may assign their respective interests under the Cheniere Marketing TUA to affiliates, as long as such assignment is not made prior to the first business day following the Cheniere Marketing TUA’s commercial start date. As permitted by the Cheniere Marketing TUA, Sabine Pass LNG has pledged its interest under the Cheniere Marketing TUA to the collateral trustee under the Sabine Pass LNG notes to secure its obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes. In addition, Cheniere Marketing may make a partial assignment of its total reserved regasification capacity (but not its rights to excess capacity described below) to non-affiliates provided that (i) the assignee agrees to be bound by the Cheniere Marketing TUA, (ii) Cheniere Marketing continues to be liable for all payments due under the Cheniere Marketing TUA, and (iii) Cheniere Marketing and the assignee designate a representative and jointly exercise all rights under the Cheniere Marketing TUA.
96
An assignment under the Cheniere Marketing TUA will terminate Cheniere Marketing’s obligations only if (i) the assignment constitutes all of Cheniere Marketing’s rights and obligations, (ii) the assignee agrees to assume all obligations of the assignor from inception of the Cheniere Marketing TUA, and (iii) the assignee demonstrates creditworthiness at the time of the assignment that is reasonably acceptable to Sabine Pass LNG (and including credit standards that will be deemed acceptable).
Cheniere Marketing may terminate the Cheniere Marketing TUA if Sabine Pass LNG has declared force majeure with respect to a period that has extended, or is projected to extend, for 18 months, or for reasons not excused by force majeure or Cheniere Marketing’s actions, if Sabine Pass LNG:
| • | fails to deliver at least 201,972,750 MMBtu of Cheniere Marketing’s total natural gas nominations in a 12 month period; |
| • | fails entirely to receive at least 17 cargoes nominated by Cheniere Marketing over a period of 90 consecutive days; or |
| • | fails to unload 53 cargoes or more scheduled for delivery by Cheniere Marketing for a 12-month period. |
Sabine Pass LNG may terminate the Cheniere Marketing TUA if Cheniere Marketing commences bankruptcy, reorganization or liquidation proceedings, or has such proceedings commenced against it, and such proceedings are not stayed within 60 days of service.
Either party may terminate the Cheniere Marketing TUA with 30 days written notice if (i) a party has failed to pay when due an amount owed to the other party that causes its cumulative delinquency to exceed three times the monthly capacity reservation fee, (ii) the cumulative delinquency has not been paid within 60 days of such notice and (iii) the other party has subsequently given 30 days’ written notice to terminate the Cheniere Marketing TUA.
The Cheniere Marketing TUA is designed to work in tandem with the Total TUA and the Chevron TUA and states that no provision of the Cheniere Marketing TUA shall be effective if and to the extent that it expressly conflicts with a provision of the Total TUA or the Chevron TUA. Any excess capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal that Sabine Pass LNG is not contractually obligated to make available to any other customer, and any capacity that any other customer elects not to use, may be used exclusively by Cheniere Marketing without any additional charge or fee except for 2% retainage and port charges in respect of vessels entering or leaving the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. This excess capacity may be available from time to time, including at completion of Phase 1 and the outset of commercial operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which is the date on which the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is projected to have capacity of 2.6 Bcf/d.
The effective date at which Cheniere Marketing is to purchase and pay for services from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is the later of January 1, 2008 or the date of commercial operations completion, which is currently expected to occur during the second quarter of 2008.
The Cheniere Marketing TUA provides that, at Cheniere Marketing’s request, Sabine Pass LNG must construct a sixth LNG storage tank with a working capacity of approximately 160,000 cubic meters of LNG for the benefit of Cheniere Marketing as soon as possible but not later than four years after notification from Cheniere Marketing. Sabine Pass LNG’s obligation to construct the additional LNG storage tank will be subject to its (i) receipt of all FERC and other required governmental permits and approvals and (ii) obtaining financing that it considers reasonably acceptable in form and content.
Cheniere Marketing has also entered into a letter agreement with Cheniere LNG, Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere, and Sabine Pass LNG, pursuant to which Cheniere Marketing has agreed to relinquish up to 200 Mmcf/d of its capacity (and proportionately reduce its fixed monthly fee) under the Cheniere Marketing TUA if Sabine Pass LNG enters into a TUA with J&S Cheniere S.A., or J&S Cheniere. J&S Cheniere is a Swiss company
97
in which Cheniere holds a minority interest. This arrangement stems from a 2003 option agreement between Cheniere LNG, Inc. and J&S Cheniere pursuant to which J&S Cheniere has an option to negotiate a TUA for up to 200 Mmcf/d of vaporization capacity and proportional LNG storage at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. The terms of the potential TUA contemplated by the J&S Cheniere option agreement have not been negotiated or finalized, and Cheniere has publicly disclosed its anticipation that definitive arrangements with J&S Cheniere may involve different terms and transaction structures than were contemplated when the option agreement was entered into in December 2003.
FERC and Other Governmental Regulation
Our LNG operations are subject to extensive regulation under federal, state and local statutes, rules, regulations and other laws. Among other matters, these laws require that we obtain certain consultations, permits and other authorizations before commencement of construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. This regulatory burden increases the cost of constructing and operating the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and failure to comply with such laws could result in substantial penalties.
Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
In order to site and construct the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Sabine Pass LNG was required to receive and is required to maintain authorization from the FERC under Section 3 of the Natural Gas Act of 1938. The FERC permitting process includes:
| • | initial public notice and public meetings; |
| • | data gathering and analysis at the FERC’s request; |
| • | issuance of a Draft Environmental Impact Statement by the FERC; |
| • | additional public meetings; |
| • | issuance of a Final Environmental Impact Statement by the FERC; and |
| • | the FERC order authorizing construction. |
Sabine Pass LNG received the FERC authorization to construct both Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1, although those authorizations are subject to specified conditions that must be satisfied throughout the construction, commissioning and operation of the terminal. Those conditions require Sabine Pass LNG to: appoint third-party environmental inspectors to monitor compliance with the FERC’s conditions;
| • | submit any material changes to the design or construction of the facility for FERC approval; |
| • | submit an implementation plan for compliance with the FERC-ordered mitigation measures; |
| • | submit monthly and weekly construction reports detailing construction progress and ongoing compliance efforts; |
| • | comply with U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service guidelines regarding lighting; |
| • | file a Coastal Zone Management Plan consistency determination; |
| • | limit construction activities to comply with noise limits and regulations and file a noise survey; and |
| • | file plans regarding the installation, implementation and operation of various safety measures and comply with those plans. |
In addition, throughout the life of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, it will be subject to regular reporting requirements to the FERC regarding the operation and maintenance of the facility.
Other Federal Governmental Permits, Approvals and Consultations
In addition to FERC authorization under Section 3 of the Natural Gas Act of 1938, the construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is also subject to additional federal permits, approvals and consultations required by certain other federal agencies, including: Advisory Counsel on Historic Preservation, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Department of Commerce, National Marine Fisheries Services, U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
98
The Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will also be subject to U.S. Department of Transportation siting requirements and regulations of the U.S. Coast Guard relating to facility security. Moreover, the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be subject to local and state laws, rules and regulations.
Energy Policy Act of 2005
In 2005, the Energy Policy Act of 2005, or EPAct, was signed into law. The EPAct contains numerous provisions relevant to the natural gas industry and to interstate pipelines. The EPAct includes several provisions which amend the Natural Gas Act of 1938. The primary provisions of interest to our operations focus on two areas: infrastructure development, and market manipulation and enforcement. Regarding infrastructure development, the EPAct states that the FERC has exclusive authority to approve or deny an application for the siting, construction, expansion or operation of an LNG receiving terminal. Regarding market manipulation and enforcement, the EPAct amends the Natural Gas Act of 1938 to prohibit market manipulation. The EPAct also amends the Natural Gas Act of 1938 and the Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978 to increase civil and criminal penalties for any violations of both laws and any rules, regulations or orders of the FERC up to $1 million per day per violation. In addition, the FERC issued a final rule effective January 26, 2006 regarding market manipulation, which makes it unlawful for any entity, in connection with the purchase or sale of natural gas or transportation service subject to the FERC’s jurisdiction, to defraud, make an untrue statement or omit a material fact or engage in any practice, act or course of business that operates or would operate as a fraud. This final rule works together with the FERC’s enhanced penalty authority to provide increased oversight of the natural gas marketplace.
Our LNG operations are subject to various federal, state and local laws and regulations relating to the protection of the environment. In some cases, these laws and regulations require us to obtain governmental permits and authorizations before we may conduct certain activities. These environmental laws and regulations may impose substantial penalties for noncompliance and substantial liabilities for pollution. Many of these laws and regulations restrict or prohibit the types, quantities and concentration of substances that can be released into the environment and can lead to substantial liabilities for non-compliance or for pollution or releases of hazardous substances, materials or compounds or otherwise require additional costs or changes in operations that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may also result in substantial civil and criminal fines and penalties. As with the industry generally, our operations will entail risks in these areas, and compliance with these laws and regulations increases our overall cost of business. While these laws and regulations affect our capital expenditures and earnings, we believe that these laws and regulations do not affect our competitive position in the industry because our competitors are similarly affected. Environmental laws and regulations have historically been subject to frequent revision and reinterpretation. Consequently, we are unable to predict the future costs or other future impacts of environmental regulations on our future operations.
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act
The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act, or CERCLA, also known as the “Superfund” law, imposes liability, without regard to fault, on certain classes of persons who are considered to be responsible for the spill or release of a hazardous substance into the environment. Potentially liable persons include the owner or operator of the site where the release occurred and persons who disposed or arranged for the disposal of hazardous substances at the site. Under CERCLA, responsible persons may be subject to joint and several liability for:
| • | the costs of cleaning up the hazardous substances that have been released into the environment; |
| • | damages to natural resources; and |
| • | the costs of certain health studies. |
99
In addition, it is not uncommon for neighboring landowners and other third parties to file claims for personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by the release of hazardous substances. Although CERCLA currently excludes petroleum, natural gas, natural gas liquids and LNG from its definition of “hazardous substances,” this exemption may be limited or modified by the U.S. Congress in the future.
Clean Air Act
Our operations are subject to the federal Clean Air Act and comparable state and local laws. We may be required to incur certain capital expenditures over the next several years for air pollution control equipment in connection with maintaining or obtaining permits and approvals addressing other air emission-related issues. We do not believe, however, that our operations will be materially adversely affected by any such requirements.
Congress is currently considering proposed legislation directed at reducing “greenhouse gas emissions.” It is not possible at this time to predict how legislation that may be enacted to address greenhouse gas emissions would impact our business. However, future laws and regulations could result in increased compliance costs or additional operating restrictions, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
Certain persons have expressed concerns that air emissions from the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which are allowed under Sabine Pass LNG’s existing permits, could adversely impact regional air quality in southeastern Texas so as to trigger future federal sanctions for that area under the Clean Air Act. While we have no reason to believe that any formal challenge will be made regarding Sabine Pass LNG’s existing permits under the Clean Air Act, such challenges may be pursued and, if pursued, may result in costs or conditions that could have a material adverse effect on our business and operations.
Clean Water Act
Our operations are also subject to the federal Clean Water Act and analogous state and local laws. Pursuant to certain requirements of the Clean Water Act, the EPA has adopted regulations concerning discharges of wastewater and storm water runoff. This program requires covered facilities to obtain individual permits, participate in a group permit or seek coverage under an EPA general permit.
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
The federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act and comparable state statutes govern the disposal of “hazardous wastes.” In the event any hazardous wastes are generated in connection with our LNG operations, we may be subject to regulatory requirements affecting the handling, transportation, treatment, storage and disposal of such wastes.
Endangered Species Act
Our operations and planned construction activities may also be restricted by requirements under the Endangered Species Act, which seeks to ensure that human activities do not jeopardize endangered or threatened animal, fish and plant species nor destroy or modify their critical habitats.
Sabine Pass LNG currently does not experience competition because the entire approximately 4.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity that will be available at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal upon completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1 has been fully reserved under three 20-year TUAs under which the terminal’s customers are generally required to pay monthly capacity fees on a “take-or-pay” basis.
According to the FERC, as of December 18, 2006, there were six existing LNG receiving terminals in North America, including one offshore facility for receiving LNG regasified aboard specialized LNG vessels, as well as 44 new LNG receiving terminals or expansions approved or proposed to be constructed in the U.S., of which six are under construction. If and when Sabine Pass LNG has to replace any TUAs, we will compete with these existing and proposed North American LNG receiving terminals and their customers. Cheniere is currently developing two of these proposed LNG receiving terminals. With the exception of Cameron LNG, we believe
100
that all of the capacity at the five existing onshore U.S. terminals and all of the capacity at the six terminals or expansions under construction is committed to customers under long-term arrangements. As of December 31, 2005, there were 51 LNG receiving terminals in 15 countries, and if and when Sabine Pass LNG has to replace any TUAs, we will compete with these and other proposed LNG receiving terminals worldwide to be the most economical delivery point for LNG production for both long-term contracted and spot volumes.
We maintain a comprehensive insurance program to insure against potential losses to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal from physical loss or damage, hurricanes and terrorism, as well as third-party liabilities, during construction and subsequent operation. We have engaged Aon Risk Services, Inc., or Aon, as our independent insurance advisor. Aon has provided independent validation regarding the appropriateness of our insurance policies compared to other selected benchmark projects. We may not be able to maintain adequate insurance in the future at rates that are considered reasonable. See “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to Development and Operation of Our Business—We are subject to significant operating hazards and uninsured risks, one or more of which may create significant liabilities for us.”
Insurance During Construction Period
During construction of Phase 1, under terms of the EPC contract, Bechtel is responsible for obtaining for Sabine Pass LNG substantially all of the required insurance covering loss or damage to assets, loss of income due to a delay in the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal’s completion, and third-party liabilities. Terrorism insurance and our primary auto liability insurance are excluded from Bechtel’s contractual obligations and have been procured by us directly. Upon substantial completion of Phase 1, we will assume responsibility of maintaining the insurance program. Bechtel has obtained expansions of Phase 1 policies to insure against Phase 2 – Stage 1 exposures.
Windstorm and Flood Insurance
For Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1, we have $400 million in total windstorm and flood insurance, $100 million of which is shared with Phase 2 – Stage 1. This aggregate $400 million limit applies to physical damage losses. Aon has deemed the current insurance package as appropriate for this type of facility and takes into account damage or loss of the plant, loss of income exposure and potential liabilities to third parties.
Physical Damage and Delayed Startup Insurance
For Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1, we have total insurance coverage against property damage of approximately $1.1 billion, subject to stated sublimits. We have $259 million in both builder’s risk and marine cargo delayed startup, or DSU, insurance in addition to the property damage insurance. This DSU limit also applies to windstorm and flood losses. For Phase 2 – Stage 1, the builder’s risk property damage limit was increased by $448 million to cover additional insurable Phase 2 – Stage 1 assets. We do not intend to acquire builder’s risk DSU or marine cargo DSU insurance for delays in the completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1. Delays in completion of Phase 1 are insured under the builder’s risk DSU and marine cargo DSU policies.
Third-Party Liability
We have $100 million of third-party liability insurance shared between Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1. Due to changes in the risk of loss and required amount of insurance for major Phase 2 – Stage 1 construction contractors, we placed an additional $100 million of third-party liability insurance during construction dedicated to only Phase 2 – Stage 1.
101
Pollution Legal Liability
We have $25 million of pollution legal liability insurance covering third-party liabilities, remediation legal liability, and legal defense expense. This limit is shared by both Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1.
Terrorism
Aon reported in October 2006 that there was limited exposure to physical damage and subsequent loss of income arising out of a terrorist act against Phase 1. Aon believes that this risk is unlikely to change significantly as a result of Phase 2 – Stage 1. Until the first LNG tanker reaches the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, we have $25 million of terrorism insurance. Prior to the arrival of the first LNG tanker, we intend to complete a terrorism maximum foreseeable loss study that incorporates Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1. We plan to assess the scope of our terrorism insurance policy upon completion of this study.
Insurance During Operational Period
Upon commencement of operations, we will have responsibility for all insurance coverage including those previously obtained for us by Bechtel. We intend to place insurance coverages that are in such form and amounts as are customary for project facilities of similar type and scale to this facility.
We have no employees. We will rely on our general partner to manage all aspects of the construction, operation and maintenance of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and the conduct of our business. Because our general partner has no employees, it will rely on subsidiaries of Cheniere to provide the personnel necessary to allow it to meet its management obligations to us and to Sabine Pass LNG. See “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” for a discussion of these arrangements.
We are not a party to any legal proceeding but may in the future be a party to various administrative, regulatory or other legal proceedings that may arise in the ordinary course of our business.
102
DESCRIPTION OF PRINCIPAL CONSTRUCTION AGREEMENTS
The following are summaries of material terms of certain agreements related to the construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. These summaries should not be considered to be a full statement of the terms and provisions of such agreements. Accordingly, the following summaries are qualified in their entirety by reference to each agreement. Copies of the agreements described below are filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. Unless otherwise stated, any reference in this prospectus to any agreement means such agreement and all schedules, exhibits and attachments thereto as amended, supplemented or otherwise modified and in effect as of the date hereof.
Scope of Work
In December 2004, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a lump-sum turnkey EPC agreement with Bechtel for the construction of Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Under the EPC agreement, Bechtel agreed to provide Sabine Pass LNG with services for the engineering, procurement and construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Except for certain specified owner and third-party work outlined in the EPC agreement, the work to be performed by Bechtel includes all of the work required to achieve substantial completion and final completion of Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal in accordance with the requirements of the EPC agreement, including achieving specified minimum acceptance criteria and performance guarantees. Bechtel is obligated to perform its work in accordance with good engineering and construction practices and applicable laws, codes and standards.
Sabine Pass LNG issued a limited notice to proceed in December 2004 and a final notice to proceed in early April 2005, which required Bechtel to commence all other aspects of the work under the EPC agreement. Bechtel must achieve substantial completion in accordance with the requirements of the EPC agreement on or before December 20, 2008. Final completion must be attained no later than 90 days after achieving substantial completion.
Payment for Work
Sabine Pass LNG agreed to pay to Bechtel a contract price of $646.9 million plus certain reimbursable costs for the work under the EPC agreement. This contract price is subject to adjustment for contingencies, change orders and other items. As of January 17, 2007, change orders for $119.5 million had been approved, increasing the total contract price to $766.4 million. Payments under the EPC agreement will be made in accordance with the payment schedule set forth in the EPC agreement. The contract price and payment schedule, including milestones, may be amended only by change order. Bechtel will be liable to Sabine Pass LNG for certain delays in achieving substantial completion, minimum acceptance criteria and performance guarantees. Bechtel will be entitled to a scheduled bonus of $12 million if on or before April 3, 2008, Bechtel completes construction sufficient to achieve, among other requirements specified in the EPC agreement, a sustained revaporized natural gas sendout at a significant rate for a preagreed period of time (currently provided to be a rate of at least 2.0 Bcf/d for a minimum sustained test period of 24 hours). The amount of such scheduled bonus will decrease by a specified amount for each day after April 3, 2008, that Bechtel fails to meet this test, up to a total of 40 days. The specified amount per day is $125,000 for the first 15 days, $300,000 for the next 10 days and $425,000 for the next 15 days. Bechtel will be entitled to receive an additional bonus of $67,000 per day (up to a maximum of $6 million) for each day that commercial operation is achieved prior to April 1, 2008.
Change Orders
Until substantial completion under the terms of the EPC agreement, Sabine Pass LNG has certain rights to request change orders, and Bechtel has the right to request change orders up to and after substantial completion in the event of specified occurrences, including, among other things:
| • | a force majeure event; |
103
| • | a suspension of work ordered by Sabine Pass LNG; |
| • | certain acts and omissions by Sabine Pass LNG (including failure to fulfill obligations), but, in each case, only where such act or omission adversely affects Bechtel’s costs of the performance of work, its ability to perform the work in accordance with the project schedule or its ability to perform any material obligation under the EPC agreement; and |
| • | certain changes in law, but only where such delay adversely affects Bechtel’s costs of the performance of the work, its ability to perform the work in accordance with the project schedule or its ability to perform any material obligation under the EPC agreement. |
Liquidated Damages
Bechtel is required to pay “delay” liquidated damages for each day of delay that Bechtel fails to complete the work necessary to commence the cool down phase at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal beyond a date estimated by Bechtel for completion of such work. The maximum aggregate amount of liquidated damages for such delay is 1% of the contract price. In addition, Bechtel is required to pay liquidated damages for each day of delay beyond December 20, 2008 that Bechtel fails to achieve substantial completion. The maximum aggregate amount of all delay liquidated damages is 10% of the contract price.
In addition, if the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal fails to achieve one or more performance guarantees relating to sendout rate and ship unloading time by December 20, 2008, but meets specified minimum acceptance criteria and all other requirements for substantial completion, then Bechtel is required to pay “performance” liquidated damages for such failure. The maximum aggregate amounts of performance liquidated damages related to send out rate and ship unloading time are 10% of the contract price and 2% of the contract price, respectively. The maximum aggregate amount of all performance liquidated damages is 10% of the contract price.
Subject to certain exceptions, Bechtel’s maximum aggregate liability under the EPC agreement (including its liability for liquidated damages) is 30% of the contract price.
Warranty
Bechtel warrants in the EPC agreement that:
| • | the equipment required for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal will be new and of good quality; |
| • | the work and the equipment will meet the requirements of the EPC agreement, including good engineering and construction practices and applicable laws, codes and standards; and |
| • | the work and the equipment will be free from encumbrances to title. |
Until 18 months after Sabine Pass LNG’s provisional acceptance of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Bechtel will be liable for promptly correcting any work that is found to be defective.
Force Majeure
Under the EPC agreement, if Bechtel experiences a force majeure event, it could be entitled to an extension of the date by which substantial completion is to be accomplished and an extension of the date by which it could earn the $12 million bonus. If any force majeure delay lasts at least 30 days, Bechtel would be entitled to an adjustment of the contract price under the EPC agreement to compensate it for its standby expenses, up to a limit of $3.8 million in the aggregate. A force majeure event generally occurs if any act or event occurs that:
| • | prevents or delays the affected party’s performance of its obligations in accordance with the terms of the EPC agreement; |
| • | is beyond the reasonable control of the affected party, not due to its fault or negligence; and |
| • | could not have been prevented or avoided by the affected party through the exercise of due diligence. |
104
Bechtel has claimed events of force majeure arising out of three hurricanes that made landfall along the U.S. Gulf Coast in 2005. Sabine Pass LNG has entered into change orders with Bechtel concerning additional activities and expenditures in order, among other things, to attract sufficient skilled labor to mitigate potential schedule delays and provide a reasonable opportunity for Bechtel to attain the initial target bonus date of April 3, 2008 (the date originally anticipated for completion of construction sufficient to achieve a sendout rate of at least 2.0 Bcf/d for a minimum sustained test period of 24 hours and that, if attained, would entitle Bechtel to a scheduled $12 million bonus). In a change order dated May 16, 2006, Sabine Pass LNG agreed to defer the date by which substantial completion of the entire project is required to be accomplished under the EPC agreement from September 3 to December 20, 2008, which is the new substantial completion date. In the absence of substantial completion by such date, Bechtel would be obligated to pay Sabine Pass LNG certain liquidated damages as provided under the terms of the contract.
Termination and Suspension
In the event of an uncured default by Bechtel, Sabine Pass LNG may terminate the EPC agreement and take any of the following actions:
| • | take possession of the facility, equipment, construction equipment, work product and books and records; |
| • | take assignment of certain subcontracts; and |
| • | complete the work. |
Following such a termination, if the cost to reach final completion exceeded the unpaid balance of the contract price, Bechtel would be liable for the difference, subject to Bechtel’s limitation of liabilities described above. If the cost to reach final completion were less than the unpaid balance of the contract price, the difference would be payable to Bechtel.
Sabine Pass LNG also has the right to terminate the EPC agreement for convenience. In the event of any such termination for convenience, Bechtel would be paid:
| • | the portion of the contract price for the work performed prior to termination, less that portion of the contract price paid previously; |
| • | actual reasonable cancellation charges owed by Bechtel to subcontractors (if Sabine Pass LNG does not take assignment of such subcontracts); |
| • | actual costs associated with demobilization charges; and |
| • | lost profits, except in certain cases, equal to 10% of the contract price less a portion of the advance payment related to the final notice to proceed. |
Sabine Pass LNG may, upon a 30-day written notice to Bechtel, suspend the work under the EPC agreement. In the event of such suspension for a period exceeding 90 consecutive days or 120 aggregate days, other than any suspension due to an event of force majeure or the fault or negligence of Bechtel or its subcontractors, Bechtel would be permitted to terminate the EPC agreement subject to giving 14 days’ notice. In the event of such a termination, Bechtel would be entitled to the compensation described above in relation to termination for convenience. If Sabine Pass LNG suspends work under the EPC agreement, Bechtel could be entitled to a change order to recover the reasonable costs of the suspension, including demobilization and remobilization costs. Bechtel may also suspend or terminate the EPC agreement upon the occurrence of certain other events, including force majeure and Sabine Pass LNG’s uncured defaults, such as:
| • | failure to pay any undisputed amounts; |
| • | failure to comply materially with material obligations under the EPC agreement; and |
| • | insolvency. |
105
Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPCM Agreement
Scope of Work
In July 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an Agreement for Engineering, Procurement, Construction and Management of Construction Services of the Phase 2 Receiving, Storage and Regasification Terminal Expansion, or the EPCM agreement, with Bechtel. Under the EPCM agreement, Bechtel will provide design and engineering services for Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal expansion project, except for such portions to be designed by other contractors and suppliers of equipment, materials and services that Sabine Pass LNG contracts with directly, who we refer to as the Sabine contractors, and those obligations that must be performed directly by Sabine Pass LNG; construction management services to manage the construction of the facility; and performance of a portion of the construction. The EPCM agreement does not contain any guaranteed completion dates, but Bechtel will provide a schedule for Sabine Pass LNG’s approval.
Payment for Work
The EPCM agreement provides for compensating Bechtel on a cost reimbursable basis, plus a fixed fee in the amount of $18.5 million. A discretionary bonus may be paid to Bechtel at Sabine Pass LNG’s sole discretion upon completion of Phase 2 – Stage 1. Payments under the EPCM agreement will be based on monthly estimates, with a reconciliation in the next month, and the fixed fee will be paid in accordance with a payment schedule set forth in the EPCM agreement. In addition to disputed amounts, Sabine Pass LNG may, upon giving prior written notice and subject to specified cure periods, withhold payment or a portion thereof, in an amount and to such extent as may be reasonably necessary to protect Sabine Pass LNG from loss due to:
| • | defective services; |
| • | liens or other encumbrances on all or a portion of the Phase 2 site or the Phase 2 facility filed by Bechtel or any subcontractor or any person acting through or under any of them; |
| • | any material breach by Bechtel of any provision of the EPCM agreement; |
| • | the assessment of any fines or penalties against Sabine Pass LNG as a result of Bechtel’s failure to comply with applicable law or applicable codes and standards; |
| • | amounts Sabine Pass LNG paid to Bechtel in a preceding month incorrectly; or |
| • | any other costs and liabilities that Sabine Pass LNG has incurred for which Bechtel is responsible under the EPCM agreement. |
Bechtel has the right to submit a change order to Sabine Pass LNG to increase the fixed fee:
| • | in the event that Sabine Pass LNG adjusts the scope of Phase 2 – Stage 1 at a cost individually or in the aggregate of $5,000,000 or more, excluding any increased costs caused by escalation in the cost of labor or materials, estimating errors or higher than expected costs for labor, materials or equipment; |
| • | for significant delays to Phase 2 – Stage 1 resulting from a force majeure event (as described below) causing a delay in excess of 90 consecutive days; |
| • | if Sabine Pass LNG suspends all or a significant portion of Phase 2 – Stage 1 for more than 60 consecutive days; or |
| • | if Sabine Pass LNG directs Bechtel or Sabine Pass LNG’s Sabine contractors to significantly delay the progress of Phase 2 – Stage 1. |
In such circumstances, Bechtel will be entitled to an adjustment in the fixed fee of $200,000 for each $5,000,000 increase in the cost of Phase 2 – Stage 1.
106
Warranty
Bechtel warrants that the materials, equipment and supplies provided by Bechtel and its subcontractors (but not Sabine Pass LNG’s contractors) will be new and of good quality; the services will be provided in accordance with all requirements of the EPCM agreement; and all equipment, materials and supplies furnished by Bechtel and its subcontractors will be free from encumbrances to title. There are three distinct defect correction periods, and during any such period and for 18 months thereafter, Bechtel is responsible for promptly correcting any defective service and performing any other services necessary to correct the defect to the Phase 2 – Stage 1 facility. Bechtel will be reimbursed on a recoverable cost basis for performing corrective services, including the cost of field labor, field supervision, materials and equipment, but Bechtel will not be entitled to payment for any costs associated with design, engineering, construction management, or for the costs of field personnel above a rank of general foreman. In addition, Bechtel will not be entitled to any increase in the fixed fee in connection with the performance of corrective services.
Limitation of Liability
Bechtel’s liability in contract, warranty, tort, strict liability, products liability, professional liability, indemnity, contribution or any other cause is limited to the amount of 50% of the fixed fee (as adjusted pursuant to a change order), except that this limitation does not apply to: (i) Bechtel’s indemnification obligations; (ii) proceeds of insurance required to be obtained by Bechtel and its subcontractors; or (iii) Bechtel’s obligation to deliver unencumbered title to Sabine Pass LNG in accordance with the EPCM agreement for materials, equipment and supplies furnished by Bechtel or its subcontractors.
Force Majeure
Because the EPCM agreement is cost-reimbursable, no change order is required for costs incurred by Bechtel related to a force majeure event, except in connection with significant delays as described under “—Payment for Work.” Any costs incurred by Bechtel in exercising reasonable efforts to prevent, avoid, overcome or mitigate the effects of force majeure on Phase 2 – Stage 1 will be recoverable under the cost reimbursable structure. A force majeure under the EPCM agreement is any act or event that:
| • | prevents or delays the affected party’s performance of its obligations in accordance with the terms of the EPCM agreement; |
| • | is beyond the reasonable control of the affected party, not due to its fault or negligence; and |
| • | could not have been prevented or avoided by the affected party through the exercise of due diligence. |
Termination and Suspension
In the event of an uncured default by Bechtel, Sabine Pass LNG may terminate the EPCM agreement and take any of the following actions:
| • | take possession of the facility, materials, equipment, construction equipment, work product, books and records and other items owned or rented by Bechtel; |
| • | take assignment of any or all subcontracts; and |
| • | complete the work. |
Following such a termination, Sabine Pass LNG has no further obligation to pay Bechtel, and Bechtel must refund any advance payments made for services not yet performed, and Bechtel will be liable for reasonable costs incurred by Sabine Pass LNG due to the default.
Sabine Pass LNG also has the right to terminate the EPCM agreement for convenience upon 30 days’ prior written notice to Bechtel. In the event of any such termination for convenience, Bechtel would be paid:
| • | all recoverable costs for services performed through the date of termination, less that portion of the recoverable costs previously paid; |
107
| • | all recoverable costs reasonably incurred by Bechtel on account of such termination, including cancellation charges owed by Bechtel to its subcontractors if Sabine Pass LNG does not take assignment of such subcontracts, and costs associated with demobilization of personnel and construction equipment; and |
| • | the fixed fee for services performed through the date of termination, less amounts previously paid. |
Bechtel’s ability to terminate the EPCM agreement is limited to the following events:
| • | Sabine Pass LNG’s failure to pay an undisputed amount, if such failure is not cured within 45 days after notice from Bechtel; |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG’s failure to materially comply with any of its material obligations under the EPCM agreement (but only to the extent such material failure and the impact thereof is not subject to adjustment by change order), and Sabine Pass LNG fails to cure such failure within 45 days (or a reasonable time beyond 45 days, not to exceed 90 days) after notice from Bechtel; or |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG experiences an insolvency event. |
In the event of any such termination event, Bechtel is entitled to the same compensation set forth above as if Sabine Pass LNG had terminated for convenience.
If any force majeure event or the effects thereof causes suspension of a substantial portion of the work at the Phase 2 site for a period exceeding 90 consecutive days or 180 days in the aggregate during any continuous 24-month period, then either party has the right to terminate the EPCM agreement by providing 14 days’ written notice to the other party. In the event of such termination, Bechtel is entitled to the same compensation set forth above as if Sabine Pass LNG had terminated the EPCM agreement for convenience.
Sabine Pass LNG may, upon 10 days’ written notice to Bechtel, suspend the work under the EPCM agreement. In the event such suspension period exceeds 90 consecutive days or 180 aggregate days, Bechtel is permitted to terminate the EPCM agreement subject to giving 14 days’ written notice to Sabine Pass LNG. Bechtel is also permitted to suspend performance of its services after 14 days’ prior written notice if Sabine Pass LNG fails to pay any undisputed amount due and owing to Bechtel and such failure continues for more than 30 days after the due date for such payment.
Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPC LNG Tank Contract
Scope of Work
In July 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an Engineer, Procure and Construct (EPC) LNG Tank Contract, or tank contract, with Zachry and Diamond (each of whom is jointly and severally liable for obligations under the tank contract), who are collectively referred to as the tank contractor, for the Phase 2 – Stage 1 expansion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Under the tank contract, the tank contractor will furnish all plant, labor, materials, tools, supplies, equipment, transportation, supervision, technical, professional and other services, and perform all operations necessary and required to satisfactorily engineer, procure the materials for and construct the two Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks, except as otherwise specified in the tank contract. In addition, Sabine Pass LNG has the option (to be elected on or before March 31, 2007) for the tank contractor to engineer, procure and construct a third tank, with the cost and completion date thereof to be agreed upon if the option is elected.
Scheduling
The target milestone completion date of the first Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank is scheduled in the first quarter of 2009, and the target milestone completion date of the second Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank is scheduled in the second quarter of 2009.
108
Payments
The tank contract provides that the tank contractor will receive a lump-sum, fixed price payment of approximately $140.9 million. The contract price is subject to adjustment based on fluctuations in the cost of labor and certain materials for the Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks, including the nickel steel used in the Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks.
Payments under the tank contract will be made in accordance with a specified milestone payment schedule. As retainage, Sabine Pass LNG withholds 5% of each milestone payment for the work performed up to provisional acceptance. One-half of the retainage will be released upon provisional acceptance of the first Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank, and the remaining retainage will be released upon provisional acceptance of the second Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank.
In addition to disputed invoice amounts, Sabine Pass LNG may, upon giving prior written notice and allowing the tank contractor an opportunity to cure, withhold payment on an invoice or a portion thereof, or collect on the letter of credit, if:
| • | the tank contractor is in default of any tank contract condition, including, but not limited to, the schedule, quality assurance and health and safety requirements; |
| • | the tank contractor has not submitted the tank contract schedule, including any revisions or updates, as required by the tank contract; |
| • | the tank contractor has failed to submit proper insurance certificates, or not provided proper coverage or proof thereof; |
| • | the tank contractor has failed to submit securities approved by Sabine Pass LNG; |
| • | the tank contractor fails to submit interim lien waivers from the tank contractor and major subcontractors; or |
| • | adjustments are due from previous overpayment or audit results. |
Letter of Credit
The tank contractor has furnished Sabine Pass LNG with an irrevocable standby letter of credit in the amount of 5% of the contract price, issued and confirmed by a bank acceptable to Sabine Pass LNG. The letter of credit will expire upon final acceptance of the two Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks and Sabine Pass LNG’s notice to the issuing bank to release the letter of credit. If at any time the contract price is increased by change order by at least 1% of the contract price, in the aggregate, the tank contractor will increase the amount of the letter of credit to 5% of the adjusted contract price. In addition, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. has executed a guarantee agreement with respect to the obligations of Diamond under the tank contract.
Change Orders
Sabine Pass LNG has the right to submit any change order, subject to certain caps on unilateral change orders (including an individual cap of 5% and an aggregate cap of 10% of the contract price).
The tank contractor has the right to submit a change order in the event of specified circumstances, including the following:
| • | a change in law; |
| • | acts or omissions by Sabine Pass LNG that constitute a change in the work under the tank contract; |
| • | force majeure; |
| • | acceleration of the work directed by Sabine Pass LNG; |
| • | if the finished work conforms with the requirements of the tank contract, but Sabine Pass LNG requires disassembling or dismantling of a tank for the purpose of inspection; |
109
| • | in the event of a delay or suspension of work ordered by or on behalf of Sabine Pass LNG; |
| • | in the event subsurface soil conditions are materially different from the information provided by Sabine Pass LNG; and |
| • | discovery of pre-existing hazardous material at the site. |
In many instances, before such a change order can be submitted by the tank contractor, such occurrences must adversely affect the tank contractor’s (i) cost of performing the work; (ii) ability to perform the work in accordance with the project schedule; or (iii) ability to perform any material obligation under the tank contract.
Liquidated Damages
The tank contractor is required to pay liquidated damages for each day of delay that the tank contractor fails to achieve mechanical completion for each Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank by the respective mechanical completion milestone date. The amount of the liquidated damages for each tank is $50,000 for each of the first 75 days of delay and $100,000 for each day thereafter, subject to a maximum of 10% of the contract price.
Limitation of Liability
The tank contractor is obligated to perform all of the work required to achieve ready for cool down for both of the Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks. Once both of the Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks are ready for cool down, liability under the tank contract or under any cause of action related to the subject matter of the tank contract, whether in contract, warranty, tort, strict liability, products liability, professional liability, indemnity, contribution or any other cause of action, is limited to an aggregate of 30% of the contract price, except that this limitation does not apply to: (i) losses caused by criminal acts, fraud or gross negligence of the tank contractor’s key personnel or their superiors; (ii) the tank contractor’s indemnification obligations under the tank contract; or (iii) proceeds of insurance required to be obtained by the tank contractor and its subcontractors and sub-subcontractors.
Warranty
The tank contractor warrants that the work (including all materials and equipment) will be new (unless otherwise agreed) and of good quality, in accordance with all requirements of the tank contract (including good engineering and construction practices, applicable law and applicable codes and standards), and free from encumbrances to title. Until the end of the defect correction period (ending 18 months after provisional acceptance of each Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank or 24 months after each Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank is ready for cool down, whichever occurs first, and subject to extension for corrected work, and up to 30 months if the Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank ceases operating solely because of defects in the work or corrections therefor, to the extent of the interruption in operations), the tank contractor is liable to promptly correct any work that is found to be defective.
Force Majeure
A force majeure event entitles the tank contractor to an extension to the project schedule if the delay caused by the force majeure event affects the performance of any work that is on the critical path of the work and causes, or will cause, the tank contractor to complete the work beyond the applicable milestone date. The tank contractor is also entitled to its reasonable incremental costs incurred as a result of a force majeure event, but only after such costs incurred with respect to any one force majeure event exceed $250,000.
A force majeure under the tank contract is any act or event that:
| • | prevents, delays or materially and adversely impacts the affected party’s performance of its obligations in accordance with the terms of the tank contract; |
| • | is beyond the reasonable control of the affected party, not due to its fault or negligence; and |
110
| • | could not have been prevented or avoided by the affected party through the exercise of commercially reasonable efforts. |
The tank contractor may terminate the tank contract upon 30 days’ prior written notice if a force majeure event causes a complete suspension of all work that continues for more than 120 consecutive days, unless Sabine Pass LNG agrees to a modification of the contract price and modifying the milestone schedule to account for such force majeure event.
Termination and Suspension
Sabine Pass LNG has the right to terminate the tank contract as a result of a default by the tank contractor, which occurs if the tank contractor:
| • | performs work that fails materially to conform to the requirements of the tank contract; |
| • | fails to make progress according to the agreed-upon tank contract schedule so as to endanger performance of the tank contract; |
| • | abandons or refuses to proceed with any of the work, including modifications thereto; |
| • | fails to fulfill or comply with any of the other material terms of the tank contract; |
| • | fails to commence the work in accordance with the provisions of the tank contract; |
| • | abandons the work; |
| • | fails to maintain insurance required under the tank contract; |
| • | materially disregards applicable law or applicable standards and codes; |
| • | engages in behavior that is dishonest, fraudulent or constitutes a conflict with the tank contractor’s obligations under the tank contract; or |
| • | suffers an insolvency event or makes a general assignment for the benefit of creditors. |
In the event of such a default (other than such set forth in the last bullet, in which case Sabine Pass LNG has an immediate right to terminate the tank contract) which remains uncured after 30 days’ notice (or a reasonable time beyond 30 days, not to exceed 90 days), Sabine Pass LNG may:
| • | terminate the tank contract in whole or in part; |
| • | complete the work in whatever manner Sabine Pass LNG deems expedient; |
| • | take possession of and utilize any data, designs, work product, licenses, materials, equipment and tools furnished by the tank contractor or subcontractors or sub-subcontractors and necessary to complete the work; |
| • | hire any or all of the tank contractor’s employees; and |
| • | take assignment of any or all of the subcontracts and sub-subcontracts. |
Notwithstanding the foregoing, Sabine Pass LNG is not entitled to terminate the tank contract for delay in achieving mechanical completion for a Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank during the first three months after the milestone date for the tank unless the tank contractor is not paying Sabine Pass LNG’s liquidated damages when owed during such three-month period or the tank contractor is not diligently performing the work, and Sabine Pass LNG is otherwise entitled to terminate the tank contract.
Following such termination, if the cost to complete the Phase 2 – Stage 1 tanks exceeds the unpaid balance of the contract price, the tank contractor will be liable for the difference. In addition, the tank contractor is also liable for liquidated damages and the cost to accelerate the work of any substitute contractor to achieve the milestone dates. All such liabilities are subject to the limitations on liquidated damages and total liabilities described above.
111
Sabine Pass LNG has the right to terminate the tank contract in whole or in part for convenience by written notice to the tank contractor. In such event, the tank contractor will be paid:
| • | the portion of the contract price for the work performed prior to termination, less that portion of the contract price paid previously; |
| • | all reasonable costs for work thereafter performed as specified in such notice; |
| • | reasonable administrative costs of settling and paying claims arising out of the termination of work under subcontracts and sub-subcontracts; |
| • | reasonable costs associated with demobilization; |
| • | a reasonable overhead and profit on the amounts; |
| • | a sum equal to 5% of the unpaid contract price, not to exceed $4,000,000; and |
| • | less all payments previously made. |
If Sabine Pass LNG fails to pay any undisputed amount due and owing to the tank contractor and such failure continues for more than 30 days after the due date for such payment, then the tank contractor may suspend performance of the work until the tank contractor receives such undisputed amounts. If Sabine Pass LNG does not cure such failure within 30 days after receipt of the notification given above, or fails to provide satisfactory evidence that such default will be corrected within 90 days, the tank contractor may, by written notice to Sabine Pass LNG, terminate in whole or in part the tank contract.
Sabine Pass LNG may, upon written notice, suspend all or any portion of the work. The tank contractor is permitted to submit a change order to recover the reasonable costs of such suspension. The tank contractor has no equivalent right to terminate or suspend the tank contract.
Phase 2 – Stage 1 EPC LNG Soil Contract
Scope of Work
In July 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an Engineer, Procure and Construct (EPC) LNG Unit Rate Soil Contract, or soil contract, with Recon, or the soil contractor, for Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal expansion project. Under the soil contract, the soil contractor is required to furnish all plant, labor, materials, tools, supplies, equipment, transportation, supervision, technical, professional and other services, and perform all operations necessary and required to satisfactorily conduct soil remediation and improvement on the Phase 2 site, unless otherwise set forth in the soil contract.
Payments
Upon issuing the final notice to proceed, Sabine Pass LNG paid the soil contractor an initial payment of approximately $2.9 million. The soil contract price is based on unit rates. Payments under the soil contract will be made based on quantities of work performed at unit rates. As retainage, Sabine Pass LNG withholds 10% of each invoiced amount, with the retainage being released upon final completion of the work.
In addition to disputed invoice amounts, Sabine Pass LNG may, upon giving prior written notice and allowing the soil contractor an opportunity to cure, withhold payment on an invoice or a portion thereof, or collect on the letter of credit, if:
| • | the soil contractor is in default of any soil contract condition, including, but not limited to, the schedule, quality assurance and health and safety requirements; |
| • | the soil contractor has not submitted the soil contract schedule, including any revisions or updates, as required by the soil contract; |
112
| • | the soil contractor has failed to submit proper insurance certificates, or not provided proper coverage or proof thereof; |
| • | the soil contractor fails to submit interim lien waivers from the soil contractor and major subcontractors; or |
| • | adjustments are due from previous overpayment or audit results. |
Letter of Credit
The soil contractor has furnished Sabine Pass LNG with an irrevocable standby letter of credit in an amount of $2,850,000, issued by a bank acceptable to Sabine Pass LNG. The letter of credit will expire upon final completion of the work. If at any time the unit rates are increased by change order by more than 10% of the unit rates, upon Sabine Pass LNG’s request, the soil contractor will increase the amount of the letter of credit to 10% of the adjusted unit rates.
Change Orders
Sabine Pass LNG has the right to submit any change order to make any change in the work that is within the scope of the soil contract.
The soil contractor has the right to submit a change order in the event of specified circumstances, including the following:
| • | a change in law; |
| • | acts or omissions by Sabine Pass LNG that constitute a change in the work under the soil contract; |
| • | force majeure; |
| • | acceleration of the work directed by Sabine Pass LNG; |
| • | in the event of a delay or suspension of work ordered by Sabine Pass LNG; |
| • | in the event subsurface soil conditions are materially different from the information provided by Sabine Pass LNG; and |
| • | discovery of pre-existing hazardous material at the site. |
In many instances, before such a change order can be submitted by the soil contractor, such occurrences must adversely affect the soil contractor’s (i) ability to perform the work in accordance with the project schedule; or (ii) ability to perform any material obligation under the soil contract.
Liquidated Damages
The soil contractor is required to pay liquidated damages for each day of delay that the soil contractor fails to achieve substantial completion for each Phase 2 – Stage 1 tank and final completion by the respective specified milestone date. The amount of the liquidated damages for failure to achieve the milestone date for substantial completion and final completion of each tank is $21,000 for each day of delay, subject in all cases to a maximum of $3,000,000.
Limitation of Liabilities
The soil contractor is obligated to perform all of the work required to achieve substantial completion. Following attainment of substantial completion, liability under the soil contract or under any cause of action related to the subject matter of the soil contract, whether in contract, warranty, tort, strict liability, products liability, professional liability, indemnity, contribution or any other cause of action, is limited to an aggregate of
113
$7,500,000, except that this limitation does not apply to: (i) losses caused by intentional misconduct or gross negligence of the soil contractor; (ii) the soil contractor’s indemnification obligations under the soil contract; or (iii) proceeds of insurance required to be obtained by the soil contractor and its subcontractors and sub-subcontractors.
Warranty
The soil contractor warrants that the work (including all materials and equipment) will be new (unless otherwise agreed) and of good quality, in accordance with all requirements of the soil contract (including good engineering and construction practices, applicable law and applicable codes and standards), and free from encumbrances to title. Until the end of the defect correction period (ending 24 months after substantial completion, subject to extension to 36 months where corrective work is performed), the soil contractor is liable to promptly correct any work that is found defective.
Force Majeure
A force majeure event entitles the soil contractor to an extension to the project schedule if the delay caused by the force majeure event affects the performance of any work that is on the critical path of the work and causes, or will cause, the soil contractor to complete the work beyond the applicable milestone date. A force majeure under the soil contract is any act or event that:
| • | prevents or delays the affected party’s performance of its obligations in accordance with the terms of the soil contract; |
| • | is beyond the reasonable control of the affected party, not due to its fault or negligence; and |
| • | could not have been prevented or avoided by the affected party through the exercise of due diligence. |
If there is a force majeure event, the soil contractor shall be entitled to an extension of the applicable milestone date, which is the soil contractor’s sole remedy for the occurrence of such delay for a continuous period of less than 30 days. For such an event that extends beyond 30 consecutive days, the soil contractor may be entitled to an adjustment to the unit rates for reimbursement of the standby time for the soil contractor’s employees and construction equipment and other standby costs that are incurred by the soil contractor after the expiration of such 30-day period and which are caused by such excusable delay, up to a maximum aggregate of 40 days of standby time.
Termination and Suspension
Sabine Pass LNG has the right to terminate the soil contract as a result of a default by the soil contractor, which occurs if the soil contractor:
| • | performs work which fails materially to conform to the requirements of the soil contract; |
| • | fails to make progress so as to endanger performance of the soil contract; |
| • | abandons or refuses to proceed with any of the work, including modifications thereto; |
| • | fails to fulfill or comply with any of the terms of the soil contract; |
| • | fails to commence the work in accordance with the provisions of the soil contract; |
| • | abandons the work; |
| • | fails to maintain insurance required under the soil contract; |
| • | materially disregards applicable law or applicable standards and codes; |
| • | engages in behavior that is dishonest, fraudulent or constitutes a conflict with the soil contractor’s obligations under the soil contract; or |
114
| • | suffers an insolvency event or makes a general assignment for the benefit of creditors. |
In the event of such a default (other than such set forth in the last bullet, which provides an immediate right of termination, or a default considered not curable or for failure to cure safety violations) which remains uncured after 48 hours’ notice (or a reasonable time beyond 48 hours, not to exceed 30 days), Sabine Pass LNG may:
| • | terminate the soil contract in whole or in part; |
| • | complete the work in whatever manner Sabine Pass LNG deems expedient; |
| • | take possession of and utilize any data, designs, work product, licenses, materials, plant, equipment, tools and property of any kind furnished by the soil contractor or subcontractors or sub-subcontractors and necessary to complete the work; |
| • | hire any or all of the soil contractor’s employees; and |
| • | take assignment of any or all of the subcontracts and sub-subcontracts. |
Following such termination, the soil contractor will be liable for liquidated damages and the cost of any substitute contractor to accelerate the work in order to achieve the substantial completion milestone dates, subject to the limitations on liquidated damages and total liabilities described above.
Sabine Pass LNG has the right to terminate the soil contract in whole or in part for convenience by written notice to the soil contractor. In this event, the soil contractor will be paid:
| • | the unit rates corresponding to the work performed prior to termination; |
| • | all reasonable costs for work thereafter performed as specified in such notice; |
| • | reasonable administrative costs of settling and paying claims arising out of the termination of work under subcontracts and sub-subcontracts; |
| • | reasonable costs incurred in demobilization and the disposition of residual material, plant and equipment; |
| • | a sum equal to 5% of the result obtained by subtracting all previous payments to the soil contractor from $30,000,000, but such sum shall not in any event exceed $1,000,000; and |
| • | less all payments previously made. |
Sabine Pass LNG may, upon written notice, suspend all or any portion of the work. The soil contractor is permitted to submit a change order to recover the reasonable costs of such suspension. The soil contractor has no equivalent right to terminate or suspend the soil contract.
115
The following are summaries of material terms of certain agreements related to our indebtedness. These summaries should not be considered to be a full statement of the terms and provisions of such agreements. Accordingly, the following summaries are qualified in their entirety by reference to each agreement. Copies of the agreements described below are filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. Unless otherwise stated, any reference in this prospectus to any agreement means such agreement and all schedules, exhibits and attachments thereto as amended, supplemented or otherwise modified and in effect as of the date hereof.
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG issued $550 million aggregate principal amount of 7.25% Senior Secured Notes due 2013, or the 2013 notes, and $1,482 million aggregate principal amount of 7.50% Senior Secured Notes due 2016, or the 2016 notes, in a private placement. We refer to the 2013 notes and the 2016 notes collectively as the Sabine Pass LNG notes. Sabine Pass LNG used the net proceeds from the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes for the following purposes:
| • | approximately $335 million to fund a reserve account for scheduled interest payments on the Sabine Pass LNG notes through the May 2009 interest payment date; |
| • | approximately $380 million to repay principal, accrued interest and fees relating to the amended Sabine Pass credit facility; |
| • | approximately $380 million to distribute funds to Cheniere Holdings for repayment of principal, accrued interest and a prepayment penalty relating to its term loan, net of other funds available at Cheniere Holdings; |
| • | approximately $18 million to pay associated debt repayment transaction costs and expenses, including costs to settle interest rate swaps related to the amended Sabine Pass credit facility; and |
| • | approximately $887 million to fund remaining construction costs to complete Phase 1 and Phase 2 – Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
Maturity; Interest
The 2013 notes and the 2016 notes mature on November 30, 2013 and November 30, 2016, respectively. The 2013 notes and the 2016 notes bear interest at 7.25% per annum and 7.50% per annum, respectively, from November 9, 2006, payable semi-annually in arrears on May 30 and November 30 of each year, beginning May 30, 2007. Sabine Pass LNG will be required to pay additional interest on the Sabine Pass LNG notes if they are not exchanged for registered notes within a specified time period. Sabine Pass LNG deposited $335 million from the sale of the Sabine Pass LNG notes in a debt service reserve account, which will be withdrawn as necessary to pay the first five interest payments on the Sabine Pass LNG notes.
Guarantees; Collateral
The Sabine Pass LNG notes are guaranteed by all of Sabine Pass LNG’s future domestic restricted subsidiaries. Sabine Pass LNG’s obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes are secured on a first-priority basis (subject to certain permitted liens) by a security interest in all of Sabine Pass LNG’s equity interests and substantially all of its operating assets, including a pledge of the stock of its future domestic subsidiaries (or 65% of the voting stock of its future foreign subsidiaries). In addition, Sabine Pass LNG’s future domestic restricted subsidiaries will grant security interests in all of their operating assets as collateral for the repayment of the Sabine Pass LNG notes.
116
Cash Waterfall
Sabine Pass LNG deposited approximately $887 million from the sale of the Sabine Pass LNG notes in a construction account. Until the Phase 1 Target Completion (as defined below), this amount will be applied only to pay construction and startup costs of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and to pay other expenses (including taxes) incidental for Sabine Pass LNG to complete construction of the terminal. “Phase 1 Target Completion” is the time when Phase 1 has been successfully completed in accordance with the target completion date performance standards set forth in the EPC agreement with Bechtel, which is currently defined to be the time when Sabine Pass LNG has completed construction and commissioning of the first two tanks, completed related equipment installation and precommissioning checks and tests, and achieved revaporized natural gas sendout at a rate of 2.0 Bcf/d or more for a continuous period of at least 24 hours.
Following completion of Phase 1, any funds remaining in the construction account that Sabine Pass LNG determines are not necessary to complete construction will be transferred to a revenue sub-account, to be used to make an offer to repurchase the Sabine Pass LNG notes at 100% of their outstanding principal balance, plus accrued interest, and to repurchase any other debt which is pari passu with the Sabine Pass LNG notes containing similar repurchase provisions. Any funds remaining in such revenue sub-account after consummation of the repurchase offer will be transferred to a revenue account. All revenues received by Sabine Pass LNG will be deposited in the revenue account and will be applied as described below under “Pre-Completion Account Flows” and “Post Completion Account Flows.”
Pre-Completion Account Flows
Prior to Phase 1 Target Completion, revenues received by Sabine Pass LNG will be applied in the following manner:
| • | first, to pay obligations, if any, under an assumption agreement executed by Sabine Pass LNG and its affiliates in settlement of certain litigation as described in the indenture; |
| • | second, to the extent that amounts on deposit in the debt service reserve account are not sufficient to pay interest on the Sabine Pass LNG notes on the next interest payment date, to such account in an amount sufficient to make such payment; and |
| • | third, to the construction account to the extent that there are not sufficient funds in the construction account to fund disbursement requests for construction and startup costs of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
Post-Completion Account Flows
After Phase 1 Target Completion, revenues received by Sabine Pass LNG will be applied in the following manner:
| • | first, to fund the operating account with amounts sufficient to cover the succeeding 45 days of operation and maintenance expenses, maintenance capital expenditures and obligations, if any, under the assumption agreement described above and the state tax sharing agreement described under “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions;” |
| • | second, on the 30th day of each month, 1/6th of the amount of interest due on the Sabine Pass LNG notes on the next interest payment date (plus any shortfall from any such month subsequent to the preceding interest payment date) will be transferred to a debt payment account; |
| • | third, to pay outstanding principal then due and payable on the Sabine Pass LNG notes; |
| • | fourth, to pay taxes payable by Sabine Pass LNG or the guarantors of the Sabine Pass LNG notes and permitted payments in respect of taxes; |
| • | fifth, to replenish the debt service reserve account when such account is not funded with the amount (or acceptable letters of credit or acceptable guarantees in respect of such amount) required to make the next interest payment on the Sabine Pass LNG notes; and |
117
| • | sixth, for all other purposes permitted by the indenture, including restricted payments (such as cash distributions), subject to the limitations contained in the indenture. |
Optional Redemption
At any time and from time to time, Sabine Pass LNG may redeem some or all of the Sabine Pass LNG notes at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount plus a make-whole premium, plus accrued and unpaid interest and additional interest, if any, to the redemption date. In addition, until November 30, 2009, Sabine Pass LNG may redeem up to 35% of the aggregate principal amount of each series of notes using the net cash proceeds of one or more equity offerings by Sabine Pass LNG, at par plus a premium equal to the coupon, plus accrued and unpaid interest and additional interest, if any, as long as at least 65% of the aggregate principal amount of the applicable series of notes remains outstanding immediately after the redemption and the redemption occurs within 90 days of the date of the closing of such equity offering.
Repurchase at the Option of Holders
Change of Control. If a change of control of the general partner of Sabine Pass LNG occurs as stated in the indenture, Sabine Pass LNG must offer to repurchase all or any portion of each note at a price equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount of each note repurchased, plus accrued and unpaid interest and additional interest, if any, as of the date of repurchase.
Asset Sales. Sabine Pass LNG is not permitted to consummate certain asset sales, including those to a third party in excess of $5 million, unless it receives consideration equal to the greater of the fair market value of the assets sold and an amount equal to the invested cost of the assets sold and at least 90% of the consideration is in the form of cash, cash equivalents or replacement assets. Within 360 days after the receipt of any net proceeds from a permitted asset sale, Sabine Pass LNG may apply the proceeds to repay senior debt or to make capital expenditures or purchase replacement assets. To the extent that any net proceeds in excess of $25 million are not so applied or invested, Sabine Pass LNG must offer to purchase the Sabine Pass LNG notes at a price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount of each note repurchased, plus accrued and unpaid interest and additional interest, if any, as of the date of repurchase.
Events of Loss. In the event of a loss, destruction or damage of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal or any condemnation, eminent domain, confiscation or requisition of the terminal, or settlement of the foregoing, Sabine Pass LNG is permitted to apply any net loss proceeds to the rebuilding, repair, replacement or construction of improvements to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. With respect to any net loss proceeds in excess of $100 million that are not reinvested (or committed for reinvestment) within 540 days following the event of loss, Sabine Pass LNG must offer to repurchase all or any portion of the Sabine Pass LNG notes at a price equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount of each note repurchased, plus accrued and unpaid interest and additional interest, if any, as of the date of repurchase.
Covenants
The indenture contains covenants that, among other things, limit the ability of Sabine Pass LNG and its restricted subsidiaries to, subject to certain exceptions specified in the indenture:
| • | make certain investments or pay dividends or distributions on Sabine Pass LNG’s equity interests or subordinated indebtedness or purchase or redeem or retire equity interests, as more fully described below under “—Restricted Payments;” |
| • | incur additional indebtedness or issue preferred stock, as more fully described below under “—Indebtedness;” |
| • | sell or transfer assets, including equity interests of Sabine Pass LNG’s restricted subsidiaries, as more fully described above under “—Repurchase at the Option of Holders—Asset Sales;” |
118
| • | incur liens; |
| • | restrict dividends or other payments by restricted subsidiaries; |
| • | consolidate, merge or sell or lease all or substantially all of Sabine Pass LNG’s assets; |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; and |
| • | enter into sale and leaseback transactions. |
Restricted Payments
Sabine Pass LNG will be permitted to pay distributions to its partners, make payments on subordinated debt, purchase any equity interest in an affiliate and make restricted investments using any available cash, as permitted under the indenture, which includes revenues available after payment of construction costs and other capital expenditures, payments of required principal and interest on indebtedness and payment of operation and maintenance expenses. Such payments can be made as long as:
| • | no default or event of default under the indenture has occurred and is continuing; |
| • | Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal has been completed in accordance with the target completion date performance standards set forth in the EPC contract with Bechtel; |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG would be permitted under the fixed charge coverage ratio of 2.0 to 1.0 to incur at least $1.00 of additional indebtedness at the time of the payment and after giving pro forma effect thereto; |
| • | the operating period debt service reserve account has been funded with at least $75 million, which is six months of interest payments; and |
| • | the debt payment account has on deposit the amount required at such time. |
Indebtedness
Pursuant to the indenture, Sabine Pass LNG is not permitted to, directly or indirectly, create, incur, issue, assume, guarantee or otherwise become directly or indirectly liable, contingently or otherwise, with respect to any indebtedness. Notwithstanding the foregoing, Sabine Pass LNG may incur indebtedness if additional equity investments in Sabine Pass LNG are made (other than to redeem or repurchase outstanding indebtedness), in which case Sabine Pass LNG may incur $1.00 of additional indebtedness for each $1.00 so contributed as long as Sabine Pass LNG has received written confirmation from Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. and Standard and Poor’s Ratings Group that there will be no decline in the credit rating on the Sabine Pass LNG notes as a result of the incurrence of such additional indebtedness.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, Sabine Pass LNG is permitted to incur the following indebtedness:
| • | indebtedness represented by the Sabine Pass LNG notes; |
| • | permitted refinancing indebtedness incurred in exchange for, or the net proceeds of which are used to renew, refund, refinance, replace, defease or discharge, any indebtedness (other than intercompany indebtedness) that was permitted by the indenture to be incurred in the first paragraph above or the first, second or fourteenth bullets of this paragraph; |
| • | the issuance by any of Sabine Pass LNG’s restricted subsidiaries to Sabine Pass LNG or to any of its restricted subsidiaries of shares of preferred stock; |
| • | the incurrence, assumption or creation of obligations pursuant to the assumption agreement described in the indenture; |
| • | the incurrence, assumption or creation of obligations pursuant to interest rate and currency hedges; |
| • | the incurrence of a guarantee of indebtedness of Sabine Pass LNG or a restricted subsidiary that was permitted to be incurred by another provision set forth in this paragraph; provided that if the |
119
| indebtedness being guaranteed is subordinated indebtedness, then the guarantee must be subordinated to the same extent as the contractual subordination applicable to the indebtedness guaranteed; |
| • | indebtedness in an amount not to exceed $100.0 million (i) in respect of cost overruns of the construction, cool down, commissioning and completion of Phase 1 and Phase 2 and (ii) to finance the restoration of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal following an event of loss; |
| • | indebtedness in respect of working capital in an amount not to exceed $20.0 million (subject to a temporary increase, in an amount not to exceed $75.0 million, which increase will terminate not later than December 31, 2010, to fund the purchase of LNG for commissioning of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and the entering into by Sabine Pass LNG of any commodity hedging arrangements relating to that LNG); |
| • | indebtedness in respect of workers’ compensation claims, self-insurance obligations, bankers’ acceptances, performance bonds, completion bonds, bid bonds, appeal bonds and surety bonds or other similar bonds or obligations, and any guarantees or letters of credit functioning as, or supporting, any of the foregoing; |
| • | indebtedness arising from the honoring by a bank or other financial institution of a check, draft or similar instrument drawn against insufficient funds in the ordinary course of business; |
| • | indebtedness incurred to the extent that the net proceeds thereof are promptly deposited to defease or to satisfy and discharge the Sabine Pass LNG notes; |
| • | indebtedness consisting of the financing of insurance premiums in customary amounts consistent with the operations and business of Sabine Pass LNG and its restricted subsidiaries in the ordinary course of business; |
| • | subordinated indebtedness between or among Sabine Pass LNG and/or any of its restricted subsidiaries; and |
| • | additional indebtedness in an aggregate principal amount (or accreted value, as applicable) at any time outstanding, including all permitted refinancing indebtedness incurred to renew, refund, refinance, replace, defease or discharge any indebtedness incurred pursuant to this bullet, not to exceed $25.0 million. |
In addition to permitted indebtedness described above, Sabine Pass LNG may incur additional indebtedness (other than parity secured debt) as long as (i) the fixed charge coverage ratio for Sabine Pass LNG’s most recently ended four full fiscal quarters (or if fewer than four fiscal quarters have elapsed since the achievement of Phase 1 Target Completion, the number of full fiscal quarters that have elapsed) for which internal financial statements are available immediately preceding the date on which such additional indebtedness is incurred would have been at least 2.0 to 1.0, determined on a pro forma basis (including a pro forma application of the net proceeds therefrom), as if the additional indebtedness had been incurred at the beginning of such period and (ii) Sabine Pass LNG has received written confirmation from each of Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. and Standard and Poor’s Ratings Group that no ratings decline with respect to the Sabine Pass LNG notes will occur as a result of the incurrence of the additional indebtedness.
The fixed charge coverage ratio means the ratio that the consolidated cash flow, as defined in the indenture, for a given period bears to the fixed charges, as defined in the indenture, for such period. In all cases, the fixed charge coverage ratio gives pro forma effect to the restricted payment or the incurrence of debt proposed to be made as if such payment or incurrence had occurred at the beginning of the applicable four-quarter reference period, and consolidated cash flow or fixed charges attributable to discontinued operations, as determined in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, are excluded from the calculation. For purposes of the indenture, consolidated cash flow means consolidated net income, determined in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, excluding:
| • | dividends declared by a subsidiary that are not actually paid or received in cash; |
| • | the cumulative effect of a change in accounting principles; and |
120
| • | any non-cash mark-to-market adjustment to assets or liabilities resulting in unrealized gains or losses in respect of interest rate or currency hedges; |
but including, to the extent such items were deducted in computing consolidated net income:
| • | any net loss realized in connection with an asset sale; plus |
| • | all extraordinary, unusual or non-recurring items of loss or expense; plus |
| • | provision for taxes based on income or profits; plus |
| • | the fixed charges for such period; plus |
| • | depreciation, amortization (including amortization of intangibles but excluding amortization of prepaid cash expenses that were paid in a prior period) and other non-cash expenses (excluding any such non-cash expense to the extent it represents an accrual of or reserve for cash expenses in any future period); plus |
| • | all non-cash charges related to restricted stock interests granted to officers, directors and employees; minus |
| • | non-cash items increasing consolidated net income, other than the accrual of revenue in the ordinary course of business. |
For purposes of the indenture, fixed charges means the sum, without duplication, of:
| • | beginning April 1, 2009, consolidated interest expense, whether paid or accrued during such period; plus |
| • | beginning April 1, 2009, the consolidated interest expense that was capitalized during such period; plus |
| • | any interest on indebtedness of any other person that is guaranteed by, or secured by a lien on the assets of, Sabine Pass LNG, whether or not the guarantee or lien is called on; plus |
| • | the after-tax cost of all dividends, whether paid or accrued and whether or not in cash, or any series of preferred stock, other than dividends payable solely in equity interests of Sabine Pass LNG or certain subsidiaries of Sabine Pass LNG or paid to Sabine Pass LNG or certain subsidiaries of Sabine Pass LNG. |
In connection with the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a collateral trust agreement, which establishes a trust to hold the collateral pledged to the collateral trustee pursuant to a security agreement, a mortgage, a pledge agreement and a deposit agreement, each described below. The collateral trust agreement also establishes trusts to hold collateral pledged to the collateral trustee to secure (i) certain future indebtedness of Sabine Pass LNG and its subsidiaries as permitted by the indenture governing the Sabine Pass LNG notes, (ii) the issuance of additional notes as permitted by the indenture and (iii) the obligations of Sabine Pass LNG under an assumption agreement described in the indenture.
Security Agreement and Mortgage
In connection with the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a mortgage and a security agreement with the collateral trustee, pursuant to which Sabine Pass LNG has granted to the collateral trustee a first lien on substantially all of its real property interests (consisting principally of leasehold interests and improvements) at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal site and a first lien on substantially all of its personal property as security for its obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes and under an assumption agreement described in the indenture and the other obligations secured under the collateral trust agreement. If an event of default occurs with respect to the Sabine Pass LNG notes, or the obligations under the assumption
121
agreement are not paid when due, the collateral trustee may exercise its rights in such collateral, including any rights of a secured party under the Uniform Commercial Code, which includes the right to sell the collateral at public or private sale. The proceeds received upon realization of the collateral would be applied first to satisfy any outstanding obligations under the assumption agreement and then to pay Sabine Pass LNG’s outstanding obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes and the other obligations secured under the collateral trust agreement.
In connection with the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a pledge agreement with the collateral trustee, Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC, pursuant to which both of Sabine Pass LNG’s general partner and limited partner, each as pledgor, granted the collateral trustee a security interest in each pledgor’s partnership interest in Sabine Pass LNG to secure Sabine Pass LNG’s obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes and the other obligations secured under the collateral trust agreement. If an event of default occurs with respect to the Sabine Pass LNG notes, or the obligations under the assumption agreement are not paid when due, the collateral trustee may exercise its rights in such collateral, including any rights of a secured party under the Uniform Commercial Code, which includes the right to sell the collateral at public or private sale. The proceeds received upon realization of the collateral would be applied first to satisfy any outstanding obligations under the assumption agreement and then to pay Sabine Pass LNG’s outstanding obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes.
In connection with the issuance of the Sabine Pass LNG notes, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a security deposit agreement, pursuant to which Sabine Pass LNG has granted to a depositary agent a security interest in the various project accounts established pursuant to the indenture, including the debt service reserve accounts, the construction account, the revenue account and the operating account to secure the obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes and the other obligations secured under the collateral trust agreement. The security deposit agreement specifies the conditions to be satisfied for the disbursement of funds from the project accounts and requires that the proceeds from certain asset sales and casualty or condemnation awards be deposited into the project accounts, including those described under the caption “—Indenture—Cash Waterfall.” If the funds in a specified project account are not sufficient to pay Sabine Pass LNG’s operation and maintenance expenses or its obligations under the Sabine Pass LNG notes, the security deposit agreement permits the depositary agent to transfer funds among the various project accounts pursuant to the priorities set forth therein for the purpose of paying such obligations.
122
Management of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC, as our general partner, will manage our operations and activities. Our general partner is not elected by our unitholders and will not be subject to re-election on a regular basis in the future. Unitholders will not be entitled to elect the directors of our general partner or to participate directly or indirectly in our management or operation.
Our general partner owes a fiduciary duty to us and our unitholders. Our general partner will be liable, as general partner, for all of our debts (to the extent not paid from our assets), except for indebtedness or other obligations that are made specifically nonrecourse to it. Whenever possible, our general partner intends to incur indebtedness or other obligations that are nonrecourse.
At least three members of the board of directors of our general partner will serve on a conflicts committee to review specific matters that the board believes may involve conflicts of interest. The conflicts committee will determine if the resolution of the conflict of interest is fair and reasonable to us. The members of the conflicts committee may not be securityholders, officers or employees of our general partner or directors, officers, or employees of its affiliates, and must meet the independence and experience standards established by the American Stock Exchange and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and other federal securities laws. Any matters approved by the conflicts committee will be conclusively deemed to be fair and reasonable to us, approved by all of our partners and not a breach by our general partner of any duties that it may owe us or our unitholders.
In addition, the board of directors of our general partner will have an audit committee of at least three directors who meet the independence and experience standards established by the American Stock Exchange and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Messrs McCain and Sutcliffe will serve as the initial members of the audit committee. The audit committee will assist the board in its oversight of the integrity of our financial statements and our compliance with legal and regulatory requirements and partnership policies and controls. The audit committee will have the sole authority to retain and terminate our independent registered public accounting firm, approve all auditing services and related fees and the terms thereof, and pre-approve any non-audit services to be rendered by our independent registered public accounting firm. The audit committee will also be responsible for confirming the independence and objectivity of our independent registered public accounting firm. Our independent registered public accounting firm will be given unrestricted access to the audit committee.
In compliance with the requirements of the American Stock Exchange, the members of the board of directors of our general partner will appoint two independent members to the board upon the closing of this offering and a third independent member within 12 months of the effective date of the registration statement. Messrs. McCain and Sutcliffe, are both independent directors and both will serve as the initial members of the conflicts and audit committees.
We are managed by the directors and officers of our general partner. All of the senior officers of our general partner are also senior officers of Cheniere and will spend a sufficient amount of time overseeing the management, operations, corporate development and future acquisition initiatives of our business. Stanley C. Horton will be the principal executive responsible for the oversight of our affairs. Each of our general partner’s directors and officers spent less than a majority of his or her time on our business in 2006. All of our operational personnel will be employees of Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P., an indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere.
123
Directors and Executive Officers of Our General Partner
We have no employees, directors or officers. We are managed by our general partner, Cheniere GP. The following sets forth information, as of February 10, 2007, regarding the individuals who currently serve on the board of directors, and as officers, of our general partner.
| Name |
Age | Position with Our General Partner | ||
| Charif Souki |
54 | Director, Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Stanley C. Horton |
57 | Director, President and Chief Operating Officer | ||
| Don A. Turkleson |
52 | Director, Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | ||
| Graham A. McArthur |
41 | Treasurer | ||
| Anne V. Vaughan |
40 | Secretary | ||
| Keith M. Meyer |
49 | Director | ||
| Meg Gentle |
32 | Director | ||
| Lon McCain(1) |
59 | Director nominee | ||
| Robert J. Sutcliffe(1) |
55 | Director nominee |
| (1) | Messrs. McCain and Sutcliffe have each consented to serve as a director of our general partner immediately following the closing of this offering. |
Charif Souki is a director and Chief Executive Officer of our general partner. Mr. Souki, a co-founder of Cheniere, is Chairman of Cheniere’s board of directors and Chief Executive Officer of Cheniere. Since December 2002, Mr. Souki has been the Chief Executive Officer of Cheniere, and he was also President of Cheniere from that time until April 2005. From June 1999 to December 2002, he was Chairman of the board of directors of Cheniere and an independent investment banker. From September 1997 until June 1999, he was co-chairman of the board of directors of Cheniere, and he served as Secretary of Cheniere from July 1996 until September 1997. Mr. Souki has over 20 years of independent investment banking experience in the industry and has specialized in providing financing for small capitalization companies with an emphasis on the oil and gas industry. Mr. Souki received a B.A. from Colgate University and an M.B.A. from Columbia University.
Stanley C. Horton is a director and President and Chief Operating Officer of our general partner. Mr. Horton is President and Chief Operating Officer of Cheniere. He has over 30 years of experience in the natural gas and energy industry. From November 2004 to April 2005, when he joined Cheniere, Mr. Horton served as President and Chief Operating Officer of Panhandle Energy, an owner and operator of 18,000 miles of interstate pipelines and the Lake Charles LNG receiving terminal. From June 2003 until November 2004, he was President and Chief Executive Officer of CrossCountry Energy, which holds interests in and operates natural gas pipeline businesses. From 1997 to June 2003, Mr. Horton was Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Enron Transportation Services which had responsibility for all of Enron’s North American interstate natural gas pipeline and transmission line companies. Mr. Horton was Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of EOTT Energy Corp., the general partner of EOTT Energy Partners, L.P., prior to the bankruptcy filings of those entities in October 2002. Mr. Horton currently serves on the Board of Directors for the Interstate Natural Gas Association of America and was its Chairman in 2001. He also has chaired the Gas Industry Standards Board (2000) and the Natural Gas Council (2002). He previously served on the Board of Directors of Portland General Electric, an electric utility, and the Board of Directors of Elektro Eletricidade e Serviços S.A., a local electricity distribution company in Sao Paolo, Brazil. Mr. Horton received a B.S. in finance from the University of Florida and an M.S. in management from Rollins College.
Don A. Turkleson is a director and Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of our general partner. Mr. Turkleson is Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Cheniere. He became a Senior Vice President of Cheniere in May 2004, relinquished the position of Treasurer of Cheniere in December 2004 and relinquished the position of Secretary in September 2006. He had served as Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, Secretary and Treasurer of Cheniere since December 1997. Prior to joining Cheniere in 1997,
124
Mr. Turkleson was employed by PetroCorp Incorporated from 1983 to 1996, as Controller until 1986, then as Vice President—Finance, Secretary and Treasurer. From 1975 to 1983, he worked as a Certified Public Accountant in the natural resources division of Arthur Andersen & Co. in Houston. Mr. Turkleson received a B.S. in accounting from Louisiana State University. He is a director and past Chairman of the Board of Neighborhood Centers, Inc., a nonprofit organization.
Graham A. McArthur is Treasurer of our general partner. Mr. McArthur is Vice President and Treasurer of Cheniere. He became a Vice President of Cheniere in January 2005 and has served as Treasurer of Cheniere since December 2004. Prior to joining Cheniere in 2004, Mr. McArthur was with Westlake Chemical Corporation since 1996, serving most recently as Assistant Treasurer. He began his career in commercial banking in 1987 before moving into a corporate treasury role in 1991. Mr. McArthur received a B.B.A. in finance from Texas A&M University in 1987 and an M.B.A. from the University of Houston in 1990.
Anne V. Vaughan is Secretary of our general partner. Ms. Vaughan is Assistant General Counsel and Secretary of Cheniere. From April 2000 until joining Cheniere in June 2006, she served as an Attorney and a Senior Attorney with Burlington Resources Inc., a large independent oil and gas company acquired by ConocoPhillips in March 2006. From October 1996 to April 2000, Ms. Vaughan was an associate with the law firm of Chamberlain, Hrdlicka, White, Williams & Martin in Houston, Texas. She received a B.S. in psychology from Tulane University and a J.D. from the University of Texas.
Keith M. Meyer is a director of our general partner. Mr. Meyer has served as Senior Vice President—LNG of Cheniere since May 2004. Prior to that time, he was Vice President—LNG of Cheniere from June 2003. He also serves as President of Cheniere LNG, Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, a position he has held since June 2003. From 2000 to 2003, Mr. Meyer was Vice President of Business Development, LNG and Supply for CMS Panhandle Companies, an interstate natural gas transmission system wholly-owned by CMS Energy and owner of Trunkline LNG, an LNG import terminal in Lake Charles, Louisiana. In that capacity, he oversaw all commercial aspects of Trunkline LNG’s activities. Mr. Meyer also served as Executive Director of CMS Energy’s international gas transmission activities. Prior to joining CMS in 1990, Mr. Meyer was with ANR Pipeline Company for 10 years in strategic planning and project development activities, serving also as Vice President of Marketing for the Empire State Pipeline in New York. He received a B.S. in finance from Wayne State University and an M.B.A. from Rice University.
Meg Gentle is a director of our general partner. She has served as Vice President of Strategic Planning of Cheniere since June 2004. Prior to joining Cheniere, Ms. Gentle spent eight years in energy market development, economic evaluation and long-range planning. She conducted international business development and strategic planning for Anadarko Petroleum Corporation, an oil and gas exploration and development company, for six years and energy market analysis for Pace Global Energy Services, an energy management and consulting firm, for two years. Ms. Gentle received her B.A. in economics and international affairs from James Madison University and an M.B.A. from Rice University.
Lon McCain has agreed to serve on our general partner’s board of directors immediately following the closing of this offering as an independent director of our general partner. Mr. McCain was Vice President, Treasurer and Chief Financial Officer of Westport Resources Corporation, a publicly traded exploration and production company, from 2001 until the sale of that company to Kerr-McGee Corporation in 2004. From 1992 until joining Westport, Mr. McCain was Senior Vice President and Principal of Petrie Parkman & Co., an investment banking firm specializing in the oil and gas industry. From 1978 until joining Petrie Parkman, Mr. McCain held senior financial management positions with Presidio Oil Company, Petro-Lewis Corporation and Ceres Capital. He is currently on the board of directors of Transzap, Inc, a provider of digital data and electronic payment solutions, and Crimson Exploration, Inc., an independent oil and gas company. Mr. McCain received a B.S. in business administration and a Masters of Business Administration/Finance from the University of Denver. Mr. McCain was also an Adjunct Professor of Finance at the University of Denver from 1982 to 2005.
125
Robert J. Sutcliffe, a lawyer and business advisor based in Los Angeles, is the Managing Director of Craftsman Capital Advisors LLC, and specializes in representation of entrepreneurs and venture investors. Mr. Sutcliffe was, until 1989, a partner and chairman of the corporate practice group in the Los Angeles office of Brobeck, Phleger & Harrison, where his practice focused on venture capital, corporations and securities. He then served as Congressional Chief of Staff to the Honorable Christopher Cox of California until 1990. He is a director of Innovative Card Technologies, Inc., a public company that develops technologies to enhance payment card functionality. He formerly served as non-executive Chairman of Miravant Medical Technologies, a public pharmaceutical development company. Mr. Sutcliffe received a B.A. in political science and international relations from the University of California, Los Angeles and a J.D. from Harvard Law School.
Executive Officer Compensation
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. and our general partner were formed in November 2006. Our general partner has paid no compensation to its executive officers since inception and has no plans to do so in the future. Officers and employees of our general partner or its affiliates may participate in employee benefit plans and arrangements sponsored by Cheniere and its affiliates, including plans that may be established by Cheniere and its affiliates in the future.
Compensation Discussion and Analysis
Our general partner has paid no cash compensation to its executive officers since inception. All of the executive officers of our general partner are also executive officers of Cheniere. Cheniere compensates these officers for the performance of their duties as executive officers of Cheniere, which will include managing our partnership after this offering. Cheniere will not allocate this compensation between services for us and services for Cheniere and its affiliates. Instead, an affiliate of Cheniere will provide us various general and administrative services following the closing of this offering, such as technical, commercial, regulatory, financial, accounting, treasury, tax and legal staffing and related support services, pursuant to a services agreement for which we will pay a non-accountable administrative fee of $10 million per year, subject to adjustment for inflation, commencing January 1, 2009. Please read “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions—Our Services Agreement.”
As described below under “—Long-Term Incentive Plan,” our general partner intends to adopt a long-term incentive plan for employees, consultants and directors of our general partner and employees and consultants of its affiliates who perform services for our general partner or its affiliates. The plan will provide for the grant of restricted units, phantom units, unit options and unit appreciation rights covering an aggregate of up to common units. The purpose of the plan will be to enhance attraction and retention of qualified individuals who are essential for the successful operation of our partnership and to encourage them to align their interests with our interests through an equity ownership stake in us.
Our general partner has paid no compensation to its directors since inception. Following the completion of this offering, officers or employees of our affiliates who also serve as directors of our general partner will not receive additional compensation. Our general partner anticipates that each independent director will receive compensation for attending meetings of the board of directors, as well as committee meetings. The amount of compensation to be paid to independent directors has not yet been determined. In addition, each non-employee director will be reimbursed for out-of-pocket expenses in connection with attending meetings of the board of directors or committees. Each director will be fully indemnified by us for actions associated with being a director to the extent permitted under Delaware law.
126
Our general partner intends to adopt the Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. Long-Term Incentive Plan for employees, consultants and directors of our general partner and employees and consultants of its affiliates who perform services for our general partner or its affiliates. The long-term incentive plan consists of four components: restricted units, phantom units, unit options and unit appreciation rights. The long-term incentive plan will permit the grant of awards covering an aggregate of common units. The plan will initially be administered by the board of directors of our general partner.
Our general partner’s board of directors, or its compensation committee, in its discretion may initiate, terminate, suspend or discontinue the long-term incentive plan at any time with respect to any award that has not yet been granted. Our general partner’s board of directors, or its compensation committee, also has the right to alter or amend the long-term incentive plan or any part of the plan from time to time, including increasing the number of units that may be granted subject to unitholder approval as required by the exchange upon which the common units are listed at that time. However, no change in any outstanding grant may be made that would materially impair the rights of the participant without the consent of the participant.
Restricted Units and Phantom Units
A restricted unit will be a common unit subject to forfeiture prior to the vesting of the award. A phantom unit will be a notional unit that entitles the grantee to receive a common unit upon the vesting of the phantom unit or, in the discretion of the board or the compensation committee, cash equivalent to the value of a common unit. The board or the compensation committee may determine to make grants under the plan of restricted units and phantom units to employees, consultants and directors containing such terms as the board or the compensation committee shall determine, including unit distribution rights, which entitle the holder to distributions made by us with respect to restricted units, or distribution equivalent rights, which entitle the holder to the equivalent of distributions made by us with respect to phantom units. The board or the compensation committee will determine the period over which restricted units and phantom units granted to employees, consultants and directors will vest. The board or the committee may base its determination upon the achievement of specified financial objectives. In addition, the restricted units and phantom units will vest upon a change of control of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P., our general partner or Cheniere, unless provided otherwise by the board or the compensation committee in the applicable award agreements.
If a grantee’s employment, service relationship or membership on the board of directors terminates for any reason, the grantee’s restricted units and phantom units will be automatically forfeited unless, and to the extent, the board or the compensation committee provides otherwise in the applicable award agreements. Common units to be delivered in connection with the grant of restricted units or upon the vesting of phantom units may be common units acquired by our general partner on the open market, common units already owned by our general partner, common units acquired by our general partner directly from us or any other person or any combination of the foregoing. Our general partner will be entitled to reimbursement by us for the cost incurred in acquiring common units. Thus, the cost of the restricted units and delivery of common units upon the vesting of phantom units will be borne by us. If we issue new common units in connection with the grant of restricted units or upon vesting of the phantom units, the total number of common units outstanding will increase. The board or the compensation committee, in its discretion, may grant tandem distribution rights with respect to restricted units and tandem distribution equivalent rights with respect to phantom units.
Unit Options and Unit Appreciation Rights
The plan will permit the grant of options covering common units and the grant of unit appreciation rights. A unit appreciation right is an award that, upon exercise, entitles the participant to receive the excess of the fair market value of a unit on the exercise date over the exercise price established for the unit appreciation right. Such excess may be paid in common units, cash or a combination thereof, as determined by the board or the compensation
127
committee in its discretion. The board or the compensation committee will be able to make grants of unit options and unit appreciation rights under the plan to employees, consultants and directors containing such terms as the board or the committee shall determine. Unit options and unit appreciation rights may not have an exercise price that is less than the fair market value of the common units on the date of grant. In general, unit options and unit appreciation rights granted will become exercisable over a period determined by the board or the compensation committee in the applicable award agreements. In addition, the unit options and unit appreciation rights will become exercisable upon a change in control of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P., our general partner or Cheniere, unless provided otherwise by the board or the committee in the applicable award agreements.
Upon exercise of a unit option (or a unit appreciation right settled in common units), our general partner will acquire common units on the open market or directly from us or any other person or use common units already owned by our general partner, or any combination of the foregoing. Our general partner will be entitled to reimbursement by us for the difference between the cost incurred by our general partner in acquiring these common units and the proceeds received from a participant at the time of exercise. Thus, the cost of the unit options (or a unit appreciation right settled in common units) will be borne by us. If we issue new common units upon exercise of the unit options (or a unit appreciation right settled in common units), the total number of common units outstanding will increase, and our general partner will pay us the proceeds that it receives from an optionee upon exercise of a unit option. The availability of unit options and unit appreciation rights is intended to furnish additional compensation to employees, consultants and directors and to align their economic interests with those of common unitholders.
Reimbursement of Expenses of Our General Partner
We will reimburse an affiliate of Cheniere for its out-of-pocket costs and expenses and pay such affiliate an administrative fee of $10 million per year (adjusted for inflation after January 1, 2007), with payment commencing January 1, 2009, for its management of us, including the compensation of employees of an affiliate of our general partner that perform services on our behalf following the closing of this offering. These expenses include all expenses necessary or appropriate to conduct our business. Please read “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Uses of Capital—Services Agreements.”
128
CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND
THE SELLING UNITHOLDER
The limited partner interest in our partnership is divided into units. The following table sets forth the beneficial ownership of our units owned of record and beneficially as of February 8, 2007:
| • | each person who beneficially owns more than 5% of the units; |
| • | each of the directors of our general partner; |
| • | each of the named executive officers of our general partner; |
| • | all directors and named executive officers of our general partner as a group; and |
| • | Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC, the selling unitholder, which is an underwriter in this offering for the common units that it sells in this offering. |
The amounts and percentage of units beneficially owned are reported on the basis of regulations of the SEC governing the determination of beneficial ownership of securities. Under the rules of the SEC, a person is deemed to be a “beneficial owner” of a security if that person has or shares “voting power,” which includes the power to vote or to direct the voting of such security, or “investment power,” which includes the power to dispose of or to direct the disposition of such security. A person is also deemed to be a beneficial owner of any securities of which that person has a right to acquire beneficial ownership within 60 days. Under these rules, more than one person may be deemed a beneficial owner of the same securities and a person may be deemed a beneficial owner of securities as to which he has no economic interest.
Except as indicated by footnote, the persons named in the table below have sole voting and investment power with respect to all units shown as beneficially owned by them, subject to community property laws where applicable.
Percentage of beneficial ownership after the transaction is based on the number of units outstanding upon the completion of the offering. The table assumes that the underwriters’ option to purchase additional units is not exercised and excludes any common units purchased in this offering by the respective beneficial owners. The address for the beneficial owners listed below is 717 Texas Avenue, Suite 3100, Houston, Texas 77002.
| Beneficial Ownership Prior to the Offering | Estimated Common Units Offered |
Beneficial Ownership After the Offering | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name of Beneficial |
Common Units |
Percent- age of |
Subor- dinated Units |
Percent- age of |
Total Units | Common Units |
Percent- age of |
Subor- dinated Units |
Percent- age of |
Total Units | ||||||||||||||||
| Cheniere Energy, Inc.(1)(3) |
21,206,026 | 100 | % | 135,383,831 | 100 | % | 156,589,857 | 7,289,669 | 13,916,357 | 52.7 | % | 135,383,831 | 100 | % | 149,300,188 | |||||||||||
| Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC(2)(3) |
21,206,026 | 100 | % | 135,383,831 | 100 | % | 156,589,857 | 7,289,669 | 13,916,357 | 52.7 | % | 135,383,831 | 100 | % | 149,300,188 | |||||||||||
| Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Charif Souki |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Stanley C. Horton |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Don A. Turkleson |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Graham A. McArthur |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Anne V. Vaughan |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Keith M. Meyer |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Meg Gentle |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Lon McCain |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Robert J. Sutcliffe |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| All named executive officers and directors as a group (9 persons) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
129
| (1) | Cheniere Energy, Inc. is the ultimate parent company of Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC and may, therefore, be deemed to beneficially own the units held by Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC. |
| (2) | Prior to this offering, Cheniere Holdings has owned 100% of the equity interests in the entities that own the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Following this offering, Cheniere Holdings will own 100% of the equity interests in our general partner and a 90.4% limited partner interest in us. |
| (3) | The allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder (and the corresponding beneficial ownership of the selling unitholder) will vary based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund the distribution reserve. |
130
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS
After this offering, Cheniere Holdings is expected to own 13,916,357 common units and 135,383,831 subordinated units representing a direct 90.4% limited partner interest in us. In addition, our general partner will own 3,302,045 general partner units representing a 2% general partner interest in us. The allocation of the common units to be sold in this offering between us and the selling unitholder (and the corresponding limited partner interest of the selling unitholder and the public) will vary based on the actual public offering price and our estimated cost to fund the distribution reserve at the time that we price the offering, which we currently believe will be approximately $96.7 million.
Distributions and Payments to Our General Partner and Its Affiliates
The following table summarizes the distributions and payments to be made to our general partner and its affiliates in connection with the formation, ongoing operation and any liquidation of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. These distributions and payments were determined by and among affiliated entities and, consequently, are not the result of arm’s-length negotiations.
Formation Stage
| The consideration received by Cheniere and its subsidiaries for the contribution of the assets and liabilities to us |
13,916,357 common units; |
135,383,831 subordinated units;
3,302,045 general partner units;
the incentive distribution rights; and
approximately $132.0 million in net proceeds of this offering.
Operational Stage
| Distributions of available cash to our general partner and its affiliates |
We will generally make cash distributions 98% to unitholders, including our general partner and its affiliates, as holders of an aggregate of 13,916,357 common units, all of the subordinated units and the remaining 2% to our general partner. |
| In addition, if distributions exceed the initial quarterly distribution and other higher target levels, our general partner will be entitled to increasing percentages of the distributions, up to 50% of the distributions above the highest target level. We refer to the rights to the increasing distributions as “incentive distribution rights.” Please read “How We Make Cash Distributions—Incentive Distribution Rights” for more information regarding the incentive distribution rights. |
131
| Assuming we have sufficient available cash to pay the full initial quarterly distribution on all of our outstanding units, our general partner would receive an annual distribution of approximately $5.6 million on its general partner units and the affiliates of our general partner described above would receive an annual distribution of approximately $253.8 million on their common units and subordinated units. |
| Payments to our general partner and its affiliates |
An affiliate of Cheniere will receive an administrative fee of $10 million per year, as adjusted for inflation after January 1, 2007, commencing January 1, 2009 for general and administrative services for the benefit of our partnership following the closing of this offering. Such affiliate will also be reimbursed for all out-of-pocket costs and expenses incurred on our behalf. |
| Pursuant to the O&M Agreement, Sabine Pass LNG will pay our general partner a fixed monthly fee of $95,000 (indexed for inflation). The fixed monthly fee will increase to $130,000 (indexed for inflation) upon substantial completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and our general partner will thereafter under certain circumstances be entitled to a bonus equal to 50% of the salary component of labor costs. In addition, Sabine Pass LNG is required to reimburse our general partner for its maintenance capital expenditures and operating expenses, which are comprised of labor, maintenance, land lease and insurance expenses. Under the services and secondment agreement, our general partner will pay O&M Services amounts that it receives from Sabine Pass LNG under the O&M Agreement. |
| Pursuant to the Sabine Pass LNG MSA, prior to substantial completion of construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, Sabine Pass LNG will pay its general partner a monthly fixed fee of $340,000 (indexed for inflation); thereafter, the monthly fixed fee will increase to $520,000 (indexed for inflation). Under a management services agreement, the general partner of Sabine Pass LNG pays Cheniere Terminals amounts that it receives from Sabine Pass LNG for management of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
| Withdrawal or removal of our general partner |
If our general partner withdraws or is removed, its general partner interest and its incentive distribution rights will either be sold to the new general partner for cash or converted into common units, in each case for an amount equal to the fair market value of those interests. Please read “The Partnership Agreement—Withdrawal or Removal of Our General Partner.” |
Liquidation Stage
| Liquidation |
Upon our liquidation, the partners, including our general partner, will be entitled to receive liquidating distributions according to their respective capital account balances. |
132
Agreements Governing the Transactions
We, our general partner, our operating subsidiary and other parties have entered into or will enter into the various documents and agreements that will effect the transactions and the application of the proceeds of this offering. These agreements will not be the result of arm’s-length negotiations, and they, or any of the transactions that they provide for, may not be effected on terms at least as favorable to the parties to these agreements as they could have been obtained from unaffiliated third parties. All of the transaction expenses incurred in connection with these transactions will be paid by the selling unitholder.
Pursuant to a contribution agreement to be effective immediately prior to the closing of this offering, Cheniere Holdings will contribute the equity interests in the general and limited partners of Sabine Pass LNG to us in exchange for units. After this contribution, we will subsequently contribute those interests to our wholly-owned subsidiary, Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC. As a result of these transfers, Sabine Pass LNG will become our indirect wholly-owned subsidiary, and we will own the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Please also read “Summary—Formation Transactions and Partnership Structure.”
Pursuant to a 20-year services agreement between us and Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc., or Cheniere Terminals, an affiliate of Cheniere, we will pay Cheniere Terminals an annual administrative fee of $10 million, adjusted for inflation after January 1, 2007, commencing January 1, 2009, for the provision of various general and administrative services for our benefit following the closing of this offering. We will also be required to reimburse Cheniere Terminals for its services in an amount equal to the sum of all out-of-pocket costs and expenses incurred by Cheniere Terminals that are directly related to our business or activities. If we acquire or construct additional assets during the term of the agreement, Cheniere Terminals will propose a revised administrative fee covering the provision of services for such additional assets. If the conflicts committee of our general partner agrees to the revised administrative fee, Cheniere Terminals will provide services for the additional assets pursuant to the agreement. The $10 million administrative fee includes expenses incurred by Cheniere Terminals to perform all technical, commercial, regulatory, financial, accounting, treasury, tax and legal staffing and related support and all management and other services necessary or reasonably requested on behalf of our partnership by our general partner in order to conduct our business as contemplated by our partnership agreement. The fee does not include reimbursements for direct expenses that Cheniere Terminals incurs on our behalf, such as salaries of operational personnel performing services on-site at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and the cost of their employee benefits, including 401(k) plan, pension and health insurance benefits.
Sabine Pass LNG Operation and Maintenance Agreement
In February 2005, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an Operation and Maintenance Agreement, or O&M Agreement, with Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P., or O&M Services, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere. Pursuant to the O&M Agreement, O&M Services has agreed to provide all necessary services required to construct, operate and maintain the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. The O&M Agreement will remain in effect until 20 years after substantial completion of the facility. Prior to substantial completion of the facility, Sabine Pass LNG is required to pay a fixed monthly fee of $95,000 (indexed for inflation). The fixed monthly fee will increase to $130,000 (indexed for inflation) upon substantial completion of the facility, and O&M Services will thereafter in certain circumstances be entitled to a bonus equal to 50% of the salary component of labor costs. In addition, Sabine Pass LNG is required to reimburse O&M Services for its operating expenses, which consist of labor, maintenance, land lease and insurance expenses, and for maintenance capital expenditures. Approval of this agreement was negotiated with the lenders under the then-existing Sabine Pass LNG credit facility and, because Sabine Pass LNG did not otherwise ascertain market terms, may not be on terms as favorable to Sabine Pass LNG as could have been obtained from an unaffiliated third party. Pursuant to the O&M Agreement, Sabine Pass LNG paid O&M Services $868,571 for services provided during 2005 and $1,140,000 for services provided during 2006.
133
At or near the closing of this offering, O&M Services will assign the O&M Agreement to our general partner, and O&M Services and our general partner will enter into a services and secondment agreement pursuant to which we anticipate that certain employees of O&M Services will be seconded to our general partner to provide operating and routine maintenance services with respect to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal under the direction, supervision and control of our general partner. Under this agreement, our general partner will pay O&M Services amounts that it receives from Sabine Pass LNG under the O&M Agreement. The services and secondment agreement will remain in effect until the O&M Agreement is terminated; however, our general partner may terminate the agreement upon 30 days written notice.
Sabine Pass LNG Management Services Agreement
In February 2005, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a Management Services Agreement, or the Sabine Pass LNG MSA, with its general partner, Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc., which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of us. Pursuant to the Sabine Pass LNG MSA, Sabine Pass LNG appointed its general partner to manage the construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, excluding those matters provided for under the O&M Agreement. The Sabine Pass LNG MSA terminates 20 years after the commercial start date set forth in the Total TUA. Prior to substantial completion of construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving facility, Sabine Pass LNG is required to pay its general partner a monthly fixed fee of $340,000 (indexed for inflation); thereafter, the monthly fixed fee will increase to $520,000 (indexed for inflation). Approval of this agreement was negotiated with the lenders under the then-existing Sabine Pass LNG credit facility and, because Sabine Pass LNG did not otherwise ascertain market terms, may not be on terms as favorable to Sabine Pass LNG as could have been obtained from an unaffiliated third party. Pursuant to the Sabine Pass LNG MSA, Sabine Pass LNG paid its general partner $3,109,000 for services provided during 2005 and $4,080,000 for services provided during 2006.
Sabine Pass LNG General Partner Management Services Agreement
In September 2006, Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. entered into a Management Services Agreement, or the general partner MSA, with Cheniere Terminals. Pursuant to the general partner MSA, Cheniere Terminals provides to the general partner the technical, financial, staffing and related support necessary to allow it to meet its obligations to Sabine Pass LNG under the Sabine Pass LNG MSA. Under the general partner MSA, Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. will pay Cheniere Terminals amounts that it receives from Sabine Pass LNG for management of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Because this is a pass-through agreement, it may not be on terms as favorable to Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. as could have been obtained from an unaffiliated third party. During 2006, Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. has incurred $1,360,000 under the general partner MSA.
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an amended and restated TUA with Cheniere Marketing for the reservation of approximately 2.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. See “Business—Customers—Cheniere Marketing TUA.”
In November 2006, Cheniere Marketing entered into a letter agreement with Cheniere LNG, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG pursuant to which Cheniere Marketing has agreed to relinquish up to 200 Mmcf/d of its regasification capacity (and proportionately reduce its fixed monthly fee) under the Cheniere Marketing TUA if required to allow Sabine Pass LNG to satisfy its obligations under a potential TUA with J&S Cheniere S.A., or J&S Cheniere. J&S Cheniere is a Swiss company in which Cheniere holds a minority interest. This arrangement stems from a 2003 option agreement between Cheniere LNG, Inc. and J&S Cheniere pursuant to which J&S Cheniere has an option to negotiate a TUA for up to 200 Mmcf/d of regasification capacity and proportional LNG storage at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. The terms of the potential TUA contemplated by the J&S Cheniere option agreement have not been negotiated or finalized, and Cheniere has publicly disclosed its anticipation that
134
definitive arrangements with J&S Cheniere may involve different terms and transaction structures than were contemplated when the option agreement was entered into in December 2003.
Under a settlement agreement dated as of June 14, 2001, Cheniere and affiliated entities engaged in the LNG business, including us and our subsidiaries, have agreed to pay a royalty, which we refer to as the Crest Royalty. The Crest Royalty is calculated based on the volume of natural gas processed through covered LNG facilities and is subject to a maximum of $10.95 million per production year beginning when natural gas is first commercially processed through a covered facility.
We do not expect to pay any Crest Royalty amounts at any time for two reasons:
| • | Freeport LNG, L.P., in which Cheniere holds a 30% limited partner interest and which we refer to as Freeport LNG, has assumed the obligation to pay the Crest Royalty based on natural gas processed at Freeport LNG’s receiving terminal. The maximum annual Crest Royalty payment of $10.95 million per contract year is payable if approximately 1.0 Bcf/d is processed. Freeport LNG has entered into TUAs with ConocoPhillips Company and with The Dow Chemical Company, under which capacity payments begin when the Freeport LNG receiving terminal begins commercial operation. The ConocoPhillips TUA reserves capacity of approximately 0.5 Bcf/d initially, which increases to 1.0 Bcf/d in October 2009. The Dow TUA reserves capacity of approximately 0.5 Bcf/d. Freeport LNG has announced that it expects to commence commercial operation in 2008. |
| • | Our ultimate parent company, Cheniere, has agreed to indemnify us against any Crest Royalty obligation and to pay any Crest Royalty amounts that may be due and not paid by Freeport LNG. |
As agreed in the 2001 settlement agreement, Cheniere and affiliated entities engaged in the LNG business, including our partnership, have each entered into an agreement, which we refer to as the Assumption Agreement, under which we each have assumed and adopted the Crest Royalty obligation and have agreed not to create any non-permitted lien, security interest or other encumbrance for borrowed money that is senior to or pari passu with the Crest Royalty obligation. In accordance with this agreement, the payment of any Crest Royalty amount that we may become obligated to pay will be secured by the same collateral as, and payable prior to any payments in respect of, the Sabine Pass LNG notes.
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into a State Tax Sharing Agreement with Cheniere pursuant to which Cheniere has agreed to prepare and file all Texas franchise tax returns which Sabine Pass LNG and Cheniere are required to file on a combined basis and to timely pay the combined tax liability. If Cheniere, in its sole discretion, demands such payment, Sabine Pass LNG will pay to Cheniere an amount equal to the Texas franchise tax that Sabine Pass LNG would be required to pay if its Texas franchise tax liability were computed on a separate company basis. The State Tax Sharing Agreement contains similar provisions for other state and local taxes required to be filed by Cheniere and Sabine Pass LNG on a combined, consolidated or unitary basis. The State Tax Sharing Agreement is effective for tax returns first due on or after January 1, 2008.
135
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST AND FIDUCIARY DUTIES
Conflicts of interest exist and may arise in the future as a result of the relationships between our general partner and its affiliates, including Cheniere, on the one hand, and us and our limited partners, on the other hand. The directors and officers of our general partner have fiduciary duties to manage our general partner in a manner beneficial to its owners. At the same time, our general partner has a fiduciary duty to manage us in a manner beneficial to us and our unitholders. Our partnership agreement contains provisions that modify and limit our general partner’s fiduciary duties to the unitholders. Our partnership agreement also restricts the remedies available to unitholders for actions taken that, without those limitations, might constitute breaches of fiduciary duty.
Whenever a conflict arises between our general partner or its affiliates, on the one hand, and us or any other partner, on the other hand, our general partner will resolve that conflict. Our general partner may, but is not required to, seek the approval of such resolution from the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner. An independent third party is not required to evaluate the fairness of the resolution.
Our general partner will not be in breach of its obligations under the partnership agreement or its duties to us or our unitholders if the resolution of the conflict is:
| • | approved by a majority of the conflicts committee, although our general partner is not obligated to seek such approval; |
| • | approved by the vote of a majority of the outstanding common units, excluding any common units owned by our general partner or any of its affiliates; |
| • | on terms no less favorable to us than those generally being provided to or available from unrelated third parties; or |
| • | fair and reasonable to us, taking into account the totality of the relationships between the parties involved, including other transactions that may be particularly favorable or advantageous to us. |
If our general partner seeks approval from the conflicts committee or does not seek approval from the conflicts committee and the board of directors of our general partner determines that the resolution or course of action taken with respect to the conflict of interest satisfies either of the standards set forth in the third and fourth bullet points above, then, in each case, it will be presumed that, in making its decision, the board of directors acted in good faith, and in any proceeding brought by or on behalf of any limited partner or the partnership, the person bringing or prosecuting such proceeding will have the burden of overcoming such presumption. Unless the resolution of a conflict is specifically provided for in our partnership agreement, our general partner or the conflicts committee may consider any factors that it determines in good faith to consider when resolving a conflict. When our partnership agreement requires someone to act in good faith, it requires that person to believe that he is acting in the best interests of the partnership. Please read “Management—Management of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.” for information about the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner.
Conflicts of interest could arise in the situations described below, among others.
Actions taken by our general partner may affect the amount of cash available to pay distributions to unitholders or accelerate the right to convert subordinated units.
The amount of cash that is available for distributions to unitholders is affected by decisions of our general partner regarding such matters as:
| • | amount and timing of asset purchases and sales; |
| • | cash expenditures; |
136
| • | borrowings; |
| • | issuance of additional units; and |
| • | the creation, reduction or increase of reserves in any quarter. |
In addition, borrowings by us and our affiliates do not constitute a breach of any duty owed by our general partner to our unitholders, including borrowings that have the purpose or effect of:
| • | enabling our general partner or its affiliates to receive distributions on any subordinated units or incentive distribution rights held by them; or |
| • | hastening the expiration of the subordination period. |
For example, in the event that we have not generated sufficient cash from our operations to pay the initial quarterly distribution on our common units and our subordinated units, our partnership agreement permits us to borrow funds, which would enable us to pay this distribution on all outstanding units. Please read “How We Make Cash Distributions—Subordination Period.”
Our partnership agreement provides that we and our subsidiaries may borrow funds from our general partner and its affiliates. Our general partner and its affiliates may not borrow funds from us or our subsidiaries.
Neither our partnership agreement nor any other agreement requires Cheniere to pursue a business strategy that favors us or utilizes our assets or dictates what markets to pursue or grow. Cheniere’s directors and officers have a fiduciary duty to make these decisions in the best interests of the stockholders of Cheniere, which may be contrary to our interests.
Because the officers and certain of the directors of our general partner are also directors and/or officers of Cheniere, such directors and officers have fiduciary duties to Cheniere that may cause them to pursue business strategies that disproportionately benefit Cheniere or which otherwise are not in our best interests.
Our general partner is allowed to take into account the interests of parties other than us, such as Cheniere, in resolving conflicts of interest.
Our partnership agreement contains provisions that reduce the standards to which our general partner would otherwise be held by state fiduciary duty law. For example, our partnership agreement permits our general partner to make a number of decisions in its individual capacity, as opposed to in its capacity as our general partner. This entitles our general partner to consider only the interests and factors that it desires, and it has no duty or obligation to give any consideration to any interest of, or factors affecting, us, our affiliates or any limited partner. Examples include the exercise of its limited call right, its voting rights with respect to the units that it owns, its registration rights and its determination whether or not to consent to any merger or consolidation of the partnership or amendment to the partnership agreement.
Our general partner has limited its liability and reduced its fiduciary duties and has also restricted the remedies available to our unitholders for actions that, without the limitations, might constitute breaches of fiduciary duty.
In addition to the provisions described above, our partnership agreement contains provisions that restrict the remedies available to our unitholders for actions that might otherwise constitute breaches of fiduciary duty. For example, our partnership agreement:
| • | provides that our general partner will not have any liability to us or our unitholders for decisions made in its capacity as a general partner so long as it acted in good faith, meaning that it believed that the decision was in the best interests of our partnership; |
137
| • | generally provides that affiliated transactions and resolutions of conflicts of interest not approved by a majority of the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner and not involving a vote of unitholders must be on terms no less favorable to us than those generally being provided to or available from unrelated third parties or be “fair and reasonable” to us, as determined by our general partner in good faith, and that, in determining whether a transaction or resolution is “fair and reasonable,” our general partner may consider the totality of the relationships between the parties involved, including other transactions that may be particularly favorable or advantageous to us; |
| • | provides that our general partner and its officers and directors will not be liable for monetary damages to us or our limited partners for any acts or omissions unless there has been a final and non-appealable judgment entered by a court of competent jurisdiction determining that our general partner or those other persons acted in bad faith or engaged in fraud, willful misconduct or, in the case of a criminal matter, acted with knowledge that such conduct was criminal; and |
| • | provides that in resolving conflicts of interest, it will be presumed that in making its decision the conflicts committee or the general partner acted in good faith, and in any proceeding brought by or on behalf of any limited partner or us, the person bringing or prosecuting such proceeding will have the burden of overcoming such presumption. |
We do not have any officers or employees and rely solely on officers and employees of our general partner and its affiliates.
Affiliates of our general partner conduct businesses and activities of their own in which we have no economic interest. If these separate activities are significantly greater than our activities, there could be material competition for the time and effort of the officers and employees who provide services to our general partner. The officers of our general partner are not required to work full time on our affairs. These officers are required to devote time to the affairs of Cheniere or its affiliates and are compensated by them for the services rendered to them.
Certain of our general partner’s officers are not required to devote their full time to our business.
All of the senior officers of our general partner are also senior officers of Cheniere and will spend sufficient amounts of their time overseeing the management, operations, corporate development and future acquisition initiatives of our business. Stanley C. Horton will be the principal executive responsible for the oversight of our affairs. Our non-executive directors will devote as much time as is necessary to prepare for and attend board of directors and committee meetings.
Our general partner intends to limit its liability regarding our obligations.
Our general partner intends to limit its liability under contractual arrangements so that the other party has recourse only to our assets and not against our general partner or its assets or any affiliate of our general partner or its assets. Our partnership agreement provides that any action taken by our general partner to limit its or our liability is not a breach of our general partner’s fiduciary duties, even if we could have obtained terms that are more favorable without the limitation on liability.
Common unitholders will have no right to enforce obligations of our general partner and its affiliates under agreements with us.
Any agreements between us, on the one hand, and our general partner and its affiliates, on the other hand, will not grant to the unitholders, separate and apart from us, the right to enforce the obligations of our general partner and its affiliates in our favor.
Contracts between us, on the one hand, and our general partner and its affiliates, on the other hand, will not be the result of arm’s-length negotiations.
Neither our partnership agreement nor any of the other agreements, contracts and arrangements between us and our general partner and its affiliates are or will be the result of arm’s-length negotiations. Our partnership
138
agreement generally provides that any affiliated transaction, such as an agreement, contract or arrangement between us and our general partner and its affiliates, must be:
| • | on terms no less favorable to us than those generally being provided to or available from unrelated third parties; or |
| • | fair and reasonable to us, taking into account the totality of the relationships between the parties involved (including other transactions that may be particularly favorable or advantageous to us). |
Our general partner will determine, in good faith, the terms of any of these transactions entered into after the sale of the common units offered in this offering.
Our general partner and its affiliates will have no obligation to permit us to use any facilities or assets of our general partner and its affiliates, except as may be provided in contracts entered into specifically dealing with that use. Our general partner may also enter into additional contractual arrangements with any of its affiliates on our behalf. There is no obligation of our general partner and its affiliates to enter into any contracts of this kind.
Except in limited circumstances, our general partner has the power and authority to conduct our business without unitholder approval.
Under our partnership agreement, our general partner has full power and authority to do all things, other than those items that require unitholder approval or with respect to which our general partner has sought conflicts committee approval, on such terms as it determines to be necessary or appropriate to conduct our business, including, but not limited to, the following:
| • | the making of any expenditures, the lending or borrowing of money, the assumption or guarantee of, or other contracting for, indebtedness and other liabilities, the issuance of evidences of indebtedness, including indebtedness that is convertible into securities of our partnership, and the incurring of any other obligations; |
| • | the making of tax, regulatory and other filings, or rendering of periodic or other reports to governmental or other agencies having jurisdiction over our business or assets; |
| • | the acquisition, disposition, mortgage, pledge, encumbrance, hypothecation or exchange of any or all of our assets or the merger or other combination of us with or into another person subject to any prior approval that may be required under our partnership agreement; |
| • | the use of our assets for any purpose consistent with the terms of our partnership agreement; |
| • | the negotiation, execution and performance of any contracts, conveyances or other instruments; |
| • | the distribution of partnership cash; |
| • | the selection and dismissal of employees and agents, outside attorneys, accountants, consultants and contractors and the determination of their compensation and other terms of employment or hiring; |
| • | the maintenance of insurance for our benefit and the benefit of our partners; |
| • | the formation of, or acquisition of an interest in, and the contribution of property and the making of loans to, any further limited or general partnerships, joint ventures, corporations, limited liability companies or other relationships subject to the restrictions in the partnership agreement; |
| • | the control of any matters affecting our rights and obligations, including the bringing and defending of actions at law or in equity and otherwise engaging in the conduct of litigation, arbitration or mediation and the incurring of legal expense and the settlement of claims and litigation; |
| • | the indemnification of any person against liabilities and contingencies to the extent permitted by law; |
| • | the entering into of listing arrangements with any national securities exchange and the delisting of some or all of our securities from, or requesting that trading be suspended on, any such exchange subject to the limitations specified in our partnership agreement; |
139
| • | the purchase, sale or other acquisition or disposition of our securities, or the issuance of options, rights, warrants and appreciation rights relating to our securities; |
| • | the undertaking of any action in connection with our participation in any affiliate; and |
| • | the entering into of agreements with any of its affiliates to render services to us or to itself in the discharge of its duties as our general partner. |
Please read “The Partnership Agreement” for information regarding the voting rights of unitholders.
Common units are subject to our general partner’s limited call right.
Our general partner may exercise its right to call and purchase common units as provided in the partnership agreement or assign this right to one of its affiliates or to us. Our general partner may use its own discretion, free of fiduciary duty restrictions, in determining whether to exercise this right. As a result, a common unitholder may have his common units purchased from him at an undesirable time or price. Please read “The Partnership Agreement—Limited Call Right.”
We may choose not to retain separate advisors for ourselves or for the holders of common units.
The attorneys, independent accountants and others who perform services for us are selected by our general partner or the conflicts committee and may also perform services for our general partner and its affiliates. We may retain separate counsel for ourselves or the holders of our common units in the event of a conflict of interest between our general partner and its affiliates, on the one hand, and us or the holders of our common units, on the other hand, depending on the nature of the conflict. We do not intend to do so in most cases.
Our general partner’s affiliates may compete with us, and neither our general partner nor its affiliates have any obligation to present business opportunities to us.
Our partnership agreement provides that our general partner will be restricted from engaging in any business activities other than those incidental to its ownership of interests in us. However, affiliates of our general partner are not prohibited from engaging in other businesses or activities, including those that might be in direct competition with us. Cheniere may acquire, construct or dispose of its planned Corpus Christi or Creole Trail LNG receiving terminals, its planned pipelines or other assets in the future without any obligation to offer us the opportunity to purchase or construct any of those assets. In addition, under our partnership agreement, the doctrine of corporate opportunity, or any analogous doctrine, will not apply to the general partner and its affiliates. As a result, neither the general partner nor any of its affiliates will have any obligation to present business opportunities to us and may take advantage of such opportunities themselves.
Our general partner is accountable to us and our unitholders as a fiduciary. Fiduciary duties owed to unitholders by our general partner are prescribed by law and the partnership agreement. The Delaware Revised Uniform Limited Partnership Act, which we refer to as the Delaware Act, provides that Delaware limited partnerships may, in their partnership agreements, expand, restrict or eliminate the fiduciary duties otherwise owed by a general partner to limited partners and the partnership.
Our partnership agreement contains various provisions modifying and restricting the fiduciary duties that might otherwise be owed by our general partner. We have adopted these provisions to allow our general partner or its affiliates to engage in transactions with us that otherwise would be prohibited by state law fiduciary standards and to take into account the interests of other parties in addition to our interests when resolving conflicts of interest. We believe this is appropriate and necessary because the board of directors of our general partner has fiduciary duties to manage our general partner in a manner beneficial both to its indirect owner, Cheniere, as well as to you. Without these modifications, our general partner’s ability to make decisions
140
involving conflicts of interests would be restricted. The modifications to the fiduciary standards benefit our general partner by enabling it to take into consideration all parties involved in the proposed action. These modifications also strengthen the ability of our general partner to attract and retain experienced and capable directors. These modifications represent a detriment to the common unitholders because they restrict the remedies available to unitholders for actions that, without those limitations, might constitute breaches of fiduciary duty, as described below, and permit our general partner to take into account the interests of third parties in addition to our interests when resolving conflicted interests. The following is a summary of:
| • | the fiduciary duties imposed on our general partner by the Delaware Act; |
| • | material modifications of these duties contained in our partnership agreement; and |
| • | certain rights and remedies of unitholders contained in the Delaware Act. |
| State law fiduciary duty standards |
Fiduciary duties are generally considered to include an obligation to act in good faith and with due care and loyalty. The duty of care, in the absence of a provision in a partnership agreement providing otherwise, would generally require a general partner to act for the partnership in the same manner as a prudent person would act on his own behalf. The duty of loyalty, in the absence of a provision in a partnership agreement providing otherwise, would generally prohibit a general partner of a Delaware limited partnership from taking any action or engaging in any transaction where a conflict of interest is present. |
| Partnership agreement modified standards |
Our partnership agreement contains provisions that waive or consent to conduct by our general partner and its affiliates that might otherwise raise issues as to compliance with fiduciary duties or applicable law. For example, Section 7.9 of our partnership agreement provides that when our general partner is acting in its capacity as our general partner, as opposed to in its individual capacity, it must act in “good faith” and will not be subject to any other standard under applicable law. In addition, when our general partner is acting in its individual capacity, as opposed to in its capacity as our general partner, it may act without any fiduciary obligation to us or the unitholders whatsoever. These standards reduce the obligations to which our general partner would otherwise be held. |
| Our partnership agreement generally provides that affiliated transactions and resolutions of conflicts of interest not involving a vote of unitholders and that are not approved by a majority of the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner must be: |
| • | on terms no less favorable to us than those generally being provided to or available from unrelated third parties; or |
| • | fair and reasonable to us, taking into account the totality of the relationships between the parties involved (including other transactions that may be particularly favorable or advantageous to us). |
| If our general partner does not seek approval from the conflicts committee and the board of directors of our general partner determines that the resolution or course of action taken with respect to |
141
| the conflict of interest satisfies either of the standards set forth in the bullet points above, then it will be presumed that, in making its decision, the board of directors, which may include board members affected by the conflict of interest, acted in good faith, and in any proceeding brought by or on behalf of any limited partner or the partnership, the person bringing or prosecuting such proceeding will have the burden of overcoming such presumption. These standards reduce the obligations to which our general partner would otherwise be held. |
| In addition to the other more specific provisions limiting the obligations of our general partner, our partnership agreement further provides that our general partner, its affiliates and their officers and directors will not be liable for monetary damages to us or our limited partners for errors of judgment or any acts or omissions, unless there has been a final and non-appealable judgment by a court of competent jurisdiction determining that our general partner or its officers and directors acted in bad faith or engaged in fraud or willful misconduct or, in the case of a criminal matter, acted with knowledge that the indemnitees’ conduct was criminal. |
| Rights and remedies of unitholders |
The Delaware Act generally provides that a limited partner may institute legal action on behalf of the partnership to recover damages from a third party where a general partner has refused to institute the action or where an effort to cause a general partner to do so is not likely to succeed. These actions include actions against a general partner for breach of its fiduciary duties or of the partnership agreement. In addition, the statutory or case law of some jurisdictions may permit a limited partner to institute legal action on behalf of itself and all other similarly situated limited partners to recover damages from a general partner for violations of its fiduciary duties to the limited partners. |
In order to become one of our limited partners, a common unitholder is required to agree to be bound by the provisions in the partnership agreement, including the provisions discussed above. Please read “Description of the Common Units—Transfer of Common Units.” This is in accordance with the policy of the Delaware Act favoring the principle of freedom of contract and the enforceability of partnership agreements. The failure of a limited partner to sign our partnership agreement does not render the partnership agreement unenforceable against that person.
Under the partnership agreement, we must indemnify our general partner and its officers, directors and members, to the fullest extent permitted by law, against liabilities, costs and expenses incurred by our general partner or these other persons. We must provide this indemnification unless there has been a final and non-appealable judgment by a court of competent jurisdiction determining that these persons acted in bad faith or engaged in fraud or willful misconduct. We also must provide this indemnification for criminal proceedings unless our general partner or these other persons acted with knowledge that their conduct was unlawful. Thus, our general partner could be indemnified for its negligent acts if it meets the requirements set forth above. To the extent that these provisions purport to include indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act, in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is contrary to public policy and therefore unenforceable. If you have questions regarding the fiduciary duties of our general partner, please read “The Partnership Agreement—Indemnification.”
142
DESCRIPTION OF THE COMMON UNITS
The common units and the subordinated units are separate classes of limited partner interests in us. The holders of units are entitled to participate in partnership distributions and exercise the rights or privileges available to limited partners under our partnership agreement. For a description of the relative rights and preferences of holders of common units and subordinated units in and to partnership distributions, please read this section and “Cash Distribution Policy and Restrictions on Distributions.” For a description of the rights and privileges of limited partners under our partnership agreement, including voting rights, please read “The Partnership Agreement.”
Duties
U.S. Stock Transfer Corporation will serve as registrar and transfer agent for the common units. We pay all fees charged by the transfer agent for transfers of common units, except the following that must be paid by unitholders:
| • | surety bond premiums to replace lost or stolen certificates, taxes and other governmental charges; |
| • | special charges for services requested by a holder of a common unit; and |
| • | other similar fees or charges. |
There is no charge to unitholders for disbursements of our cash distributions. We will indemnify the transfer agent against all claims and losses that may arise out of all actions of the transfer agent or its agents or subcontractors for their activities in that capacity, except for any liability due to any gross negligence or willful misconduct of the transfer agent or its agents or subcontractors.
Resignation or Removal
The transfer agent may resign, by notice to us, or be removed by us. The resignation or removal of the transfer agent will become effective upon our appointment of a successor transfer agent and registrar and its acceptance of the appointment. If no successor has been appointed and has accepted the appointment within 30 days after notice of the resignation or removal, our general partner may act as the transfer agent and registrar until a successor is appointed.
The transfer of our common units to persons that purchase directly from the underwriters will be accomplished through the proper completion, execution and delivery of a transfer application by the investor. Any later transfers of a common unit will not be recorded by the transfer agent or recognized by us unless the transferee executes and delivers a properly completed transfer application. By executing and delivering a transfer application, the transferee of common units:
| • | becomes the record holder of our common units and is an assignee until admitted into our partnership as a substituted limited partner; |
| • | requests admission as a substituted limited partner in our partnership; |
| • | executes and agrees to comply with and be bound by the terms and conditions of our partnership agreement; |
| • | represents that the transferee has the right, power and authority and, if an individual, the capacity to enter into our partnership agreement; |
143
| • | grants powers of attorney to the officers of our general partner and any liquidator of us as specified in our partnership agreement; and |
| • | makes the waivers and gives the consents and approvals contained in our partnership agreement, such as the approval of all transactions and agreements we are entering into in connection with our formation and this offering. |
An assignee will become a substituted limited partner of our partnership for the transferred common units automatically upon the recording of the transfer on our books and records. Our general partner will cause any unrecorded transfers for which a properly completed and duly executed transfer application has been received to be recorded on our books and records no less frequently than quarterly.
A transferee’s broker, agent or nominee may, but is not obligated to, complete, execute and deliver a transfer application. We are entitled to treat the nominee holder of a common unit as the absolute owner. In that case, the beneficial holder’s rights are limited solely to those that it has against the nominee holder as a result of any agreement between the beneficial owner and the nominee holder.
Common units are securities and are transferable according to the laws governing transfer of securities. In addition to other rights acquired upon transfer, the transferor gives the transferee the right to request admission as a substituted limited partner in our partnership for the transferred common units. A purchaser or transferee of common units who does not execute and deliver a properly completed transfer application obtains only:
| • | the right to negotiate the common units to a purchaser or other transferee; and |
| • | the right to transfer the right to request admission as a substituted limited partner in our partnership for the transferred common units. |
Thus, a purchaser or transferee of common units who does not execute and deliver a properly completed transfer application:
| • | will not receive cash distributions; |
| • | will not be allocated any of our income, gain, deduction, losses or credits for federal income tax or other tax purposes; |
| • | may not receive some federal income tax information or reports furnished to record holders of common units; and |
| • | will have no voting rights; |
unless the common units are held in a nominee or “street name” account and the nominee or broker has executed and delivered a transfer application and certification as to itself and any beneficial holders.
The transferor of common units has a duty to provide the transferee with all information that may be necessary to transfer the common units. The transferor does not have a duty to ensure the execution of the transfer application by the transferee and has no liability or responsibility if the transferee neglects or chooses not to execute and deliver a properly completed transfer application to the transfer agent. Please read “—Status as Limited Partner or Assignee” below.
Until a common unit has been transferred on our books, we and the transfer agent may treat the record holder of the unit as the absolute owner for all purposes, except as otherwise required by law or stock exchange regulations.
144
The following is a summary of the material provisions of our partnership agreement. The form of our partnership agreement is included in this prospectus as Appendix A. We will provide prospective investors with a copy of the partnership agreement upon request at no charge.
We summarize the following provisions of our partnership agreement elsewhere in this prospectus:
| • | with regard to distributions of available cash, please read “How We Make Cash Distributions;” |
| • | with regard to the fiduciary duties of our general partner, please read “Conflicts of Interest and Fiduciary Duties;” |
| • | with regard to the transfer of common units, please read “Description of the Common Units—Transfer of Common Units;” and |
| • | with regard to allocations of taxable income and taxable loss, please read “Material Tax Consequences.” |
We were organized on November 21, 2006 and have a perpetual existence.
Our purpose under our partnership agreement is to engage in, directly or indirectly, any business activity that is approved by our general partner and in any event that lawfully may be conducted by a limited partnership organized under Delaware law; provided, that our general partner may not cause us to engage, directly or indirectly, in any business activity that our general partner determines would cause us to be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise taxable as an entity for federal income tax purposes. Any decision by our general partner to cause us or our subsidiaries to invest in activities will, to the fullest extent permitted by law, be free from any fiduciary or other duty or obligation whatsoever to us or the limited partners, including any duty to act in good faith or in the best interests of us and our limited partners. In general, our general partner is authorized to perform all acts it determines to be necessary or appropriate to carry out our purposes and to conduct our business.
Each limited partner and each person who acquires a unit from a unitholder and executes and delivers a transfer application grants to our general partner and, if appointed, a liquidator, a power of attorney to, among other things, execute and file documents required for our qualification, continuance or dissolution. The power of attorney also grants our general partner the authority to amend, and to make consents and waivers under, our partnership agreement.
Unitholders are not obligated to make additional capital contributions, except as described below under “—Limited Liability.”
The approval of specified matters requires the limited partner vote specified below. Various matters require the approval of a “unit majority,” which means:
| • | during the subordination period, the approval of a majority of the outstanding common units, excluding those common units held by our general partner and its affiliates, and a majority of the subordinated units, voting as separate classes; and |
| • | after the subordination period, the approval of a majority of the outstanding common units. |
145
In voting their common and subordinated units, our general partner and its affiliates will have no fiduciary duty or obligation whatsoever to us or the limited partners, including any duty to act in good faith or in the best interests of us and our limited partners.
The following is a summary of the vote requirements specified for certain matters under our partnership agreement:
| Issuance of additional units |
During the subordination period, we may not issue any additional common units or units senior to or pari passu with our common units without the approval of the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner. |
| Amendment of our partnership agreement |
Certain amendments may be made by our general partner without the approval of the limited partners. Other amendments generally require the approval of a unit majority. Please read “—Amendment of Our Partnership Agreement.” |
| Merger or conversion of our partnership or the sale of all or substantially all of our assets |
Unit majority in certain circumstances. Please read “—Merger, Conversion, Sale or Other Disposition of Assets.” |
| Dissolution of our partnership |
Unit majority. Please read “—Termination and Dissolution.” |
| Continuation of our partnership upon dissolution |
Unit majority. Please read “—Termination and Dissolution.” |
| Withdrawal of our general partner |
Under most circumstances, the approval of a majority of the common units, excluding common units held by our general partner and its affiliates, is required for the withdrawal of our general partner prior to March 31, 2017 in a manner that would cause a dissolution of our partnership. Please read “—Withdrawal or Removal of Our General Partner.” |
| Removal of our general partner |
Not less than 66 2/3% of the outstanding common and subordinated units, voting as a single class, including common and subordinated units held by our general partner and its affiliates. Please read “—Withdrawal or Removal of Our General Partner.” |
| Transfer of our general partner interest |
Our general partner may transfer all, but not less than all, of its general partner interest in us, without a vote of our limited partners, to an affiliate or to another person in connection with its merger or consolidation with or into, or sale of all or substantially all of its assets to, such person. The approval of a majority of the common units, excluding common units held by our general partner and its affiliates, is required in other circumstances for a transfer of the general partner interest to a third party prior to March 31, 2017. Please read “—Transfer of General Partner Interest.” |
146
| Transfer of incentive distribution rights |
Except for transfers to an affiliate or to another person in connection with our general partner’s merger or consolidation with or into, or sale of all or substantially all of its assets to, such person, the approval of a majority of the common units, excluding common units held by our general partner and its affiliates, is required in most circumstances for a transfer of the incentive distribution rights to a third party prior to March 31, 2017. Please read “—Transfer of Incentive Distribution Rights.” |
| Transfer of ownership interests in our general partner |
No approval required at any time. Please read “—Transfer of Ownership Interests in Our General Partner.” |
We will deposit all of the net proceeds that we receive from this offering as a distribution reserve in a separate account. The deposited amount will be invested in U.S. treasury securities maturing as to principal and interest at such times and in such amounts as will be sufficient to pay the $0.425 initial quarterly distribution per common unit for all common units, as well as related distributions to our general partner, through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. Any net proceeds that we receive in excess of the amount necessary to fund the distribution reserve will be distributed to the selling unitholder, and any shortfall in that amount will be contributed to us by the selling unitholder. In the event that we issue additional common units prior to June 30, 2009, we will use a portion of the net proceeds from such issuance to increase the distribution reserve by an amount that our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines is required to fund the initial quarterly distribution for such additional common units and related general partner units from their date of issuance through the distribution made in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. Any amount remaining in the distribution reserve on August 15, 2009 will be distributed to Cheniere Holdings. We may distribute amounts in the distribution reserve to Cheniere Holdings prior to August 15, 2009 if our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines that such reserves are not necessary to provide for distributions on all of our common units and general partner units for any quarter ending on or prior to June 30, 2009. If we generate cash from operations during the period from the closing of this offering to June 30, 2009, we will make quarterly distributions for our common units from such cash generated from operations and, if the amount of such cash is insufficient to make the full quarterly distribution, from amounts in the distribution reserve.
Assuming that a limited partner does not participate in the control of our business within the meaning of the Delaware Act and that it otherwise acts in conformity with the provisions of our partnership agreement, its liability under the Delaware Act will be limited, subject to possible exceptions, to the amount of capital that it is obligated to contribute to us for its common units plus its share of any undistributed profits and assets. If it were determined, however, that the right of, or exercise of the right by, the limited partners as a group:
| • | to remove or replace our general partner; |
| • | to approve some amendments to our partnership agreement; or |
| • | to take other action under our partnership agreement; |
constituted “participation in the control” of our business for the purposes of the Delaware Act, then the limited partners could be held personally liable for our obligations under the laws of Delaware to the same extent as our
147
general partner. This liability would extend to persons who transact business with us who reasonably believe that the limited partner is a general partner. Neither our partnership agreement nor the Delaware Act specifically provides for legal recourse against our general partner if a limited partner were to lose limited liability through any fault of our general partner. While this does not mean that a limited partner could not seek legal recourse, we know of no precedent for such a claim in Delaware case law.
Under the Delaware Act, a limited partnership may not make a distribution to a partner if, after the distribution, all liabilities of the limited partnership, other than liabilities to partners on account of their partnership interests and liabilities for which the recourse of creditors is limited to specific property of the partnership, would exceed the fair value of the assets of the limited partnership. For the purpose of determining the fair value of the assets of a limited partnership, the Delaware Act provides that the fair value of property subject to liability for which recourse of creditors is limited shall be included in the assets of the limited partnership only to the extent that the fair value of that property exceeds the nonrecourse liability. The Delaware Act provides that a limited partner who receives a distribution and knew at the time of the distribution that the distribution was in violation of the Delaware Act shall be liable to the limited partnership for the amount of the distribution for three years. Under the Delaware Act, an assignee who becomes a substituted limited partner of a limited partnership is liable for the obligations of his assignor to make contributions to the partnership, except the assignee is not obligated for liabilities unknown to him at the time he became a limited partner and that could not be ascertained from our partnership agreement.
We conduct business in two states. We may conduct business in other states in the future. Maintenance of our limited liability may require compliance with legal requirements in the jurisdictions in which Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC conducts business, including qualifying our subsidiaries to do business there. Limitations on the liability of limited partners for the obligations of a limited partnership have not been clearly established in many jurisdictions. If, by virtue of our membership interest in Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC or otherwise, it were determined that we were conducting business in any state without compliance with the applicable limited partnership statute, or that the right of, or exercise of the right, by the limited partners as a group, to remove or replace our general partner, to approve some amendments to our partnership agreement, or to take other action under our partnership agreement constituted “participation in the control” of our business for purposes of the statutes of any relevant jurisdiction, then the limited partners could be held personally liable for our obligations under the law of that jurisdiction to the same extent as our general partner under the circumstances. We will operate in a manner that our general partner considers reasonable and necessary or appropriate to preserve the limited liability of the limited partners.
Issuance of Additional Securities
During the subordination period, we may not issue any additional common units or units senior to or on a parity with our common units without the approval of the conflicts committee of the board of directors of our general partner. For any common units or parity units that we issue prior to June 30, 2009, we must increase the distribution reserve by an amount that our general partner, with the concurrence of the conflicts committee of its board of directors, determines is required to fund the initial quarterly distribution on such additional common units or parity units and related general partner units from their date of issuance through the distribution in respect of the quarter ending June 30, 2009. After the subordination period, our partnership agreement authorizes us to issue an unlimited number of additional partnership securities for the consideration and on the terms and conditions determined by our general partner without the approval of the conflicts committee.
It is possible that we will fund acquisitions through the issuance of additional common units, subordinated units or other partnership securities. Holders of any additional common units we issue will be entitled to share equally with the then-existing holders of common units in our distributions of available cash. In addition, the issuance of additional common units or other partnership securities may dilute the value of the interests of the then-existing holders of common units in our net assets.
148
In accordance with Delaware law and the provisions of our partnership agreement, we may also issue additional partnership securities that, as determined by our general partner, have special voting rights to which the common units are not entitled. In addition, our partnership agreement does not prohibit the issuance by our subsidiaries of equity securities, which may effectively rank senior to the common units.
Upon issuance of additional partnership securities, our general partner will have the right, but not the obligation, to make additional capital contributions to the extent necessary to maintain its 2% general partner interest in us. Our general partner’s 2% interest in us will thus be reduced if we issue additional partnership securities in the future and our general partner does not contribute a proportionate amount of capital to us to maintain its 2% general partner interest. In addition, our general partner will have the right, which it may from time to time assign in whole or in part to any of its affiliates, to purchase common units, subordinated units or other partnership securities to the extent necessary to maintain its and its affiliates’ percentage interest in us, whenever, and on the same terms that, we issue those securities to persons other than our general partner and its affiliates. The holders of common units will not have preemptive rights to acquire additional common units or other partnership securities.
Amendment of Our Partnership Agreement
General
Amendments to our partnership agreement may be proposed only by our general partner. However, our general partner will have no duty or obligation to propose any amendment and may decline to do so free of any fiduciary duty or obligation whatsoever to us or the limited partners, including any duty to act in good faith or in the best interests of us or the limited partners. In order to adopt a proposed amendment, other than the amendments discussed below, our general partner must seek written approval of the holders of the number of units required to approve the amendment or call a meeting of the limited partners to consider and vote upon the proposed amendment. Except as described below, an amendment must be approved by a unit majority.
Prohibited Amendments
No amendment may:
(1) enlarge the obligations of any limited partner without its consent, unless approved by at least a majority of the type or class of limited partner interests so affected; or
(2) enlarge the obligations of, restrict in any way any action by or rights of, or reduce in any way the amounts distributable, reimbursable or otherwise payable by us to our general partner or any of its affiliates without the consent of our general partner, which may be given or withheld at its option.
The provision of our partnership agreement preventing the amendments having the effects described in clauses (1) and (2) above can be amended upon the approval of the holders of at least 90% of the outstanding limited partner units, voting together as a single class (including units owned by our general partner and its affiliates). Upon completion of this offering, affiliates of our general partner will own 92.3% of the outstanding limited partner units (approximately 91.1% if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional common units in full).
No Limited Partner Approval
Our general partner may generally make amendments to the partnership agreement without the approval of any limited partner or assignee to reflect:
| • | a change in our name, the location of our principal place of business, our registered agent or our registered office; |
| • | the admission, substitution, withdrawal or removal of partners in accordance with our partnership agreement; |
149
| • | a change that our general partner determines to be necessary or appropriate for us to qualify or to continue our qualification as a limited partnership or a partnership in which the limited partners have limited liability under the laws of any state or to ensure that we and our subsidiaries will not be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise taxed as an entity for federal income tax purposes; |
| • | an amendment that is necessary, in the opinion of our counsel, to prevent us or our general partner or its directors, officers, trustees or agents from in any manner being subjected to the provisions of the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, or “plan asset” regulations adopted under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, or ERISA, whether or not substantially similar to plan asset regulations currently applied or proposed; |
| • | an amendment that our general partner determines to be necessary or appropriate for the creation, authorization or issuance of additional partnership securities; |
| • | any amendment expressly permitted in our partnership agreement to be made by our general partner acting alone; |
| • | an amendment effected, necessitated or contemplated by a merger agreement that has been approved under the terms of our partnership agreement; |
| • | any amendment that our general partner determines to be necessary or appropriate to reflect and account for our formation of, or our investment in, any corporation, partnership, joint venture, limited liability company or other entity, as otherwise permitted by our partnership agreement; |
| • | a change in our fiscal year or taxable year and related changes; |
| • | mergers with or conveyances to another limited liability entity that is newly formed and has no assets, liabilities or operations at the time of the merger or conveyance other than those it receives by way of the merger or conveyance; or |
| • | any other amendments substantially similar to any of the matters described above. |
In addition, our general partner may make amendments to our partnership agreement without the approval of any limited partner or assignee if our general partner determines that those amendments:
| • | do not adversely affect in any material respect the limited partners considered as a whole or any particular class of limited partners; |
| • | are necessary or appropriate to satisfy any requirements, conditions, or guidelines contained in any opinion, directive, order, ruling, or regulation of any federal or state agency or judicial authority or contained in any federal or state statute; |
| • | are necessary or appropriate to facilitate the trading of limited partner interests or to comply with any rule, regulation, guideline, or requirement of any securities exchange on which the limited partner interests are or will be listed for trading; |
| • | are necessary or appropriate for any action taken by our general partner relating to splits or combinations of units under the provisions of our partnership agreement; or |
| • | are required to effect the intent expressed in this prospectus or the intent of the provisions of our partnership agreement or are otherwise contemplated by our partnership agreement. |
Opinion of Counsel and Limited Partner Approval
Our general partner will not be required to obtain an opinion of counsel that an amendment will not result in a loss of limited liability to the limited partners or result in our being treated as an entity for federal income tax purposes in connection with any of the amendments described under “—No Limited Partner Approval.” No other amendments to our partnership agreement will become effective without the approval of holders of at least 90%
150
of the outstanding limited partner units voting as a single class unless we first obtain an opinion of counsel to the effect that the amendment will not affect the limited liability under Delaware law of any of our limited partners.
In addition to the above restrictions, any amendment that would have a material adverse effect on the rights or preferences of any type or class of outstanding units in relation to other classes of units will require the approval of at least a majority of the type or class of units so affected. Any amendment that reduces the voting percentage required to take any action must be approved by the affirmative vote of limited partners whose aggregate outstanding units constitute not less than the voting requirement sought to be reduced.
Merger, Conversion, Sale or Other Disposition of Assets
A merger, consolidation or conversion of us requires the prior consent of our general partner. However, our general partner will have no duty or obligation to consent to any merger, consolidation or conversion and may decline to do so free of any fiduciary duty or obligation whatsoever to us or the limited partners, including any duty to act in good faith or in the best interest of us or the limited partners.
In addition, our partnership agreement generally prohibits our general partner, without the prior approval of the holders of units representing a unit majority, from causing us to, among other things, sell, exchange or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of our assets in a single transaction or a series of related transactions, including by way of merger, consolidation, other combination, or sale of ownership interests of our subsidiaries. Our general partner may, however, mortgage, pledge, hypothecate or grant a security interest in all or substantially all of our assets without that approval. Our general partner may also sell all or substantially all of our assets under a foreclosure or other realization upon those encumbrances without that approval.
Our general partner may consummate any merger without the prior approval of our limited partners if we are the surviving entity in the transaction, the transaction would not result in a material amendment to our partnership agreement, each of our units will be an identical unit of our partnership following the transaction, the units to be issued do not exceed 20% of our outstanding units immediately prior to the transaction and our general partner has received an opinion of counsel regarding certain limited liability and tax matters.
If the conditions specified in our partnership agreement are satisfied, our general partner may convert us or any of our subsidiaries into a new limited liability entity or merge us or any of our subsidiaries into, or convey all of our assets to, a newly formed entity if our general partner has received an opinion of counsel regarding certain limited liability and tax matters, the sole purpose of that conversion, merger or conveyance is to effect a mere change in our legal form into another limited liability entity and the governing instruments of the new entity provide our partners with the same rights and obligations contained in our partnership agreement. The limited partners are not entitled to dissenters’ rights of appraisal under our partnership agreement or applicable Delaware law in the event of a conversion, merger or consolidation, a sale of substantially all of our assets or any other transaction or event.
We will continue as a limited partnership until terminated under our partnership agreement. We will dissolve upon:
(1) the election of our general partner to dissolve us, if approved by the holders of units representing a unit majority;
(2) at any time there are no limited partners, unless the partnership is continued without dissolution in accordance with the Delaware Act;
(3) the entry of a decree of judicial dissolution of our partnership pursuant to the provisions of the Delaware Act; or
151
(4) the withdrawal or removal of our general partner or any other event that results in its ceasing to be our general partner other than by reason of a transfer of its general partner interest in accordance with our partnership agreement.
Upon a dissolution under clause (4), the holders of a unit majority may also elect, within 180 days thereafter, to reconstitute us and continue our business on the same terms and conditions described in our partnership agreement by appointing as general partner an entity approved by the holders of units representing a unit majority, subject to our receipt of an opinion of counsel to the effect that:
| • | the action would not result in the loss of limited liability under Delaware law of any limited partner; and |
| • | neither our partnership nor any of our subsidiaries would be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise be taxable as an entity for federal income tax purposes upon the exercise of that right to continue (to the extent not already so treated or taxed). |
Liquidation and Distribution of Proceeds
Upon our dissolution, unless we are reconstituted and continued as a new limited partnership, the liquidator authorized to wind up our affairs will, acting with all of the powers of our general partner that are necessary or appropriate, liquidate our assets and apply the proceeds of the liquidation as described in “How We Make Cash Distributions—Distributions of Cash Upon Liquidation.” The liquidator may defer liquidation or distribution of our assets for a reasonable period of time or distribute assets to partners in kind if it determines that an immediate sale would be impractical or would cause undue loss to our partners.
Withdrawal or Removal of Our General Partner
Except as described below, our general partner has agreed not to withdraw voluntarily as our general partner prior to March 31, 2017 without giving 90 days’ notice, obtaining the approval of the holders of at least a majority of the outstanding common units, excluding common units held by our general partner and its affiliates, and furnishing an opinion of counsel regarding limited liability and tax matters. On or after March 31, 2017, our general partner may withdraw as general partner, without first obtaining approval of any unitholder, by giving 90 days’ written notice, and such withdrawal will not constitute a violation of our partnership agreement. Notwithstanding the information above, our general partner may withdraw without common unitholder approval upon 90 days’ notice to the limited partners if at least 50% of the outstanding common units are held or controlled by one person and its affiliates other than our general partner and its affiliates. In addition, our partnership agreement permits our general partner in some instances to sell or otherwise transfer all of its general partner interest in us without the approval of the limited partners. Please read “—Transfer of General Partner Interest” and “—Transfer of Incentive Distribution Rights.”
Upon withdrawal of our general partner under any circumstances, other than as a result of a transfer by our general partner of all or a part of its general partner interest in us, the holders of a unit majority may select a successor to that withdrawing general partner. If a successor is not elected, or is elected but an opinion of counsel regarding limited liability and tax matters cannot be obtained, we will be dissolved, wound up and liquidated, unless within a specified period of time after that withdrawal, the holders of a unit majority agree in writing to continue our business and to appoint a successor general partner. Please read “—Termination and Dissolution.”
Our general partner may not be removed unless that removal is approved by the vote of the holders of not less than 66 2/3% of the outstanding common and subordinated units, voting together as a single class, including units held by our general partner and its affiliates. Any removal of our general partner is also subject to the approval of a successor general partner by the vote of the holders of a majority of the outstanding common units and subordinated units, voting as separate classes. The ownership of more than 33 1/3% of the outstanding common and subordinated units by our general partner and its affiliates would give them the practical ability to prevent our general partner’s removal. At the closing of this offering, affiliates of our general partner will own 92.3% of the outstanding common and subordinated units, in the aggregate (approximately 91.1% if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional common units in full).
152
Our partnership agreement also provides that if our general partner is removed as our general partner under circumstances where cause does not exist and no units held by our general partner and its affiliates are voted in favor of that removal:
| • | the subordination period will end and all outstanding subordinated units will immediately convert into common units on a one-for-one basis; |
| • | any existing arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units will be extinguished; and |
| • | our general partner will have the right to convert its general partner interest and its incentive distribution rights into common units or to receive cash in exchange for those interests based on the fair market value of the interests at the time. |
In the event of removal of our general partner under circumstances where cause exists, or withdrawal of our general partner where that withdrawal violates our partnership agreement, a successor general partner will have the option to purchase the general partner interest and incentive distribution rights of the departing general partner for a cash payment equal to the fair market value of those interests. Under all other circumstances where our general partner withdraws or is removed by the limited partners, the departing general partner will have the option to require the successor general partner to purchase the general partner interest of the departing general partner and its incentive distribution rights for their fair market value. In each case, this fair market value will be determined by agreement between the departing general partner and the successor general partner. If no agreement is reached, an independent investment banking firm or other independent expert selected by the departing general partner and the successor general partner will determine the fair market value. Or, if the departing general partner and the successor general partner cannot agree upon an expert, then an expert chosen by agreement of the experts selected by each of them will determine the fair market value.
If the option described above is not exercised by either the departing general partner or the successor general partner, the departing general partner shall become a limited partner and the departing general partner’s general partner interest and its incentive distribution rights will automatically convert into common units equal to the fair market value of those interests as determined by an investment banking firm or other independent expert selected in the manner described in the preceding paragraph.
In addition, we will be required to reimburse the departing general partner for all amounts due to it, including, without limitation, all employee-related liabilities, including severance liabilities, incurred for the termination of any employees employed by the departing general partner or its affiliates for our benefit.
Transfer of General Partner Interest
Except for the transfer by our general partner of all, but not less than all, of its general partner interest to:
| • | an affiliate of our general partner (other than an individual), or |
| • | another entity in connection with the merger or consolidation of our general partner with or into such other entity or the transfer by our general partner of all or substantially all of its assets to such other entity, |
our general partner may not transfer all or any part of its general partner interest in our partnership to another person prior to March 31, 2017 without the approval of the holders of at least a majority of the outstanding common units, excluding common units held by our general partner and its affiliates. As a condition of this transfer, the transferee must, among other things, assume the rights and duties of our general partner, agree to be bound by the provisions of our partnership agreement and furnish an opinion of counsel regarding limited liability and tax matters.
153
Our general partner and its affiliates may at any time transfer units to one or more persons, without unitholder approval.
Transfer of Ownership Interests in Our General Partner
At any time, the owners of our general partner may sell or transfer all or part of their ownership interests in our general partner to an affiliate or a third party without the approval of our unitholders.
Transfer of Incentive Distribution Rights
Prior to March 31, 2017, our general partner, its affiliates or a subsequent holder may transfer their incentive distribution rights to an affiliate of the holder (other than an individual) or to another entity as part of the merger or consolidation of such holder with or into such entity, the transfer by such holder of all or substantially all of its assets to such entity, or the sale of all of the ownership interest in such holder without the prior approval of the unitholders. Any other transfers of the incentive distribution rights prior to March 31, 2017, will require the affirmative vote of holders of a majority of the outstanding common units, excluding common units held by our general partner and its affiliates. On or after March 31, 2017, the incentive distribution rights will be freely transferable.
Our partnership agreement contains specific provisions that are intended to discourage a person or group from attempting to remove Cheniere GP as our general partner or otherwise change management. If any person or group, other than our general partner and its affiliates, acquires beneficial ownership of 20% or more of any class of units, that person or group loses voting rights on all of its units. This loss of voting rights does not apply to any person or group that acquires the units from our general partner or its affiliates and any transferees of that person or group approved by our general partner provided that our general partner has notified such transferees in writing that the loss of voting rights shall not apply, or to any person or group who acquires the units with the prior approval of the board of directors of our general partner.
Our partnership agreement provides that if our general partner is removed without cause and no units held by our general partner and its affiliates are voted in favor of that removal:
| • | the subordination period will end and all outstanding subordinated units will immediately convert into common units on a one-for-one basis; |
| • | any existing arrearages in payment of the initial quarterly distribution on the common units will be extinguished; and |
| • | our general partner will have the right to convert its general partner interest and its incentive distribution rights into common units or to receive cash in exchange for those interests based on the fair market value of the interests at the time. |
Our partnership agreement also contains specific provisions that are intended to discourage a person or group from attempting to take control of our partnership without the approval of the board of directors of our general partner. Specifically, our partnership agreement provides that we will elect to have Section 203 of the DGCL apply to transactions in which an interested unitholder (as described below) seeks to enter into a merger or business combination with us. Under this provision, such a holder will not be permitted to enter into a merger or business combination with us unless:
| • | prior to the time the unitholder becomes an interested unitholder, the board of directors of our general partner approved either the business combination or the transaction that resulted in the unitholder becoming an interested unitholder; |
| • | upon consummation of the transaction that resulted in the unitholder’s becoming an interested unitholder, the interested unitholder owned at least 85% of our outstanding limited partner units at the |
154
| time the transaction commenced, excluding for purposes of determining the number of common units outstanding those common units owned: |
| • | by persons who are directors and also officers; and |
| • | by employee common unit plans in which employee participants do not have the right to determine confidentially whether common units held subject to the plan will be tendered in a tender or exchange offer; or |
| • |
at or subsequent to such time the business combination is approved by the board of directors of our general partner and authorized at an annual or special meeting of our common unitholders, and not by written consent, by the affirmative vote of the holders of at least 66 2/3% of our outstanding voting common units that are not owned by the interested unitholder. |
With respect to our partnership, a “business combination” under Section 203 of the DGCL would generally include:
| • | any merger or consolidation involving the partnership and the interested unitholder; |
| • | any sale, lease, exchange, mortgage, pledge, transfer or other disposition of 10% or more of the assets of the partnership involving the interested common unitholder; |
| • | subject to certain exceptions, any transaction that results in the issuance or transfer by the partnership of any common units of the partnership to the interested common unitholder; |
| • | any transaction involving the partnership that has the effect of increasing the proportionate share of the units of any class or series of the partnership beneficially owned by the interested common unitholder; or |
| • | the receipt by the interested common unitholder of the benefit of any loans, advances, guarantees, pledges or other financial benefits provided by or through the partnership. |
In general, by reference to Section 203, an “interested common unitholder” is any person or entity, other than our general partner and its affiliates, that beneficially owns (or within three years did own) 15% or more of the outstanding limited partner units of the partnership and any entity or person affiliated or associated with such entity or person.
The existence of this provision is expected to have an anti-takeover effect with respect to transactions not approved in advance by the board of directors of our general partner, thereby discouraging attempts that might result in a premium over the market price for common units held by common unitholders.
If at any time our general partner and its affiliates hold more than 80% of the total limited partner interest of any class then outstanding, our general partner will have the right, which it may assign in whole or in part to any of its affiliates or to us, to acquire all, but not less than all, of the remaining limited partner interests of the class held by unaffiliated persons. Following this offering, affiliates of our general partner will own approximately 52.7% of the common units (approximately 45.6% if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional common units in full). If the subordinated units convert into common units, an affiliate of our general partner will own approximately 92.3% of the common units (approximately 91.1% if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional common units in full).
The purchase price in the event of such an acquisition will be the greater of:
(1) the average of the daily closing prices of the partnership securities of such class over the 20 trading days preceding the date three days before the date the notice is mailed; and
(2) the highest price paid by our general partner or any of its affiliates for any partnership securities of the class purchased within the 90 days preceding the date on which our general partner first mails notice of its election to purchase those partnership securities.
155
As a result of our general partner’s rights to purchase outstanding units, a holder of units may have his units purchased at an undesirable time or price. The tax consequences to a unitholder of the exercise of this call right are the same as a sale by that unitholder of his common units in the market. Please read “Material Tax Consequences—Disposition of Common Units.”
Non-Eligible Citizen; Redemption
If we or any of our subsidiaries is or becomes subject to any federal, state or local law or regulation that our general partner determines would create a substantial risk of cancellation or forfeiture of any property in which we or any of our subsidiaries has an interest based on the nationality, citizenship or other related status of a unitholder, our general partner, acting on our behalf, may at any time require any unitholder to certify that the unitholder is an Eligible Citizen. For this purpose, an Eligible Citizen means a person or entity qualified to hold an interest in real property in jurisdictions in which we or any of our subsidiaries does business or proposes to do business from time to time, and whose status as a unitholder our general partner determines does not or would not subject us or any of our subsidiaries to a significant risk of cancellation or forfeiture of any of its properties or any interest therein.
If a unitholder fails to furnish a citizenship certification containing the required certification within 30 days after request or our general partner determines, with the advice of counsel, that a unitholder is not an Eligible Citizen we will have the right, which we may assign to any of our affiliates, to acquire all but not less than all of the units held by such unitholder. Further, the units will not be entitled to any allocations of income or loss, distributions or voting rights while held by such unitholder.
The purchase price in the event of such an acquisition for each unit held by such unitholder will be equal to the current market price as of the date three days before the date the notice is mailed.
The purchase price will be paid in cash or by delivery of a promissory note, as determined by our general partner. Any such promissory note will bear interest at the rate of 5% annually and be payable in three equal annual installments of principal and accrued interest, commencing one year after the redemption date.
Non-Taxpaying Assignees; Redemption
Our partnership agreement provides that if our general partner, with the advice of counsel, determines that our status as a pass-through entity for federal, state or local income tax purposes, coupled with the tax status (or lack of proof thereof) of one or more of our limited partners, has, or will have, a material adverse effect on our economic interests, then our general partner may, in its sole discretion, adopt such amendments to our partnership agreement as it determines necessary or advisable to:
| • | obtain proof of the federal income tax status of our limited partners (and their owners, to the extent relevant); and |
| • | permit our general partner to redeem the units held by any limited partner whose tax status has or is reasonably likely to have such a material adverse effect or who fails to comply with the procedures instituted by our general partner to obtain proof of the federal income tax status. The redemption price in the case of such a redemption will be the average of the daily closing prices per unit for the 20 consecutive trading days immediately prior to the date set for redemption. |
Except as described below regarding a person or group owning 20% or more of any class of units then outstanding, unitholders or assignees who are record holders of units on the record date will be entitled to notice of, and to vote at, meetings of our limited partners and to act upon matters for which approvals may be solicited. Common units that are owned by an assignee who is a record holder, but who has not yet been admitted as a limited partner, will be voted by our general partner at the written direction of the record holder. Absent direction of this kind, the common units will not be voted.
156
Our general partner does not anticipate that any meeting of unitholders will be called in the foreseeable future. Any action that is required or permitted to be taken by the unitholders may be taken either at a meeting of the unitholders or without a meeting if consents in writing describing the action so taken are signed by holders of the number of units necessary to authorize or take that action at a meeting. Meetings of the unitholders may be called by our general partner or by unitholders owning at least 20% of the outstanding limited partner units of the class for which a meeting is proposed. Unitholders may vote either in person or by proxy at meetings. The holders of a majority of the outstanding units of the class or classes for which a meeting has been called, represented in person or by proxy, will constitute a quorum unless any action by the unitholders requires approval by holders of a greater percentage of the units, in which case the quorum will be the greater percentage.
Each record holder of a unit has a vote according to his percentage interest in us, although additional limited partner interests having special voting rights could be issued. Please read “—Issuance of Additional Securities.” However, if at any time any person or group, other than our general partner and its affiliates, or a direct or subsequently approved transferee of our general partner or its affiliates, acquires, in the aggregate, beneficial ownership of 20% or more of any class of units then outstanding, that person or group will lose voting rights on all of its units and the units may not be voted on any matter and will not be considered to be outstanding when sending notices of a meeting of unitholders, calculating required votes, determining the presence of a quorum, or for other similar purposes. Common units held in nominee or street name account will be voted by the broker or other nominee in accordance with the instruction of the beneficial owner unless the arrangement between the beneficial owner and his nominee provides otherwise. Except as our partnership agreement otherwise provides, subordinated units will vote together with common units as a single class.
Any notice, demand, request, report, or proxy material required or permitted to be given or made to record holders of common units under our partnership agreement will be delivered to the record holder by us or by the transfer agent.
Status as Limited Partner or Assignee
Except as described above under “—Limited Liability,” the common units will be fully paid, and unitholders will not be required to make additional contributions.
An assignee of a common unit, after executing and delivering a transfer application, but pending its admission as a substituted limited partner, is entitled to an interest equivalent to that of a limited partner with respect to allocations and distributions from us, including liquidating distributions. Our general partner will exercise the voting rights attributable to common units owned by an assignee that has not become a substituted limited partner at the written direction of the assignee. Please read “—Meetings; Voting.” An assignee has no other rights of a limited partner. Transferees who do not execute and deliver a transfer application and certification will not be treated as assignees or as record holders of common units, and will not receive cash distributions, federal income tax allocations, or reports furnished to holders of common units. Please read “—Transfer of Common Units.”
Under our partnership agreement we will indemnify the following persons in most circumstances, to the fullest extent permitted by law, from and against all losses, claims, damages, or similar events:
(1) our general partner;
(2) any departing general partner;
(3) any person who is or was an affiliate of our general partner or any departing general partner;
(4) any person who is or was a member, manager, partner, director, officer, fiduciary or trustee of any entity described in (1), (2) or (3) above (other than any person who is or was our limited partner in such person’s capacity as such);
157
(5) any person who is or was serving as an officer, director, member, manager, partner, fiduciary or trustee of another person at the request of our general partner or any departing general partner or any of their affiliates; or
(6) any person designated by our general partner.
Any indemnification under these provisions will only be out of our assets. Unless it otherwise agrees, our general partner will not be personally liable for, or have any obligation to contribute or loan funds or assets to us to enable us to effectuate, indemnification. We may purchase insurance against liabilities asserted against and expenses incurred by persons for our activities, regardless of whether we would have the power to indemnify the person against liabilities under our partnership agreement.
Our partnership agreement requires us to reimburse our general partner or Cheniere LNG Terminals, without duplication, for all direct expenses it incurs or payments it makes on our behalf and all other expenses allocable to us or our subsidiaries or otherwise incurred in connection with operating our business. These expenses include the fees and expenses payable by us pursuant to management services agreements. Please read “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions.”
Our general partner is required to keep appropriate books and records of our business at our principal offices. The books will be maintained for financial reporting purposes on an accrual basis. Our fiscal year is the calendar year.
We will mail or make available (by posting on our website or other reasonable means) to record holders of common units, within 120 days after the close of each fiscal year, an annual report containing audited financial statements and a report on those financial statements by our independent public accountants. Except for our fourth quarter, we will also mail or make available summary financial information within 90 days after the close of each quarter.
We will furnish each record holder of a unit with information reasonably required for tax reporting purposes within 90 days after the close of each calendar year. This information is expected to be furnished in summary form so that some complex calculations normally required of partners can be avoided. Our ability to furnish this summary information to unitholders will depend on the cooperation of unitholders in supplying us with specific information. Every unitholder will receive information to assist him in determining his federal and state tax liability and filing his federal and state income tax returns, regardless of whether he supplies us with information.
Right to Inspect Our Books and Records
Our partnership agreement provides that a limited partner can, for a purpose reasonably related to his interest as a limited partner, upon reasonable written demand and at his own expense, have furnished to him:
(1) a current list of the name and last known address of each partner;
(2) a copy of our tax returns;
(3) information as to the amount of cash, and a description and statement of the agreed value of any other property or services, contributed or to be contributed by each partner and the date on which each became a partner;
(4) copies of our partnership agreement, our certificate of limited partnership, related amendments and powers of attorney under which they have been executed;
158
(5) information regarding the status of our business and financial condition; and
(6) any other information regarding our affairs as is just and reasonable.
Our general partner may, and intends to, keep confidential from the limited partners trade secrets or other information the disclosure of which our general partner believes in good faith is not in our best interests or that we are required by law or by agreements with third parties to keep confidential.
Under our partnership agreement, we have agreed to register for resale under the Securities Act and applicable state securities laws any common units, subordinated units or other partnership securities proposed to be sold by our general partner or any of its affiliates or their assignees if an exemption from the registration requirements is not otherwise available. These registration rights continue for two years following any withdrawal or removal of Cheniere GP as our general partner. We are obligated to pay all expenses incidental to the registration, excluding underwriting discounts and commissions. Please read “Units Eligible for Future Sale.”
159
UNITS ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
After the sale of the common units offered by this prospectus, our general partner and its affiliates will hold, directly and indirectly, an aggregate of 13,916,357 common units and 135,383,831 subordinated units. All of the subordinated units will convert into common units at the end of the subordination period. The sale of these common and subordinated units could have an adverse impact on the price of the common units or on any trading market that may develop.
The common units sold in this offering will generally be freely transferable without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act, except that any common units held by an “affiliate” of ours may not be resold publicly except in compliance with the registration requirements of the Securities Act or under an exemption under Rule 144 or otherwise. Rule 144 permits securities acquired by an affiliate of the issuer to be sold into the market in an amount that does not exceed, during any three month period, the greater of:
| • | 1% of the total number of the securities outstanding; or |
| • | the average weekly reported trading volume of the common units for the four calendar weeks prior to the sale. |
Sales under Rule 144 are also subject to specific manner of sale provisions, holding period requirements, notice requirements and the availability of current public information about us. A person who is not deemed to have been an affiliate of ours at any time during the three months preceding a sale, and who has beneficially owned his common units for at least two years, would be entitled to sell common units under Rule 144 without regard to the public information requirements, volume limitations, manner of sale provisions and notice requirements of Rule 144.
The partnership agreement does not restrict our ability to issue equity securities at any time. Any issuance of additional common units or other equity securities would result in a corresponding decrease in the proportionate ownership interest in us represented by, and could adversely affect the cash distributions to and market price of, common units then outstanding. Please read “The Partnership Agreement—Issuance of Additional Securities.”
Under our partnership agreement, our general partner and its affiliates have the right to cause us to register under the Securities Act and applicable state securities laws the offer and sale of any units that they hold. Subject to the terms and conditions of our partnership agreement, these registration rights allow our general partner and its affiliates or their assignees holding any units to require registration of any of these units and to include any of these units in a registration by us of other units, including units offered by us or by any unitholder. Our general partner will continue to have these registration rights for two years following its withdrawal or removal as our general partner. In connection with any registration of this kind, we will indemnify each unitholder participating in the registration and its officers, directors and controlling persons from and against any liabilities under the Securities Act or any applicable state securities laws arising from the registration statement or prospectus. We will bear all costs and expenses incidental to any registration, excluding any underwriting discounts and commissions. Except as described below, our general partner and its affiliates may sell their units in private transactions at any time, subject to compliance with applicable laws.
We, our subsidiaries and our general partner and its affiliates, including the directors and executive officers of our general partner, have agreed not to sell any common units for a period of 180 days after the date of this prospectus, subject to certain exceptions. Please read “Underwriting” for a description of these lock-up provisions.
160
This section is a discussion of the material tax considerations that may be relevant to prospective unitholders who are individual citizens or residents of the United States and, unless otherwise noted in the following discussion, is the opinion of Andrews Kurth LLP, counsel to our general partner and us, insofar as it relates to matters of United States federal income tax law and legal conclusions with respect to those matters. This section is based upon current provisions of the Internal Revenue Code, existing and proposed regulations and current administrative rulings and court decisions, all of which are subject to change. Later changes in these authorities may cause the tax consequences to vary substantially from the consequences described below. Unless the context otherwise requires, references in this section to “us” or “we” are references to Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. and Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC.
The following discussion does not address all federal income tax matters affecting us or the unitholders. Moreover, the discussion focuses on unitholders who are individual citizens or residents of the United States and has only limited application to corporations, estates, trusts, nonresident aliens or other unitholders subject to specialized tax treatment, such as tax-exempt institutions, foreign persons, individual retirement accounts (IRAs), real estate investment trusts (REITs), employee benefit plans or mutual funds. Accordingly, we urge each prospective unitholder to consult, and depend on, his own tax advisor in analyzing the federal, state, local and foreign tax consequences particular to him of the ownership or disposition of common units.
All statements as to matters of law and legal conclusions, but not as to factual matters, contained in this section, unless otherwise noted, are the opinion of Andrews Kurth LLP and are based on the accuracy of the representations made by us and our general partner.
No ruling has been or will be requested from the IRS regarding any matter affecting us or prospective unitholders. Instead, we will rely on opinions of Andrews Kurth LLP. Unlike a ruling, an opinion of counsel represents only that counsel’s best legal judgment and does not bind the IRS or the courts. Accordingly, the opinions and statements made in this discussion may not be sustained by a court if contested by the IRS. Any contest of this sort with the IRS may materially and adversely impact the market for the common units and the prices at which common units trade. In addition, the costs of any contest with the IRS, principally legal, accounting and related fees, will result in a reduction in cash available for distribution to our unitholders and our general partner and thus will be borne indirectly by our unitholders and our general partner. Furthermore, the tax treatment of us, or of an investment in us, may be significantly modified by future legislative or administrative changes or court decisions. Any modifications may or may not be retroactively applied.
For the reasons described below, Andrews Kurth LLP has not rendered an opinion with respect to the following specific federal income tax issues: the treatment of a unitholder whose common units are loaned to a short seller to cover a short sale of common units (please read “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Treatment of Short Sales”); whether our monthly convention for allocating taxable income and losses is permitted by existing Treasury Regulations (please read “—Disposition of Common Units—Allocations Between Transferors and Transferees”); and whether our method for depreciating Section 743 adjustments is sustainable in certain cases (please read “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Section 754 Election” and “—Uniformity of Units”).
A partnership is not a taxable entity and incurs no federal income tax liability. Instead, each partner of a partnership is required to take into account his share of items of income, gain, loss and deduction of the partnership in computing his federal income tax liability, regardless of whether cash distributions are made to him by the partnership. Distributions by a partnership to a partner are generally not taxable to the partner unless the amount of cash distributed is in excess of the partner’s adjusted basis in his partnership interest.
161
Section 7704 of the Internal Revenue Code provides that publicly traded partnerships will, as a general rule, be taxed as corporations. However, an exception, referred to as the “Qualifying Income Exception,” exists with respect to publicly traded partnerships of which 90% or more of the gross income for every taxable year consists of “qualifying income.” Qualifying income includes income and gains derived from the transportation, storage and processing of crude oil, natural gas and products thereof. Other types of qualifying income include interest (other than from a financial business), dividends, gains from the sale of real property and gains from the sale or other disposition of capital assets held for the production of income that otherwise constitutes qualifying income. We estimate that less than % of our current income is not qualifying income; however, this estimate could change from time to time. Based on and subject to this estimate, the factual representations made by us and our general partner and a review of the applicable legal authorities, Andrews Kurth LLP is of the opinion that at least 90% of our current gross income constitutes qualifying income. The portion of our income that is qualifying income can change from time to time.
No ruling has been or will be sought from the IRS and the IRS has made no determination as to our status for federal income tax purposes or whether our operations generate “qualifying income” under Section 7704 of the Internal Revenue Code. Instead, we will rely on the opinion of Andrews Kurth LLP that, based upon the Internal Revenue Code, its regulations, published revenue rulings and court decisions and the representations described below, we will be classified as a partnership and Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC will be disregarded as an entity separate from us for federal income tax purposes.
In rendering its opinion, Andrews Kurth LLP has relied on factual representations made by us and our general partner. The representations made by us and our general partner upon which Andrews Kurth LLP has relied include:
(a) Neither we nor Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC has elected nor will elect to be treated as a corporation; and
(b) For each taxable year, more than 90% of our gross income will be income that Andrews Kurth LLP has opined or will opine is “qualifying income” within the meaning of Section 7704(d) of the Internal Revenue Code.
If we fail to meet the Qualifying Income Exception, other than a failure that is determined by the IRS to be inadvertent and that is cured within a reasonable time after discovery, we will be treated as if we had transferred all of our assets, subject to liabilities, to a newly formed corporation, on the first day of the year in which we fail to meet the Qualifying Income Exception, in return for stock in that corporation, and then distributed that stock to the unitholders in liquidation of their interests in us. This deemed contribution and liquidation should be tax-free to unitholders and us so long as we, at that time, do not have liabilities in excess of the tax basis of our assets. Thereafter, we would be treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes.
If we were taxable as a corporation in any taxable year, either as a result of a failure to meet the Qualifying Income Exception or otherwise, our items of income, gain, loss and deduction would be reflected only on our tax return rather than being passed through to the unitholders, and our net income would be taxed to us at corporate rates. In addition, any distribution made to a unitholder would be treated as either taxable dividend income, to the extent of our current or accumulated earnings and profits, or, in the absence of earnings and profits, a nontaxable return of capital, to the extent of the unitholder’s tax basis in his common units, or taxable capital gain, after the unitholder’s tax basis in his common units is reduced to zero. Accordingly, taxation as a corporation would result in a material reduction in a unitholder’s cash flow and after-tax return and thus would likely result in a substantial reduction of the value of the units.
The discussion below is based on Andrews Kurth LLP’s opinion that we will be classified as a partnership for federal income tax purposes.
162
Unitholders who have become limited partners of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. will be treated as partners of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. for federal income tax purposes. Also, unitholders whose common units are held in street name or by a nominee and who have the right to direct the nominee in the exercise of all substantive rights attendant to the ownership of their common units will be treated as partners of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. for federal income tax purposes.
A beneficial owner of common units whose units have been transferred to a short seller to complete a short sale would appear to lose his status as a partner with respect to those units for federal income tax purposes. Please read “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Treatment of Short Sales.”
Items of our income, gain, loss and deduction would not appear to be reportable by a unitholder who is not a partner for federal income tax purposes, and any cash distributions received by a unitholder who is not a partner for federal income tax purposes would therefore appear to be fully taxable as ordinary income. These holders are urged to consult their own tax advisors with respect to their tax consequences of holding common units in Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. The references to “unitholders” in the discussion that follow are to persons who are treated as partners in Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership
Flow-Through of Taxable Income. We will not pay any federal income tax. Instead, each unitholder will be required to report on his income tax return his share of our income, gains, losses and deductions without regard to whether corresponding cash distributions are received by him. Consequently, we may allocate income to a unitholder even if he has not received a cash distribution. Each unitholder will be required to include in income his allocable share of our income, gains, losses and deductions for our taxable year ending with or within his taxable year. Our taxable year ends on December 31.
Treatment of Distributions. Distributions by us to a unitholder generally will not be taxable to the unitholder for federal income tax purposes, except to the extent the amount of any such cash distribution exceeds his tax basis in his common units immediately before the distribution. Our cash distributions in excess of a unitholder’s tax basis in his common units generally will be considered to be gain from the sale or exchange of the common units, taxable in accordance with the rules described under “—Disposition of Common Units” below. Any reduction in a unitholder’s share of our liabilities for which no partner, including our general partner, bears the economic risk of loss, known as “nonrecourse liabilities,” will be treated as a distribution of cash to that unitholder. To the extent our distributions cause a unitholder’s “at risk” amount to be less than zero at the end of any taxable year, he must recapture any losses deducted in previous years. Please read “—Limitations on Deductibility of Losses.”
A decrease in a unitholder’s percentage interest in us because of our issuance of additional common units will decrease his share of our nonrecourse liabilities, and thus will result in a corresponding deemed distribution of cash. A non-pro rata distribution of money or property may result in ordinary income to a unitholder, regardless of his tax basis in his common units, if the distribution reduces the unitholder’s share of our “unrealized receivables,” including depreciation recapture, and/or substantially appreciated “inventory items,” both as defined in Section 751 of the Internal Revenue Code, and collectively, “Section 751 Assets.” To that extent, he will be treated as having been distributed his proportionate share of the Section 751 Assets and having exchanged those assets with us in return for the non-pro rata portion of the actual distribution made to him. This latter deemed exchange will generally result in the unitholder’s realization of ordinary income, which will equal the excess of the non-pro rata portion of that distribution over the unitholder’s tax basis for the share of Section 751 Assets deemed relinquished in the exchange.
Ratio of Taxable Income to Distributions. We estimate that a purchaser of common units in this offering who owns those common units from the date of closing of this offering through the record date for distributions
163
for the period ending December 31, 2009, will be allocated an amount of federal taxable income for that period that will be less than % of the cash distributed with respect to that period. We anticipate that after the taxable year ending December 31, 2009, the ratio of allocable taxable income to cash distributions to the unitholders will increase. These estimates are based upon assumptions with respect to the establishment of cash reserves, capital expenditures, cash flow, net working capital and anticipated cash distributions. These estimates and assumptions are subject to, among other things, numerous business, economic, regulatory, competitive and political uncertainties beyond our control. Further, the estimates are based on current tax law and tax reporting positions that we will adopt and with which the IRS could disagree. Accordingly, we cannot assure you that these estimates will prove to be correct. The actual percentage of distributions that will constitute taxable income could be higher or lower than our estimate above, and any differences could be material and could materially affect the value of the common units.
Basis of Common Units. A unitholder’s initial tax basis for his common units will be the amount he paid for the common units plus his share of our nonrecourse liabilities. That basis will be increased by his share of our income and by any increases in his share of our nonrecourse liabilities. That basis will be decreased, but not below zero, by distributions from us, by the unitholder’s share of our losses, by any decreases in his share of our nonrecourse liabilities and by his share of our expenditures that are not deductible in computing taxable income and are not required to be capitalized. A unitholder will have no share of our debt that is recourse to our general partner, but will have a share, generally based on his share of profits, of our nonrecourse liabilities. Please read “—Disposition of Common Units—Recognition of Gain or Loss.”
Limitations on Deductibility of Losses. The deduction by a unitholder of his share of our losses will be limited to the tax basis in his units and, in the case of an individual unitholder or a corporate unitholder, if more than 50% of the value of the corporate unitholder’s stock is owned directly or indirectly by or for five or fewer individuals or some tax-exempt organizations, to the amount for which the unitholder is considered to be “at risk” with respect to our activities, if that amount is less than his tax basis. A unitholder must recapture losses deducted in previous years to the extent that distributions cause his at risk amount to be less than zero at the end of any taxable year. Losses disallowed to a unitholder or recaptured as a result of these limitations will carry forward and will be allowable as a deduction in a later year to the extent that his tax basis or at risk amount, whichever is the limiting factor, is subsequently increased. Upon the taxable disposition of a unit, any gain recognized by a unitholder can be offset by losses that were previously suspended by the at risk limitation but may not be offset by losses suspended by the basis limitation. Any excess loss above that gain previously suspended by the at risk or basis limitations is no longer utilizable.
In general, a unitholder will be at risk to the extent of the tax basis of his units, excluding any portion of that basis attributable to his share of our nonrecourse liabilities, reduced by any amount of money he borrows to acquire or hold his units, if the lender of those borrowed funds owns an interest in us, is related to the unitholder or can look only to the units for repayment. A unitholder’s at risk amount will increase or decrease as the tax basis of the unitholder’s units increases or decreases, other than tax basis increases or decreases attributable to increases or decreases in his share of our nonrecourse liabilities.
The passive loss limitations generally provide that individuals, estates, trusts and some closely-held corporations and personal service corporations are permitted to deduct losses from passive activities, which are generally corporate or partnership activities in which the taxpayer does not materially participate, only to the extent of the taxpayer’s income from those passive activities. The passive loss limitations are applied separately with respect to each publicly traded partnership. Consequently, any passive losses we generate will only be available to offset our passive income generated in the future and will not be available to offset income from other passive activities or investments, including our investments or investments in other publicly traded partnerships, or a unitholder’s salary or active business income. Passive losses that are not deductible because they exceed a unitholder’s share of income we generate may be deducted in full when the unitholder disposes of his entire investment in us in a fully taxable transaction with an unrelated party. The passive activity loss rules are applied after other applicable limitations on deductions, including the at risk rules and the basis limitation.
164
A unitholder’s share of our net income may be offset by any of our suspended passive losses, but it may not be offset by any other current or carryover losses from other passive activities, including those attributable to other publicly traded partnerships.
Limitations on Interest Deductions. The deductibility of a non-corporate taxpayer’s “investment interest expense” is generally limited to the amount of that taxpayer’s “net investment income.” Investment interest expense includes:
| • | interest on indebtedness properly allocable to property held for investment; |
| • | our interest expense attributed to portfolio income; and |
| • | the portion of interest expense incurred to purchase or carry an interest in a passive activity to the extent attributable to portfolio income. |
The computation of a unitholder’s investment interest expense will take into account interest on any margin account borrowing or other loan incurred to purchase or carry a unit. Net investment income includes gross income from property held for investment and amounts treated as portfolio income under the passive loss rules, less deductible expenses, other than interest, directly connected with the production of investment income, but generally does not include gains attributable to the disposition of property held for investment. The IRS has indicated that net passive income earned by a publicly traded partnership will be treated as investment income to its unitholders. In addition, the unitholder’s share of our portfolio income will be treated as investment income.
Entity-Level Collections. If we are required or elect under applicable law to pay any federal, state, local or foreign income tax on behalf of any unitholder or our general partner or any former unitholder, we are authorized to pay those taxes from our funds. That payment, if made, will be treated as a distribution of cash to the partner on whose behalf the payment was made. If the payment is made on behalf of a person whose identity cannot be determined, we are authorized to treat the payment as a distribution to all current unitholders. We are authorized to amend the partnership agreement in the manner necessary to maintain uniformity of intrinsic tax characteristics of units and to adjust later distributions, so that after giving effect to these distributions, the priority and characterization of distributions otherwise applicable under our partnership agreement is maintained as nearly as is practicable. Payments by us as described above could give rise to an overpayment of tax on behalf of an individual unitholder in which event the unitholder would be required to file a claim in order to obtain a credit or refund.
Allocation of Income, Gain, Loss and Deduction. In general, if we have a net profit, our items of income, gain, loss and deduction will be allocated among our general partner and the unitholders in accordance with their percentage interests in us. At any time that distributions are made to the common units in excess of distributions to the subordinated units, or incentive distributions are made to our general partner, gross income will be allocated to the recipients to the extent of these distributions. If we have a net loss for the entire year, that loss will be allocated first to our general partner and the unitholders in accordance with their percentage interests in us to the extent of their positive capital accounts and, second, to our general partner.
Specified items of our income, gain, loss and deduction will be allocated under Section 704(c) to account for the difference between the tax basis and fair market value of property contributed to us by our general partner and its affiliates, referred to in this discussion as “Contributed Property.” These allocations are required by the Internal Revenue Code to eliminate the difference between a partner’s “book” capital account, credited with the fair market value of Contributed Property, and “tax” capital account credited with the tax basis of Contributed Property, referred to in the discussion as the “Book-Tax Disparity.” The effect of these allocations to a unitholder purchasing common units in this offering will be essentially the same as if the tax basis of our assets were equal to their fair market value at the time of this offering. In the event we issue additional common units or engage in certain other transactions in the future, “reverse Section 704(c) allocations,” similar to the Section 704(c) allocations described above, will be made to all holders of partnership interests, including purchasers of common
165
units in this offering, to account for the difference between the “book” basis for purposes of maintaining capital accounts and the fair market value of all property we hold at the time of the future transaction. In addition, items of recapture income will be allocated to the extent possible to the unitholder who was allocated the deduction giving rise to the treatment of that gain as recapture income in order to minimize the recognition of ordinary income by some unitholders. Finally, although we do not expect that our operations will result in the creation of negative capital accounts, if negative capital accounts nevertheless result, items of our income and gain will be allocated in such amount and manner as is needed to eliminate the negative balance as quickly as possible.
An allocation of items of our income, gain, loss or deduction, other than an allocation required by Section 704(c), will generally be given effect for federal income tax purposes in determining a partner’s share of an item of income, gain, loss or deduction only if the allocation has substantial economic effect. In any other case, a partner’s share of an item will be determined on the basis of his interest in us, which will be determined by taking into account all the facts and circumstances, including:
| • | his relative contributions to us; |
| • | the interests of all the partners in profits and losses; |
| • | the interest of all the partners in cash flow; and |
| • | the rights of all the partners to distributions of capital upon liquidation. |
Andrews Kurth LLP is of the opinion that, with the exception of the issues described in “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Section 754 Election,” “—Uniformity of Units” and “—Disposition of Common Units—Allocations Between Transferors and Transferees,” allocations under our partnership agreement will be given effect for federal income tax purposes in determining a partner’s share of an item of income, gain, loss or deduction.
Treatment of Short Sales. A unitholder whose units are loaned to a “short seller” to cover a short sale of units may be considered as having disposed of those units. If so, he would no longer be treated for tax purposes as a partner with respect to those units during the period of the loan and may recognize gain or loss from the disposition. As a result, during this period:
| • | any of our income, gain, loss or deduction with respect to those units would not be reportable by the unitholder; |
| • | any cash distributions received by the unitholder as to those units would be fully taxable; and |
| • | all of these distributions would appear to be ordinary income. |
Andrews Kurth LLP has not rendered an opinion regarding the treatment of a unitholder where common units are loaned to a short seller to cover a short sale of common units; therefore, unitholders desiring to assure their status as partners and avoid the risk of gain recognition from a loan to a short seller are urged to modify any applicable brokerage account agreements to prohibit their brokers from loaning their units. The IRS has announced that it is studying issues relating to the tax treatment of short sales of partnership interests. Please read “—Disposition of Common Units—Recognition of Gain or Loss.”
Alternative Minimum Tax. Each unitholder will be required to take into account his distributive share of any items of our income, gain, loss or deduction for purposes of the alternative minimum tax. The current minimum tax rate for non-corporate taxpayers is 26% on the first $175,000 of alternative minimum taxable income in excess of the exemption amount and 28% on any additional alternative minimum taxable income. Prospective unitholders are urged to consult with their tax advisors as to the impact of an investment in units on their liability for the alternative minimum tax.
Tax Rates. In general, the highest effective United States federal income tax rate for individuals is currently 35% and the maximum United States federal income tax rate for net capital gains of an individual is currently 15% if the asset disposed of was held for more than 12 months at the time of disposition.
166
Section 754 Election. We will make the election permitted by Section 754 of the Internal Revenue Code. That election is irrevocable without the consent of the IRS. The election will generally permit us to adjust a common unit purchaser’s tax basis in our assets (“inside basis”) under Section 743(b) of the Internal Revenue Code to reflect his purchase price. This election does not apply to a person who purchases common units directly from us. The Section 743(b) adjustment belongs to the purchaser and not to other unitholders. For purposes of this discussion, a unitholder’s inside basis in our assets will be considered to have two components: (1) his share of our tax basis in our assets (“common basis”) and (2) his Section 743(b) adjustment to that basis.
Where the remedial allocation method is adopted (which we will adopt, except as we otherwise determine with respect to certain goodwill properties), Treasury Regulations under Section 743 of the Internal Revenue Code require a portion of the Section 743(b) adjustment attributable to recovery property to be depreciated over the remaining cost recovery period for the Section 704(c) built-in gain. If we elect a method other than the remedial method with respect to a goodwill property, Treasury Regulation Section 1.197-2(g)(3) generally requires that the Section 743(b) adjustment attributable to an amortizable Section 197 intangible, which includes goodwill property, should be treated as a newly-acquired asset placed in service in the month when the purchaser acquires the common unit. Under Treasury Regulation Section 1.167(c)-1(a)(6), a Section 743(b) adjustment attributable to property subject to depreciation under Section 167 of the Internal Revenue Code, rather than cost recovery deductions under Section 168, is generally required to be depreciated using either the straight-line method or the 150% declining balance method. If we elect a method other than the remedial method, the depreciation and amortization methods and useful lives associated with the Section 743(b) adjustment, therefore, may differ from the methods and useful lives generally used to depreciate the inside basis in such properties. Under our partnership agreement, our general partner is authorized to take a position to preserve the uniformity of units even if that position is not consistent with these and any other Treasury Regulations. If we elect a method other than the remedial method with respect to a goodwill property, the common basis of such property is not amortizable. Please read “—Uniformity of Units.”
Although Andrews Kurth LLP is unable to opine as to the validity of this approach because there is no controlling authority on this issue, we intend to depreciate the portion of a Section 743(b) adjustment attributable to unrealized appreciation in the value of Contributed Property, to the extent of any unamortized Book-Tax Disparity, using a rate of depreciation or amortization derived from the depreciation or amortization method and useful life applied to the common basis of the property, or treat that portion as non-amortizable to the extent attributable to property the common basis of which is not amortizable. This method is consistent with the methods employed by other publicly traded partnerships but is arguably inconsistent with Treasury Regulation Section 1.167(c)-1(a)(6), which is not expected to directly apply to a material portion of our assets, and Treasury Regulation Section 1.197-2(g)(3). To the extent this Section 743(b) adjustment is attributable to appreciation in value in excess of the unamortized Book-Tax Disparity, we will apply the rules described in the Treasury Regulations and legislative history. If we determine that this position cannot reasonably be taken, we may take a depreciation or amortization position under which all purchasers acquiring units in the same month would receive depreciation or amortization, whether attributable to common basis or a Section 743(b) adjustment, based upon the same applicable rate as if they had purchased a direct interest in our assets. This kind of aggregate approach may result in lower annual depreciation or amortization deductions than would otherwise be allowable to some unitholders. Please read “—Uniformity of Units.” A unitholder’s tax basis for his common units is reduced by his share of our deductions (whether or not such deductions were claimed on an individual’s income tax return) so that any position we take that understates deductions will overstate the unitholder’s basis in his common units, which may cause the unitholder to understate gain or overstate loss on any sale of such units. Please read “—Disposition of Common Units—Recognition of Gain or Loss.” The IRS may challenge our position with respect to depreciating or amortizing the Section 743(b) adjustment we take to preserve the uniformity of the units. If such a challenge were sustained, the gain from the sale of units might be increased without the benefit of additional deductions.
A Section 754 election is advantageous if the transferee’s tax basis in his units is higher than the units’ share of the aggregate tax basis of our assets immediately prior to the transfer. In that case, as a result of the election,
167
the transferee would have, among other items, a greater amount of depreciation deductions and his share of any gain or loss on a sale of our assets would be less. Conversely, a Section 754 election is disadvantageous if the transferee’s tax basis in his units is lower than those units’ share of the aggregate tax basis of our assets immediately prior to the transfer. Thus, the fair market value of the units may be affected either favorably or unfavorably by the election. A basis adjustment is required regardless of whether a Section 754 election is made in the case of a transfer of an interest in us if we have a substantial built-in loss immediately after the transfer, or if we distribute property and have a substantial basis reduction. Generally a basis reduction or a built-in loss is substantial if it exceeds $250,000.
The calculations involved in the Section 754 election are complex and will be made on the basis of assumptions as to the value of our assets and other matters. For example, the allocation of the Section 743(b) adjustment among our assets must be made in accordance with the Internal Revenue Code. The IRS could seek to reallocate some or all of any Section 743(b) adjustment we allocated to our tangible assets to goodwill instead. Goodwill, an intangible asset, is generally nonamortizable or amortizable over a longer period of time or under a less accelerated method than our tangible assets. We cannot assure you that the determinations we make will not be successfully challenged by the IRS and that the deductions resulting from them will not be reduced or disallowed altogether. Should the IRS require a different basis adjustment to be made, and should, in our opinion, the expense of compliance exceed the benefit of the election, we may seek permission from the IRS to revoke our Section 754 election. If permission is granted, a subsequent purchaser of units may be allocated more income than he would have been allocated had the election not been revoked.
Accounting Method and Taxable Year. We use the year ending December 31 as our taxable year and the accrual method of accounting for federal income tax purposes. Each unitholder will be required to include in income his share of our income, gain, loss and deduction for our taxable year ending within or with his taxable year. In addition, a unitholder who has a taxable year ending on a date other than December 31 and who disposes of all of his units following the close of our taxable year but before the close of his taxable year must include his share of our income, gain, loss and deduction in income for his taxable year, with the result that he will be required to include in income for his taxable year his share of more than one year of our income, gain, loss and deduction. Please read “—Disposition of Common Units—Allocations Between Transferors and Transferees.”
Initial Tax Basis, Depreciation and Amortization. The tax basis of our assets will be used for purposes of computing depreciation and cost recovery deductions and, ultimately, gain or loss on the disposition of these assets. The federal income tax burden associated with the difference between the fair market value of our assets and their tax basis immediately prior to this offering will be borne by our general partner and its affiliates. Please read “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Allocation of Income, Gain, Loss and Deduction.”
To the extent allowable, we may elect to use the depreciation and cost recovery methods that will result in the largest deductions being taken in the early years after assets are placed in service. Because we may determine not to adopt the remedial method of allocation with respect to any difference between the tax basis and the fair market value of goodwill at the time of an offering, we may not be entitled to any amortization deductions with respect to any goodwill conveyed to us on formation or held by us at the time of any future offering. Please read “—Uniformity of Units.” Property we subsequently acquire or construct may be depreciated using accelerated methods permitted by the Internal Revenue Code.
If we dispose of depreciable property by sale, foreclosure or otherwise, all or a portion of any gain, determined by reference to the amount of depreciation previously deducted and the nature of the property, may be subject to the recapture rules and taxed as ordinary income rather than capital gain. Similarly, a unitholder who has taken cost recovery or depreciation deductions with respect to property we own will likely be required to recapture some or all of those deductions as ordinary income upon a sale of his interest in us. Please read “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Allocation of Income, Gain, Loss and Deduction” and “—Disposition of Common Units—Recognition of Gain or Loss.”
168
The costs we incur in selling our units (called “syndication expenses”) must be capitalized and cannot be deducted currently, ratably or upon our termination. There are uncertainties regarding the classification of costs as organization expenses, which we may be able to amortize, and as syndication expenses, which we may not amortize. The underwriting discounts and commissions we incur will be treated as syndication expenses.
Valuation and Tax Basis of Our Properties. The federal income tax consequences of the ownership and disposition of units will depend in part on our estimates of the relative fair market values, and the tax bases, of our assets. Although we may from time to time consult with professional appraisers regarding valuation matters, we will make many of the relative fair market value estimates ourselves. These estimates and determinations of basis are subject to challenge and will not be binding on the IRS or the courts. If the estimates of fair market value or basis are later found to be incorrect, the character and amount of items of income, gain, loss or deductions previously reported by unitholders might change, and unitholders might be required to adjust their tax liability for prior years and incur interest and penalties with respect to those adjustments.
Recognition of Gain or Loss. Gain or loss will be recognized on a sale of units equal to the difference between the unitholder’s amount realized and the unitholder’s tax basis for the units sold. A unitholder’s amount realized will be measured by the sum of the cash or the fair market value of other property received by him plus his share of our nonrecourse liabilities. Because the amount realized includes a unitholder’s share of our nonrecourse liabilities, the gain recognized on the sale of units could result in a tax liability in excess of any cash received from the sale.
Prior distributions from us in excess of cumulative net taxable income for a common unit that decreased a unitholder’s tax basis in that common unit will, in effect, become taxable income if the common unit is sold at a price greater than the unitholder’s tax basis in that common unit, even if the price received is less than his original cost.
Except as noted below, gain or loss recognized by a unitholder, other than a “dealer” in units, on the sale or exchange of a unit held for more than one year will generally be taxable as capital gain or loss. Capital gain recognized by an individual on the sale of units held more than 12 months will generally be taxed at a maximum rate of 15%. However, a portion of this gain or loss will be separately computed and taxed as ordinary income or loss under Section 751 of the Internal Revenue Code to the extent attributable to assets giving rise to depreciation recapture or other “unrealized receivables” or to “inventory items” we own. The term “unrealized receivables” includes potential recapture items, including depreciation recapture. Ordinary income attributable to unrealized receivables, inventory items and depreciation recapture may exceed net taxable gain realized on the sale of a unit and may be recognized even if there is a net taxable loss realized on the sale of a unit. Thus, a unitholder may recognize both ordinary income and a capital loss upon a sale of units. Net capital losses may offset capital gains and no more than $3,000 of ordinary income, in the case of individuals, and may only be used to offset capital gains in the case of corporations.
The IRS has ruled that a partner who acquires interests in a partnership in separate transactions must combine those interests and maintain a single adjusted tax basis for all those interests. Upon a sale or other disposition of less than all of those interests, a portion of that tax basis must be allocated to the interests sold using an “equitable apportionment” method, which generally means that the tax basis allocated to the interest sold equals an amount that bears the same relation to the partner’s tax basis in his entire interest in the partnership as the value of the interest sold bears to the value of the partner’s entire interest in the partnership. Treasury Regulations under Section 1223 of the Internal Revenue Code allow a selling unitholder who can identify common units transferred with an ascertainable holding period to elect to use the actual holding period of the common units transferred. Thus, according to the ruling, a common unitholder will be unable to select high or low basis common units to sell as would be the case with corporate stock, but, according to the regulations, may designate specific common units sold for purposes of determining the holding period of units transferred. A
169
unitholder electing to use the actual holding period of common units transferred must consistently use that identification method for all subsequent sales or exchanges of common units. A unitholder considering the purchase of additional units or a sale of common units purchased in separate transactions is urged to consult his tax advisor as to the possible consequences of this ruling and application of the regulations.
Specific provisions of the Internal Revenue Code affect the taxation of some financial products and securities, including partnership interests, by treating a taxpayer as having sold an “appreciated” partnership interest, one in which gain would be recognized if it were sold, assigned or terminated at its fair market value, if the taxpayer or related persons enter(s) into:
| • | a short sale; |
| • | an offsetting notional principal contract; or |
| • | a futures or forward contract with respect to the partnership interest or substantially identical property. |
Moreover, if a taxpayer has previously entered into a short sale, an offsetting notional principal contract or a futures or forward contract with respect to the partnership interest, the taxpayer will be treated as having sold that position if the taxpayer or a related person then acquires the partnership interest or substantially identical property. The Secretary of the Treasury is also authorized to issue regulations that treat a taxpayer that enters into transactions or positions that have substantially the same effect as the preceding transactions as having constructively sold the financial position.
Allocations Between Transferors and Transferees. In general, our taxable income and losses will be determined annually, will be prorated on a monthly basis and will be subsequently apportioned among the unitholders in proportion to the number of units owned by each of them as of the opening of the applicable exchange on the first business day of the month, which we refer to in this prospectus as the “Allocation Date.” However, gain or loss realized on a sale or other disposition of our assets other than in the ordinary course of business will be allocated among the unitholders on the Allocation Date in the month in which that gain or loss is recognized. As a result, a unitholder transferring units may be allocated income, gain, loss and deduction realized after the date of transfer.
The use of this method may not be permitted under existing Treasury Regulations. Accordingly, Andrews Kurth LLP is unable to opine on the validity of this method of allocating income and deductions between unitholders. If this method is not allowed under the Treasury Regulations, or only applies to transfers of less than all of the unitholder’s interest, our taxable income or losses might be reallocated among the unitholders. We are authorized to revise our method of allocation between unitholders, as well as among unitholders whose interests vary during a taxable year, to conform to a method permitted under future Treasury Regulations.
A unitholder who owns units at any time during a quarter and who disposes of them prior to the record date set for a cash distribution for that quarter will be allocated items of our income, gain, loss and deductions attributable to that quarter but will not be entitled to receive that cash distribution.
Notification Requirements. A unitholder who sells any of his units, other than through a broker, generally is required to notify us in writing of that sale within 30 days after the sale (or, if earlier, January 15 of the year following the sale). A purchaser of units who purchases units from another unitholder is generally required to notify us in writing of that purchase within 30 days after the purchase. We are required to notify the IRS of that transaction and to furnish specified information to the transferor and transferee. Failure to notify us of a purchase may, in some cases, lead to the imposition of penalties. However, these reporting requirements do not apply to a sale by an individual who is a citizen of the United States and who effects the sale or exchange through a broker who will satisfy such requirement.
Constructive Termination. We will be considered to have been terminated for tax purposes if there is a sale or exchange of 50% or more of the total interests in our capital and profits within a 12-month period. A
170
constructive termination results in the closing of our taxable year for all unitholders. In the case of a unitholder reporting on a taxable year different from our taxable year, the closing of our taxable year may result in more than 12 months of our taxable income or loss being includable in his taxable income for the year of termination. We would be required to make new tax elections after a termination, including a new election under Section 754 of the Internal Revenue Code, and a termination would result in a deferral of our deductions for depreciation. A termination could also result in penalties if we were unable to determine that the termination had occurred. Moreover, a termination might either accelerate the application of, or subject us to, any tax legislation enacted before the termination.
Because we cannot match transferors and transferees of units, we must maintain uniformity of the economic and tax characteristics of the units to a purchaser of these units. In the absence of uniformity, we may be unable to completely comply with a number of federal income tax requirements, both statutory and regulatory. A lack of uniformity can result from a literal application of Treasury Regulation Section 1.167(c)-1(a)(6) and Treasury Regulation Section 1.197-2(g)(3). Any non-uniformity could have a negative impact on the value of the units. Please read “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Section 754 Election.”
We intend to depreciate the portion of a Section 743(b) adjustment attributable to unrealized appreciation in the value of Contributed Property, to the extent of any unamortized Book-Tax Disparity, using a rate of depreciation or amortization derived from the depreciation or amortization method and useful life applied to the common basis of that property, or treat that portion as nonamortizable, to the extent attributable to property the common basis of which is not amortizable, consistent with the regulations under Section 743 of the Internal Revenue Code, even though that position may be inconsistent with Treasury Regulation Section 1.167(c)-1(a)(6), which is not expected to directly apply to a material portion of our assets, and Treasury Regulation Section 1.197-2(g)(3). Please read “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Section 754 Election.” To the extent that the Section 743(b) adjustment is attributable to appreciation in value in excess of the unamortized Book-Tax Disparity, we will apply the rules described in the Treasury Regulations and legislative history. If we determine that this position cannot reasonably be taken, we may adopt a depreciation and amortization position under which all purchasers acquiring units in the same month would receive depreciation and amortization deductions, whether attributable to a common basis or Section 743(b) adjustment, based upon the same applicable rate as if they had purchased a direct interest in our property. If this position is adopted, it may result in lower annual depreciation and amortization deductions than would otherwise be allowable to some unitholders and risk the loss of depreciation and amortization deductions not taken in the year that these deductions are otherwise allowable. This position will not be adopted if we determine that the loss of depreciation and amortization deductions will have a material adverse effect on the unitholders. If we choose not to utilize this aggregate method, we may use any other reasonable depreciation and amortization method to preserve the uniformity of the intrinsic tax characteristics of any units that would not have a material adverse effect on the unitholders. Our counsel is unable to opine on the validity of any of these positions. The IRS may challenge any method of depreciating the Section 743(b) adjustment described in this paragraph. If this challenge were sustained, the uniformity of units might be affected, and the gain from the sale of units might be increased without the benefit of additional deductions. Please read “—Disposition of Common Units—Recognition of Gain or Loss.”
Tax-Exempt Organizations and Other Investors
Ownership of units by employee benefit plans, other tax-exempt organizations, non-resident aliens, foreign corporations and other foreign persons raises issues unique to those investors and, as described below, may have substantially adverse tax consequences to them.
Employee benefit plans and most other organizations exempt from federal income tax, including individual retirement accounts and other retirement plans, are subject to federal income tax on unrelated business taxable
171
income. Virtually all of our income allocated to a unitholder that is a tax-exempt organization will be unrelated business taxable income and will be taxable to them.
Non-resident aliens and foreign corporations, trusts or estates that own units will be considered to be engaged in business in the United States because of the ownership of units. As a consequence, they will be required to file federal tax returns to report their share of our income, gain, loss or deduction and pay federal income tax at regular rates on their share of our net income or gain. Moreover, under rules applicable to publicly traded partnerships, we will withhold tax at the highest applicable effective tax rate from cash distributions made quarterly to foreign unitholders. Each foreign unitholder must obtain a taxpayer identification number from the IRS and submit that number to our transfer agent on a Form W-8BEN or applicable substitute form in order to obtain credit for these withholding taxes. A change in applicable law may require us to change these procedures.
In addition, because a foreign corporation that owns units will be treated as engaged in a United States trade or business, that corporation may be subject to the United States branch profits tax at a rate of 30%, in addition to regular federal income tax, on its share of our income and gain, as adjusted for changes in the foreign corporation’s “U.S. net equity,” that is effectively connected with the conduct of a United States trade or business. That tax may be reduced or eliminated by an income tax treaty between the United States and the country in which the foreign corporate unitholder is a “qualified resident.” In addition, this type of unitholder is subject to special information reporting requirements under Section 6038C of the Internal Revenue Code.
Under a ruling of the IRS, a foreign unitholder who sells or otherwise disposes of a unit will be subject to federal income tax on gain realized on the sale or disposition of that unit to the extent that this gain is effectively connected with a United States trade or business of the foreign unitholder. Apart from the ruling, a foreign unitholder will not be taxed or subject to withholding upon the sale or disposition of a unit if he has owned less than 5% in value of the units during the five-year period ending on the date of the disposition and if the units are regularly traded on an established securities market at the time of the sale or disposition.
Information Returns and Audit Procedures. We intend to furnish to each unitholder, within 90 days after the close of each taxable year, specific tax information, including a Schedule K-1, which describes his share of our income, gain, loss and deduction for our preceding taxable year. In preparing this information, which will not be reviewed by counsel, we will take various accounting and reporting positions, some of which have been mentioned earlier, to determine each unitholder’s share of income, gain, loss and deduction. We cannot assure you that those positions will in all cases yield a result that conforms to the requirements of the Internal Revenue Code, Treasury Regulations or administrative interpretations of the IRS. Neither we nor Andrews Kurth LLP can assure prospective unitholders that the IRS will not successfully contend in court that those positions are impermissible. Any challenge by the IRS could negatively affect the value of the units.
The IRS may audit our federal income tax information returns. Adjustments resulting from an IRS audit may require each unitholder to adjust a prior year’s tax liability, and possibly may result in an audit of his return. Any audit of a unitholder’s return could result in adjustments not related to our returns as well as those related to our returns.
Partnerships generally are treated as separate entities for purposes of federal tax audits, judicial review of administrative adjustments by the IRS and tax settlement proceedings. The tax treatment of partnership items of income, gain, loss and deduction are determined in a partnership proceeding rather than in separate proceedings with the partners. The Internal Revenue Code requires that one partner be designated as the “Tax Matters Partner” for these purposes. The partnership agreement names our general partner as our Tax Matters Partner.
The Tax Matters Partner will make some elections on our behalf and on behalf of unitholders. In addition, the Tax Matters Partner can extend the statute of limitations for assessment of tax deficiencies against unitholders
172
for items in our returns. The Tax Matters Partner may bind a unitholder with less than a 1% profits interest in us to a settlement with the IRS unless that unitholder elects, by filing a statement with the IRS, not to give that authority to the Tax Matters Partner. The Tax Matters Partner may seek judicial review, by which all the unitholders are bound, of a final partnership administrative adjustment and, if the Tax Matters Partner fails to seek judicial review, judicial review may be sought by any unitholder having at least a 1% interest in profits or by any group of unitholders having in the aggregate at least a 5% interest in profits. However, only one action for judicial review will go forward, and each unitholder with an interest in the outcome may participate.
A unitholder must file a statement with the IRS identifying the treatment of any item on his federal income tax return that is not consistent with the treatment of the item on our return. Intentional or negligent disregard of this consistency requirement may subject a unitholder to substantial penalties.
Nominee Reporting. Persons who hold an interest in us as a nominee for another person are required to furnish to us:
(a) the name, address and taxpayer identification number of the beneficial owner and the nominee;
(b) whether the beneficial owner is:
1. a person that is not a United States person;
2. a foreign government, an international organization or any wholly-owned agency or instrumentality of either of the foregoing; or
3. a tax-exempt entity;
(c) the amount and description of units held, acquired or transferred for the beneficial owner; and
(d) specific information including the dates of acquisitions and transfers, means of acquisitions and transfers, and acquisition cost for purchases, as well as the amount of net proceeds from sales.
Brokers and financial institutions are required to furnish additional information, including whether they are United States persons and specific information on units they acquire, hold or transfer for their own account. A penalty of $50 per failure, up to a maximum of $100,000 per calendar year, is imposed by the Internal Revenue Code for failure to report that information to us. The nominee is required to supply the beneficial owner of the units with the information furnished to us.
Accuracy-Related Penalties
An additional tax equal to 20% of the amount of any portion of an underpayment of tax that is attributable to one or more specified causes, including negligence or disregard of rules or regulations, substantial understatements of income tax and substantial valuation misstatements, is imposed by the Internal Revenue Code. No penalty will be imposed, however, for any portion of an underpayment if it is shown that there was a reasonable cause for that portion and that the taxpayer acted in good faith regarding that portion.
For individuals, a substantial understatement of income tax in any taxable year exists if the amount of the understatement exceeds the greater of 10% of the tax required to be shown on the return for the taxable year or $5,000. The amount of any understatement subject to penalty generally is reduced if any portion is attributable to a position adopted on the return:
(1) for which there is, or was, “substantial authority;” or
(2) as to which there is a reasonable basis and the pertinent facts of that position are disclosed on the return.
If any item of income, gain, loss or deduction included in the distributive shares of unitholders might result in that kind of an “understatement” of income for which no “substantial authority” exists, we must disclose the
173
pertinent facts on our return. In addition, we will make a reasonable effort to furnish sufficient information for unitholders to make adequate disclosure on their returns and to take other actions as may be appropriate to permit unitholders to avoid liability for this penalty. More stringent rules apply to “tax shelters,” which we do not believe includes us.
A substantial valuation misstatement exists if the value of any property, or the adjusted basis of any property, claimed on a tax return is 200% or more of the amount determined to be the correct amount of the valuation or adjusted basis. No penalty is imposed unless the portion of the underpayment attributable to a substantial valuation misstatement exceeds $5,000 ($10,000 for most corporations). If the valuation claimed on a return is 400% or more than the correct valuation, the penalty imposed increases to 40%.
Reportable Transactions. If we were to engage in a “reportable transaction,” we (and possibly you and others) would be required to make a detailed disclosure of the transaction to the IRS. A transaction may be a reportable transaction based upon any of several factors, including the fact that it is a type of tax avoidance transaction publicly identified by the IRS as a “listed transaction” or that it produces certain kinds of losses in excess of $2 million. Our participation in a reportable transaction could increase the likelihood that our federal income tax information return (and possibly your tax return) would be audited by the IRS. Please read “—Information Returns and Audit Procedures” above.
Moreover, if we were to participate in a reportable transaction with a significant purpose to avoid or evade tax, or in any listed transaction, you may be subject to the following provisions of the American Jobs Creation Act of 2004:
| • | accuracy-related penalties with a broader scope, significantly narrower exceptions, and potentially greater amounts than described above at “—Accuracy-Related Penalties,” |
| • | for those persons otherwise entitled to deduct interest on federal tax deficiencies, nondeductibility of interest on any resulting tax liability, and |
| • | in the case of a listed transaction, an extended statute of limitations. |
We do not expect to engage in any “reportable transactions.”
State, Local and Other Tax Considerations
In addition to federal income taxes, you likely will be subject to other taxes, such as state and local income taxes, unincorporated business taxes, and estate, inheritance or intangible taxes that may be imposed by the various jurisdictions in which we do business or own property or in which you are a resident. Although an analysis of those various taxes is not presented here, each prospective unitholder should consider their potential impact on his investment in us. We will initially own property or do business in Louisiana and Texas. We may also own property or do business in other jurisdictions. Although you may not be required to file a return and pay taxes in some jurisdictions because your income from that jurisdiction falls below the filing and payment requirement, you will be required to file income tax returns and to pay income taxes in many of these jurisdictions in which we do business or own property and may be subject to penalties for failure to comply with those requirements. In some jurisdictions, tax losses may not produce a tax benefit in the year incurred and may not be available to offset income in subsequent taxable years. Some of the jurisdictions may require us, or we may elect, to withhold a percentage of income from amounts to be distributed to a unitholder who is not a resident of the jurisdiction. Withholding, the amount of which may be greater or less than a particular unitholder’s income tax liability to the jurisdiction, generally does not relieve a nonresident unitholder from the obligation to file an income tax return. Amounts withheld will be treated as if distributed to unitholders for purposes of determining the amounts distributed by us. Please read “—Tax Consequences of Unit Ownership—Entity-Level Collections.” Based on current law and our estimate of our future operations, our general partner anticipates that any amounts required to be withheld will not be material.
174
It is the responsibility of each unitholder to investigate the legal and tax consequences, under the laws of pertinent jurisdictions, of his investment in us. Accordingly, each prospective unitholder is urged to consult, and depend on, his own tax counsel or other advisor with regard to those matters. Further, it is the responsibility of each unitholder to file all state and local, as well as United States federal tax returns, that may be required of him. Andrews Kurth LLP has not rendered an opinion on the state, local or foreign tax consequences of an investment in us.
175
INVESTMENT IN CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
BY EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
An investment in us by an employee benefit plan is subject to additional considerations because the investments of these plans are subject to the fiduciary responsibility and prohibited transaction provisions of ERISA, and restrictions imposed by Section 4975 of the Internal Revenue Code. For these purposes, the term “employee benefit plan” includes, but is not limited to, qualified pension, profit-sharing and stock bonus plans, Keogh plans, simplified employee pension plans and tax deferred annuities or IRAs established or maintained by an employer or employee organization. Among other things, consideration should be given to:
| • | whether the investment is prudent under Section 404(a)(1)(B) of ERISA; |
| • | whether in making the investment, that plan will satisfy the diversification requirements of Section 404(a)(l)(C) of ERISA; and |
| • | whether the investment will result in recognition of unrelated business taxable income by the plan and, if so, the potential after-tax investment return. |
The person with investment discretion with respect to the assets of an employee benefit plan, often called a fiduciary, should determine whether an investment in us is authorized by the appropriate governing instrument and is a proper investment for the plan.
Section 406 of ERISA and Section 4975 of the Internal Revenue Code prohibits employee benefit plans, and IRAs that are not considered part of an employee benefit plan, from engaging in specified transactions involving “plan assets” with parties that are “parties in interest” under ERISA or “disqualified persons” under the Internal Revenue Code with respect to the plan.
In addition to considering whether the purchase of common units is a prohibited transaction, a fiduciary of an employee benefit plan should consider whether the plan will, by investing in us, be deemed to own an undivided interest in our assets, with the result that our general partner also would be fiduciaries of the plan and our operations would be subject to the regulatory restrictions of ERISA, including its prohibited transaction rules, as well as the prohibited transaction rules of the Internal Revenue Code.
The Department of Labor regulations provide guidance with respect to whether the assets of an entity in which employee benefit plans acquire equity interests would be deemed “plan assets” under some circumstances. Under these regulations, an entity’s assets would not be considered to be “plan assets” if, among other things:
| • | the equity interests acquired by employee benefit plans are publicly offered securities; i.e., the equity interests are widely held by 100 or more investors independent of the issuer and each other, freely transferable and registered under some provisions of the federal securities laws; |
| • | the entity is an “operating company,”—i.e., it is primarily engaged in the production or sale of a product or service other than the investment of capital either directly or through a majority owned subsidiary or subsidiaries; or |
| • | there is no significant investment by “benefit plan investors,” which is defined to mean that less than 25% of the value of each class of equity interest, disregarding some interests held by our general partner, its affiliates, and some other persons, is held by the employee benefit plans referred to above and IRAs (employee benefit plans not subject to ERISA, including governmental plans are not counted as “benefit plan investors”). |
Our assets should not be considered “plan assets” under these regulations because it is expected that the investment will satisfy the requirements in the first bullet point above.
Plan fiduciaries contemplating a purchase of common units should consult with their own counsel regarding the consequences under ERISA and the Internal Revenue Code in light of the serious penalties imposed on persons who engage in prohibited transactions or other violations.
176
Citigroup Global Markets Inc., Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated and Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC are acting as joint book-running managers of the offering and representatives of the underwriters named below. Subject to the terms and conditions stated in the underwriting agreement dated the date of this prospectus, each underwriter named below has severally agreed to purchase, and we have agreed to sell to that underwriter, the number of common units set forth opposite the underwriter’s name.
| Underwriters |
Number of Common Units | |
| Citigroup Global Markets Inc. |
||
| Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated |
||
| Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC. |
||
| Total |
12,500,000 | |
The underwriting agreement provides that the obligations of the underwriters to purchase the common units included in this offering are subject to approval of legal matters by counsel and to other conditions. The underwriters are obligated to purchase all the units (other than those covered by their option to purchase additional units described below) if they purchase any units.
The underwriters propose to offer some of the units directly to the public at the public offering price set forth on the cover page of this prospectus and some of the units to dealers at the public offering price less a concession not to exceed $ per unit. If all of the units are not sold at the initial offering price, the representatives may change the public offering price and the other selling terms. The representatives have advised us that the underwriters do not intend sales to discretionary accounts to exceed five percent of the total number of our units offered by them.
The selling unitholder has granted to the underwriters an option, exercisable for 30 days from the date of this prospectus, to purchase up to 1,875,000 additional common units at the public offering price less the underwriting discount. The underwriters may exercise the option solely for the purpose of covering over-allotments, if any, in connection with this offering. To the extent the option is exercised, each underwriter must purchase a number of additional units approximately proportionate to that underwriter’s initial purchase commitment.
We, our general partner, all of the officers and directors of our general partner and our principal beneficial unitholders have agreed that, for a period of 180 days from the date of this prospectus, we and they will not, without the prior written consent of Citigroup Global Markets Inc., dispose of or hedge any of our common units or any securities convertible into or exchangeable for our common units. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if (1) during the last 17 days of the 180-day period, we issue an earnings release, or material news or a material event relating to us occurs; or (2) prior to the expiration of the 180-day restricted period, we announce that we will release earnings results during the 16-day period beginning on the last day of the 180-day period, the restrictions described above shall continue to apply until the expiration of the 18-day period beginning on the issuance of the earnings release or the occurrence of the material news or material event.
Citigroup Global Markets Inc. in its sole discretion may release any of the securities subject to these lock-up agreements at any time without notice. Citigroup Global Markets Inc. has no present intent or arrangement to release any of the securities subject to these lock-up agreements. The release of any lock-up is considered on a case-by-case basis. Factors in deciding whether to release common units may include the length of time before the lock-up expires, the number of units involved, the reason for the requested release, market conditions, the trading price of our common units, historical trading volumes of our common units and whether the person seeking the release is an officer, director or affiliate of us.
177
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common units. Consequently, the initial public offering price for the units will be determined by negotiations among our general partner, the selling unitholder and the representatives. Among the factors considered in determining the initial public offering price will be our results of operations, our current financial condition, our future prospects, our markets, the economic conditions in and future prospects for the industry in which we compete, our management, and currently prevailing general conditions in the equity securities markets, including current market valuations of publicly traded partnerships considered comparable to our partnership. We cannot assure you, however, that the prices at which the units will sell in the public market after this offering will not be lower than the initial public offering price or that an active trading market in our common units will develop and continue after this offering.
We have applied to list our common units listed on the American Stock Exchange under the symbol “CQP.”
The following table shows the underwriting discounts and commissions that we and the selling unitholder are to pay to the underwriters in connection with this offering. These amounts are shown assuming both no exercise and full exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional common units.
| No Exercise |
Full Exercise | |||||
| Paid by us per unit |
$ | $ | ||||
| Paid by the selling unitholder per unit |
||||||
| Total |
$ | $ | ||||
We and the selling unitholder will pay our respective proportionate shares of a structuring fee equal to an aggregate of 0.50% of the gross proceeds from this offering. This fee will be paid to Citigroup Global Markets Inc. for evaluation, analysis and structuring of our partnership.
We estimate that the total expenses of this offering, excluding underwriting discounts and commissions and the structuring fee, will be $3.3 million, all of which will be paid by the selling unitholder.
In connection with the offering, the representatives on behalf of the underwriters may purchase and sell common units in the open market. These transactions may include short sales, syndicate covering transactions and stabilizing transactions. Short sales involve syndicate sales of common units in excess of the number of units to be purchased by the underwriters in the offering, which creates a syndicate short position. “Covered” short sales are sales of units made in an amount up to the number of units represented by the underwriters’ option to purchase additional common units. In determining the source of units to close out the covered syndicate short position, the underwriters will consider, among other things, the price of units available for purchase in the open market compared to the price at which they may purchase units through their option to purchase additional common units. Transactions to close out the covered syndicate short position involve either purchases of the common units in the open market after the distribution has been completed or the exercise of their option to purchase additional common units. The underwriters may also make “naked” short sales of units in excess of their option to purchase additional common units. The underwriters must close out any naked short position by purchasing common units in the open market. A naked short position is more likely to be created if the underwriters are concerned that there may be downward pressure on the price of the units in the open market after pricing that could adversely affect investors who purchase in the offering. Stabilizing transactions consist of bids for or purchases of units in the open market while the offering is in progress.
The underwriters also may impose a penalty bid. Penalty bids permit the underwriters to reclaim a selling concession from a syndicate member when an underwriter repurchases units originally sold by that syndicate member in order to cover syndicate short positions or make stabilizing purchases.
Any of these activities, as well as purchases by the underwriters for their own accounts, may have the effect of preventing or retarding a decline in the market price of the units. They may also cause the price of the units to
178
be higher than the price that would otherwise exist in the open market in the absence of these transactions. The underwriters may conduct these transactions on the American Stock Exchange or otherwise. If the underwriters commence any of these transactions, they may discontinue them at any time.
Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated have performed from time to time investment banking and advisory services for us for which they have received and will receive customary fees and expenses. Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC, one of the underwriters in this offering, was an initial purchaser in Sabine Pass LNG’s private placement of the Sabine Pass LNG notes. Affiliates of Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated own an approximate one percent fully diluted, indirect ownership interest in us. In addition, John Deutch, a director of Citigroup, also serves on the board of directors of Cheniere. The underwriters may, from time to time, engage in other transactions with and perform other services for us in the ordinary course of our business.
A prospectus in electronic format may be made available by one or more of the underwriters. The representatives may agree to allocate a number of units to underwriters for sale to their online brokerage account holders. The representatives will allocate units to underwriters that may make Internet distributions on the same basis as other allocations. In addition, units may be sold by the underwriters to securities dealers who resell units to online brokerage account holders.
Other than the prospectus in electronic format, the information on any underwriter’s web site and any information contained in any other web site maintained by an underwriter is not part of the prospectus or the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, has not been approved and/or endorsed by us or any underwriter in its capacity as an underwriter and should not be relied upon by investors.
We, our general partner and Cheniere (or our successors) have agreed to indemnify the underwriters against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act, and to contribute to payments that the underwriters may be required to make for any such liabilities.
Because the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc. views the common units offered by this prospectus as interests in a direct participation program, the offering is being made in compliance with Rule 2810 of the NASD’s Conduct Rules. Investor suitability with respect to the common units should be judged similarly to the suitability with respect to other securities that are listed for trading on a national securities exchange.
179
The validity of the common units will be passed upon for us and the selling unitholder by Andrews Kurth LLP, Houston, Texas. Certain legal matters in connection with the common units offered hereby will be passed upon for the underwriters by Baker Botts L.L.P., Houston, Texas.
The combined financial statements of the Combined Predecessor Entities as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, and for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2006 and the period from October 20, 2003 (date of inception) to December 31, 2006 included in this prospectus have been audited by UHY LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report appearing herein and have been so included in reliance upon the report of such firm given upon their authority as experts in accounting and auditing.
The consolidated balance sheet of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. as of December 31, 2006 included in this prospectus has been audited by UHY LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report appearing herein, and has been included in reliance upon the report of such firm given upon their authority as experts in accounting and auditing.
The balance sheet of Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC as of December 31, 2006 included in this prospectus has been audited by UHY LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report appearing herein and has been so included in reliance upon the report of such firm given upon their authority as experts in accounting and auditing.
Stone & Webster Management Consultants Inc. has prepared the Independent Engineer’s report that is included as Appendix B to this prospectus. The Independent Engineer’s report should be read in its entirety for complete information with respect to the subjects and issues discussed therein. As stated in the Independent Engineer’s report, the Independent Engineer has made a number of assumptions in reaching its conclusions, which are set forth therein, and has used the sources of information described therein. The Independent Engineer believes that the use of such information and assumptions is reasonable for the purposes of the Independent Engineer’s report. The Independent Engineer’s report has been included in this prospectus in reliance upon the conclusions therein and upon the Independent Engineer’s experience in the review of the design, development, construction and operation of projects similar to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-l regarding the common units. This prospectus does not contain all of the information found in the registration statement. For further information regarding us and the common units offered by this prospectus, you may desire to review the full registration statement, including its exhibits and schedules, filed under the Securities Act. The registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, including its exhibits and schedules, may be inspected and copied at the public reference room maintained by the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Room 1580, Washington, D.C. 20549. Copies of the materials may also be obtained from the SEC at prescribed rates by writing to the public reference room maintained by the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Room 1580, Washington, D.C. 20549. You may obtain information on the operation of the public reference room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330.
The SEC maintains a web site on the Internet at http://www.sec.gov. Our registration statement, of which this prospectus constitutes a part, can be downloaded from the SEC’s web site and can also be inspected and copied at the offices of the American Stock Exchange, 86 Trinity Place, New York, New York 10006.
180
In this prospectus, unless the context otherwise requires:
| • | Bcf means billion cubic feet; |
| • | Bcf/d means billion cubic feet per day; |
| • | EPC means engineering, procurement and construction; |
| • | EPCM means engineering, procurement, construction and management; |
| • | FERC means the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission; |
| • | LNG means liquefied natural gas; |
| • | MMcf/d means million cubic feet per day; |
| • | MMbtu means million British thermal units; |
| • | Tcf means trillion cubic feet; and |
| • | TUA means terminal use agreement. |
REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements, which are statements other than statements of historical fact. Forward-looking statements include, among others:
| • | statements regarding our ability to pay distributions to our unitholders; |
| • | statements relating to the construction and operation of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, including statements concerning the completion or expansion thereof by certain dates or at all, the costs related thereto and certain characteristics, including amounts of regasification and storage capacity, the number of storage tanks and docks, pipeline deliverability and the number of pipeline interconnections, if any; |
| • | statements relating to the construction and operation of facilities related to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; |
| • | statements regarding our expected receipt of cash distributions from Sabine Pass LNG; |
| • | statements regarding our ability to make any acquisitions in the future or, if made, our ability to integrate them into our existing business and to operate them in a profitable manner; |
| • | statements regarding future levels of domestic natural gas production, supply or consumption; future levels of LNG imports into North America; sales of natural gas in North America; and the transportation, other infrastructure or prices related to natural gas, LNG or other energy sources or hydrocarbon products; |
| • | statements regarding any financing transactions or arrangements, or ability to enter into such transactions or arrangements; |
| • | statements regarding any TUA or other agreement to be entered into or performed substantially in the future, including any cash distributions and revenues anticipated to be received and the anticipated timing thereof, and statements regarding the amounts of total LNG regasification capacity that are, or may become, subject to TUAs or other contracts; |
| • | statements regarding counterparties to our TUAs, construction contracts and other contracts; |
| • | statements regarding any business strategy, any business plans or any other plans, forecasts, projections or objectives, any or all of which are subject to change; |
181
| • | statements regarding any independent engineer’s or other expert’s assumptions, estimates, projections or conclusions; |
| • | statements regarding conflicts of interest with Cheniere and its affiliates; |
| • | statements regarding legislative, governmental, regulatory, administrative or other public body actions, requirements, permits, investigations, proceedings or decisions; and |
| • | any other statements that relate to non-historical or future information. |
These forward-looking statements are often identified by the use of terms such as “achieve,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “forecast,” “plan,” “project,” “propose,” “strategy” and similar terms. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in these forward-looking statements are reasonable, they involve assumptions, risks and uncertainties, and these expectations may prove to be incorrect. You should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date of this prospectus.
Our actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of a variety of factors, including those discussed in “ Risk Factors.” All forward-looking statements attributable to us or persons acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by these risk factors. Other than as required under the securities laws, we assume no obligation to update or revise these forward-looking statements or provide reasons why actual results may differ.
182
| Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. Combined Predecessor Entities Financial Statements: |
||
| F-2 | ||
| F-3 | ||
| F-4 | ||
| F-5 | ||
| F-6 | ||
| F-7 | ||
| Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. Unaudited Pro Forma Combined Financial Statements: |
||
| Unaudited Pro Forma Combined Financial Statements Basis of Presentation |
F-22 | |
| F-23 | ||
| F-24 | ||
| Notes to Unaudited Pro Forma Combined Condensed Financial Statements |
F-25 | |
| Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. |
||
| F-27 | ||
| F-28 | ||
| F-29 | ||
| Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC Financial Statement: |
||
| F-30 | ||
| F-31 | ||
| F-32 | ||
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Partners, Members and Stockholders of the
Combined Predecessor Entities
Houston, Texas
We have audited the accompanying combined balance sheets of the Combined Predecessor Entities (the “Company”), as defined in Note 1 to the combined financial statements, as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, and the related combined statements of operations, cash flows and changes in owners’ equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2006 and for the period from October 20, 2003 (date of inception) to December 31, 2006. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion of these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the combined financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the combined financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall combined financial statements presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the combined financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the combined financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, and the combined results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2006 and for the period from October 20, 2003 (date of inception) to December 31, 2006 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ UHY LLP
Houston, Texas
February 9, 2007
F-2
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(As Defined in Note 1)
A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE
(in thousands)
| December 31, | |||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | ||||||
| ASSETS |
|||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS |
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 7 | $ | 5 | |||
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents |
355,327 | 8,871 | |||||
| Interest receivable |
5,226 | 5 | |||||
| Advances to EPC contractor |
— | 8,087 | |||||
| Advances to affiliate |
379 | 242 | |||||
| Short-term unrealized derivative asset |
— | 423 | |||||
| Prepaid expenses |
385 | 415 | |||||
| TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS |
361,324 | 18,048 | |||||
| NON-CURRENT RESTRICTED CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
803,610 | — | |||||
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
651,676 | 270,740 | |||||
| DEBT ISSUANCE COSTS, NET |
33,970 | 18,497 | |||||
| ADVANCES UNDER LONG-TERM CONTRACTS |
7,250 | — | |||||
| LNG INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
18 | 17 | |||||
| LONG-TERM DERIVATIVE ASSETS |
— | 1,837 | |||||
| OTHER |
266 | — | |||||
| TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 1,858,114 | $ | 309,139 | |||
| LIABILITY AND OWNERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
|||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 758 | $ | — | |||
| Accounts payable—affiliate |
223 | — | |||||
| Accrued liabilities |
36,670 | 44,403 | |||||
| Accrued liabilities—affiliate |
652 | 435 | |||||
| TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES |
38,303 | 44,838 | |||||
| LONG-TERM DEBT |
2,032,000 | — | |||||
| DEFERRED REVENUE |
40,000 | 40,000 | |||||
| LONG-TERM DEBT—AFFILIATE |
— | 37,377 | |||||
| PAYABLE TO AFFILIATE |
— | 35,108 | |||||
| INTEREST PAYABLE—AFFILIATE |
— | 120 | |||||
| OTHER |
1,149 | — | |||||
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
— | — | |||||
| OWNERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
|||||||
| Owners’ equity (deficit), including deficit accumulated during development stage of $72,452 and $11,672 at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively. |
(253,338 | ) | 149,882 | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income |
— | 1,814 | |||||
| TOTAL OWNERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
(253,338 | ) | 151,696 | ||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND OWNERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
$ | 1,858,114 | $ | 309,139 | |||
See accompanying notes to combined financial statements.
F-3
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(As Defined in Note 1)
A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE
Combined Statements of Operations
(in thousands)
| Years Ended December 31, | Period from 2006 |
|||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||
| REVENUES |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
| EXPENSES |
||||||||||||||||
| Legal |
2 | 203 | 1,434 | 2,227 | ||||||||||||
| Professional |
571 | 281 | 568 | 1,571 | ||||||||||||
| Technical consulting |
27 | — | 2,579 | 4,577 | ||||||||||||
| Land site rental |
1,515 | — | — | 1,515 | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation expense |
50 | 13 | — | 63 | ||||||||||||
| Overhead charge from affiliates |
3,450 | 4,094 | — | 7,544 | ||||||||||||
| Phase 2 development reimbursement to affiliate |
4,527 | — | — | 4,527 | ||||||||||||
| Other |
135 | 128 | 101 | 417 | ||||||||||||
| TOTAL EXPENSES |
10,277 | 4,719 | 4,682 | 22,441 | ||||||||||||
| LOSS FROM OPERATIONS |
(10,277 | ) | (4,719 | ) | (4,682 | ) | (22,441 | ) | ||||||||
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest income |
9,306 | 113 | 28 | 9,447 | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(15,463 | ) | — | — | (15,463 | ) | ||||||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt |
(23,761 | ) | — | — | (23,761 | ) | ||||||||||
| Derivative gain (loss), net |
(20,577 | ) | 343 | — | (20,234 | ) | ||||||||||
| TOTAL OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
(50,495 | ) | 456 | 28 | (50,011 | ) | ||||||||||
| NET LOSS |
$ | (60,772 | ) | $ | (4,263 | ) | $ | (4,654 | ) | $ | (72,452 | ) | ||||
See accompanying notes to combined financial statements.
F-4
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(As Defined in Note 1)
A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE
Combined Statements of Owners’ Equity (Deficit)
(in thousands)
| Owners’ Equity Excluding Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Total Owners’ Equity (Deficit) |
||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2003 |
(2,763 | ) | — | (2,763 | ) | |||||||
| Distributions |
(10,000 | ) | — | (10,000 | ) | |||||||
| Comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||
| Net loss |
(4,654 | ) | — | (4,654 | ) | |||||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(4,654 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2004 |
(17,417 | ) | — | (17,417 | ) | |||||||
| Capital contributions |
161,562 | 161,562 | ||||||||||
| Rescinded distribution |
10,000 | — | 10,000 | |||||||||
| Comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of derivative instrument |
— | 1,814 | 1,814 | |||||||||
| Net loss |
(4,263 | ) | — | (4,263 | ) | |||||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(2,449 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2005 |
149,882 | 1,814 | 151,696 | |||||||||
| Capital contributions |
35,900 | — | 35,900 | |||||||||
| Distributions |
(378,348 | ) | — | (378,348 | ) | |||||||
| Comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||
| Change in fair value of derivative instrument |
— | (1,814 | ) | (1,814 | ) | |||||||
| Net loss |
(60,772 | ) | (60,772 | ) | ||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(62,586 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2006 |
$ | (253,338 | ) | $ | — | $ | (253,338 | ) | ||||
See accompanying notes to combined financial statements.
F-5
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(As Defined in Note 1)
A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE
Combined Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | Period
from 2006 |
|||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (60,772 | ) | $ | (4,263 | ) | $ | (4,654 | ) | $ | (72,452 | ) | ||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation |
50 | 13 | — | 63 | ||||||||||||
| Non-cash derivative (gain) loss |
23 | (362 | ) | — | (339 | ) | ||||||||||
| Amortization of debt issuance costs |
695 | — | — | 695 | ||||||||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt |
23,750 | — | — | 23,750 | ||||||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest receivable |
(5,221 | ) | 19 | (23 | ) | (5,226 | ) | |||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
12,399 | 191 | 1,315 | 13,905 | ||||||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities—affiliate |
97 | 555 | — | 652 | ||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | 18,000 | 22,000 | 40,000 | ||||||||||||
| Payable to affiliate |
— | (7,418 | ) | 4,554 | — | |||||||||||
| Other |
1,067 | (416 | ) | — | 651 | |||||||||||
| NET CASH PROVIDED BY (USED IN) OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
(27,912 | ) | 6,319 | 23,192 | 1,699 | |||||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
||||||||||||||||
| Investment in restricted cash and cash equivalents |
(1,150,066 | ) | (8,871 | ) | — | (1,158,937 | ) | |||||||||
| LNG terminal construction-in-progress |
(387,724 | ) | (229,073 | ) | — | (624,884 | ) | |||||||||
| Advances to EPC contractor, net of transfers to construction-in-progress |
— | (8,087 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
| Advances to affiliate |
(137 | ) | (242 | ) | — | (379 | ) | |||||||||
| Other assets |
(6,481 | ) | (64 | ) | (124 | ) | (6,768 | ) | ||||||||
| NET CASH USED IN INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
(1,544,408 | ) | (246,337 | ) | (124 | ) | (1,790,968 | ) | ||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
— | |||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of senior notes |
2,032,000 | — | — | 2,032,000 | ||||||||||||
| Debt issuance costs |
(43,966 | ) | (15,847 | ) | (1,246 | ) | (61,060 | ) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from subordinated note—affiliate |
— | 37,377 | — | 37,377 | ||||||||||||
| Repayment of subordinated note—affiliate |
(37,377 | ) | — | — | (37,377 | ) | ||||||||||
| Borrowings from Sabine Pass credit facility |
383,400 | — | — | 383,400 | ||||||||||||
| Repayment of Sabine Pass credit facility |
(383,400 | ) | — | — | (383,400 | ) | ||||||||||
| Distribution to limited partner |
(378,348 | ) | — | — | (378,348 | ) | ||||||||||
| Affiliate payable |
3 | 35,109 | — | 35,112 | ||||||||||||
| Limited partner contributions |
10 | 161,562 | — | 161,572 | ||||||||||||
| NET CASH PROVIDED BY (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
1,572,322 | 218,201 | (1,246 | ) | 1,789,276 | |||||||||||
| NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
2 | (21,817 | ) | 21,822 | 7 | |||||||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS—beginning of year |
5 | 21,822 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS—end of year |
$ | 7 | $ | 5 | $ | 21,822 | $ | 7 | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to combined financial statements.
F-6
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1—NATURE OF OPERATIONS
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. (“Cheniere Energy Partners”) is a Delaware limited partnership formed on November 21, 2006 by Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC (the “Limited Partner”) and Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC (the “General Partner”), both of which are indirect, wholly-owned subsidiaries of Cheniere Energy, Inc. (“Cheniere”). Cheniere Energy Partners was formed to develop, own and operate the Sabine Pass liquefied natural gas, or LNG, receiving and regasification facility, in western Cameron Parish, Louisiana on the Sabine Pass Channel (the “Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal”). Cheniere Energy Partners is in the process of registering its common units, representing limited partner interests, to be sold in an initial public offering (the “Offering”).
In accordance with the Rules and Regulations of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, the following entities are included in the combined financial statements:
| • | Cheniere Energy Partners; |
| • | Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC is a Delaware limited liability company owned by Cheniere Energy Partners and was formed on November 21, 2006 to hold 100% of the ownership interests in Sabine Pass GP and Sabine Pass LP; |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. (“Sabine Pass GP”) is a Delaware corporation owned by the Limited Partner and was formed in 2004 to be the general partner of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (“Sabine Pass LNG”); |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC (“Sabine Pass LP”) is a Delaware limited liability company owned by the Limited Partner and was formed in 2004 to be the limited partner of Sabine Pass LNG; and |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG is a Delaware limited partnership, formed with one general partner, Sabine Pass GP, and one limited partner, Sabine Pass LP, which owns the entire interest in the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Sabine Pass LNG is in the development stage, and the purpose of this limited partnership is to own and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
At the closing of the Offering, the equity interests in Sabine Pass GP and Sabine Pass LP will be contributed to Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC, thereby resulting in Sabine Pass GP, Sabine Pass LP and Sabine Pass LNG becoming indirect, wholly-owned subsidiaries of Cheniere Energy Partners. As used in these Notes to the Combined Financial Statements, the terms “we”, “us” and “our” refer to the foregoing entities on a combined basis (the “Combined Predecessor Entities”).
NOTE 2—DEVELOPMENT STAGE OPERATIONS
We were formed on October 20, 2003 (the earliest formation date of the Combined Predecessor Entities). Operations to date have been devoted to pre-construction and construction activities. Our ultimate profitability will depend on, among other factors, the successful completion of construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal and commencement of commercial operation, which is not expected until the second quarter of 2008 at the earliest.
NOTE 3—SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
Because common control exists among the Combined Predecessor Entities, our Combined Financial Statements reflect the financial statements of each Combined Predecessor Entity on a combined basis for the periods presented and consistent with consolidated financial statement principles that will be applied after the Offering is completed. All intercompany items have been eliminated.
F-7
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Our Combined Financial Statements were prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider all highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
LNG Site Related Costs
LNG site related costs include costs related to options to lease land that is used for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Such costs are capitalized and are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives.
Land Site Rentals
From inception to December 31, 2005, rental costs associated with ground or building operating leases that were incurred during the construction period were capitalized as part of LNG terminal construction-in-progress. However, beginning January 1, 2006, these rental costs have been expensed in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued FASB Staff Position (“FSP”) 13-1, Accounting for Rental Costs Incurred During a Construction Period, which is discussed below.
LNG Intangible Assets
LNG intangible assets include the costs of certain permits for the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Amortization will begin when the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is operational and will be calculated on the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
Debt Issuance Costs
Debt issuance costs consist primarily of fees incurred that are directly related to the issuance of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes (see Note 11). These costs are capitalized and are amortized to interest expense over the term of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes.
Revenue Recognition
LNG regasification capacity fees are recognized as revenue over the term of the respective terminal use agreements (“TUAs”). Advance capacity reservation fees are initially deferred. For a discussion of potential revenue from related parties, please read Note 13.
Income Taxes
With the exception of Sabine Pass GP, the Combined Predecessor Entities are not subject to either federal or state income tax, as the partners are taxed individually on their proportionate share of our earnings. Sabine Pass GP is a corporation and is subject to both federal and state income tax. However, since Sabine Pass GP’s inception, its activities have been strictly limited to holding a non-income or loss bearing general partner interests in Sabine Pass LNG and thus, this entity has not realized any taxable net income to date and is not expected to realize any taxable net income in the future.
F-8
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Pursuant to the indenture entered into in connection with the issuance of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes (as defined in Note 4), Sabine Pass LNG is permitted to make distributions (“Tax Distributions”) for any fiscal year or portion thereof in which Sabine Pass LNG is a limited partnership, disregarded entity or other substantially similar pass-through entity for federal and state income tax purposes. The permitted Tax Distributions are equal to the tax that Sabine Pass LNG would owe if Sabine Pass LNG were a corporation subject to federal and state income tax that filed separate federal and state income tax returns, excluding the amounts covered by the State Tax Sharing Agreement discussed immediately below. The Tax Distributions are limited to the amount of federal and/or state income taxes paid by Cheniere to the appropriate taxing authorities and are payable by Sabine Pass LNG within 30 days of the date that Cheniere is required to make federal or state income tax payments to the appropriate taxing authorities.
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG and Cheniere entered into a state franchise tax sharing agreement (the “State Tax Sharing Agreement”) pursuant to which Cheniere has agreed to prepare and file all Texas franchise tax returns which Sabine Pass LNG and Cheniere are required to file on a combined basis and to timely pay the combined Texas franchise tax liability. If Cheniere, in its sole discretion, demands payment, then Sabine Pass LNG will pay to Cheniere an amount equal to the Texas franchise tax that Sabine Pass LNG would be required to pay if its Texas franchise tax liability were computed on a separate company basis. The State Tax Sharing Agreement contains similar provisions for other state and local taxes required to be filed by Cheniere and Sabine Pass LNG on a combined, consolidated or unitary basis. The State Tax Sharing Agreement is effective for tax returns first due on or after January 1, 2008.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject us to a concentration of credit risk consist principally of cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash. We maintain cash balances at financial institutions, which may at times be in excess of federally insured levels. We have not incurred losses related to these balances to date.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost. Expenditures for major renewals and betterments are capitalized while expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred. Interest costs incurred on debt obtained for the construction of property, plant and equipment are capitalized as construction-in-progress over the construction period or related debt, whichever is shorter. Once the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is placed into service, the LNG terminal construction-in-progress costs will be depreciated using the straight-line depreciation method. We are in the process of determining the most appropriate approach in grouping identifiable components with similar estimated useful lives. Estimated useful lives for components, once construction is completed, are currently estimated to range between 10 and 50 years. Depreciation of computer and office equipment, computer software, leasehold improvements and vehicles is computed using the straight-line method over estimated useful lives of the assets, which range from two to ten years. Upon retirement or other disposition of property, plant and equipment, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the account, and the resulting gains or losses are recorded in operations.
In accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 144, Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-lived Assets, management periodically reviews for impairment of property, plant and equipment whenever events or changes in circumstances have indicated that the carry amount of property, plant and equipment might not be recoverable. No such impairment has been recorded for the years ended December 31, 2006 or 2005.
F-9
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Cash Flow Hedges
As defined in SFAS No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, cash flow hedge transactions hedge the exposure to variability in expected future cash flows (i.e., in our case, the variability of floating interest rate exposure). In the case of cash flow hedges, the hedged item (the underlying risk) is generally unrecognized (i.e., not recorded on the balance sheet prior to settlement), and any changes in the fair value, therefore, will not be recorded within earnings. Conceptually, if a cash flow hedge is effective, this means that a variable, such as a movement in interest rates, has been effectively fixed so that any fluctuations will have no net result on either cash flows or earnings. Therefore, if the changes in fair value of the hedged item are not recorded in earnings, then the changes in fair value of the hedging instrument (the derivative) must also be excluded from the income statement or else a one-sided net impact on earnings will be reported, despite the fact that the establishment of the effective hedge results in no net economic impact. To prevent such a scenario from occurring, SFAS No. 133 requires that the fair value of a derivative instrument designated as a cash flow hedge be recorded as an asset or liability on the balance sheet, but with the offset reported as part of other comprehensive income, to the extent that the hedge is effective. We assess both at the inception of each hedge and on an on-going basis, whether the derivatives that are used in our hedging transactions are highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows of the hedged items. On an on-going basis, we monitor the actual dollar offset of the hedges’ market values compared to hypothetical cash flow hedges. Any ineffective portion will be reflected in earnings. Ineffectiveness is the amount of gains or losses from derivative instruments that are not offset by corresponding and opposite gains or losses on the expected future transaction.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts in the Combined Financial Statements and accompanying Notes to the Combined Financial Statements. Actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 155, Accounting for Certain Hybrid Financial Instruments. SFAS No. 155 provides entities with relief from having to separately determine the fair value of an embedded derivative that would otherwise be required to be bifurcated from its host contract in accordance with SFAS No. 133. SFAS No. 155 allows an entity to make an irrevocable election to measure such a hybrid financial instrument at fair value in its entirety, with changes in fair value recognized in earnings. SFAS No. 155 is effective for all financial instruments acquired, issued or subject to a remeasurement event occurring after the beginning of an entity’s first fiscal year that begins after September 15, 2006. We believe that the adoption of SFAS No. 155 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In March 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 156, Accounting for Servicing of Financial Assets—An Amendment to FASB Statement No. 140. SFAS No. 156 requires entities to recognize a servicing asset or liability each time they undertake an obligation to service a financial asset by entering into a servicing contract in certain situations. This statement also requires all separately recognized servicing assets and servicing liabilities to be initially measured at fair value and permits a choice of either the amortization or fair value measurement method for subsequent measurement. The effective date of this statement is for annual periods beginning after September 15, 2006, with earlier adoption permitted as of the beginning of an entity’s fiscal year provided the entity has not issued any financial statements for that year. We are currently assessing the impact on our combined financial statements.
F-10
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
In July 2006, the FASB issued FASB Interpretation, or FIN, No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—An Interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109. FIN No. 48 clarifies the accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in an enterprise’s financial statements in accordance with SFAS No. 109, Accounting for Income Taxes. It prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. This new standard also provides guidance on derecognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosure, and transition. The provisions of FIN No. 48 are to be applied to all tax positions upon initial adoption of this standard. Only tax positions that meet the more likely-than-not recognition threshold at the effective date may be recognized or continue to be recognized upon adoption of FIN No. 48. The cumulative effect of applying the provisions of FIN No. 48 should be reported as an adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings (or other appropriate components of equity or net assets in the statement of financial position) for that fiscal year. The provisions of FIN No. 48 are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2006. Earlier application is permitted as long as the enterprise has not yet issued financial statements, including interim financial statements, in the period of adoption. We believe that the adoption of FIN No. 48 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In September 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 157, Fair Value Measurements. SFAS No. 157 clarifies the principle that fair value should be based on the assumptions market participants would use when pricing an asset or liability and establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the information used to develop those assumptions. Under the standard, fair value measurements would be separately disclosed by level within the fair value hierarchy. SFAS No. 157 is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007, and interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted. We believe that the adoption of SFAS No. 157 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In September 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 158, Employers’ Accounting for Defined Benefit Pension and Other Postretirement Plan—an amendment of FASB Statement No. 87, 88, 106 and 132(R). SFAS No. 158 requires an employer to recognize the overfunded or underfunded status of a defined benefit postretirement plan as an asset or liability in its statement of financial position and recognize changes in the funded status in the year in which the changes occur. SFAS No. 158 is effective for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2006. We believe that the adoption of SFAS No. 158 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In September 2006, the FASB issued FSP No. AUG AIR-1, Accounting for Planned Major Maintenance Activities. FSP No. AUG AIR-1 prohibits the use of the accrue-in-advance method for accounting for major maintenance activities and confirms the acceptable methods of accounting for planned major maintenance activities. FSP No. AUG AIR-1 is effective the first fiscal year beginning after December 15, 2006. We believe that the adoption of FSP No. AUG AIR-1 will not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
NOTE 4—RESTRICTED CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS
In November 2006, we consummated a private offering of an aggregate principle amount of $2.0 billion of senior secured notes consisting of $550 million of 7 1/4% Senior Secured Notes due 2013 (the “2013 Notes”) and $1.5 billion of 7 1/2% Senior Secured Notes due 2016 (the “2016 Notes” and, collectively with the 2013 Notes, the “Sabine Pass Senior Notes”) (see Note 11). Under the terms of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes, we were required to fund cash reserve accounts for approximately $335 million related to future interest payments through May 2009 and approximately $887 million to pay the remaining costs to complete Phase 1 and Phase 2—Stage 1
F-11
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
of our LNG receiving terminal. These cash accounts are controlled by a collateral agent, and therefore, are shown as restricted cash and cash equivalents on the accompanying Combined Balance Sheet. As of December 31, 2006, $355.3 million related to future interest payments and accrued construction costs have been classified as a current asset, and $803.6 million related to remaining construction costs have been classified as a non-current asset on the accompanying Combined Balance Sheet.
At December 31, 2005, we had a restricted cash and cash equivalents balance of $8.9 million, classified as a current asset, under the terms of Sabine Pass LNG’s amended and restated credit facility, which was subsequently terminated using a portion of the proceeds from the issuance of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes in November 2006.
NOTE 5—ADVANCES TO EPC CONTRACTOR
In December 2004, we entered into an engineering, procurement and construction (“EPC”) contract with Bechtel to construct Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. We were required to make a 5% advance payment to Bechtel upon issuance of the final notice to proceed (“NTP”) related to the construction of Phase 1. A payment of $32.3 million was made to Bechtel in March 2005 when the NTP was issued and that amount was classified as a current asset on the Combined Balance Sheet. In accordance with the payment schedule included in the EPC contract, $2.7 million per month was being reclassified to construction-in-progress over a twelve-month period. As of December 31, 2006 and 2005, the remaining balance of the advance was zero and $8.1 million, respectively.
NOTE 6—PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
Property, plant and equipment is comprised of LNG terminal construction-in-progress expenditures, LNG site and related costs and fixed assets, as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||
| LNG TERMINAL COSTS |
||||||||
| LNG terminal construction-in-progress |
$ | 651,369 | $ | 270,489 | ||||
| LNG site and related costs, net |
197 | 204 | ||||||
| Total LNG terminal costs |
651,566 | 270,693 | ||||||
| FIXED ASSETS |
||||||||
| Computer and office equipment |
31 | 4 | ||||||
| Computer software |
33 | 20 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
10 | 10 | ||||||
| Vehicles |
99 | 26 | ||||||
| Accumulated depreciation |
(63 | ) | (13 | ) | ||||
| Total fixed assets, net |
110 | 47 | ||||||
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
$ | 651,676 | $ | 270,740 | ||||
Once the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal is placed into service, the LNG terminal construction-in-progress costs will be depreciated using the straight-line depreciation method. We are in the process of determining the most appropriate approach in grouping identifiable components with similar estimated useful lives. Estimated useful lives for components, once construction is completed, are currently estimated to range between 10 and 50 years.
F-12
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
In February 2005 and July 2006, Phase 1 and Phase 2—Stage 1, respectively, of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal satisfied the criteria for capitalization. Accordingly, costs associated with the construction of Phase 1 and Phase 2—Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal have been capitalized as construction-in-progress since those times. During the year ended December 31, 2006 and 2005, we capitalized $22.3 million and $5.3 million, respectively, of interest expense, which consisted of interest expense qualifying to be capitalized, amortization of debt issuance costs and commitment fees under the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility and the Sabine Pass Senior Notes during 2006 and only the Sabine Pass credit facility in 2005.
NOTE 7—DEBT ISSUANCE COSTS
As of December 31, 2005, we capitalized $18.5 million (net of accumulated amortization of $1.7 million), of costs directly associated with the arrangement of the original Sabine Pass credit facility. The debt issuance costs were amortized over a period of ten years, the term of the original Sabine Pass credit facility. Although there were no borrowings outstanding as of December 31, 2005, the amortization of the debt issuance cost was recorded to interest expense and subsequently capitalized as construction-in-progress during the construction period of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. For the year ended December 31, 2005, the amount amortized and capitalized was $1.7 million.
When we amended and restated the Sabine Pass credit facility in July 2006, we incurred additional debt issuance costs of $9.1 million that were capitalized. These costs, along with the debt issuance costs capitalized as part of the original Sabine Pass credit facility, were amortized using straight-line amortization through July 1, 2015.
In November 2006, we paid off and terminated the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility using a portion of the proceeds received from the issuance of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes. As a result of the early termination of the Amended Sabine Pass credit facility, we were required to immediately expense the debt issuance costs capitalized related to the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility. For the year ended December 31, 2006, we expensed debt issuance costs of $23.8 million, which is presented on the Combined Statements of Operations as a loss on early extinguishment of debt.
As of December 31, 2006, we had capitalized $34.6 million of costs directly associated with the Sabine Pass Senior Notes offering consummated in November 2006, net of accumulated amortization, as follows (in thousands):
| Long-term Debt | Debt Issuance Costs | Amortization Period |
Accumulated Amortization |
Net Costs | ||||||||
| 2013 Notes | $ | 9,361 | 7 years | $ | (212 | ) | $ | 9,149 | ||||
| 2016 Notes | 25,223 | 10 years | (402 | ) | 24,821 | |||||||
| $ | 34,584 | $ | (614 | ) | $ | 33,970 | ||||||
Scheduled amortization of the debt issuance costs related to the Sabine Pass Senior Notes for the next five years is estimated to be $19.3 million.
NOTE 8—DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
Interest Rate Derivative Instruments
In connection with the closing of the original Sabine Pass credit facility in February 2005, we entered into swap agreements (“Sabine Swaps”) with HSBC Bank, USA and Société Générale. Under the terms of the Sabine
F-13
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Swaps, we were able to hedge against rising interest rates, to a certain extent, with respect to our drawings under the original Sabine Pass credit facility, up to a maximum amount of $700 million. The Sabine Swaps had the effect of fixing the LIBOR component of the interest rate payable under the original Sabine Pass credit facility with respect to hedged drawings under the original Sabine Pass credit facility up to a maximum of $700 million at 4.49% from July 25, 2005 through March 25, 2009 and at 4.98% from March 26, 2009 through March 25, 2012. The final termination date of the Sabine Swaps was March 25, 2012.
In connection with the closing of the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility in July 2006, we entered into additional interest rate swap agreements with HSBC Bank, USA and Société Générale (the “Amended Sabine Swaps” and collectively with the Sabine Swaps, the “Swaps”). The Swaps had the combined effect of fixing the LIBOR component of the interest rate payable on borrowings up to a maximum of $1.25 billion at a blended rate of 5.26% from July 25, 2006 through July 1, 2015.
In conjunction with the termination of the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility in November 2006, we terminated the Swaps and recognized a loss of $20.6 million. In accordance with EITF 00-9, Classification of a Gain or Loss from a Hedge of Debt That Is Extinguished, the loss recognized as a result of early settlement of the Swaps is presented on the Combined Statements of Operations as a Derivative loss.
Accounting for Hedges
SFAS No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, as amended (“SFAS No. 133”) and interpreted by other related accounting literature, establishes accounting and reporting standards for derivative instruments. Under SFAS No. 133, we were required to record derivatives on our Combined Balance Sheets as either an asset or liability measured at their fair value, unless exempted from derivative treatment under the normal purchase and normal sale exception. Changes in the fair value of derivatives are recognized currently in earnings unless specific hedge criteria are met. These criteria require that the derivative is determined to be effective as a hedge and that it is formally documented and designated as a hedge.
We determined that the Swaps qualified as cash flow hedges within the meaning of SFAS No. 133 and designated them as such. We assessed both at the inception of each of the Swaps and on an on-going basis, whether the Swaps that were used in our hedging transactions were highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows of the hedged items. At inception, we determined the hedging relationship of the Swaps and the underlying debt to be highly effective. On an on-going basis, we monitored the actual dollar offset of the Swaps’ market values compared to hypothetical cash flow hedges. Any ineffective portion of the cash flow hedges will be reflected in earnings. Ineffectiveness is the amount of gains or losses from derivative instruments that are not offset by corresponding and opposite gains or losses on the expected future transaction. We continued to assess the hedge effectiveness of the Swaps on a quarterly basis in accordance with the provisions of SFAS No. 133 until they were terminated in November 2006.
SFAS No. 133 provides that the effective portion of the gain or loss on a derivative instrument designated and qualifying as a cash flow hedging instrument be reported as a component of other comprehensive income (“OCI”) and be reclassified into earnings in the same period during which the hedged forecasted transaction affects earnings. In our case, the impact on earnings was a reduction of interest expense by $1.0 million and zero for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively. If the forecasted transaction was no longer probable of occurring, the associated gain or loss recorded in OCI was recognized currently in earnings.
F-14
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
NOTE 9—ACCRUED LIABILITIES
Accrued liabilities consisted of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||
| Interest and related debt fees |
$ | 21,815 | $ | 4,640 | ||
| LNG terminal construction costs |
13,899 | 39,730 | ||||
| Affiliate |
652 | 435 | ||||
| Other |
956 | 33 | ||||
| $ | 37,322 | $ | 44,838 | |||
NOTE 10—DEFERRED REVENUE
In November 2004, Total LNG USA, Inc. (“Total”) paid us a nonrefundable advance capacity reservation fee of $10.0 million in connection with the reservation of approximately 1.0 Bcf/d of LNG regasification capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. An additional advance capacity reservation fee payment of $10.0 million was paid by Total to us in April 2005. The advance capacity reservation fee payments will be amortized over a 10-year period after operations commence as a reduction of Total’s regasification capacity fee under its TUA. As a result, we recorded the advance capacity reservation fee payments that we received, although non-refundable, as deferred revenue to be amortized to income over the corresponding 10-year period.
In November 2004, we also entered into a TUA to provide Chevron USA, Inc. (“Chevron”), with approximately 700 MMcf/d of LNG regasification capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. In December 2005, Chevron exercised its option to increase its reserved capacity by approximately 300 MMcf/d to approximately 1.0 Bcf/d and paid us an additional $3.0 million advance terminal capacity reservation fee. As of December 31, 2005, Chevron had made advance terminal capacity reservation fee payments to us totaling $20.0 million, with $12.0 million paid in 2004 and $8.0 million paid in 2005. These advance terminal capacity reservation fee payments will be amortized over a 10-year period as a reduction of Chevron’s regasification capacity fee under the TUA. As a result, we recorded the advance capacity reservation fee payments that we received, although non-refundable, as deferred revenue to be amortized to income over the corresponding 10-year period.
As of December 31, 2006 and 2005, we recorded $40.0 million as deferred revenue on the Combined Balance Sheets related to advance capacity reservation fee payments.
NOTE 11—LONG-TERM DEBT
As of December 31, 2006 and 2005, our long-term debt consisted of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||
| Sabine Pass Senior Notes |
$ | 2,032,000 | $ | — | ||
| Subordinated Promissory Note—affiliate |
— | 37,377 | ||||
| Total long-term debt |
$ | 2,032,000 | $ | 37,377 | ||
F-15
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Sabine Pass Senior Notes
In November 2006, we consummated a private offering of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes to qualified institutional buyers pursuant to Rule 144A under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and in offshore transactions to non-United States persons in reliance on Regulation S under the Securities Act. At closing, net proceeds of approximately $2 billion, net of commissions, from the offering were used as follows: approximately $380 million to repay borrowings under, and replace, the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility; approximately $380 million was distributed to Sabine Pass LNG-LP; approximately $335 million was used to fund a reserve account for scheduled interest payments on the Sabine Pass Senior Notes through May 2009; and approximately $18 million was used to terminate the Sabine Pass Swaps and for other expenses. The remaining approximately $887 million of net proceeds from the offering will be used to fund the remaining costs to complete Phase 1 and Phase 2—Stage 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
We may redeem some or all of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount plus a make-whole premium, plus accrued and unpaid interest and additional interest, if any, to the redemption date. Until November 30, 2009, we may redeem up to 35% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2013 Notes and up to 35% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2016 Notes with the net cash proceeds of one or more equity offerings by us with the proceeds that we retain or that are contributed to us, as applicable, at par plus a premium equal to the coupon, plus accrued and unpaid interest and additional interest, if any, as long as at least 65% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2013 Notes and the 2016 Notes, respectively, remains outstanding immediately after such optional redemption and such optional redemption occurs within 90 days of the date of the closing of such equity offering.
Under the indenture governing the Sabine Pass Senior Notes, except for permitted tax distributions, Sabine Pass LNG may not make distributions until certain conditions are satisfied. The indenture requires that Sabine Pass LNG apply its net operating cash flow (i) first, to fund with monthly deposits Sabine Pass LNG’s next semi-annual payment of approximately $75.5 million of interest on the Sabine Pass Senior Notes, and (ii) second, to fund a one-time, permanent debt service reserve fund equal to one semi-annual interest payment of approximately $75.5 million on the Sabine Pass Senior Notes. Distributions will be permitted only after Phase 1 Target Completion, as defined in the indenture governing the Sabine Pass Senior Notes, or such earlier date as project revenues are received, upon satisfaction of the foregoing funding requirements, after satisfying a fixed charge coverage ratio of 2:1 and after satisfying other conditions specified in the indenture.
Sabine Pass Credit Facility
In February 2005, we entered into the original Sabine Pass credit facility, which was subsequently amended and restated in July 2006. The Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility increased the amount of the loans available to us from $822 million to $1.5 billion to finance a substantial majority of the costs of constructing and placing into operation Phase 1 and Phase 2—Stage 1 of our Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. In November 2006, as discussed above, borrowings under the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility were repaid, and the Sabine Pass credit facility was terminated in conjunction with the issuance of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes.
Borrowings under the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility bore interest at a variable rate equal to LIBOR plus the applicable margin. The applicable margin varied from 0.875% to 1.125% during the term of the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility. Interest was calculated on the unpaid principal amount outstanding and was payable semi-annually in arrears. A commitment fee of 0.50% per annum on the daily, undrawn portion of the lenders’ commitment was required. Administrative fees were also paid annually to the agent and the collateral agent.
F-16
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Subordinated Promissory Note—Affiliate
In November 2005, to fund expenditures related to the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, we entered into a subordinated promissory note with an affiliate, Cheniere LNG Financial Services, Inc., that bore interest at LIBOR plus a 3.00% margin and was to terminate on June 30, 2015. As of December 31, 2005, the unpaid principal balance of the subordinated promissory note was $37.4 million. The entire principal was due and payable to Cheniere LNG Financial Services, Inc. on June 30, 2015. In July 2006, we repaid the subordinated promissory note to our affiliate with borrowings from the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility.
NOTE 12—FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The estimated fair value of financial instruments is the amount at which the instrument could be exchanged currently between willing parties. The carrying amounts reported on the balance sheet for cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable approximate fair value due to their short-term nature. We use available marketing data and valuation methodologies to estimate the fair value of debt. This disclosure is presented in accordance with SFAS No. 107, Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments, and does not impact our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Long-Term Debt:
| December 31, 2006 | ||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||
| Carrying Amount |
Estimated Value | |||||
| 2013 Notes (1) |
$ | 550,000 | $ | 547,250 | ||
| 2016 Notes (1) |
1,482,000 | 1,478,295 | ||||
| $ | 2,032,000 | $ | 2,025,545 | |||
| (1) | The fair value of the Sabine Pass Senior Notes was based on quotations obtained from broker-dealers who made markets in these and similar instruments as of December 29, 2006. |
NOTE 13—RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
In August 2006, we reimbursed an affiliate for certain previously incurred costs directly related to Phase 2—Stage 1 of our Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. These costs, which amounted to $14.9 million, were reimbursed in connection with borrowings under the Amended Sabine Pass Credit Facility. We accounted for these reimbursed costs consistent with how the affiliated company recorded these costs, which was consistent with our accounting policy related to accounting for LNG activities. The reimbursed costs were recorded by us as a $4.5 million Phase 2 development reimbursement expense on the Combined Statements of Operations, $6.4 million as an addition to LNG terminal construction-in-progress, $3.7 million as advances under long-term contracts and $0.3 million as debt issuance costs on the Combined Balance Sheets. In addition to the August 2006 reimbursement, an affiliate contributed $0.8 million to us for additional Phase 2—Stage 1 costs.
As of December 31, 2006 and 2005, we had $0.4 million and $0.2 million, respectively, of advances to affiliates.
During 2006 and 2005, we paid a management fee of $0.4 million per month as required under the O&M Agreement and the general partner MSA (both described below under Note 14) totaling $5.2 million and $4.0
F-17
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
million, respectively. These costs are included as an overhead charge from affiliates, net of capitalized general and administrative costs, within the accompanying Combined Statements of Operations. As of December 31, 2006 and 2005, we had $0.4 million and $0.4 million, respectively, of accrued liabilities to our affiliates related to these management fees.
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LP made a $35.2 million non-cash capital contribution to us that released us from our obligation to Sabine Pass LP for such amount.
In November 2006, Sabine Pass LNG entered into an amended and restated TUA with Cheniere Marketing for the reservation of approximately 2.0 Bcf/d of regasification capacity at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
NOTE 14—COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Lease Commitments
The following is a schedule by years of future minimum rental payments required as of December 31, 2006 under the LNG site leases described below (in thousands):
| Year ending December 31: |
|||
| 2007 |
$ | 1,507 | |
| 2008 |
1,506 | ||
| 2009 |
1,506 | ||
| 2010 |
1,501 | ||
| 2011 |
1,501 | ||
| Later years (1) |
124,583 | ||
| Total minimum payments required |
$ | 132,104 | |
| (1) | The later years include the remaining initial term and the six 10-year extensions, as the lease option renewals were reasonably assured, as defined in SFAS No. 13, Accounting for Leases. |
LNG Site Lease
In January 2005, we exercised our options and entered into three land leases for the site of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. The leases have an initial term of 30 years, with options to renew for six 10-year extensions with similar terms as the initial term. In February 2005, two of the three leases were amended, thereby increasing the total acreage under lease to 853 acres and increasing the annual lease payments to $1.5 million. The annual lease payment will be adjusted for inflation based on a consumer price index, as defined in the lease agreements, every five years. For 2005, these payments were capitalized ($1.5 million) as part of the construction cost of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal; however, beginning January 2006, these lease payments have been expensed as required by FSP FAS 13-1 and resulted in $1.5 million being recognized as land site rental expense on the Combined Statements of Operations for 2006.
EPC Agreements
Phase 1 EPC Agreements
In December 2004, we entered into a lump-sum turnkey EPC agreement with Bechtel pursuant to which Bechtel is providing services for the engineering, procurement and construction of Phase 1 of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. In December 2004, a limited notice to proceed (“NTP”) was issued and accepted by Bechtel, at which time Bechtel was required to promptly commence performance of certain off-site engineering and preparatory work under the EPC agreement. In early April 2005, a final NTP was issued, and Bechtel
F-18
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
commenced all other aspects of work under the EPC agreement. We agreed to pay Bechtel a contract price of $646.9 million plus certain reimbursable costs. This contract price is subject to adjustment for changes in certain commodity prices, contingencies, change orders and other items. Payments under the EPC agreement will be made in accordance with the payment schedule set forth in the EPC agreement. The contract price and payment schedule, including milestones, may be amended only by change order. Bechtel will be liable to us for certain delays in achieving substantial completion, minimum acceptance criteria and performance guarantees. Bechtel will be entitled to a scheduled bonus of $12.0 million, or a lesser amount in certain cases, if on or before April 3, 2008, Bechtel completes construction sufficient to achieve, among other requirements specified in the EPC agreement, a sendout rate of at least 2.0 Bcf/d for a minimum sustained test period of 24 hours. Bechtel will be entitled to receive an additional bonus of up to $67,000 per day (up to a maximum of $6.0 million) for each day that commercial operation is achieved prior to April 1, 2008. As of January 17, 2007, change orders for $119.5 million had been approved, increasing the total contract price to $766.4 million.
Phase 2—Stage 1 EPC Agreements
In July 2006, we entered into an engineering, procurement, construction and management (“EPCM”) agreement for Phase 2—Stage 1 with Bechtel for engineering, procurement, construction and management of construction services in connection with the 1.4 Bcf/d expansion at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Under the terms of the EPCM agreement, Bechtel will be paid on a cost reimbursable basis, plus a fixed fee in the amount of $18.5 million. A discretionary bonus may be paid to Bechtel at our sole discretion upon completion of Phase 2—Stage 1.
In July 2006, we entered into an EPC LNG Unit Rate Soil Improvement Contract with Remedial Construction Services, L.P. (“Remedial”) for engineering, procurement and construction of soil improvement work. Work includes, but is not limited to, design, surveying, estimating, procurement and transportation of materials, equipment, labor, supervision and construction activities necessary to satisfactorily complete work on the Phase 2—Stage 1 site. The estimated total contract price is $28.5 million. A 10% initial payment of $2.9 million was made to Remedial in August 2006 and is classified under Advances under long-term contracts on the Combined Balance Sheets. Additional progress payments will be paid based on quantities of work performed at unit rates, minus 10% retainage that will be paid upon final completion as well as any credits and early payment discounts applicable.
In July 2006, we entered into an EPC LNG Tank Contract with Diamond LNG LLC (“Diamond”) and Zachry Construction Corporation (“Zachry” and collectively with Diamond, the “Tank Contractor”) for the construction of two Phase 2—Stage 1 LNG storage tanks. In addition, we have the option (to be elected on or before March 31, 2007) for the Tank Contractor to engineer, procure and construct a sixth LNG storage tank, with the cost and completion date thereof to be agreed upon if the option is elected. The estimated total contract price for the two Phase 2—Stage 1 LNG storage tanks is $140.9 million. An initial payment of $6.4 million was made to Diamond and Zachry in August 2006. Additional milestone payments for work incurred, minus a 5% retainage that will be paid upon final completion, will be based on a lump-sum, fixed price, subject to adjustments based on fluctuations in the cost of labor and materials.
LNG Commitments
We have entered into TUAs with Total, Chevron and Cheniere Marketing, Inc., an affiliate and a wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere (“Cheniere Marketing”), to provide berthing for LNG tankers and for the unloading, storage and regasification of LNG at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal.
F-19
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Service Agreements
Operation and Maintenance Agreement
In February 2005, we entered into an Operation and Maintenance Agreement (“O&M Agreement”), with Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P. (“O&M Services”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere. Pursuant to the O&M Agreement, O&M Services agreed to provide all necessary services required to construct, operate and maintain the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. The O&M Agreement will remain in effect until 20 years after substantial completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Prior to substantial completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, we are required to pay a fixed monthly fee of $95,000 (indexed for inflation). The fixed monthly fee will increase to $130,000 (indexed for inflation) upon substantial completion of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, and O&M Services will thereafter be entitled to a bonus equal to 50% of the salary component of labor costs in certain circumstances to be agreed upon between us and O&M Services at the beginning of each operating year. In addition, we are required to reimburse O&M Services for its maintenance capital expenditures and operating expenses, which consist of labor, maintenance, land lease and insurance expenses.
Management Services Agreement
In September 2006, Sabine Pass GP entered into a Management Services Agreement (the “general partner MSA”) with Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc. (“Cheniere Terminals”). Pursuant to the general partners MSA, Cheniere Terminals provides to Sabine Pass GP the technical, financial, staffing and related support necessary to allow it to meet its obligations to Sabine Pass LNG under the management services agreement entered into between Sabine Pass LNG and Sabine Pass GP. Under the general partners MSA, Sabine Pass GP will pay Cheniere Terminals amounts that it receives from Sabine Pass LNG for management of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, which, prior to substantial completion of construction of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, is a monthly fixed fee of $340,000 (indexed for inflation) and thereafter, $520,000 (indexed for inflation).
Other Commitments
Cheniere Marketing’s Option for a Sixth LNG Storage Tank
In November 2006, we entered into the Cheniere Marketing TUA to provide berthing for LNG vessels and for the unloading, storage and regasification of LNG at the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Under the Cheniere Marketing TUA, Cheniere Marketing has the option to require us to construct a sixth LNG storage tank, which we may have to incur additional debt to construct. As described above under the Phase 2—Stage 1 agreements, we have an option, exercisable on or before March 31, 2007, to require Zachry and Diamond to engineer, procure and construct the sixth LNG storage tank, with the cost and completion date to be agreed upon if the option is exercised. If Cheniere Marketing exercises its option after March 31, 2007, we may have to negotiate one or more new construction agreements with one or more new contractors.
State Tax Sharing Agreement
In November 2006, we entered into a State Tax Sharing Agreement with Cheniere pursuant to which Cheniere has agreed to prepare and file all Texas franchise tax returns which we and Cheniere are required to file on a combined basis and to timely pay the combined Texas franchise tax liability. If Cheniere, in its sole discretion, demands such payments, we will pay to Cheniere an amount equal to the Texas franchise tax that we would be required to pay if our Texas franchise tax liability were computed on a separate company basis. The
F-20
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE)
NOTES TO COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
State Tax Sharing Agreement contains similar provisions for other state and local taxes required to be filed by Cheniere and us on a combined, consolidated or unitary basis. The State Tax Sharing Agreement is effective for tax returns first due on or after January 1, 2008. As of December 31, 2006, we had made no payments to Cheniere under this State Tax Sharing Agreement.
Legal Proceedings
We may in the future be involved as a party to various legal proceedings, which are incidental to the ordinary course of business. We regularly analyze current information and, as necessary, provide accruals for probable liabilities on the eventual disposition of these matters. In the opinion of management and legal counsel, as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, there were no threatened or pending legal matters that would have a material impact on our combined results of operations, financial position or cash flows.
NOTE 15—SUPPLEMENTAL CASH FLOW INFORMATION AND DISCLOSURES OF NON-CASH TRANSACTIONS
The following table provides supplemental disclosure of cash flow information (in thousands):
| Period from October 20, 2003 (Date of Inception) to December 31, 2006 | |||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||||||
| Cash paid for interest (1) |
$ | 12,287 | $ | 2,066 | $ | — | $ | 14,353 | |||||
| Non-cash distribution payable |
$ | — | $ | (10,000 | ) | $ | 10,000 | $ | — | ||||
| Non-cash equity contribution |
$ | 35,890 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 35,890 | |||||
| Construction-in-progress and debt issuance additions funded with accrued liabilities |
$ | 16,018 | $ | 42,812 | $ | — | $ | 16,018 | |||||
| (1) | All cash paid for interest was capitalized as construction-in-progress. |
F-21
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
BASIS OF PRESENTATION
The following unaudited pro forma combined financial statements give effect to the formation of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. (“Cheniere Energy Partners”) and the contribution of equity interests of certain entities (collectively, the “Combined Predecessor Entities”), as described in Note 1 to these unaudited pro forma combined financial statements and after giving effect to the following transactions (the “Formation Transactions”) upon the closing of Cheniere Energy Partners’ planned initial public offering:
| • | Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC (“Cheniere Holdings”) will contribute through us to our wholly-owned subsidiary, Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC, all of its equity interests in Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC, which own all of the equity interests in Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.; |
| • | we will issue to Cheniere Holdings 21,206,026 common units and 135,383,831 subordinated units; |
| • | we will issue to our general partner, a direct wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere Holdings, 3,302,045 general partner units representing a 2% general partner interest in us and all of our incentive distribution rights, which will entitle our general partner to increasing percentages of the cash that we distribute in excess of $0.489 per unit per quarter; |
| • | we will issue an estimated 5,210,331 common units to the public in the offering; and |
| • | we will use our net proceeds from the offering to deposit approximately $96.7 million into a distribution reserve restricted cash account. |
These statements are based on the historical audited financial statements of the Combined Predecessor Entities. Given that the Combined Predecessor Entities are all affiliated and under common control, these unaudited pro forma financial statements have been prepared on a carryover basis of historical cost as opposed to recognition at fair value under the purchase method of accounting.
The unaudited pro forma combined balance sheet gives effect to the Formation Transactions as if they had occurred on December 31, 2006. The unaudited pro forma combined statement of operations gives effect to the Formation Transactions as if they were consummated on January 1, 2006. These unaudited pro forma combined financial statements should be read in conjunction with the audited financial statements and notes thereto of the Combined Predecessor Entities. These unaudited pro forma financial statements should not be construed to be indicative of future results or results that actually would have occurred if the Formation Transactions and the offering had occurred at the dates presented.
F-22
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA COMBINED CONDENSED BALANCE SHEET
(As Defined in Note 1)
December 31, 2006
(in thousands)
| Total Combined |
Pro Forma Offering Adjustments |
Pro Forma as Adjusted |
||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) | |||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 7 | $ | — | $ | 7 | ||||||
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents |
355,327 | 96,652 | (a) | 451,979 | ||||||||
| Interest receivable |
5,226 | — | 5,226 | |||||||||
| Advances to affiliate |
379 | — | 379 | |||||||||
| Prepaid expenses |
385 | — | 385 | |||||||||
| TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS |
361,324 | 96,652 | 457,976 | |||||||||
| NON-CURRENT RESTRICTED CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
803,610 | — | 803,610 | |||||||||
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
651,676 | — | 651,676 | |||||||||
| DEBT ISSUANCE COSTS, NET |
33,970 | — | 33,970 | |||||||||
| ADVANCES UNDER LONG-TERM CONTRACTS |
7,250 | — | 7,250 | |||||||||
| LNG INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
18 | — | 18 | |||||||||
| OTHER |
266 | — | 266 | |||||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 1,858,114 | $ | 96,652 | $ | 1,954,766 | ||||||
| LIABILITY AND OWNERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
|
|||||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES |
||||||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 758 | $ | — | $ | 758 | ||||||
| Accounts payable—affiliate |
223 | — | 223 | |||||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
36,670 | — | 36,670 | |||||||||
| Accrued liabilities—affiliate |
652 | — | 652 | |||||||||
| TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES |
38,303 | — | 38,303 | |||||||||
| LONG-TERM DEBT |
2,032,000 | — | 2,032,000 | |||||||||
| DEFERRED REVENUE |
40,000 | — | 40,000 | |||||||||
| OTHER |
1,149 | — | 1,149 | |||||||||
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| OWNERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
||||||||||||
| Owners’ deficit. |
(253,338 | ) | 253,338 | (b) | — | |||||||
| Common units. |
— | 96,652 | (a) | 73,548 | ||||||||
| (23,104 | )(b) | |||||||||||
| Subordinated units. |
— | (224,762 | )(b) | (224,762 | ) | |||||||
| General partner units. |
— | (5,472 | )(b) | (5,472 | ) | |||||||
| TOTAL OWNERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
(253,338 | ) | 96,652 | (156,686 | ) | |||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND OWNERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
$ | 1,858,114 | $ | 96,652 | $ | 1,954,766 | ||||||
See accompanying notes to combined financial statements.
F-23
THE COMBINED PREDECESSOR ENTITIES
UNAUDITED PRO FORMA COMBINED CONDENSED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
(As Defined in Note 1)
(in thousands, except for per unit amounts)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| Total Combined |
Pro Forma Offering Adjustments |
Pro Forma | ||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) | |||||||||||
| REVENUES |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| EXPENSES |
||||||||||||
| Legal |
2 | — | 2 | |||||||||
| Professional |
571 | 2,500 | (c) | 3,071 | ||||||||
| Technical consulting |
27 | — | 27 | |||||||||
| Land site rental |
1,515 | — | 1,515 | |||||||||
| Depreciation expense |
50 | — | 50 | |||||||||
| Overhead charge from affiliates |
3,450 | — | 3,450 | |||||||||
| Phase 2 development reimbursement to affiliate |
4,527 | — | 4,527 | |||||||||
| Other |
135 | — | 135 | |||||||||
| TOTAL EXPENSES |
10,277 | 2,500 | 12,777 | |||||||||
| LOSS FROM OPERATIONS |
(10,277 | ) | (2,500 | ) | (12,777 | ) | ||||||
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
||||||||||||
| Interest income |
9,306 | — | 9,306 | |||||||||
| Interest expense |
(15,463 | ) | — | (15,463 | ) | |||||||
| Loss on early extinguishment of debt |
(23,761 | ) | — | (23,761 | ) | |||||||
| Derivative gain (loss), net |
(20,577 | ) | — | (20,577 | ) | |||||||
| TOTAL OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
(50,495 | ) | — | (50,495 | ) | |||||||
| NET LOSS |
$ | (60,772 | ) | $ | (2,500 | ) | $ | (63,272 | ) | |||
| General partners’ interest in net loss |
— | — | (1,265 | ) | ||||||||
| Limited partners’ interest in net loss |
— | — | (62,007 | ) | ||||||||
| Net loss per limited partners’ units |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
— | — | (0.38 | ) | ||||||||
| Diluted |
— | — | (0.38 | ) | ||||||||
| Weighted average limited partners’ units outstanding |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
— | — | (161,800 | )(d) | ||||||||
| Diluted |
— | — | (161,800 | )(d) | ||||||||
See accompanying unaudited notes to pro forma combined financial statements.
F-24
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
UNAUDITED NOTES TO PRO FORMA COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1—NATURE OF OPERATIONS
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. (“Cheniere Energy Partners”) is a Delaware limited partnership formed on November 21, 2006 by Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC (the “Limited Partner”) and Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC (the “General Partner”), both of which are indirect, wholly-owned subsidiaries of Cheniere Energy, Inc. (“Cheniere”). Cheniere Energy Partners was formed to develop, own and operate the Sabine Pass liquefied natural gas, or LNG, receiving and regasification facility, in western Cameron Parish, Louisiana on the Sabine Pass Channel (the “Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal”). Cheniere Energy Partners is in the process of registering its common units, representing limited partner interests, to be sold in an initial public offering (the “Offering”).
In accordance with the Rules and Regulations of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, the following entities are included in the combined financial statements:
| • | Cheniere Energy Partners; |
| • | Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC is a Delaware limited liability company owned by Cheniere Energy Partners and was formed on November 21, 2006 to hold 100% of the ownership interests in Sabine Pass GP and Sabine Pass LP; |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. (“Sabine Pass GP”) is a Delaware corporation owned by the Limited Partner and was formed in 2004 to be the general partner of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (“Sabine Pass LNG”); |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC (“Sabine Pass LP”) is a Delaware limited liability company owned by the Limited Partner and was formed in 2004 to be the limited partner of Sabine Pass LNG; and |
| • | Sabine Pass LNG is a Delaware limited partnership, formed with one general partner, Sabine Pass GP, and one limited partner, Sabine Pass LP, which owns the entire interest in the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. Sabine Pass LNG is in the development stage, and the purpose of this limited partnership is to own and operate the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal. |
At the closing of the Offering, the equity interests in Sabine Pass GP and Sabine Pass LP will be contributed to Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC, thereby resulting in Sabine Pass GP, Sabine Pass LP and Sabine Pass LNG becoming indirect, wholly-owned subsidiaries of Cheniere Energy Partners. As used in these Notes to the Combined Financial Statements, the terms “we”, “us” and “our” refer to the foregoing entities on a combined basis (the “Combined Predecessor Entities”).
NOTE 2—PRO FORMA ADJUSTMENTS
(a) Reflects estimated net proceeds of $96.7 million from the issuance and sale of 5.2 million common units at an initial public offering price of $20.00 per unit including underwriting discounts and commissions of $7.5 million.
(b) Reflects the contribution of the net tangible book value of the Combined Predecessor Entities in exchange for general, common and subordinated units of Cheniere Energy Partners upon the closing of the Offering.
(c) Reflects estimated on-going and administrative costs that will be incurred as a result of being a public entity, including, among other things, estimated incremental accounting and audit fees, legal fees, director fees, tax fees, director and officer liability insurance expenses and other miscellaneous costs. This adjustment does not include the $10.0 million annual administrative fee that will begin January 1, 2009, payable to Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of Cheniere.
F-25
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
UNAUDITED NOTES TO PRO FORMA COMBINED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
(d) The weighted-average limited partners’ units outstanding used in the net loss per unit calculation includes the limited partners’ common and subordinated units and excludes the general partner interest. The weighted-average limited partners’ units outstanding have been adjusted to reflect the common units and subordinated units issued in connection with the Offering as if these units have been outstanding since January 1, 2006.
NOTE 3—PRO FORMA NET LOSS PER UNIT
Pro forma net loss per limited partner unit for the year ended December 31, 2006 is determined by dividing the pro forma net loss that would have been allocated to the holders of the common units and subordinated units, which is 98% of the pro forma net loss, by the number of common units and subordinated units expected to be outstanding at the close of the Offering. For purposes of this calculation, the number of common units and subordinated units outstanding of 161.8 million was assumed to have been outstanding since January 1, 2006. Pursuant to the Cheniere Energy Partners partnership agreement, to the extent that the quarterly distribution exceeds certain thresholds, the general partner is entitled to certain incentive distributions, which will result in less income proportionately being allocated to the holders of the common units and subordinated units. The pro forma net loss per unit for the year ended December 31, 2006 does not reflect the incentive distributions due to the incentive distribution not being met for any quarter during 2006.
NOTE 4—DESCRIPTION OF EQUITY INTEREST
The common units and subordinated units represent limited partner interest in us. The holders of the units are entitled to participate in partnership distributions and exercise the rights and privileges available to limited partners under the Cheniere Energy Partners partnership agreement.
The common units will have the right to receive minimum quarterly distributions of $0.425 per unit, plus any arrearages on the common units, before any distribution is made to the holders of the subordinated units.
During the subordination period, the subordinated units will not be entitled to receive any distributions until the common units have received $0.425 plus any arrearages from prior quarters. Subordinated units will covert into common units on a one-for-one basis when the subordinated period ends. The subordinated period will end when we meet financial tests specified in the partnership agreement but generally cannot end before June 30, 2008.
The general partner interest is entitled to at least 2% of all distributions made by us. In addition, the general partner holds incentive distribution rights, which allow the general partner to receive a higher percentage of quarterly distributions of available cash from operating surplus after the minimum distributions have been achieved and as additional target levels are met. The higher percentages range from 15% up to 50%. The pro forma financial statements assume that no incentive distributions were made to the general partner, other than actual incentive distributions earned. In subsequent periods, we will apply the hypothetical liquidation at book value method in allocating income to the various partnership interests.
F-26
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Partners of
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
Houston, Texas
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. (the “Partnership”) and its wholly-owned subsidiary, as of December 31, 2006. This consolidated financial statement is the responsibility of the Partnership’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on this consolidated financial statement based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated balance sheet is free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated balance sheet, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall consolidated balance sheet presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated balance sheet presents fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. and its wholly-owned subsidiary, as of December 31, 2006 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ UHY LLP
Houston, Texas
February 9, 2007
F-27
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE
DECEMBER 31, 2006
| ASSETS |
|||
| Cash |
$ | 1,000 | |
| Total Assets |
$ | 1,000 | |
| PARTNERS’ CAPITAL |
|||
| Partners’ Capital |
|||
| Limited partner |
$ | 980 | |
| General partner |
20 | ||
| Total partners’ capital |
$ | 1,000 | |
See accompanying note to consolidated balance sheet.
F-28
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
(A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE )
NOTE TO CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
NOTE 1—ORGANIZATION AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. (the “Partnership”) is a Delaware limited partnership formed on November 21, 2006 by Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC (the “Limited Partner”) and Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC (the “General Partner”), both of which are indirect, wholly-owned subsidiaries of Cheniere Energy, Inc. (“Cheniere”). On November 21, 2006, the Partnership also formed a wholly-owned subsidiary, Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC (“Cheniere Energy Investments”), a Delaware limited liability company. The Partnership was formed to develop, own and operate the Sabine Pass liquefied natural gas, or LNG, receiving and regasification terminal, in western Cameron Parish, Louisiana on the Sabine Pass Channel (the “Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal”). The Partnership is in the process of registering its common units, representing limited partner interests, to be sold in an initial public offering (the “Offering”). The Partnership has been formed and capitalized; however, the Partnership has not conducted any material operations since its formation, and as such is a Development Stage Enterprise.
The consolidated balance sheet includes the accounts of the Partnership and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Cheniere Energy Investments. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
At the closing of the Offering, the equity interests in Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC, which are the general partner and limited partner, respectively, of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., the owner of the Sabine Pass LNG receiving terminal, will be contributed to Cheniere Energy Investments, resulting in such entities becoming indirect, wholly-owned subsidiaries of the Partnership.
F-29
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Member of
Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC
Houston, Texas
We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2006. This financial statement is the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on this financial statement based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the balance sheet is free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the balance sheet, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall balance sheet presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such balance sheet presents fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC as of December 31, 2006 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ UHY LLP
Houston, Texas
February 9, 2007
F-30
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS GP, LLC
A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE
DECEMBER 31, 2006
| ASSETS |
|||
| Cash |
$ | 1,000 | |
| Investment in Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. |
20 | ||
| Total Assets |
$ | 1,020 | |
| LIABILITIES AND MEMBERS’ CAPITAL |
|||
| Payable to Affiliate |
$ | 188 | |
| Members’ Capital |
832 | ||
| Total members’ capital |
$ | 1,020 | |
See accompanying note to balance sheet.
F-31
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS GP, LLC
A DEVELOPMENT STAGE ENTERPRISE
December 31, 2006
NOTE 1—ORGANIZATION
Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC (the “General Partner”) is a Delaware limited liability company formed on November 21, 2006, to become the general partner of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. (the “Partnership”). The General Partner has invested $20 in the Partnership for its 2% general partner interest. The General Partner has not conducted any operations since its formation.
F-32
APPENDIX A
FIRST AMENDED AND RESTATED
AGREEMENT OF LIMITED PARTNERSHIP
OF
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
A-i
A-ii
| ARTICLE X | ||||
| ADMISSION OF PARTNERS | ||||
| Section 10.1 |
A-60 | |||
| Section 10.2 |
A-61 | |||
| Section 10.3 |
A-61 | |||
| Section 10.4 |
A-61 | |||
| Section 10.5 |
Amendment of Agreement and Certificate of Limited Partnership |
A-62 | ||
| ARTICLE XI | ||||
| WITHDRAWAL OR REMOVAL OF PARTNERS | ||||
| Section 11.1 |
A-62 | |||
| Section 11.2 |
A-63 | |||
| Section 11.3 |
Interest of Departing General Partner and Successor General Partner |
A-64 | ||
| Section 11.4 |
A-65 | |||
| Section 11.5 |
A-65 | |||
| ARTICLE XII | ||||
| DISSOLUTION AND LIQUIDATION | ||||
| Section 12.1 |
A-65 | |||
| Section 12.2 |
A-66 | |||
| Section 12.3 |
A-66 | |||
| Section 12.4 |
A-66 | |||
| Section 12.5 |
A-67 | |||
| Section 12.6 |
A-67 | |||
| Section 12.7 |
A-67 | |||
| Section 12.8 |
A-67 | |||
| ARTICLE XIII | ||||
|
AMENDMENT OF PARTNERSHIP AGREEMENT; MEETINGS; RECORD DATE | ||||
| Section 13.1 |
A-68 | |||
| Section 13.2 |
A-69 | |||
| Section 13.3 |
A-69 | |||
| Section 13.4 |
A-69 | |||
| Section 13.5 |
A-70 | |||
| Section 13.6 |
A-70 | |||
| Section 13.7 |
A-70 | |||
| Section 13.8 |
A-70 | |||
| Section 13.9 |
A-71 | |||
| Section 13.10 |
A-71 | |||
| Section 13.11 |
A-71 | |||
| Section 13.12 |
A-72 | |||
| ARTICLE XIV | ||||
| MERGER, CONSOLIDATION OR CONVERSION | ||||
| Section 14.1 |
A-72 | |||
| Section 14.2 |
A-72 | |||
A-iii
| Section 14.3 |
Approval by Limited Partners of Merger, Consolidation or Conversion |
A-74 | ||
| Section 14.4 |
A-75 | |||
| Section 14.5 |
A-75 | |||
| Section 14.6 |
A-75 | |||
| Section 14.7 |
A-75 | |||
| ARTICLE XV | ||||
| RIGHT TO ACQUIRE LIMITED PARTNER INTERESTS | ||||
| Section 15.1 |
A-76 | |||
| ARTICLE XVI | ||||
| GENERAL PROVISIONS | ||||
| Section 16.1 |
A-77 | |||
| Section 16.2 |
A-77 | |||
| Section 16.3 |
A-77 | |||
| Section 16.4 |
A-77 | |||
| Section 16.5 |
A-77 | |||
| Section 16.6 |
A-77 | |||
| Section 16.7 |
A-78 | |||
| Section 16.8 |
A-78 | |||
| Section 16.9 |
A-78 | |||
| Section 16.10 |
A-78 | |||
| Section 16.11 |
A-78 | |||
| Section 16.12 |
A-78 | |||
A-iv
FIRST AMENDED AND RESTATED
AGREEMENT OF LIMITED PARTNERSHIP OF
CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P.
THIS FIRST AMENDED AND RESTATED AGREEMENT OF LIMITED PARTNERSHIP OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P., dated as of , 2007, is entered into by and between Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, as the General Partner, and Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, as the Organizational Limited Partner, together with any other Persons who become Partners in the Partnership or parties hereto as provided herein. In consideration of the covenants, conditions and agreements contained herein, the parties agree as follows:
The following definitions shall be for all purposes, unless otherwise clearly indicated to the contrary, applied to the terms used in this Agreement.
“Acquisition” means any transaction in which any Group Member acquires (through an asset acquisition, merger, stock acquisition or other form of investment) control over all or a portion of the assets, properties or business of another Person for the purpose of increasing the operating capacity or asset base of the Partnership Group from the operating capacity or asset base of the Partnership Group existing immediately prior to such transaction.
“Additional Book Basis” means the portion of any remaining Carrying Value of an Adjusted Property that is attributable to positive adjustments made to such Carrying Value as a result of Book-Up Events. For purposes of determining the extent that Carrying Value constitutes Additional Book Basis:
(a) Any negative adjustment made to the Carrying Value of an Adjusted Property as a result of either a Book-Down Event or a Book-Up Event shall first be deemed to offset or decrease that portion of the Carrying Value of such Adjusted Property that is attributable to any prior positive adjustments made thereto pursuant to a Book-Up Event or Book-Down Event.
(b) If Carrying Value that constitutes Additional Book Basis is reduced as a result of a Book-Down Event and the Carrying Value of other property is increased as a result of such Book-Down Event, an allocable portion of any such increase in Carrying Value shall be treated as Additional Book Basis; provided, that the amount treated as Additional Book Basis pursuant hereto as a result of such Book-Down Event shall not exceed the amount by which the Aggregate Remaining Net Positive Adjustments after such Book-Down Event exceeds the remaining Additional Book Basis attributable to all of the Partnership’s Adjusted Property after such Book-Down Event (determined without regard to the application of this clause (b) to such Book-Down Event).
“Additional Book Basis Derivative Items” means any Book Basis Derivative Items that are computed with reference to Additional Book Basis. To the extent that the Additional Book Basis attributable to all of the Partnership’s Adjusted Property as of the beginning of any taxable period exceeds the Aggregate Remaining Net Positive Adjustments as of the beginning of such period (the “Excess Additional Book Basis”), the Additional Book Basis Derivative Items for such period shall be reduced by the amount that bears the same ratio to the amount of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items determined without regard to this sentence as the Excess Additional Book Basis bears to the Additional Book Basis as of the beginning of such period.
“Additional Limited Partner” means a Person admitted to the Partnership as a Limited Partner pursuant to Section 10.4 and who is shown as such on the books and records of the Partnership.
A-1
“Adjusted Capital Account” means the Capital Account maintained for each Partner as of the end of each fiscal year of the Partnership, (a) increased by any amounts that such Partner is obligated to restore under the standards set by Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(ii)(c) (or is deemed obligated to restore under Treasury Regulation Sections 1.704-2(g) and 1.704-2(i)(5)) and (b) decreased by (i) the amount of all losses and deductions that, as of the end of such fiscal year, are reasonably expected to be allocated to such Partner in subsequent years under Sections 704(e)(2) and 706(d) of the Code and Treasury Regulation Section 1.751-1(b)(2)(ii), and (ii) the amount of all distributions that, as of the end of such fiscal year, are reasonably expected to be made to such Partner in subsequent years in accordance with the terms of this Agreement or otherwise to the extent they exceed offsetting increases to such Partner’s Capital Account that are reasonably expected to occur during (or prior to) the year in which such distributions are reasonably expected to be made (other than increases as a result of a minimum gain chargeback pursuant to Section 6.1(d)(i) or 6.1(d)(ii)). The foregoing definition of Adjusted Capital Account is intended to comply with the provisions of Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(ii)(d) and shall be interpreted consistently therewith. The “Adjusted Capital Account” of a Partner in respect of a General Partner Unit, a Common Unit, a Subordinated Unit, an Incentive Distribution Right or any other Partnership Interest shall be the amount that such Adjusted Capital Account would be if such General Partner Unit, Common Unit, Subordinated Unit, Incentive Distribution Right or other Partnership Interest were the only interest in the Partnership held by such Partner from and after the date on which such General Partner Unit, Common Unit, Subordinated Unit, Incentive Distribution Right or other Partnership Interest was first issued.
“Adjusted Operating Surplus” means, with respect to any period, Operating Surplus generated with respect to such period (a) less (i) any net increase in Working Capital Borrowings with respect to such period and (ii) any net decrease in cash reserves for Operating Expenditures with respect to such period not relating to an Operating Expenditure made with respect to such period, and (b) plus (i) any net decrease in Working Capital Borrowings with respect to such period, and (ii) any net increase in cash reserves for Operating Expenditures with respect to such period required by any debt instrument for the repayment of principal, interest or premium. Adjusted Operating Surplus does not include that portion of Operating Surplus included in clause (a)(i) of the definition of Operating Surplus. Cash amounts held in the Distribution Reserve Account or amounts released therefrom shall not constitute Adjusted Operating Surplus.
“Adjusted Property” means any property the Carrying Value of which has been adjusted pursuant to Section 5.5(d)(i) or 5.5(d)(ii).
“Affiliate” means, with respect to any Person, any other Person that directly or indirectly through one or more intermediaries controls, is controlled by or is under common control with, the Person in question. As used herein, the term “control” means the possession, direct or indirect, of the power to direct or cause the direction of the management and policies of a Person, whether through ownership of voting securities, by contract or otherwise.
“Aggregate Remaining Net Positive Adjustments” means, as of the end of any taxable period, the sum of the Remaining Net Positive Adjustments of all the Partners.
“Agreed Allocation” means any allocation, other than a Required Allocation, of an item of income, gain, loss or deduction pursuant to the provisions of Section 6.1, including a Curative Allocation (if appropriate to the context in which the term “Agreed Allocation” is used).
“Agreed Value” of any Contributed Property means the fair market value of such property or other consideration at the time of contribution as determined by the General Partner. The General Partner shall use such method as it determines to be appropriate to allocate the aggregate Agreed Value of Contributed Properties contributed to the Partnership in a single or integrated transaction among each separate property on a basis proportional to the fair market value of each Contributed Property.
“Agreement” means this First Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P., as it may be amended, supplemented or restated from time to time.
A-2
“Assignee” means a Person to whom one or more Limited Partner Interests have been transferred in a manner permitted under this Agreement and who has executed and delivered a Transfer Application, as required by this Agreement, but who has not been admitted as a Substituted Limited Partner.
“Assignment Agreement” means the Assignment Agreement, dated as of , 2007, between O&M Services and the General Partner.
“Associate” means, when used to indicate a relationship with any Person, (a) any corporation or organization of which such Person is a director, officer or partner or is, directly or indirectly, the owner of 20% or more of any class of voting stock or other voting interest; (b) any trust or other estate in which such Person has at least a 20% beneficial interest or as to which such Person serves as trustee or in a similar fiduciary capacity; and (c) any relative or spouse of such Person, or any relative of such spouse, who has the same principal residence as such Person.
“Available Cash” means, with respect to any Quarter ending prior to the Liquidation Date:
(a) the sum of (i) all cash and cash equivalents of the Partnership Group (or the Partnership’s proportionate share of cash and cash equivalents in the case of Subsidiaries that are not wholly owned) on hand at the end of such Quarter, (ii) all additional cash and cash equivalents of the Partnership Group (or the Partnership’s proportionate share of cash and cash equivalents in the case of Subsidiaries that are not wholly owned) on hand on the date of determination of Available Cash with respect to such Quarter resulting from Working Capital Borrowings made subsequent to the end of such Quarter and (iii) the amount in the Distribution Reserve Account equal to the sum of the Initial Quarterly Distribution times the number of Outstanding Common Units and Outstanding General Partner Units on the Record Date for such Quarter (or, for the Quarter in which the closing of the Initial Public Offering occurs, such amount multiplied by a fraction, of which the numerator is the number of days in the period from the closing of the Initial Public Offering through the end of such Quarter and of which the denominator is the number of days in such Quarter) but only to the extent such amounts are necessary to make distributions required pursuant to Section 6.4 for such Quarter, less
(b) the amount of any cash reserves (or the Partnership’s proportionate share of cash reserves in the case of Subsidiaries that are not wholly owned) established by the General Partner to (i) provide for the proper conduct of the business of the Partnership Group (including reserves for future capital expenditures, for anticipated future credit needs of the Partnership Group and for refunds of collected rates reasonably likely to be refunded as a result of a settlement or hearing relating to FERC rate proceedings) subsequent to such Quarter, (ii) comply with applicable law or any loan agreement, security agreement, mortgage, debt instrument or other agreement or obligation to which any Group Member is a party or by which it is bound or its assets are subject or (iii) provide funds for distributions under Section 6.4 or 6.5 in respect of any one or more of the next four Quarters; provided, however, that the General Partner may not establish cash reserves pursuant to clause (iii) above if the effect of such reserves would be that the Partnership is unable to distribute the Initial Quarterly Distribution on all Common Units, plus any Cumulative Common Unit Arrearage on all Common Units, with respect to such Quarter or would prevent the Partnership from using the Distribution Reserve Amount to distribute the Initial Quarterly Distribution on all Outstanding Common Units and Outstanding General Partner Units with respect to such Quarter; and, provided further, that disbursements made by a Group Member or cash reserves established, increased or reduced after the end of such Quarter but on or before the date of determination of Available Cash with respect to such Quarter shall be deemed, for purposes of determining Available Cash, to have been made, established, increased or reduced within such Quarter if the General Partner so determines.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, “Available Cash” with respect to the Quarter in which the Liquidation Date occurs and any subsequent Quarter shall equal zero.
“Board of Directors” means, with respect to the Board of Directors of the General Partner, its board of directors or managers, as applicable, if a corporation or limited liability company, or if a limited partnership, the board of directors or board of managers of the general partner of the General Partner.
A-3
“Book Basis Derivative Items” means any item of income, deduction, gain or loss included in the determination of Net Income or Net Loss that is computed with reference to the Carrying Value of an Adjusted Property (e.g., depreciation, depletion, or gain or loss with respect to an Adjusted Property).
“Book-Down Event” means an event that triggers a negative adjustment to the Capital Accounts of the Partners pursuant to Section 5.5(d).
“Book-Tax Disparity” means with respect to any item of Contributed Property or Adjusted Property, as of the date of any determination, the difference between the Carrying Value of such Contributed Property or Adjusted Property and the adjusted basis thereof for federal income tax purposes as of such date. A Partner’s share of the Partnership’s Book-Tax Disparities in all of its Contributed Property and Adjusted Property will be reflected by the difference between such Partner’s Capital Account balance as maintained pursuant to Section 5.5 and the hypothetical balance of such Partner’s Capital Account computed as if it had been maintained strictly in accordance with federal income tax accounting principles.
“Book-Up Event” means an event that triggers a positive adjustment to the Capital Accounts of the Partners pursuant to Section 5.5(d).
“Business Day” means Monday through Friday of each week, except that a legal holiday recognized as such by the government of the United States of America or the States of New York or Texas shall not be regarded as a Business Day.
“Capital Account” means the capital account maintained for a Partner pursuant to Section 5.5. The “Capital Account” of a Partner in respect of a General Partner Unit, a Common Unit, a Subordinated Unit, an Incentive Distribution Right or any other Partnership Interest shall be the amount that such Capital Account would be if such General Partner Unit, Common Unit, Subordinated Unit, Incentive Distribution Right or other Partnership Interest were the only interest in the Partnership held by such Partner from and after the date on which such General Partner Unit, Common Unit, Subordinated Unit, Incentive Distribution Right or other Partnership Interest was first issued.
“Capital Contribution” means any cash, cash equivalents or the Net Agreed Value of Contributed Property (which, in the case of a Capital Contribution by the General Partner pursuant to Section 5.2(b) may include Units (other than General Partner Units) owned by the General Partner) that a Partner contributes to the Partnership.
“Capital Improvement” means any (a) addition or improvement to the capital assets owned by any Group Member, (b) acquisition of existing, or the construction of new, capital assets (including pipelines, gathering lines, regasification facilities, processing plants, LNG carriers, docks, terminals, truck racks, pipeline compression facilities, tankage and other storage, gathering and distribution facilities and related or similar assets) or (c) capital contribution by a Group Member to a Person that is not a Subsidiary in which a Group Member has an equity interest, to fund the Group Member’s pro rata share of the cost of the acquisition of existing, or the construction of new, capital assets (including pipelines, gathering lines, regasification facilities, processing plants, LNG carriers, docks, terminals, truck racks, pipeline compression facilities, tankage and other storage, gathering and distribution facilities and related or similar assets), in each case if such addition, improvement, acquisition or construction is made to increase the operating capacity or asset base of the Partnership Group, in the case of clauses (a) and (b), or such Person, in the case of clause (c), from the operating capacity or asset base of the Partnership Group or such Person, as the case may be, immediately prior to such addition, improvement, acquisition or construction; provided, however, that to the extent any such addition, improvement, acquisition or construction is made solely for investment purposes it shall not constitute a Capital Improvement under this Agreement.
“Capital Surplus” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 6.3(a).
A-4
“Carrying Value” means (a) with respect to a Contributed Property, the Agreed Value of such property reduced (but not below zero) by all depreciation, amortization and cost recovery deductions charged to the Partners’ and Assignees’ Capital Accounts in respect of such Contributed Property, and (b) with respect to any other Partnership property, the adjusted basis of such property for federal income tax purposes, all as of the time of determination. The Carrying Value of any property shall be adjusted from time to time in accordance with Sections 5.5(d)(i) and 5.5(d)(ii) and to reflect changes, additions or other adjustments to the Carrying Value for dispositions and acquisitions of Partnership properties, as deemed appropriate by the General Partner.
“Cause” means a court of competent jurisdiction has entered a final, non-appealable judgment finding the General Partner liable for actual fraud or willful misconduct in its capacity as a general partner of the Partnership.
“Certificate” means (a) a certificate (i) substantially in the form of Exhibit A to this Agreement, (ii) issued in global form in accordance with the rules and regulations of the Depositary or (iii) in such other form as may be adopted by the General Partner, issued by the Partnership evidencing ownership of one or more Common Units; or (b) a certificate, in such form as may be adopted by the General Partner, issued by the Partnership evidencing ownership of one or more other Partnership Securities.
“Certificate of Limited Partnership” means the Certificate of Limited Partnership of the Partnership filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware as referenced in Section 7.2, as such Certificate of Limited Partnership may be amended, supplemented or restated from time to time.
“Cheniere LNG Holdings” means Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company.
“Cheniere Marketing” means Cheniere Marketing, Inc., a Delaware corporation.
“Citizenship Certification” means a properly completed certificate in such form as may be specified by the General Partner by which an Assignee or a Limited Partner certifies that such Assignee or Limited Partner (and if such Assignee or Limited Partner is a nominee holding for the account of another Person, that to the best of such Assignee’s or Limited Partner’s knowledge such other Person) is an Eligible Citizen.
“claim” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 7.12(d).
“Closing Date” means the first date on which Common Units are issued and sold by the Partnership to the Underwriters pursuant to the provisions of the Underwriting Agreement.
“Closing Price” means, in respect of any class of Limited Partner Interests, as of the date of determination, the official closing price on such day, regular way, or, if no official closing price is available, the last sale price on such day, regular way, or in case no such sale takes place on such day, the average of the closing bid and asked prices on such day, regular way, as reported in the principal consolidated transaction reporting system with respect to securities listed on the principal National Securities Exchange (other than the Nasdaq Global Market) on which the respective Limited Partner Interests are listed or admitted to trading or, if such Limited Partner Interests are not listed or admitted to trading on any National Securities Exchange (other than the Nasdaq Global Market), the last quoted price on such day or, if not so quoted, the average of the high bid and low asked prices on such day in the over-the-counter market, as reported by the Nasdaq Global Market or such other system then in use, or, if on any such day such Limited Partner Interests of such class are not quoted by any such organization, the average of the closing bid and asked prices on such day as furnished by a professional market maker making a market in such Limited Partner Interests of such class selected by the General Partner, or if on any such day no market maker is making a market in such Limited Partner Interests of such class, the fair value of such Limited Partner Interests on such day as determined by the General Partner.
“Code” means the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended and in effect from time to time. Any reference herein to a specific section or sections of the Code shall be deemed to include a reference to any corresponding provision of any successor law.
A-5
“Combined Interest” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 11.3(a).
“Commences Commercial Service” means the date upon which a Capital Improvement is first put into commercial service following construction and testing.
“Commission” means the United States Securities and Exchange Commission.
“Commodity Hedge Contract” means any commodity exchange, swap, forward, cap, floor collar or other similar agreement or arrangement entered into for the purpose of reducing the exposure of the Partnership Group to fluctuations in the price of hydrocarbons (including liquefied natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas) in their operations and not for speculative purposes.
“Common Unit” means a Unit representing a fractional part of the Partnership Interests of all Limited Partners and Assignees having the rights and obligations specified with respect to Common Units in this Agreement. The term “Common Unit” does not include a Subordinated Unit prior to its conversion into a Common Unit pursuant to the terms hereof.
“Common Unit Arrearage” means, with respect to any Common Unit, whenever issued, as to any Quarter within the Subordination Period, the excess, if any, of (a) the Initial Quarterly Distribution with respect to a Common Unit in respect of such Quarter over (b) the sum of all Available Cash distributed with respect to a Common Unit in respect of such Quarter pursuant to Section 6.4(a)(i).
“Conflicts Committee” means a committee of the Board of Directors of the General Partner composed entirely of two or more directors, each of whom (a) is not a security holder, officer or employee of the General Partner, (b) is not an officer, director or employee of any Affiliate of the General Partner, (c) is not a holder of any ownership interest in the Partnership Group other than Common Units or any other class of Limited Partner Units then listed for trading on any National Securities Exchange and (d) meets the independence standards required of directors who serve on an audit committee of a board of directors established by the Securities Exchange Act and the rules and regulations of the Commission thereunder and by any National Securities Exchange on which the Common Units are listed or admitted to trading.
“Contributed Property” means each property or other asset, in such form as may be permitted by the Delaware Act, but excluding cash, contributed to the Partnership. Once the Carrying Value of a Contributed Property is adjusted pursuant to Section 5.5(d), such property shall no longer constitute a Contributed Property, but shall be deemed an Adjusted Property.
“Contribution Agreement” means that certain Contribution and Conveyance Agreement dated as of the Closing Date, among and certain other parties, together with the additional conveyance documents and instruments contemplated or referenced thereunder, as such may be amended, supplemented or restated from time to time.
“Crest Royalty Agreement” means the assumption, assignment and indemnity agreement, dated as of the Closing Date, among the Partnership, the General Partner, Cheniere LNG Holdings and Cheniere Energy, Inc.
“Cumulative Common Unit Arrearage” means, with respect to any Common Unit, whenever issued, and as of the end of any Quarter, the excess, if any, of (a) the sum resulting from adding together the Common Unit Arrearage as to an Initial Common Unit for each of the Quarters within the Subordination Period ending on or before the last day of such Quarter over (b) the sum of any distributions theretofore made pursuant to Section 6.4(a)(ii) and the second sentence of Section 6.5 with respect to an Initial Common Unit (including any distributions to be made in respect of the last of such Quarters).
A-6
“Curative Allocation” means any allocation of an item of income, gain, deduction, loss or credit pursuant to the provisions of Section 6.1(d)(xi).
“Current Market Price” means, in respect of any class of Limited Partner Interests, as of the date of determination, the average of the daily Closing Prices per Limited Partner Interest of such class for the 20 consecutive Trading Days immediately prior to such date.
“Delaware Act” means the Delaware Revised Uniform Limited Partnership Act, 6 Del C. Section 17-101, et seq., as amended, supplemented or restated from time to time, and any successor to such statute.
“Departing General Partner” means a former General Partner from and after the effective date of any withdrawal or removal of such former General Partner pursuant to Section 11.1 or 11.2.
“Depositary” means, with respect to any Units issued in global form, The Depository Trust Company and its successors and permitted assigns.
“DGCL” has the meaning set forth in Section 14.7 of this Agreement.
“Distribution Reserve Account” means the account established by the General Partner in which any Distribution Reserve Amount is deposited, held and disbursed as provided in Section 5.11 of this Agreement.
“Distribution Reserve Amount” means (a) in connection with the Initial Public Offering, an amount in Distribution Treasury Securities maturing as to principal and interest at such times and in such amounts as will equal the amount necessary to timely pay the aggregate Initial Quarterly Distributions on the Outstanding General Partner Units and the Common Units issued from the date of issuance of such Common Units through the Quarter ending June 30, 2009 and (b) in connection with each issuance of Common Units during the period commencing after the closing of the Initial Public Offering and ending immediately prior to the Record Date for distributions payable for the Quarter ending June 30, 2009, an amount in (i) cash or (ii) Distribution Treasury Securities maturing as to principal and interest at such times and in such amounts as will equal the amount necessary to timely pay the aggregate Initial Quarterly Distributions on the additional Common Units and additional General Partner Units, if any, so issued by the Partnership for each Quarter in the period commencing with the Quarter in which such additional Common Units and General Partner Units are so issued through the Quarter ending on June 30, 2009.
“Distribution Reserve Period” means the period commencing on the closing of the Initial Public Offering and ending on the Distribution Reserve Period Termination Date.
“Distribution Reserve Period Termination Date” means August 15, 2009.
“Distribution Treasury Securities” means securities issued or directly and fully guaranteed or insured by the United States government or instrumentality of the United States government (provided that the full faith and credit of the United States is pledged in support of those securities).
“Economic Risk of Loss” has the meaning set forth in Treasury Regulation Section 1.752-2(a).
“Eligible Citizen” means a Person qualified to own interests in real property in jurisdictions in which any Group Member does business or proposes to do business from time to time, and whose status as a Limited Partner or Assignee the General Partner determines does not or would not subject such Group Member to a significant risk of cancellation or forfeiture of any of its properties or any interest therein.
“Eligible Investments” means
(1) United States dollars;
A-7
(2) securities issued or directly and fully guaranteed or insured by the United States government or instrumentality of the United States government (provided that the full faith and credit of the United States is pledged in support of those securities);
(3) certificates of deposit and eurodollar time deposits with maturities of one year or less from the date of acquisition, bankers’ acceptances with maturities not exceeding one year and overnight bank deposits, in each case, with any domestic commercial bank having capital and surplus in excess of $500 million and a Thomson Bank Watch Rating of “B” or better;
(4) repurchase obligations with a term of not more than seven days for underlying securities of the types described in clauses (2) and (3) above entered into with any financial institution meeting the qualifications specified in clause (3) above;
(5) commercial paper or tax exempt obligations having one of the two highest ratings obtainable from Moody’s or S&P and, in each case, maturing within one year after the date of acquisition; and
(6) money market funds at least 95% of the assets of which constitute cash equivalents of the kinds described in clauses (1) through (5) of this definition or a money market fund or a qualified investment fund given one of the two highest long-term ratings available from S&P or Moody’s.
“Employee Benefit Plans” means any qualified or non-qualified plan of deferred compensation or other arrangement (whether or not covered by ERISA), plan or agreement providing compensation or incentives to current, future or retired officers, directors, employees or consultants for the performance of services.
“ERISA” means the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended from time to time, or any successor law, and all rules, regulations, rulings and interpretations adopted by the Internal Revenue Service or the Department of Labor thereunder.
“Estimated Incremental Quarterly Tax Amount” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 6.9.
“Event of Withdrawal” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 11.1(a).
“Expansion Capital Expenditures” means cash expenditures for Acquisitions or Capital Improvements. Expansion Capital Expenditures shall not include Maintenance Capital Expenditures or Investment Capital Expenditures. Expansion Capital Expenditures shall include interest (and related fees) on debt incurred and distributions on equity issued, in each case, to finance the construction or development of a Capital Improvement and paid during the period beginning on the date that the Partnership enters into a binding commitment to commence construction or development of a Capital Improvement and ending on the earlier to occur of the date that such Capital Improvement Commences Commercial Service and the date that such Capital Improvement is abandoned or disposed of. Debt incurred or equity issued to fund such construction period interest payments or such construction period distributions on equity paid during such period, shall also be deemed to be debt or equity, as the case may be, issued to finance the construction or development of a Capital Improvement.
“FERC” means the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission.
“Final Subordinated Units” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 6.1(d)(x).
“First Liquidation Target Amount” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 6.1(c)(i)(D).
“First Target Distribution” means $0.489 per Unit per Quarter (or, with respect to the period commencing on the Closing Date and ending on the last day of the Quarter in which the Closing Date occurred, it means the product of $0.489 multiplied by a fraction, of which the numerator is the number of days in such period, and of which the denominator is the number of days in such Quarter), subject to adjustment in accordance with the definition of Initial Quarterly Distribution and Sections 6.6 and 6.9.
“Fully Diluted Basis” means, when calculating the number of Outstanding Units for any period, a basis that includes, in addition to the Outstanding Units, all Partnership Securities and options, rights, warrants and
A-8
appreciation rights relating to an equity interest in the Partnership (a) that are convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for Units that are senior to or pari passu with the Subordinated Units, (b) whose conversion, exercise or exchange price is less than the Current Market Price on the date of such calculation, (c) that may be converted into or exercised or exchanged for such Units prior to or during the Quarter immediately following the end of the period for which the calculation is being made without the satisfaction of any contingency beyond the control of the holder other than the payment of consideration and the compliance with administrative mechanics applicable to such conversion, exercise or exchange and (d) that were not converted into or exercised or exchanged for such Units during the period for which the calculation is being made; provided, however, that for purposes of determining the number of Outstanding Units on a Fully Diluted Basis when calculating whether the Subordination Period has ended or the Subordinated Units are entitled to convert into Common Units pursuant to Section 5.7, such Partnership Securities, options, rights, warrants and appreciation rights shall be deemed to have been Outstanding Units only for the four Quarters that comprise the last four Quarters of the measurement period; provided, further, that if consideration will be paid to any Group Member in connection with such conversion, exercise or exchange, the number of Units to be included in such calculation shall be that number equal to the excess, if positive, of (i) the number of Units issuable upon such conversion, exercise or exchange over (ii) the number of Units that such consideration would purchase at the Current Market Price.
“General Partner” means Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, and its successors and permitted assigns that are admitted to the Partnership as general partner of the Partnership, in its capacity as general partner of the Partnership (except as the context otherwise requires).
“General Partner Interest” means the ownership interest of the General Partner in the Partnership (in its capacity as a general partner without reference to any Limited Partner Interest held by it), which is evidenced by General Partner Units, and includes any and all benefits to which the General Partner is entitled as provided in this Agreement, together with all obligations of the General Partner to comply with the terms and provisions of this Agreement.
“General Partner Unit” means a fractional part of the General Partner Interest having the rights and obligations specified with respect to the General Partner Interest. A General Partner Unit is not a Unit.
“Group” means a Person that with or through any of its Affiliates or Associates has any agreement, contract, arrangement, understanding or relationship for the purpose of acquiring, holding, voting (except voting pursuant to a revocable proxy or consent given to such Person in response to a proxy or consent solicitation made to 10 or more Persons), exercising investment power or disposing of any Partnership Interests with any other Person that beneficially owns, or whose Affiliates or Associates beneficially own, directly or indirectly, Partnership Interests.
“Group Member” means a member of the Partnership Group.
“Group Member Agreement” means the partnership agreement of any Group Member, other than the Partnership, that is a limited or general partnership, the limited liability company agreement of any Group Member that is a limited liability company, the certificate of incorporation and bylaws or similar organizational documents of any Group Member that is a corporation, the joint venture agreement or similar governing document of any Group Member that is a joint venture and the governing or organizational or similar documents of any other Group Member that is a Person other than a limited or general partnership, limited liability company, corporation or joint venture, as such may be amended, supplemented or restated from time to time.
“Holder” as used in Section 7.12, has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 7.12(a).
“Incentive Distribution Right” means a non-voting Limited Partner Interest issued to the General Partner in connection with the transactions contemplated pursuant to the Contribution Agreement, which Limited Partner Interest will confer upon the holder thereof only the rights and obligations specifically provided in this Agreement with respect to Incentive Distribution Rights (and no other rights otherwise available to or other obligations of a holder of a Partnership Interest). Notwithstanding anything in this Agreement to the contrary, the
A-9
holder of an Incentive Distribution Right shall not be entitled to vote such Incentive Distribution Right on any Partnership matter except as may otherwise be required by law.
“Incentive Distributions” means any amount of cash distributed to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights pursuant to Sections 6.4(a)(v), (vi) and (vii), Sections 6.4(b)(iii), (iv) and (v).
“Incremental Income Taxes” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 6.9.
“Indemnified Persons” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 7.12(d).
“Indemnitee” means (a) the General Partner, (b) any Departing General Partner, (c) any Person who is or was an Affiliate of the General Partner or any Departing General Partner, (d) any Person who is or was a member, manager, partner, director, officer, fiduciary or trustee of any Group Member (other than any Person who is or was a Limited Partner of the Partnership in such Person’s capacity as such), the General Partner or any Departing General Partner or any Affiliate of any Group Member, the General Partner or any Departing General Partner, (e) any Person who is or was serving at the request of the General Partner or any Departing General Partner or any Affiliate of the General Partner or any Departing General Partner as an officer, director, member, manager, partner, fiduciary or trustee of another Person; provided that a Person shall not be an Indemnitee by reason of providing, on a fee-for-services basis, trustee, fiduciary or custodial services, and (f) any Person the General Partner designates as an “Indemnitee” for purposes of this Agreement.
“Ineligible Holder” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 4.11.
“Initial Common Unit” means a Common Unit sold in the Initial Public Offering.
“Initial Limited Partners” means Cheniere LNG Holdings, the General Partner (with respect to the Incentive Distribution Rights received by it pursuant to Section 5.2(a)), and the Underwriters upon issuance by the Partnership of Common Units as described in Section 5.3 in connection with the Initial Public Offering.
“Initial Public Offering” means the initial public offering and sale of Common Units to the public, as described in the Registration Statement.
“Initial Quarterly Distribution” means $0.425 per Unit per Quarter (or with respect to the period commencing on the Closing Date and ending on the last day of the Quarter in which the Closing Date occurred, it means the product of $0.425 multiplied by a fraction of which the numerator is the number of days in such period and of which the denominator is the number of days in such Quarter), subject to adjustment in accordance with Sections 6.6 and 6.9.
“Initial Unit Price” means (a) with respect to the Common Units and the Subordinated Units, the initial public offering price per Common Unit at which the Underwriters offered the Common Units for sale to the public as set forth on the cover page of the prospectus included as part of the Registration Statement and first issued at or after the time the Registration Statement first became effective; or (b) with respect to any other class or series of Units, the price per Unit at which such class or series of Units is initially sold by the Partnership, as determined by the General Partner, in each case adjusted as the General Partner determines to be appropriate to give effect to any distribution, subdivision or combination of Units.
“Interim Capital Transactions” means the following transactions if they occur prior to the Liquidation Date: (a) borrowings, refinancings or refundings of indebtedness (other than Working Capital Borrowings and other than for items purchased on open account in the ordinary course of business) by any Group Member and sales of debt securities of any Group Member; (b) sales of equity interests of any Group Member (excluding any such sales to the extent the proceeds thereof are placed in the Distribution Reserve Account); (c) sales or other voluntary or involuntary dispositions of any assets of any Group Member other than (i) sales or other dispositions of inventory, accounts receivable and other assets in the ordinary course of business, and (ii) sales or other
A-10
dispositions of assets as part of normal retirements or replacements; (d) the termination of Commodity Hedge Contracts or interest rate swap agreements prior to the termination date otherwise specified therein; (e) capital contributions received; and (f) corporate reorganizations or restructurings.
“Investment Capital Expenditures” means capital expenditures other than Maintenance Capital Expenditures and Expansion Capital Expenditures.
“Issue Price” means the price at which a Unit is purchased from the Partnership, reduced by any sales commission or underwriting discount charged to the Partnership.
“Letter Agreement” means that certain letter agreement, dated as of November , 2006, among Sabine Pass LNG, Cheniere Marketing and Cheniere LNG, Inc. regarding the J&S Cheniere S.A. Option Agreement.
“Limited Partner” means, unless the context otherwise requires, (a) the Organizational Limited Partner prior to its withdrawal from the Partnership, each Initial Limited Partner, each Substituted Limited Partner, each Additional Limited Partner and any Departing General Partner upon the change of its status from General Partner to Limited Partner pursuant to Section 11.3(b), in each case, in such Person’s capacity as a limited partner of the Partnership or (b) solely for purposes of Articles V, VI, VII, IX and XII, each Assignee; provided, however, that when the term “Limited Partner” is used herein in the context of any vote or other approval, including Articles XIII and XIV, such term shall not, solely for such purpose, include any holder of an Incentive Distribution Right (solely with respect to its Incentive Distribution Rights and not with respect to any other Limited Partner Interest held by such Person) except as may otherwise be required by law.
“Limited Partner Interest” means the ownership interest of a Limited Partner or Assignee in the Partnership, which may be evidenced by Common Units, Subordinated Units, Incentive Distribution Rights or other Partnership Securities or a combination thereof or interest therein, and includes any and all benefits to which such Limited Partner or Assignee is entitled as provided in this Agreement, together with all obligations of such Limited Partner or Assignee to comply with the terms and provisions of this Agreement; provided, however, that when the term “Limited Partner Interest” is used herein in the context of any vote or other approval, including Articles XIII and XIV, such term shall not, solely for such purpose, include any Incentive Distribution Right except as may be required by law.
“Limited Partner Unit” means each of the Common Units, Subordinated Units and other Units representing fractional parts of the Partnership Interests of all Limited Partners and Assignees (but shall not include the Incentive Distribution Rights).
“Liquidation Date” means (a) in the case of an event giving rise to the dissolution of the Partnership of the type described in clauses (a) and (b) of the first sentence of Section 12.2, the date on which the applicable time period during which the holders of Outstanding Units have the right to elect to continue the business of the Partnership has expired without such an election being made, and (b) in the case of any other event giving rise to the dissolution of the Partnership, the date on which such event occurs.
“Liquidator” means one or more Persons selected by the General Partner, pursuant to Section 12.3, to perform the functions described in Section 12.4 as liquidating trustee of the Partnership within the meaning of the Delaware Act.
“Maintenance Capital Expenditures” means cash expenditures (including expenditures for the addition or improvement to the asset base owned by any Group Member or for the acquisition of existing, or the construction or development of new, capital assets) if such expenditures are made to maintain, including over the long term, the operating capacity or asset base of the Partnership Group. Maintenance Capital Expenditures shall not include (a) Expansion Capital Expenditures or (b) Investment Capital Expenditures. Maintenance Capital Expenditures
A-11
shall include interest (and related fees) on debt incurred and distributions on equity issued, in each case, to finance the construction or development of a replacement asset and paid during the period beginning on the date that the Partnership enters into a binding obligation to commence constructing or developing a replacement asset and ending on the earlier to occur of the date that such replacement asset Commences Commercial Service and the date that such replacement asset is abandoned or disposed of. Debt incurred to pay or equity issued to fund construction or development period interest payments, or such construction or development period distributions on equity, shall also be deemed to be debt incurred or equity, as the case may be, issued to finance the construction or development of a replacement asset.
“Management Services Agreements” means, collectively, the Management Services Agreement, dated February 25, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG and Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and the Management Services Agreement, dated September 1, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc.
“Merger Agreement” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 14.1.
“Moody’s” means Moody’s Investors Services, Inc.
“National Securities Exchange” means an exchange registered with the Commission under Section 6(a) of the Securities Exchange Act, and any successor to such statute.
“Net Agreed Value” means, (a) in the case of any Contributed Property, the Agreed Value of such property reduced by any liabilities either assumed by the Partnership upon such contribution or to which such property is subject when contributed, and (b) in the case of any property distributed to a Partner or Assignee by the Partnership, the Partnership’s Carrying Value of such property (as adjusted pursuant to Section 5.5(d)(ii)) at the time such property is distributed, reduced by any indebtedness either assumed by such Partner or Assignee upon such distribution or to which such property is subject at the time of distribution, in either case, as determined under Section 752 of the Code.
“Net Income” means, for any taxable year, the excess, if any, of the Partnership’s items of income and gain (other than those items taken into account in the computation of Net Termination Gain or Net Termination Loss) for such taxable year over the Partnership’s items of loss and deduction (other than those items taken into account in the computation of Net Termination Gain or Net Termination Loss) for such taxable year. The items included in the calculation of Net Income shall be determined in accordance with Section 5.5(b) and shall not include any items specially allocated under Section 6.1(d); provided, that the determination of the items that have been specially allocated under Section 6.1(d) shall be made as if Section 6.1(d)(xii) were not in this Agreement.
“Net Loss” means, for any taxable year, the excess, if any, of the Partnership’s items of loss and deduction (other than those items taken into account in the computation of Net Termination Gain or Net Termination Loss) for such taxable year over the Partnership’s items of income and gain (other than those items taken into account in the computation of Net Termination Gain or Net Termination Loss) for such taxable year. The items included in the calculation of Net Loss shall be determined in accordance with Section 5.5(b) and shall not include any items specially allocated under Section 6.1(d); provided, that the determination of the items that have been specially allocated under Section 6.1(d) shall be made as if Section 6.1(d)(xii) were not in this Agreement.
“Net Positive Adjustments” means, with respect to any Partner, the excess, if any, of the total positive adjustments over the total negative adjustments made to the Capital Account of such Partner pursuant to Book-Up Events and Book-Down Events.
“Net Termination Gain” means, for any taxable year, the sum, if positive, of all items of income, gain, loss or deduction recognized by the Partnership after the Liquidation Date. The items included in the determination of Net Termination Gain shall be determined in accordance with Section 5.5(b) and shall not include any items of income, gain or loss specially allocated under Section 6.1(d).
A-12
“Net Termination Loss” means, for any taxable year, the sum, if negative, of all items of income, gain, loss or deduction recognized by the Partnership after the Liquidation Date. The items included in the determination of Net Termination Loss shall be determined in accordance with Section 5.5(b) and shall not include any items of income, gain or loss specially allocated under Section 6.1(d).
“Non-citizen Assignee” means a Person whom the General Partner has determined does not constitute an Eligible Citizen and as to whose Partnership Interest the General Partner has become the Substituted Limited Partner, pursuant to Section 4.9.
“Nonrecourse Built-in Gain” means with respect to any Contributed Properties or Adjusted Properties that are subject to a mortgage or pledge securing a Nonrecourse Liability, the amount of any taxable gain that would be allocated to the Partners pursuant to Sections 6.2(b)(i)(A), 6.2(b)(ii)(A) and 6.2(b)(iii) if such properties were disposed of in a taxable transaction in full satisfaction of such liabilities and for no other consideration.
“Nonrecourse Deductions” means any and all items of loss, deduction or expenditure (including any expenditure described in Section 705(a)(2)(B) of the Code) that, in accordance with the principles of Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(b), are attributable to a Nonrecourse Liability.
“Nonrecourse Liability” has the meaning set forth in Treasury Regulation Section 1.752-1(a)(2).
“Notice of Election to Purchase” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 15.1(b).
“O&M Agreement” means the Operation and Maintenance Agreement, dated February 25, 2005, between O&M Services and Sabine Pass LNG.
“O&M Services” means Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P., a Delaware limited partnership.
“Operating Expenditures” means all Partnership Group expenditures (or the Partnership’s proportionate share of expenditures in the case of Subsidiaries that are not wholly owned), including, but not limited to, taxes, payments to the General Partner in reimbursement of expenses incurred by the General Partner on behalf of the Partnership Group, non-Pro Rata repurchases of Units, repayment of Working Capital Borrowings, debt service payments, interest payments, payments made in the ordinary course of business under Commodity Hedge Contracts (excluding payments made in connection with any termination of a Commodity Hedge Contract prior to its stated expiration or termination date), provided that with respect to amounts paid in connection with the initial purchase or placing of a Commodity Hedge Contract, such amount(s) shall be amortized over the expected term of the applicable Commodity Hedge Contract and, if earlier, upon its termination, and Maintenance Capital Expenditures, subject to the following:
(a) repayment of Working Capital Borrowings deducted from Operating Surplus pursuant to clause (b)(iii) of the definition of Operating Surplus shall not constitute Operating Expenditures when actually repaid;
(b) payments (including prepayments) of principal of and premium on indebtedness other than Working Capital Borrowings shall not constitute Operating Expenditures; and
(c) Operating Expenditures shall not include (i) Expansion Capital Expenditures, (ii) Investment Capital Expenditures, (iii) payment of transaction expenses (including taxes) relating to Interim Capital Transactions, (iv) distributions to Partners or (v) non-Pro Rata repurchases of Units of any class made with the proceeds of an Interim Capital Transaction. Where capital expenditures are made in part for Expansion Capital Expenditures and in part for other purposes, the General Partner, with the concurrence of the Conflicts Committee, shall determine the allocation between the amounts paid for each.
“Operating Surplus” means, with respect to any period ending prior to the Liquidation Date, on a cumulative basis and without duplication,
(a) the sum of (i) $30 million, (ii) all cash receipts of the Partnership Group (or the Partnership’s proportionate share of cash receipts in the case of Subsidiaries that are not wholly owned) for the period
A-13
beginning on the Closing Date and ending on the last day of such period, but excluding cash receipts from Interim Capital Transactions, (iii) all cash receipts of the Partnership Group (or the Partnership’s proportionate share of cash receipts in the case of Subsidiaries that are not wholly owned) after the end of such period but on or before the date of determination of Operating Surplus with respect to such period resulting from Working Capital Borrowings, (iv) all cash distributions from the Distribution Reserve Account, including cash in the Distribution Reserve Account released in accordance with Sections 5.11(d) and 5.11(e), and (v) the amount of distributions paid on equity issued in connection with the construction or development of a Capital Improvement or replacement assets and paid during the period beginning on the date that the Partnership enters into a binding commitment to commence construction or development of such Capital Improvement or replacement asset and ending on the earlier to occur of the date that such Capital Improvement or replacement asset Commences Commercial Service and the date that it is abandoned or disposed of (equity issued to fund the construction period interest payments on debt incurred (including periodic net payments under related interest rate swap agreements), or construction period distributions on equity issued, to finance the construction of a Capital Improvement or replacement asset shall also be deemed to be equity issued to finance the construction or development of a Capital Improvement or replacement asset for purposes of this clause (v)), less
(b) the sum of (i) Operating Expenditures for the period beginning on the Closing Date and ending on the last day of such period, (ii) the amount of cash reserves (or the Partnership’s proportionate share of cash reserves in the case of Subsidiaries that are not wholly owned) established by the General Partner to provide funds for future Operating Expenditures and (iii) all Working Capital Borrowings not repaid within twelve months after having been incurred or repaid within such twelve-month period with the proceeds of additional Working Capital Borrowings;
provided, however, that disbursements made (including contributions to a Group Member or disbursements on behalf of a Group Member) or cash reserves established, increased or reduced after the end of such period but on or before the date of determination of Available Cash with respect to such period shall be deemed to have been made, established, increased or reduced, for purposes of determining Operating Surplus, within such period if the General Partner so determines.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, “Operating Surplus” with respect to the Quarter in which the Liquidation Date occurs and any subsequent Quarter shall equal zero.
“Opinion of Counsel” means a written opinion of counsel (who may be regular counsel to the Partnership or the General Partner or any of its Affiliates) acceptable to the General Partner.
“Organizational Limited Partner” means Cheniere LNG Holdings in its capacity as the organizational limited partner of the Partnership pursuant to this Agreement.
“Outstanding” means, with respect to Partnership Securities, all Partnership Securities that are issued by the Partnership and reflected as outstanding on the Partnership’s books and records as of the date of determination; provided, however, that if at any time any Person or Group (other than the General Partner and its Affiliates) beneficially owns 20% or more of the Outstanding Partnership Securities of any class then Outstanding, all Partnership Securities owned by such Person or Group shall not be voted on any matter and shall not be considered to be Outstanding when sending notices of a meeting of Limited Partners to vote on any matter (unless otherwise required by law), calculating required votes, determining the presence of a quorum or for other similar purposes under this Agreement, except that Units so owned shall be considered to be Outstanding for purposes of Section 11.1(b)(iv) (such Units shall not, however, be treated as a separate class of Partnership Securities for purposes of this Agreement); provided, further, that the foregoing limitation shall not apply to (i) any Person or Group who acquired 20% or more of the Outstanding Partnership Securities of any class then Outstanding directly from the General Partner or its Affiliates, (ii) any Person or Group who acquired 20% or more of the Outstanding Partnership Securities of any class then Outstanding directly or indirectly from a Person
A-14
or Group described in clause (i) provided that the General Partner shall have notified such Person or Group in writing that such limitation shall not apply, or (iii) any Person or Group who acquired 20% or more of any Partnership Securities issued by the Partnership with the prior approval of the Board of Directors.
“Over-Allotment Option” means the over-allotment option granted to the Underwriters by the Selling Unitholder pursuant to the Underwriting Agreement.
“Partner” means a General Partner or a Limited Partner and Assignees thereof, if applicable.
“Partner Nonrecourse Debt” has the meaning set forth in Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(b)(4).
“Partner Nonrecourse Debt Minimum Gain” has the meaning set forth in Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(i)(2).
“Partner Nonrecourse Deductions” means any and all items of loss, deduction or expenditure (including any expenditure described in Section 705(a)(2)(B) of the Code) that, in accordance with the principles of Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(i), are attributable to a Partner Nonrecourse Debt.
“Partnership” means Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P., a Delaware limited partnership.
“Partnership Group” means the Partnership and its Subsidiaries treated as a single entity.
“Partnership Interest” means an interest in the Partnership, which shall include the General Partner Interest and Limited Partner Interests.
“Partnership Minimum Gain” means that amount determined in accordance with the principles of Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(d).
“Partnership Security” means any class or series of equity interest in the Partnership (but excluding any options, rights, warrants and appreciation rights relating to an equity interest in the Partnership), including Common Units, Subordinated Units, General Partner Units and Incentive Distribution Rights.
“Percentage Interest” means as of any date of determination (a) as to the General Partner with respect to General Partner Units and as to any Unitholder or Assignee with respect to Units, the product obtained by multiplying (i) 100% less the percentage applicable to clause (b) below by (ii) the quotient obtained by dividing (A) the number of General Partner Units held by the General Partner or the number of Units held by such Unitholder or Assignee, as the case may be, by (B) the total number of all Outstanding Units and all General Partner Units, and (b) as to the holders of other Partnership Securities issued by the Partnership in accordance with Section 5.6, the percentage established as a part of such issuance. The Percentage Interest with respect to an Incentive Distribution Right shall at all times be zero.
“Person” means an individual or a corporation, limited liability company, partnership, joint venture, trust, unincorporated organization, association, government agency or political subdivision thereof or other entity.
“Per Unit Capital Amount” means, as of any date of determination, the Capital Account, stated on a per Unit basis, underlying any Unit held by a Person other than the General Partner or any Affiliate of the General Partner who holds Units.
“Pro Rata” means (a) when used with respect to Units or any class thereof, apportioned equally among all designated Units in accordance with their relative Percentage Interests, (b) when used with respect to Partners and Assignees or Record Holders, apportioned among all Partners and Assignees or Record Holders in accordance with their relative Percentage Interests and (c) when used with respect to holders of Incentive Distribution Rights, apportioned equally among all holders of Incentive Distribution Rights in accordance with the relative number or percentage of Incentive Distribution Rights held by each such holder.
A-15
“Purchase Date” means the date determined by the General Partner as the date for purchase of all Outstanding Limited Partner Interests of a certain class (other than Limited Partner Interests owned by the General Partner and its Affiliates) pursuant to Article XV.
“Quarter” means, unless the context requires otherwise, a fiscal quarter of the Partnership, or, with respect to the fiscal quarter of the Partnership including the Closing Date, the portion of such fiscal quarter after the Closing Date.
“Recapture Income” means any gain recognized by the Partnership (computed without regard to any adjustment required by Section 734 or Section 743 of the Code) upon the disposition of any property or asset of the Partnership, which gain is characterized as ordinary income because it represents the recapture of deductions previously taken with respect to such property or asset.
“Record Date” means any date established by the General Partner or otherwise in accordance with this Agreement for determining (a) the identity of the Record Holders entitled to notice of, or to vote at, any meeting of Limited Partners or entitled to vote by ballot or give approval of Partnership action in writing without a meeting or entitled to exercise rights in respect of any lawful action of Limited Partners or (b) the identity of Record Holders entitled to receive any report or distribution or to participate in any offer.
“Record Holder” means the Person in whose name a Unit is registered on the books of the Transfer Agent as of the opening of business on a particular Business Day, or with respect to other Partnership Interests, the Person in whose name any such other Partnership Interest is registered on the books that the General Partner has caused to be kept as of the opening of business on such Business Day.
“Redeemable Interests” means any Partnership Interests for which a redemption notice has been given, and has not been withdrawn, pursuant to Section 4.10.
“Registration Statement” means the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-139572, as it has been or as it may be amended or supplemented from time to time, filed by the Partnership with the Commission under the Securities Act to register the offering and sale of the Common Units in the Initial Public Offering.
“Remaining Net Positive Adjustments” means as of the end of any taxable period, (i) with respect to the Unitholders holding Common Units or Subordinated Units, the excess of (a) the Net Positive Adjustments of the Unitholders holding Common Units or Subordinated Units as of the end of such period over (b) the sum of those Partners’ Share of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items for each prior taxable period, (ii) with respect to the General Partner (as holder of the General Partner Units), the excess of (a) the Net Positive Adjustments of the General Partner as of the end of such period over (b) the sum of the General Partner’s Share of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items with respect to the General Partner Units for each prior taxable period, and (iii) with respect to the holders of Incentive Distribution Rights, the excess of (a) the Net Positive Adjustments of the holders of Incentive Distribution Rights as of the end of such period over (b) the sum of the Share of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items of the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights for each prior taxable period.
“Required Allocations” means (a) any limitation imposed on any allocation of Net Losses or Net Termination Losses under Section 6.1(b) or 6.1(c)(ii) and (b) any allocation of an item of income, gain, loss or deduction pursuant to Section 6.1(d)(i), 6.1(d)(ii), 6.1(d)(iv), 6.1(d)(vii) or 6.1(d)(ix).
“Residual Gain” or “Residual Loss” means any item of gain or loss, as the case may be, of the Partnership recognized for federal income tax purposes resulting from a sale, exchange or other disposition of a Contributed Property or Adjusted Property, to the extent such item of gain or loss is not allocated pursuant to Section 6.2(b)(i)(A) or 6.2(b)(ii)(A), respectively, to eliminate Book-Tax Disparities.
“Retained Converted Subordinated Unit” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 5.5(c)(ii).
A-16
“S&P” means Standard & Poor’s, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
“Sabine Pass LNG” means Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., a Delaware limited partnership.
“Second Liquidation Target Amount” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 6.1(c)(i)(E).
“Secondment Agreement” means the Services and Secondment Agreement, dated as of , 2007, between O&M Services and the General Partner.
“Second Target Distribution” means $0.531 per Unit per Quarter (or, with respect to the period commencing on the Closing Date and ending on the last day of the Quarter in which the Closing Date occurred, it means the product of $0.531 multiplied by a fraction, of which the numerator is equal to the number of days in such period and of which the denominator is the number of days in such Quarter), subject to adjustment in accordance with the definition of Initial Quarterly Distribution and Sections 6.6 and 6.9.
“Securities Act” means the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, supplemented or restated from time to time and any successor to such statute.
“Securities Exchange Act” means the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, supplemented or restated from time to time and any successor to such statute.
“Services Agreement” means the Services Agreement, dated as of the Closing Date, between the Partnership and Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc.
“Selling Unitholder” has the meaning assigned to such term in the Underwriting Agreement.
“Share of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items” means in connection with any allocation of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items for any taxable period, (i) with respect to the Unitholders holding Limited Partner Units, the amount that bears the same ratio to such Additional Book Basis Derivative Items as the Unitholders’ Remaining Net Positive Adjustments as of the end of such period bears to the Aggregate Remaining Net Positive Adjustments as of that time, (ii) with respect to the General Partner (as holder of the General Partner Units), the amount that bears the same ratio to such Additional Book Basis Derivative Items as the General Partner’s Remaining Net Positive Adjustments as of the end of such period bears to the Aggregate Remaining Net Positive Adjustment as of that time, and (iii) with respect to the Partners holding Incentive Distribution Rights, the amount that bears the same ratio to such Additional Book Basis Derivative Items as the Remaining Net Positive Adjustments of the Partners holding the Incentive Distribution Rights as of the end of such period bears to the Aggregate Remaining Net Positive Adjustments as of that time.
“Special Approval” means approval by a majority of the members of the Conflicts Committee acting in good faith.
“Subordinated Unit” means a Unit representing a fractional part of the Partnership Interests of all Limited Partners and Assignees having the rights and obligations specified with respect to Subordinated Units in this Agreement. The term “Subordinated Unit” does not include a Common Unit. A Subordinated Unit that is convertible into a Common Unit shall not constitute a Common Unit until such conversion occurs.
“Subordination Period” means the period commencing on the Closing Date and ending on the first to occur of the following dates:
(a) the first date on which there are no longer any Outstanding Subordinated Units due to the automatic conversion of the Subordinated Units into Common Units pursuant to Section 5.7; and
(b) the date on which the General Partner is removed as general partner of the Partnership upon the requisite vote by holders of Outstanding Units under circumstances where Cause does not exist and no Units held by the General Partner and its Affiliates are voted in favor of such removal.
A-17
“Subsidiary” means, with respect to any Person, (a) a corporation of which more than 50% of the voting power of shares entitled (without regard to the occurrence of any contingency) to vote in the election of directors or other governing body of such corporation is owned, directly or indirectly, at the date of determination, by such Person, by one or more Subsidiaries of such Person or a combination thereof, (b) a partnership (whether general or limited) in which such Person or a Subsidiary of such Person is, at the date of determination, a general or limited partner of such partnership, but only if more than 50% of the partnership interests of such partnership (considering all of the partnership interests of the partnership as a single class) is owned, directly or indirectly, at the date of determination, by such Person, by one or more Subsidiaries of such Person, or a combination thereof, or (c) any other Person (other than a corporation or a partnership) in which such Person, one or more Subsidiaries of such Person, or a combination thereof, directly or indirectly, at the date of determination, has (i) at least a majority ownership interest or (ii) the power to elect or direct the election of a majority of the directors or other governing body of such Person.
“Substituted Limited Partner” means a Person who is admitted as a Limited Partner to the Partnership pursuant to Section 10.2 in place of and with all the rights of a Limited Partner and who is shown as a Limited Partner on the books and records of the Partnership.
“Surviving Business Entity” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 14.2(b).
“Tax Certificate” means the certificate described in Section 4.11.
“Tax Sharing Agreement” means the Tax Sharing Agreement, dated as of , between Sabine Pass LNG and Cheniere Energy, Inc.
“Third Liquidation Target Amount” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 6.1(c)(i)(F).
“Third Target Distribution” means $0.638 per Unit per Quarter (or, with respect to the period commencing on the Closing Date and ending on the last day of the Quarter in which the Closing Date occurred, it means the product of $0.638 multiplied by a fraction, of which the numerator is equal to the number of days in such period and of which the denominator is the number of days in such Quarter), subject to adjustment in accordance with the definition of Initial Quarterly Distribution and Sections 6.6 and 6.9.
“Trading Day” means, for the purpose of determining the Current Market Price of any class of Limited Partner Interests, a day on which the principal National Securities Exchange on which such class of Limited Partner Interests are listed is open for the transaction of business or, if Limited Partner Interests of a class are not listed on any National Securities Exchange, a day on which banking institutions in New York City generally are open.
“transfer” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 4.4(a).
“Transfer Agent” means such bank, trust company or other Person (including the General Partner or one of its Affiliates) as shall be appointed from time to time by the General Partner to act as registrar and transfer agent for the Common Units; provided, that if no Transfer Agent is specifically designated for any other Partnership Securities, the General Partner shall act in such capacity.
“Transfer Application” means an application and agreement for transfer of Units in the form set forth on the back of a Certificate or in a form substantially to the same effect in a separate instrument.
“Underwriter” means each Person named as an underwriter in Schedule I to the Underwriting Agreement who purchases Common Units pursuant thereto.
“Underwriting Agreement” means that certain Underwriting Agreement dated as of , 2007 among the Underwriters, the Partnership, the General Partner and the other parties thereto, providing for the purchase of Common Units by the Underwriters.
A-18
“Unit” means a Partnership Security that is designated as a “Unit” and shall include Common Units and Subordinated Units but shall not include (i) General Partner Units (or the General Partner Interest represented thereby) or (ii) Incentive Distribution Rights.
“Unitholders” means the holders of Units.
“Unit Majority” means (a) during the Subordination Period, at least (i) a majority of the Outstanding Common Units (excluding Outstanding Common Units owned by the General Partner and its Affiliates) voting as a class and at least (ii) a majority of the Outstanding Subordinated Units voting as a single class, and (b) after the end of the Subordination Period, at least a majority of the Outstanding Common Units.
“Unpaid IQD” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 6.1(c)(i)(B).
“Unrealized Gain” attributable to any item of Partnership property means, as of any date of determination, the excess, if any, of (a) the fair market value of such property as of such date (as determined under Section 5.5(d)) over (b) the Carrying Value of such property as of such date (prior to any adjustment to be made pursuant to Section 5.5(d) as of such date).
“Unrealized Loss” attributable to any item of Partnership property means, as of any date of determination, the excess, if any, of (a) the Carrying Value of such property as of such date (prior to any adjustment to be made pursuant to Section 5.5(d) as of such date) over (b) the fair market value of such property as of such date (as determined under Section 5.5(d)).
“Unrecovered Initial Unit Price” means at any time, with respect to a Unit, the Initial Unit Price less the sum of all distributions constituting Capital Surplus theretofore made in respect of an Initial Common Unit, and any distributions of cash (or the Net Agreed Value of any distributions in kind) in connection with the dissolution and liquidation of the Partnership theretofore made in respect of an Initial Common Unit, adjusted as the General Partner determines to be appropriate to give effect to any distribution, subdivision or combination of such Units.
“U.S. GAAP” means United States generally accepted accounting principles consistently applied.
“Withdrawal Opinion of Counsel” has the meaning assigned to such term in Section 11.1(b).
“Working Capital Borrowings” means borrowings used solely for working capital purposes or to pay distributions to Partners, made pursuant to a credit facility, commercial paper facility or similar financing arrangement; provided that when incurred it is the intent of the borrower to repay such borrowings within 12 months from other than additional Working Capital Borrowings.
Unless the context requires otherwise: (a) any pronoun used in this Agreement shall include the corresponding masculine, feminine or neuter forms, and the singular form of nouns, pronouns and verbs shall include the plural and vice versa; (b) references to Articles and Sections refer to Articles and Sections of this Agreement; (c) the terms “include”, “includes”, “including” and words of like import shall be deemed to be followed by the words “without limitation”; and (d) the terms “hereof”, “herein” and “hereunder” refer to this Agreement as a whole and not to any particular provision of this Agreement. The table of contents and headings contained in this Agreement are for reference purposes only, and shall not affect in any way the meaning or interpretation of this Agreement.
A-19
The General Partner and the Organizational Limited Partner have previously formed the Partnership as a limited partnership pursuant to the provisions of the Delaware Act and hereby amend and restate the original Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. in its entirety. This amendment and restatement shall become effective on the date of this Agreement. Except as expressly provided to the contrary in this Agreement, the rights, duties (including fiduciary duties), liabilities and obligations of the Partners and the administration, dissolution and termination of the Partnership shall be governed by the Delaware Act. All Partnership Interests shall constitute personal property of the owner thereof for all purposes.
The name of the Partnership shall be “Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.” The Partnership’s business may be conducted under any other name or names as determined by the General Partner, including the name of the General Partner. The words “Limited Partnership,” “L.P.,” “Ltd.” or similar words or letters shall be included in the Partnership’s name where necessary for the purpose of complying with the laws of any jurisdiction that so requires. The General Partner may change the name of the Partnership at any time and from time to time and shall notify the Limited Partners of such change in the next regular communication to the Limited Partners.
Section 2.3 Registered Office; Registered Agent; Principal Office; Other Offices.
Unless and until changed by the General Partner, the registered office of the Partnership in the State of Delaware shall be located at 2711 Centerville Road, Suite 400, Wilmington, Delaware 19808-1645, and the registered agent for service of process on the Partnership in the State of Delaware at such registered office shall be Corporation Service Company. The principal office of the Partnership shall be located at 717 Texas Avenue, Suite 3100, Houston, Texas 77002 and, after May 15, 2007, at 711 Louisiana, Suite 800, Houston, Texas 77002, or such other place as the General Partner may from time to time designate by notice to the Limited Partners, by any reasonable means (including posting on the Partnership’s website). The Partnership may maintain offices at such other place or places within or outside the State of Delaware as the General Partner shall determine necessary or appropriate. The address of the General Partner shall be 717 Texas Avenue, Suite 3100, Houston, Texas 77002 and, after May 15, 2007, at 711 Louisiana, Suite 800, Houston, Texas 77002, or such other place as the General Partner may from time to time designate by notice, by any reasonable means (including posting on the Partnership’s website).
Section 2.4 Purpose and Business.
The purpose and nature of the business to be conducted by the Partnership shall be (a) to engage directly in, or enter into or form, hold and dispose of any corporation, partnership, joint venture, limited liability company or other arrangement to engage indirectly in, any business activity that is approved by the General Partner and in any event that lawfully may be conducted by a limited partnership organized pursuant to the Delaware Act, and, in connection therewith, to exercise all of the rights and powers conferred upon the Partnership pursuant to the agreements relating to such business activity, and (b) to do anything necessary or appropriate to the foregoing, including the making of capital contributions or loans to a Group Member; provided, however, that the General Partner shall not cause the Partnership to engage, directly or indirectly, in any business activity that the General Partner determines would cause the Partnership to be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise taxable as an entity for federal income tax purposes. To the fullest extent permitted by law and notwithstanding any obligation existing at law or in equity: the General Partner shall have no duty or obligation to propose or approve, and the General Partner may decline to propose or approve, the conduct by the Partnership of any business free of any fiduciary or other duty or obligation whatsoever to the Partnership, any Limited
A-20
Partner or Assignee; and, in declining to so propose or approve the General Partner, shall not be required to act in good faith or pursuant to any other standard imposed by this Agreement, any Group Member Agreement, any other agreement contemplated hereby or under the Delaware Act or any other law, rule or regulation or at equity.
The Partnership shall be empowered to do any and all acts and things necessary or appropriate for the furtherance and accomplishment of the purposes and business described in Section 2.4 and for the protection and benefit of the Partnership.
Section 2.6 Power of Attorney.
(a) Each Limited Partner and each Assignee hereby constitutes and appoints the General Partner and, if a Liquidator shall have been selected pursuant to Section 12.3, the Liquidator, severally (and any successor to the Liquidator by merger, transfer, assignment, election or otherwise) and each of their authorized officers and attorneys-in-fact, as the case may be, with full power of substitution, as his true and lawful agent and attorney-in-fact, with full power and authority in his name, place and stead, to:
(i) execute, swear to, acknowledge, deliver, file and record in the appropriate public offices (A) all certificates, documents and other instruments (including this Agreement and the Certificate of Limited Partnership and all amendments or restatements hereof or thereof) that the General Partner or the Liquidator determines to be necessary or appropriate to form, qualify or continue the existence or qualification of the Partnership as a limited partnership (or a partnership in which the limited partners have limited liability) in the State of Delaware and in all other jurisdictions in which the Partnership may conduct business or own property; (B) all certificates, documents and other instruments that the General Partner or the Liquidator determines to be necessary or appropriate to reflect, in accordance with its terms, any amendment, change, modification or restatement of this Agreement; (C) all certificates, documents and other instruments (including conveyances and a certificate of cancellation) that the General Partner or the Liquidator determines to be necessary or appropriate to reflect the dissolution and liquidation of the Partnership pursuant to the terms of this Agreement; (D) all certificates, documents and other instruments relating to the admission, withdrawal, removal or substitution of any Partner pursuant to, or other events described in, Article IV, X, XI or XII; (E) all certificates, documents and other instruments relating to the determination of the rights, preferences and privileges of any class or series of Partnership Securities issued pursuant to Section 5.6; and (F) all certificates, documents and other instruments (including agreements and a certificate of merger or conversion) relating to a merger, consolidation or conversion of the Partnership pursuant to Article XIV; and
(ii) execute, swear to, acknowledge, deliver, file and record all ballots, consents, approvals, waivers, certificates, documents and other instruments that the General Partner or the Liquidator determines to be necessary or appropriate to (A) make, evidence, give, confirm or ratify any vote, consent, approval, agreement or other action that is made or given by the Partners hereunder or is consistent with the terms of this Agreement or (B) effectuate the terms or intent of this Agreement; provided, that when required by Section 13.3 or any other provision of this Agreement that establishes a percentage of the Limited Partners or of the Limited Partners of any class or series required to vote on, consent to or approve the taking of any action, the General Partner and the Liquidator may exercise the power of attorney made in this Section 2.6(a)(ii) only after the necessary vote, consent or approval of the Limited Partners or of the Limited Partners of such class or series, as applicable.
Nothing contained in this Section 2.6(a) shall be construed as authorizing the General Partner to amend this Agreement except in accordance with Article XIII or as may be otherwise expressly provided for in this Agreement.
(b) The foregoing power of attorney is hereby declared to be irrevocable and a power coupled with an interest, and it shall survive and, to the maximum extent permitted by law, not be affected by the subsequent death, incompetency, disability, incapacity, dissolution, bankruptcy or termination of any Limited Partner or
A-21
Assignee and the transfer of all or any portion of such Limited Partner’s or Assignee’s Partnership Interest and shall extend to such Limited Partner’s or Assignee’s heirs, successors, assigns and personal representatives. Each such Limited Partner or Assignee hereby agrees to be bound by any representation made by the General Partner or the Liquidator acting in good faith pursuant to such power of attorney; and each such Limited Partner or Assignee, to the maximum extent permitted by law, hereby waives any and all defenses that may be available to contest, negate or disaffirm the action of the General Partner or the Liquidator taken in good faith under such power of attorney. Each Limited Partner or Assignee shall execute and deliver to the General Partner or the Liquidator, within 15 days after receipt of the request therefor, such further designation, powers of attorney and other instruments as the General Partner or the Liquidator may request in order to effectuate this Agreement and the purposes of the Partnership.
The term of the Partnership commenced upon the filing of the Certificate of Limited Partnership in accordance with the Delaware Act and shall continue in existence until the dissolution of the Partnership in accordance with the provisions of Article XII. The existence of the Partnership as a separate legal entity shall continue until the cancellation of the Certificate of Limited Partnership as provided in the Delaware Act.
Section 2.8 Title to Partnership Assets.
Title to Partnership assets, whether real, personal or mixed and whether tangible or intangible, shall be deemed to be owned by the Partnership as an entity, and no Partner or Assignee, individually or collectively, shall have any ownership interest in such Partnership assets or any portion thereof. Title to any or all of the Partnership assets may be held in the name of the Partnership, the General Partner, one or more of its Affiliates or one or more nominees, as the General Partner may determine. The General Partner hereby declares and warrants that any Partnership assets for which record title is held in the name of the General Partner or one or more of its Affiliates or one or more nominees shall be held by the General Partner or such Affiliate or nominee for the use and benefit of the Partnership in accordance with the provisions of this Agreement; provided, however, that the General Partner shall use reasonable efforts to cause record title to such assets (other than those assets in respect of which the General Partner determines that the expense and difficulty of conveyancing makes transfer of record title to the Partnership impracticable) to be vested in the Partnership as soon as reasonably practicable; provided, further, that, prior to the withdrawal or removal of the General Partner or as soon thereafter as practicable, the General Partner shall use reasonable efforts to effect the transfer of record title to the Partnership and, prior to any such transfer, will provide for the use of such assets in a manner satisfactory to the General Partner. All Partnership assets shall be recorded as the property of the Partnership in its books and records, irrespective of the name in which record title to such Partnership assets is held.
Section 3.1 Limitation of Liability.
The Limited Partners and the Assignees shall have no liability under this Agreement except as expressly provided in this Agreement or the Delaware Act.
Section 3.2 Management of Business.
No Limited Partner or Assignee, in its capacity as such, shall participate in the operation, management or control (within the meaning of the Delaware Act) of the Partnership’s business, transact any business in the Partnership’s name or have the power to sign documents for or otherwise bind the Partnership. Any action taken by any Affiliate of the General Partner or any officer, director, employee, manager, member, general partner, agent or trustee of the General Partner or any of its Affiliates, or any officer, director, employee, manager, member, general partner, agent or trustee of a Group Member, in its capacity as such, shall not be deemed to be
A-22
participation in the control of the business of the Partnership by a limited partner of the Partnership (within the meaning of Section 17-303(a) of the Delaware Act) and shall not affect, impair or eliminate the limitations on the liability of the Limited Partners or Assignees under this Agreement.
Section 3.3 Outside Activities of the Limited Partners.
Subject to the provisions of Section 7.5, which shall continue to be applicable to the Persons referred to therein, but otherwise notwithstanding any duty existing at law or in equity, any Limited Partner or Assignee shall be entitled to and may have business interests and engage in business activities in addition to those relating to the Partnership, including business interests and activities in direct competition with the Partnership Group. Neither the Partnership nor any of the other Partners or Assignees shall have any rights by virtue of this Agreement in any business ventures of any Limited Partner or Assignee.
Section 3.4 Rights of Limited Partners.
(a) In addition to other rights provided by this Agreement or by applicable law, and except as limited by Section 3.4(b), each Limited Partner shall have the right, for a purpose reasonably related to such Limited Partner’s interest as a Limited Partner in the Partnership, upon reasonable written demand stating the purpose of such demand, and at such Limited Partner’s own expense:
(i) to obtain true and full information regarding the status of the business and financial condition of the Partnership (provided that the requirements of this Section 3.4(a)(i) shall be satisfied by furnishing to a Limited Partner upon its demand pursuant to this Section 3.4(a)(i) the Partnership’s most recent filings with the Commission on Form 10-K and any subsequent filings on Form 10-Q and 8-K);
(ii) promptly after its becoming available, to obtain a copy of the Partnership’s federal, state and local income tax returns for each year;
(iii) to obtain a current list of the name and last known business, residence or mailing address of each Partner;
(iv) to obtain a copy of this Agreement and the Certificate of Limited Partnership and all amendments thereto, together with copies of all executed powers of attorney pursuant to which this Agreement, the Certificate of Limited Partnership and all amendments thereto have been executed;
(v) to obtain true and full information regarding the amount of cash and a description and statement of the Net Agreed Value of any other Capital Contribution by each Partner and that each Partner has agreed to contribute in the future, and the date on which each became a Partner; and
(vi) to obtain such other information regarding the affairs of the Partnership as is just and reasonable.
(b) The General Partner may keep confidential from the Limited Partners and Assignees, for such period of time as the General Partner deems reasonable, (i) any information that the General Partner reasonably believes to be in the nature of trade secrets or (ii) other information the disclosure of which the General Partner in good faith believes (A) is not in the best interests of the Partnership Group, (B) could damage the Partnership Group or its business or (C) that any Group Member is required by law or by agreement with any third party to keep confidential (other than agreements with Affiliates of the Partnership the primary purpose of which is to circumvent the obligations set forth in this Section 3.4).
A-23
TRANSFER OF PARTNERSHIP INTERESTS;
REDEMPTION OF PARTNERSHIP INTERESTS
Upon the Partnership’s issuance of Common Units or Subordinated Units to any Person, the Partnership shall issue, upon the request of such Person, one or more Certificates in the name of such Person (or, if issued in global form, in the name of the Depositary or its nominee) evidencing the number of such Units being so issued. In addition, (a) upon the General Partner’s request, the Partnership shall issue to it one or more Certificates in the name of the General Partner evidencing its General Partner Units and (b) upon the request of any Person owning Incentive Distribution Rights or any other Partnership Securities other than Common Units or Subordinated Units, the Partnership shall issue to such Person one or more certificates evidencing such Incentive Distribution Rights or other Partnership Securities other than Common Units or Subordinated Units. Certificates shall be executed by the General Partner on behalf of the Partnership by the President or any Executive Vice President, Senior Vice President, Vice President or the Chief Financial Officer and the Secretary or any Assistant Secretary of the General Partner. No Common Unit Certificate shall be valid for any purpose until it has been countersigned by the Transfer Agent; provided, however, that if the General Partner elects to issue certificates for Common Units in global form, the Common Unit Certificates shall be valid upon receipt of a certificate from the Transfer Agent certifying that the Common Units have been duly registered in accordance with the directions of the Partnership. Subject to the requirements of Section 6.7, the Partners holding Certificates evidencing Subordinated Units may exchange such Certificates for Certificates evidencing Common Units on or after the date on which such Subordinated Units are converted into Common Units pursuant to the terms of Section 5.7.
Section 4.2 Mutilated, Destroyed, Lost or Stolen Certificates.
(a) If any mutilated Certificate is surrendered to the Transfer Agent, the appropriate officers of the General Partner on behalf of the Partnership shall execute, and the Transfer Agent shall countersign and deliver in exchange therefor, a new Certificate evidencing the same number and type of Partnership Securities as the Certificate so surrendered.
(b) The appropriate officers of the General Partner on behalf of the Partnership shall execute and deliver, and the Transfer Agent shall countersign, a new Certificate in place of any Certificate previously issued if the Record Holder of the Certificate:
(i) makes proof by affidavit, in form and substance satisfactory to the General Partner, that a previously issued Certificate has been lost, destroyed or stolen;
(ii) requests the issuance of a new Certificate before the General Partner has notice that the Certificate has been acquired by a purchaser for value in good faith and without notice of an adverse claim;
(iii) if requested by the General Partner, delivers to the General Partner a bond, in form and substance satisfactory to the General Partner, with surety or sureties and with fixed or open penalty as the General Partner may direct to indemnify the Partnership, the Partners, the General Partner and the Transfer Agent against any claim that may be made on account of the alleged loss, destruction or theft of the Certificate; and
(iv) satisfies any other reasonable requirements imposed by the General Partner.
If a Limited Partner or Assignee fails to notify the General Partner within a reasonable period of time after he has notice of the loss, destruction or theft of a Certificate, and a transfer of the Limited Partner Interests represented by the Certificate is registered before the Partnership, the General Partner or the Transfer Agent receives such notification, the Limited Partner or Assignee shall be precluded from making any claim against the Partnership, the General Partner or the Transfer Agent for such transfer or for a new Certificate.
A-24
(c) As a condition to the issuance of any new Certificate under this Section 4.2, the General Partner may require the payment of a sum sufficient to cover any tax or other governmental charge that may be imposed in relation thereto and any other expenses (including the fees and expenses of the Transfer Agent) reasonably connected therewith.
The Partnership shall be entitled to recognize the Record Holder as the Partner or Assignee with respect to any Partnership Interest and, accordingly, shall not be bound to recognize any equitable or other claim to, or interest in, such Partnership Interest on the part of any other Person, regardless of whether the Partnership shall have actual or other notice thereof, except as otherwise provided by law or any applicable rule, regulation, guideline or requirement of any National Securities Exchange on which such Partnership Interests are listed or admitted to trading. Without limiting the foregoing, when a Person (such as a broker, dealer, bank, trust company or clearing corporation or an agent of any of the foregoing) is acting as nominee, agent or in some other representative capacity for another Person in acquiring and/or holding Partnership Interests, as between the Partnership on the one hand, and such other Persons on the other, such representative Person (a) shall be the Partner or Assignee (as the case may be) of record and beneficially, and (b) shall be bound by this Agreement and shall have the rights and obligations of a Partner or Assignee (as the case may be) hereunder and as, and to the extent, provided for herein.
Section 4.4 Transfer Generally.
(a) The term “transfer,” when used in this Agreement with respect to a Partnership Interest, shall be deemed to refer to a transaction (i) by which the General Partner assigns its General Partner Units to another Person or by which a holder of Incentive Distribution Rights assigns its Incentive Distribution Rights to another Person, and includes a sale, assignment, gift, pledge, encumbrance, hypothecation, mortgage, exchange or any other disposition by law or otherwise or (ii) by which the holder of a Limited Partner Interest (other than an Incentive Distribution Right) assigns such Limited Partner Interest to another Person who is or becomes a Limited Partner or an Assignee, and includes a sale, assignment, gift, exchange or any other disposition by law or otherwise, excluding a pledge, encumbrance, hypothecation or mortgage but including any transfer upon foreclosure of any pledge, encumbrance, hypothecation or mortgage.
(b) No Partnership Interest shall be transferred, in whole or in part, except in accordance with the terms and conditions set forth in this Article IV. Any transfer or purported transfer of a Partnership Interest not made in accordance with this Article IV shall be, to the fullest extent permitted by law, null and void.
(c) Nothing contained in this Agreement shall be construed to prevent a disposition by any stockholder, member, partner or other owner of the General Partner of any or all of the shares of stock, membership interests, partnership interests or other ownership interests in the General Partner.
Section 4.5 Registration and Transfer of Limited Partner Interests.
(a) The General Partner shall keep or cause to be kept on behalf of the Partnership a register in which, subject to such reasonable regulations as it may prescribe and subject to the provisions of Section 4.5(b), the Partnership will provide for the registration and transfer of Limited Partner Interests. The Transfer Agent is hereby appointed registrar and transfer agent for the purpose of registering Common Units and transfers of such Common Units as herein provided. The Partnership shall not recognize transfers of Certificates evidencing Limited Partner Interests unless such transfers are effected in the manner described in this Section 4.5. Upon surrender of a Certificate for registration of transfer of any Limited Partner Interests evidenced by a Certificate, and subject to the provisions of Section 4.5(b), the appropriate officers of the General Partner on behalf of the Partnership shall execute and deliver, and in the case of Common Units, the Transfer Agent shall countersign and deliver, in the name of the holder or the designated transferee or transferees, as required pursuant to the holder’s instructions, one or more new Certificates evidencing the same aggregate number and type of Limited Partner Interests as was evidenced by the Certificate so surrendered.
A-25
(b) The General Partner shall not recognize any transfer of Limited Partner Interests until the Certificates evidencing such Limited Partner Interests are surrendered for registration of transfer and such Certificates are accompanied by a Transfer Application, properly completed and duly executed by the transferee (or the transferee’s attorney-in-fact duly authorized in writing). No charge shall be imposed by the General Partner for such transfer; provided, that as a condition to the issuance of any new Certificate under this Section 4.5, the General Partner may require the payment of a sum sufficient to cover any tax or other governmental charge that may be imposed with respect thereto. No changes in distributions or allocations will be made in respect of the Limited Partner Interests until a properly completed Transfer Application has been delivered with respect to such Limited Partner Interests.
(c) Limited Partner Interests may be transferred only in the manner described in this Section 4.5. The transfer of any Limited Partner Interests and the admission of any new Limited Partner shall not constitute an amendment to this Agreement.
(d) Until admitted as a Substituted Limited Partner pursuant to Section 10.2, the Record Holder of a Limited Partner Interest shall be an Assignee in respect of such Limited Partner Interest. Limited Partners may include custodians, nominees or any other individual or entity in its own or any representative capacity.
(e) A transferee of a Limited Partner Interest who has completed and delivered a Transfer Application shall be deemed to have (i) requested admission as a Substituted Limited Partner, (ii) agreed to comply with and be bound by and to have executed this Agreement, (iii) represented and warranted that such transferee has the right, power and authority and, if an individual, the capacity to enter into this Agreement, (iv) granted the powers of attorney set forth in this Agreement, and (v) given the consents and approvals and made the waivers contained in this Agreement.
(f) Subject to (i) the foregoing provisions of this Section 4.5, (ii) Section 4.3, (iii) Section 4.8, (iv) with respect to any class or series of Limited Partner Interests, the other provisions of this Agreement, including any statement of designations or amendment to this Agreement, establishing or otherwise relating to such class or series, (v) any contractual provisions binding on any Limited Partner and (vi) provisions of applicable law, including the Securities Act and the Securities Exchange Act and the rules and regulations thereunder, Limited Partner Interests (other than the Incentive Distribution Rights, the transfer of which is subject to Section 4.7) shall be freely transferable.
(g) The General Partner, the Organizational Limited Partner and their respective Affiliates shall have the right at any time to transfer their Subordinated Units and Common Units (whether issued upon conversion of the Subordinated Units or otherwise) to one or more Persons.
Section 4.6 Transfer of the General Partner’s General Partner Interest.
(a) Subject to Section 4.6(c) below, prior to March 31, 2017, the General Partner shall not transfer all or any part of its General Partner Interest (represented by General Partner Units) to a Person unless such transfer (i) has been approved by the prior written consent or vote of the holders of at least a majority of the Outstanding Common Units (excluding Common Units held by the General Partner and its Affiliates) or (ii) is of all, but not less than all, of its General Partner Interest to (A) an Affiliate of the General Partner (other than an individual) or (B) another Person (other than an individual) in connection with the merger or consolidation of the General Partner with or into such other Person or the transfer by the General Partner of all or substantially all of its assets to such other Person.
(b) Subject to Section 4.6(c) below, on or after March 31, 2017, the General Partner may transfer all or any of its General Partner Interest without the approval of the holder(s) of any class or series of Units.
(c) Notwithstanding anything herein to the contrary, no transfer by the General Partner of all or any part of its General Partner Interest to another Person shall be permitted unless (i) the transferee agrees to assume the
A-26
rights and duties of the General Partner under this Agreement and to be bound by the provisions of this Agreement, (ii) the Partnership receives an Opinion of Counsel that such transfer would not result in the loss of limited liability under Delaware law of any Limited Partner or cause the Partnership to be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise to be taxed as an entity for federal income tax purposes (to the extent not already so treated or taxed) and (iii) such transferee also agrees to purchase all (or the appropriate portion thereof, if applicable) of the partnership or membership or limited liability company interest of the General Partner as the general partner or managing member, if any, of each other Group Member. In the case of a transfer pursuant to and in compliance with this Section 4.6, the transferee or successor (as the case may be) shall, subject to compliance with the terms of Section 10.3, be admitted to the Partnership as the General Partner immediately prior to the transfer of the General Partner Interest, and the business of the Partnership shall continue without dissolution.
Section 4.7 Transfer of Incentive Distribution Rights.
Prior to March 31, 2017, a holder of Incentive Distribution Rights may transfer any or all of the Incentive Distribution Rights held by such holder without any consent of the Unitholders to (a) an Affiliate of such holder (other than an individual) or (b) another Person (other than an individual) in connection with (i) the merger or consolidation of such holder of Incentive Distribution Rights with or into such other Person, (ii) the transfer by such holder of Incentive Distribution Rights of all or substantially all of its assets to such other Person or (iii) the sale of all the ownership interests in such holder of Incentive Distribution Rights, provided that, in the case of a transfer pursuant to this clause (iii) the initial holder of the Incentive Distribution Rights continues to remain as the General Partner following such sale. Any other transfer of the Incentive Distribution Rights prior to March 31, 2017 shall require the prior approval of holders of at least a majority of the Outstanding Common Units (excluding Common Units held by the General Partner and its Affiliates). On or after March 31, 2017, the General Partner or any other holder of Incentive Distribution Rights may transfer any or all of its Incentive Distribution Rights without Unitholder approval. Notwithstanding anything herein to the contrary, no transfer of Incentive Distribution Rights to another Person shall be permitted unless the transferee agrees to be bound by the provisions of this Agreement. The General Partner and any transferee or transferees of the Incentive Distribution Rights may agree in a separate instrument as to the General Partner’s exercise of its rights with respect to the Incentive Distribution Rights under Section 11.3 hereof.
Section 4.8 Restrictions on Transfers.
(a) Except as provided in Section 4.8(d) below, but notwithstanding the other provisions of this Article IV, no transfer of any Partnership Interests shall be made if such transfer would (i) violate the then applicable federal or state securities laws or rules and regulations of the Commission, any state securities commission or any other governmental authority with jurisdiction over such transfer, (ii) terminate the existence or qualification of the Partnership under the laws of the jurisdiction of its formation, or (iii) cause the Partnership to be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise to be taxed as an entity for federal income tax purposes (to the extent not already so treated or taxed).
(b) The General Partner may impose restrictions on the transfer of Partnership Interests if (i) it receives an Opinion of Counsel that such restrictions are necessary to avoid a significant risk of the Partnership becoming taxable as a corporation or otherwise becoming taxable as an entity for federal income tax purposes or (ii) the holding of Units by a Person (A) not subject to United States federal income taxation on the income generated by the Partnership or (B) in the case of entities that are pass-through entities for United States federal income tax purposes all of whose beneficial owners are not subject to United States federal income taxation on the income generated by the Partnership, would have a material adverse effect on the economic interests of the Partnership. The General Partner may impose such restrictions by amending this Agreement; provided, however, that any amendment that would result in the delisting or suspension of trading of any class of Limited Partner Interests on the principal National Securities Exchange on which such class of Limited Partner Interests is then listed or admitted to trading must be approved, prior to such amendment being effected, by the holders of at least a majority of the Outstanding Limited Partner Interests of such class.
A-27
(c) The transfer of a Subordinated Unit that has converted into a Common Unit shall be subject to the restrictions imposed by Section 6.7.
(d) Nothing contained in this Article IV, or elsewhere in this Agreement, shall preclude the settlement of any transactions involving Partnership Interests entered into through the facilities of any National Securities Exchange on which such Partnership Interests are listed or admitted to trading.
(e) Each certificate evidencing Partnership Interests shall bear a conspicuous legend in substantially the following form:
THE HOLDER OF THIS SECURITY ACKNOWLEDGES FOR THE BENEFIT OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. THAT THIS SECURITY MAY NOT BE SOLD, OFFERED, RESOLD, PLEDGED OR OTHERWISE TRANSFERRED IF SUCH TRANSFER WOULD (A) VIOLATE THE THEN APPLICABLE FEDERAL OR STATE SECURITIES LAWS OR RULES AND REGULATIONS OF THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION, ANY STATE SECURITIES COMMISSION OR ANY OTHER GOVERNMENTAL AUTHORITY WITH JURISDICTION OVER SUCH TRANSFER, (B) TERMINATE THE EXISTENCE OR QUALIFICATION OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF DELAWARE, OR (C) CAUSE CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. TO BE TREATED AS AN ASSOCIATION TAXABLE AS A CORPORATION OR OTHERWISE TO BE TAXED AS AN ENTITY FOR FEDERAL INCOME TAX PURPOSES (TO THE EXTENT NOT ALREADY SO TREATED OR TAXED). CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS GP, LLC, THE GENERAL PARTNER OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P., MAY IMPOSE ADDITIONAL RESTRICTIONS ON THE TRANSFER OF THIS SECURITY IF IT RECEIVES AN OPINION OF COUNSEL THAT SUCH RESTRICTIONS ARE NECESSARY TO AVOID A SIGNIFICANT RISK OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. BECOMING TAXABLE AS A CORPORATION OR OTHERWISE BECOMING TAXABLE AS AN ENTITY FOR FEDERAL INCOME TAX PURPOSES. THE RESTRICTIONS SET FORTH ABOVE SHALL NOT PRECLUDE THE SETTLEMENT OF ANY TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING THIS SECURITY ENTERED INTO THROUGH THE FACILITIES OF ANY NATIONAL SECURITIES EXCHANGE ON WHICH THIS SECURITY IS LISTED OR ADMITTED TO TRADING.
Section 4.9 Citizenship Certificates; Non-citizen Assignees.
(a) If any Group Member is or becomes subject to any federal, state or local law or regulation that the General Partner determines would create a substantial risk of cancellation or forfeiture of any property in which the Group Member has an interest based on the nationality, citizenship or other related status of a Limited Partner or Assignee, the General Partner may request any Limited Partner or Assignee to furnish to the General Partner, within 30 days after receipt of such request, an executed Citizenship Certification or such other information concerning such Limited Partner’s or Assignee’s nationality, citizenship or other related status (or, if the Limited Partner or Assignee is a nominee holding for the account of another Person, the nationality, citizenship or other related status of such Person) as the General Partner may request. If a Limited Partner or Assignee fails to furnish to the General Partner within the aforementioned 30-day period such Citizenship Certification or other requested information or if upon receipt of such Citizenship Certification or other requested information the General Partner determines that a Limited Partner or Assignee is not an Eligible Citizen, the Limited Partner Interests owned by such Limited Partner or Assignee shall be subject to redemption in accordance with the provisions of Section 4.10. In addition, the General Partner may require that the status of any such Limited Partner or Assignee be changed to that of a Non-citizen Assignee and, thereupon, such Non-citizen Assignee shall cease to be a Partner and shall have no voting rights, whether arising hereunder, under the Delaware Act, at law, in equity or otherwise, in respect of the Non-citizen Assignee’s Limited Partner Interests. The General Partner shall be substituted for such Non-citizen Assignee as the Limited Partner or Assignee in respect of the Non-citizen Assignee’s Limited Partner Interests and shall vote such Limited Partner Interests in accordance with Section 4.9(b).
A-28
(b) The General Partner shall, in exercising voting rights in respect of Limited Partner Interests held by it on behalf of Non-citizen Assignees, distribute the votes in the same ratios as the votes of Partners (including the General Partner) in respect of Limited Partner Interests other than those of Non-citizen Assignees are cast, either for, against or abstaining as to the matter.
(c) Upon dissolution of the Partnership, a Non-citizen Assignee shall have no right to receive a distribution in kind pursuant to Section 12.4 but shall be entitled to the cash equivalent thereof, and the Partnership shall provide cash in exchange for an assignment of the Non-citizen Assignee’s share of any distribution in kind. Such payment and assignment shall be treated for Partnership purposes as a purchase by the Partnership from the Non-citizen Assignee of such Non-citizen Assignee’s Limited Partner Interest (representing such Non-citizen Assignee’s right to receive such Non-citizen Assignee’s share of such distribution in kind).
(d) At any time after a Non-citizen Assignee can and does certify that such Non-citizen Assignee has become an Eligible Citizen, a Non-citizen Assignee may, upon application to the General Partner, request admission as a Substituted Limited Partner with respect to any Limited Partner Interests of such Non-citizen Assignee not redeemed pursuant to Section 4.10, and upon such Non-citizen Assignee’s admission pursuant to Section 10.2, the General Partner shall cease to be deemed to be the Limited Partner in respect of the Non-citizen Assignee’s Limited Partner Interests.
Section 4.10 Redemption of Partnership Interests of Non-citizen Assignees.
(a) If at any time a Limited Partner or Assignee fails to furnish a Citizenship Certification or other information requested within the 30-day period specified in Section 4.9(a), or if upon receipt of such Citizenship Certification or other information the General Partner determines, with the advice of counsel, that a Limited Partner or Assignee is not an Eligible Citizen, the Partnership may, unless the Limited Partner or Assignee establishes to the satisfaction of the General Partner that such Limited Partner or Assignee is an Eligible Citizen or has transferred such Limited Partner’s or Assignee’s Partnership Interests to a Person who is an Eligible Citizen and who furnishes a Citizenship Certification to the General Partner prior to the date fixed for redemption as provided below, redeem the Limited Partner Interest of such Limited Partner or Assignee as follows:
(i) The General Partner shall, not later than the 30th day before the date fixed for redemption, give notice of redemption to the Limited Partner or Assignee, at such Limited Partner’s or Assignee’s last address designated on the records of the Partnership or the Transfer Agent, by registered or certified mail, postage prepaid. The notice shall be deemed to have been given when so mailed. The notice shall specify the Redeemable Interests, the date fixed for redemption, the place of payment, that payment of the redemption price will be made upon surrender of the Certificate evidencing the Redeemable Interests and that on and after the date fixed for redemption no further allocations or distributions to which the Limited Partner or Assignee would otherwise be entitled in respect of the Redeemable Interests will accrue or be made.
(ii) The aggregate redemption price for Redeemable Interests shall be an amount equal to the Current Market Price (the date of determination of which shall be the date fixed for redemption) of Limited Partner Interests of the class to be so redeemed multiplied by the number of Limited Partner Interests of each such class included among the Redeemable Interests. The redemption price shall be paid, as determined by the General Partner, in cash or by delivery of a promissory note of the Partnership in the principal amount of the redemption price, bearing interest at the rate of 5% annually and payable in three equal annual installments of principal together with accrued interest, commencing one year after the redemption date.
(iii) Upon surrender by or on behalf of the Limited Partner or Assignee, at the place specified in the notice of redemption, of the Certificate evidencing the Redeemable Interests, duly endorsed in blank or accompanied by an assignment duly executed in blank, the Limited Partner or Assignee or such Limited Partner’s or Assignee’s duly authorized representative shall be entitled to receive the payment therefor.
(iv) After the redemption date, Redeemable Interests shall no longer constitute issued and Outstanding Limited Partner Interests.
A-29
(b) The provisions of this Section 4.10 shall also be applicable to Limited Partner Interests held by a Limited Partner or Assignee as nominee of a Person determined to be other than an Eligible Citizen.
(c) Nothing in this Section 4.10 shall prevent the recipient of a notice of redemption from transferring such recipient’s Limited Partner Interest before the redemption date if such transfer is otherwise permitted under this Agreement. Upon receipt of notice of such a transfer, the General Partner shall withdraw the notice of redemption, provided the transferee of such Limited Partner Interest certifies to the satisfaction of the General Partner in a Citizenship Certification delivered in connection with the Transfer Application that such transferee is an Eligible Citizen. If the transferee fails to make such certification, such redemption shall be effected from the transferee on the original redemption date.
Section 4.11 Taxation Certificates and Related Matters.
If at any time the General Partner determines, with the advice of counsel, that the Partnership’s status as an entity not taxable as a corporation and not otherwise subject to an entity-level tax for federal, state or local income tax purposes, coupled with the tax status (or lack of proof of the federal income tax status) of one or more Limited Partners, has or will have a material adverse effect on the economic interests of the Partnership, then the General Partner may adopt such amendments to this Agreement, without the approval of any class or classes of Limited Partners, as it determines to be necessary or advisable to (i) obtain such proof of the federal income tax status of the Limited Partners and, to the extent relevant, their beneficial owners and thereby determine those Limited Partners whose federal income tax status has or will reasonably likely in the future have such a material adverse effect (such Limited Partners, together with any Limited Partner who fails to comply with the procedures instituted by the General Partner, an “Ineligible Holder”) and (ii) permit the General Partner to redeem Units held by any Ineligible Holder, at the Current Market Price. Such amendments may include provisions requiring all Limited Partners to certify as to their federal income tax status upon demand and on a regular basis, as determined by the General Partner, and may require transferees of Units to so certify prior to being admitted to the Partnership as a Limited Partner.
ISSUANCE OF PARTNERSHIP INTERESTS
Section 5.1 Organizational Contributions.
In connection with the formation of the Partnership under the Delaware Act, the General Partner made an initial Capital Contribution to the Partnership in the amount of $20.00, for a General Partner Interest in the Partnership equivalent to a 2% Percentage Interest and has been admitted as the General Partner of the Partnership, and the Organizational Limited Partner made an initial Capital Contribution to the Partnership in the amount of $980.00 for a Limited Partner Interest in the Partnership equivalent to a 98% Percentage Interest and has been admitted as a Limited Partner of the Partnership. As of the Closing Date, the interest of the Organizational Limited Partner shall be redeemed as provided in the Contribution Agreement; and the initial Capital Contribution of the Organizational Limited Partner shall thereupon be refunded. Ninety-eight percent of any interest or other profit that may have resulted from the investment or other use of such initial Capital Contributions prior to the Closing Date shall be allocated and distributed to the Organizational Limited Partner, and the balance thereof shall be allocated and distributed to the General Partner.
Section 5.2 Contributions by the General Partner and its Affiliates.
(a) On the Closing Date and pursuant to the Contribution Agreement: (i) the General Partner shall contribute to the Partnership, as a Capital Contribution, all of its ownership interests in Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC in exchange for (A) 3,302,045 General Partner Units representing a continuation of its 2% Percentage Interest, subject to all of the rights, privileges and duties of the General Partner under this Agreement, and (B) the
A-30
Incentive Distribution Rights, and (ii) Cheniere LNG Holdings shall contribute to the Partnership, as a Capital Contribution, all of its ownership interests in Cheniere Energy Investments, LLC in exchange for (A) 21,206,026 Common Units, (B) 135,383,831 Subordinated Units, (C) the right to receive distributions, if any, from the Distribution Reserve Account pursuant to the terms of Section 5.11 and (D) to the extent that the Net Funding Amount (as defined in the Contribution Agreement) is not sufficient to purchase Distribution Treasury Securities in an amount sufficient to fund the Distribution Reserve Amount, the obligation to make an additional capital contribution to the MLP of cash in an amount needed to purchase the necessary Distribution Treasury Securities.
(b) Upon the issuance of any additional Limited Partner Interests by the Partnership (other than the Common Units issued in the Initial Offering), the General Partner may, in exchange for a proportionate number of General Partner Units, make additional Capital Contributions in an amount equal to the product obtained by multiplying (I) the quotient determined by dividing (A) the General Partner’s Percentage Interest by (B) 100% minus the General Partner’s Percentage Interest immediately prior to the issuance of such additional Limited Partner Interests by the Partnership times (II) the amount contributed to the Partnership by the Limited Partners in exchange for such additional Limited Partner Interests. Except as set forth in Article XII, the General Partner shall not be obligated to make any additional Capital Contributions to the Partnership.
Section 5.3 Contributions by Initial Limited Partners.
(a) On the Closing Date and pursuant to Underwriting Agreement, each Underwriter shall contribute to the Partnership cash in an amount equal to the Issue Price per Initial Common Unit, multiplied by the number of Common Units specified in the Underwriting Agreement to be purchased by such Underwriter on the Closing Date. In exchange for such Capital Contributions by the Underwriter, the Partnership shall issue Common Units to each Underwriter on whose behalf such Capital Contribution is made in an amount equal to the quotient obtained by dividing (i) the cash contribution to the Partnership by or on behalf of such Underwriter by (ii) the Issue Price per Initial Common Unit.
(b) No Limited Partner Interests will be issued or issuable as of or at the Closing Date other than (i) Common Units issuable pursuant to subparagraph (a) hereof in an aggregate number equal to 5,210,331, (ii) the 135,383,831 Subordinated Units issuable pursuant to Section 5.2 hereof, (iii) the 21,206,026 Common Units issuable pursuant to Section 5.2 and (iv) the Incentive Distribution Rights.
No interest shall be paid by the Partnership on Capital Contributions. No Partner or Assignee shall be entitled to the withdrawal or return of its Capital Contribution, except to the extent, if any, that distributions made pursuant to this Agreement or upon dissolution of the Partnership may be considered as such by law and then only to the extent provided for in this Agreement. Except to the extent expressly provided in this Agreement, no Partner or Assignee shall have priority over any other Partner or Assignee either as to the return of Capital Contributions or as to profits, losses or distributions. Any such return shall be a compromise to which all Partners and Assignees agree within the meaning of Section 17-502(b) of the Delaware Act.
(a) The Partnership shall maintain for each Partner (or a beneficial owner of Partnership Interests held by a nominee in any case in which the nominee has furnished the identity of such owner to the Partnership in accordance with Section 6031(c) of the Code or any other method acceptable to the General Partner) owning a Partnership Interest a separate Capital Account with respect to such Partnership Interest in accordance with the rules of Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(iv). Such Capital Account shall be increased by (i) the amount of all Capital Contributions made to the Partnership with respect to such Partnership Interest and (ii) all items of Partnership income and gain (including income and gain exempt from tax) computed in accordance with Section 5.5(b) and allocated to such Partner with respect to such Partnership Interest pursuant to Section 6.1, and decreased by (x) the amount of cash or Net Agreed Value of all actual and deemed distributions of cash or
A-31
property made to such Partner with respect to such Partnership Interest and (y) all items of Partnership deduction and loss computed in accordance with Section 5.5(b) and allocated to such Partner with respect to such Partnership Interest pursuant to Section 6.1.
(b) For purposes of computing the amount of any item of income, gain, loss or deduction to be allocated pursuant to Article VI and reflected in the Partners’ Capital Accounts, the determination, recognition and classification of any such item shall be the same as its determination, recognition and classification for federal income tax purposes (including any method of depreciation, cost recovery or amortization used for that purpose), provided, that:
(i) Solely for purposes of this Section 5.5, the Partnership shall be treated as owning directly its proportionate share (as determined by the General Partner based upon the provisions of the applicable Group Member Agreement) of all property owned by any other Group Member that is classified as a partnership for federal income tax purposes.
(ii) All fees and other expenses incurred by the Partnership to promote the sale of (or to sell) a Partnership Interest that can neither be deducted nor amortized under Section 709 of the Code, if any, shall, for purposes of Capital Account maintenance, be treated as an item of deduction at the time such fees and other expenses are incurred and shall be allocated among the Partners pursuant to Section 6.1.
(iii) Except as otherwise provided in Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(iv)(m), the computation of all items of income, gain, loss and deduction shall be made without regard to any election under Section 754 of the Code that may be made by the Partnership and, as to those items described in Section 705(a)(1)(B) or 705(a)(2)(B) of the Code, without regard to the fact that such items are not includable in gross income or are neither currently deductible nor capitalized for federal income tax purposes. To the extent an adjustment to the adjusted tax basis of any Partnership asset pursuant to Section 734(b) or 743(b) of the Code is required, pursuant to Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(iv)(m), to be taken into account in determining Capital Accounts, the amount of such adjustment to the Capital Accounts shall be treated as an item of gain or loss.
(iv) Any income, gain or loss attributable to the taxable disposition of any Partnership property shall be determined as if the adjusted basis of such property as of such date of disposition were equal in amount to the Partnership’s Carrying Value with respect to such property as of such date.
(v) In accordance with the requirements of Section 704(b) of the Code, any deductions for depreciation, cost recovery or amortization attributable to any Contributed Property shall be determined as if the adjusted basis of such property on the date it was acquired by the Partnership were equal to the Agreed Value of such property. Upon an adjustment pursuant to Section 5.5(d) to the Carrying Value of any Partnership property subject to depreciation, cost recovery or amortization, any further deductions for such depreciation, cost recovery or amortization attributable to such property shall be determined (A) as if the adjusted basis of such property were equal to the Carrying Value of such property immediately following such adjustment and (B) using a rate of depreciation, cost recovery or amortization derived from the same method and useful life (or, if applicable, the remaining useful life) as is applied for federal income tax purposes; provided, however, that, if the asset has a zero adjusted basis for federal income tax purposes, depreciation, cost recovery or amortization deductions shall be determined using any method that the General Partner may adopt.
(vi) If the Partnership’s adjusted basis in a depreciable or cost recovery property is reduced for federal income tax purposes pursuant to Section 48(q)(1) or 48(q)(3) of the Code, the amount of such reduction shall, solely for purposes hereof, be deemed to be an additional depreciation or cost recovery deduction in the year such property is placed in service and shall be allocated among the Partners pursuant to Section 6.1. Any restoration of such basis pursuant to Section 48(q)(2) of the Code shall, to the extent possible, be allocated in the year of such restoration in the same manner to the Partners to whom such deemed deduction was allocated.
(c)(i) A transferee of a Partnership Interest shall succeed to a pro rata portion of the Capital Account of the transferor relating to the Partnership Interest so transferred.
A-32
(ii) Subject to Section 6.7(c), immediately prior to the transfer of a Subordinated Unit or of a Subordinated Unit that has converted into a Common Unit pursuant to Section 5.7 by a holder thereof (other than a transfer to an Affiliate unless the General Partner elects to have this subparagraph 5.5(c)(ii) apply), the Capital Account maintained for such Person with respect to its Subordinated Units or converted Subordinated Units will (A) first, be allocated to the Subordinated Units or converted Subordinated Units to be transferred in an amount equal to the product of (x) the number of such Subordinated Units or converted Subordinated Units to be transferred and (y) the Per Unit Capital Amount for a Common Unit, and (B) second, any remaining balance in such Capital Account will be retained by the transferor, regardless of whether it has retained any Subordinated Units or converted Subordinated Units (“Retained Converted Subordinated Units”). Following any such allocation, the transferor’s Capital Account, if any, maintained with respect to the retained Subordinated Units or Retained Converted Subordinated Units, if any, will have a balance equal to the amount allocated under clause (B) hereinabove, and the transferee’s Capital Account established with respect to the transferred Subordinated Units or converted Subordinated Units will have a balance equal to the amount allocated under clause (A) hereinabove.
(d)(i) In accordance with Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(iv)(f), on an issuance of additional Partnership Interests for cash or Contributed Property, the issuance of Partnership Interests as consideration for the provision of services, or the conversion of the General Partner’s Combined Interest to Common Units pursuant to Section 11.3(b), the Capital Accounts of all Partners and the Carrying Value of each Partnership property immediately prior to such issuance shall be adjusted upward or downward to reflect any Unrealized Gain or Unrealized Loss attributable to such Partnership property, as if such Unrealized Gain or Unrealized Loss had been recognized on an actual sale of each such property immediately prior to such issuance and had been allocated to the Partners at such time pursuant to Section 6.1 in the same manner as any item of gain or loss actually recognized during such period would have been allocated. In determining such Unrealized Gain or Unrealized Loss, the aggregate cash amount and fair market value of all Partnership assets (including cash or cash equivalents) immediately prior to the issuance of additional Partnership Interests shall be determined by the General Partner using such method of valuation as it may adopt; provided, however, that the General Partner, in arriving at such valuation, must take fully into account the fair market value of the Partnership Interests of all Partners at such time. The General Partner shall allocate such aggregate value among the assets of the Partnership (in such manner as it determines) to arrive at a fair market value for individual properties.
(ii) In accordance with Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(iv)(f), immediately prior to any actual or deemed distribution to a Partner of any Partnership property (other than a distribution of cash that is not in redemption or retirement of a Partnership Interest, the Capital Accounts of all Partners and the Carrying Value of all Partnership property shall be adjusted upward or downward to reflect any Unrealized Gain or Unrealized Loss attributable to such Partnership property, as if such Unrealized Gain or Unrealized Loss had been recognized in a sale of such property immediately prior to such distribution for an amount equal to its fair market value, and had been allocated to the Partners, at such time, pursuant to Section 6.1 in the same manner as any item of gain or loss actually recognized during such period would have been allocated. In determining such Unrealized Gain or Unrealized Loss the aggregate cash amount and fair market value of all Partnership assets (including cash or cash equivalents) immediately prior to a distribution shall (A) in the case of an actual distribution that is not made pursuant to Section 12.4 or in the case of a deemed distribution, be determined and allocated in the same manner as that provided in Section 5.5(d)(i) or (B) in the case of a liquidating distribution pursuant to Section 12.4, be determined and allocated by the Liquidator using such method of valuation as it may adopt.
Section 5.6 Issuances of Additional Partnership Securities.
(a) The Partnership may issue additional Partnership Securities and options, rights, warrants and appreciation rights relating to the Partnership Securities for any Partnership purpose at any time and from time to time to such Persons for such consideration and on such terms and conditions as the General Partner shall determine, all without the approval of any Limited Partners; provided, however, that during the Subordination
A-33
Period the Partnership must obtain Special Approval prior to issuing any additional Common Units or Units with designations, preferences, rights, powers and duties senior to or pari passu with the Common Units.
(b) Each additional Partnership Security authorized to be issued by the Partnership pursuant to Section 5.6(a) may be issued in one or more classes, or one or more series of any such classes, with such designations, preferences, rights, powers and duties (which, subject to the provision contained in Section 5.6(a), may be senior to existing classes and series of Partnership Securities), as shall be fixed by the General Partner, including (i) the right to share in Partnership profits and losses or items thereof; (ii) the right to share in Partnership distributions; (iii) the rights upon dissolution and liquidation of the Partnership; (iv) whether, and the terms and conditions upon which, the Partnership may or shall be required to redeem the Partnership Security (including sinking fund provisions); (v) whether such Partnership Security is issued with the privilege of conversion or exchange and, if so, the terms and conditions of such conversion or exchange; (vi) the terms and conditions upon which each Partnership Security will be issued, evidenced by certificates and assigned or transferred; (vii) the method for determining the Percentage Interest as to such Partnership Security; and (viii) the right, if any, of each such Partnership Security to vote on Partnership matters, including matters relating to the relative rights, preferences and privileges of such Partnership Security.
(c) The General Partner shall take all actions that it determines to be necessary or appropriate in connection with (i) each issuance of Partnership Securities and options, rights, warrants and appreciation rights relating to Partnership Securities pursuant to this Section 5.6, (ii) the conversion of the General Partner Interest or any Incentive Distribution Rights into Units pursuant to the terms of this Agreement, (iii) the admission of Additional Limited Partners and (iv) all additional issuances of Partnership Securities. The General Partner shall determine the relative rights, powers and duties of the holders of the Units or other Partnership Securities being so issued. The General Partner shall do all things necessary to comply with the Delaware Act and is authorized and directed to do all things that it determines to be necessary or appropriate in connection with any future issuance of Partnership Securities or in connection with the conversion of the General Partner Interest or any Incentive Distribution Rights into Units pursuant to the terms of this Agreement, including compliance with any statute, rule, regulation or guideline of any federal, state or other governmental agency or any National Securities Exchange on which the Units or other Partnership Securities are listed or admitted to trading.
Section 5.7 Conversion of Subordinated Units.
(a) All of the Subordinated Units will convert into Common Units on a one-for-one basis on the first Business Day following the distribution of Available Cash to Partners pursuant to Section 6.4(a) in respect of any Quarter ending on or after June 30, 2010, in respect of which:
(i) distributions of Available Cash from Operating Surplus under Section 6.4(a) on each of the Outstanding Common Units, Subordinated Units, General Partner Units and any other Outstanding Units that are senior or equal in right of distribution to the Subordinated Units with respect to each of the three consecutive, non-overlapping four-Quarter periods immediately preceding such date (which three consecutive, non-overlapping four-Quarter periods commence on or after the Closing Date) equaled or exceeded the sum of the Initial Quarterly Distribution on all of the Outstanding Common Units, Subordinated Units, General Partner Units and any other Outstanding Units that are senior or equal in right of distribution to the Subordinated Units during such periods;
(ii) the Adjusted Operating Surplus for each of the three consecutive, non-overlapping four-Quarter periods immediately preceding such date (which three consecutive, non-overlapping four-Quarter periods commence on or after the Closing Date) equaled or exceeded the sum of the Initial Quarterly Distribution on all of the Outstanding Common Units, Subordinated Units, General Partner Units and any other Units that are senior or equal in right of distribution to the Subordinated Units that were Outstanding during such periods on a Fully Diluted Basis; and
(iii) there are no Cumulative Common Unit Arrearages.
A-34
(b) Notwithstanding Section 5.7(a), all of the Outstanding Subordinated Units will convert into Common Units on a one-for-one basis on the first Business Day following the distribution of Available Cash to Partners pursuant to Section 6.4 in respect of any Quarter ending on or after June 30, 2008 in respect of which:
(i) distributions of Available Cash from Operating Surplus under Section 6.4(a) on each of the Outstanding Common Units, Subordinated Units, General Partner Units and any other Outstanding Units that are senior or equal in right of distribution to the Subordinated Units with respect to each of the four consecutive Quarters immediately preceding such date (which four-consecutive Quarter period commences after the Closing Date) equaled or exceeded the sum of the Third Target Distribution on all of the Outstanding Common Units, Subordinated Units, General Partner Units and any other Outstanding Units that are senior or equal in right of distribution to the Subordinated Units during such period;
(ii) the Adjusted Operating Surplus for each of the four consecutive Quarters immediately preceding such date (which four consecutive Quarter period commences after the Closing Date) equaled or exceeded the sum of the Third Target Distribution on all of the Outstanding Common Units, Subordinated Units and General Partner Units and any other Units that are senior or equal in right of distribution to the Subordinated Units that were Outstanding during such periods on a Fully Diluted Basis with respect to such Quarter; and
(iii) there are no Cumulative Common Unit Arrearages.
(c) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Agreement, all the Subordinated Units will automatically convert into Common Units on a one-for-one basis as set forth in, and pursuant to the terms of, Section 11.4.
(d) A Subordinated Unit that has converted into a Common Unit shall be subject to the provisions of Section 6.7.
Section 5.8 Limited Preemptive Right.
Except as provided in this Section 5.8 and in Section 5.2, no Person shall have any preemptive, preferential or other similar right with respect to the issuance of any Partnership Security, whether unissued, held in the treasury or hereafter created. The General Partner shall have the right, which it may from time to time assign in whole or in part to any of its Affiliates, to purchase Partnership Securities from the Partnership whenever, and on the same terms that, the Partnership issues Partnership Securities to Persons other than the General Partner and its Affiliates, to the extent necessary to maintain the Percentage Interests of the General Partner and its Affiliates equal to any or all of those Percentage Interests that existed immediately prior to the issuance of such Partnership Securities.
Section 5.9 Splits and Combinations.
(a) Subject to Sections 5.9(d), 6.6 and 6.9 (dealing with adjustments of distribution levels), the Partnership may make a Pro Rata distribution of Partnership Securities to all Record Holders or may effect a subdivision or combination of Partnership Securities so long as, after any such event, each Partner shall have the same Percentage Interest in the Partnership as before such event, and any amounts calculated on a per Unit basis (including any Common Unit Arrearage or Cumulative Common Unit Arrearage) or stated as a number of Units are proportionately adjusted.
(b) Whenever such a Pro Rata distribution or a subdivision or combination of Partnership Securities is declared, the General Partner shall select a Record Date as of which the distribution, subdivision or combination shall be effective and shall send notice thereof at least 20 days prior to such Record Date to each Record Holder as of a date not less than 10 days prior to the date of such notice. The General Partner also may cause a firm of independent public accountants selected by it to calculate the number of Partnership Securities to be held by each Record Holder after giving effect to such distribution, subdivision or combination. In addition, with respect to any such a distribution, subdivision or combination of any class of Partnership Securities that is convertible into another class of Partnership Securities or into which any class of Partnership Securities is convertible or
A-35
exchangeable, appropriate adjustment shall be made either to assure that the specified conversion or exchange ratio is maintained or, alternatively, is appropriately adjusted to give effect to such Pro Rata distribution or subdivision or combination, as the case may be, as the General Partner determines to be appropriate. The General Partner shall be entitled to rely on any certificate provided by such firm as conclusive evidence of the accuracy of such calculation.
(c) Promptly following any such distribution, subdivision or combination, the Partnership may issue Certificates to the Record Holders of Partnership Securities as of the applicable Record Date representing the new number of Partnership Securities held by such Record Holders, or the General Partner may adopt such other procedures that it determines to be necessary or appropriate to reflect such changes. If any such combination results in a smaller total number of Partnership Securities Outstanding, the Partnership shall require, as a condition to the delivery to a Record Holder of such new Certificate, the surrender of any Certificate held by such Record Holder immediately prior to such Record Date.
(d) The Partnership shall not issue fractional Units upon any distribution, subdivision or combination of Units. If a distribution, subdivision or combination of Units would result in the issuance of fractional Units but for the provisions of this Section 5.9(d), each fractional Unit shall be rounded to the nearest whole Unit (and a 0.5 Unit shall be rounded to the next higher Unit).
Section 5.10 Fully Paid and Non-Assessable Nature of Limited Partner Interests.
All Limited Partner Interests issued pursuant to, and in accordance with the requirements of, this Article V shall be fully paid and non-assessable Limited Partner Interests in the Partnership, except as such non-assessability may be affected by Sections 17-607 and 17-804 of the Delaware Act and the other provisions of this Agreement.
Section 5.11 Distribution Reserve Account.
(a) Immediately prior to the closing of the Initial Public Offering, the Partnership shall have established the Distribution Reserve Account with a commercial bank organized under the laws of the United States, or any state thereof, and having total assets in excess of $500,000,000 and a combined capital and surplus of at least $100,000,000.
(b) Upon closing of (i) the Initial Public Offering and (ii) each subsequent issuance of additional Common Units occurring prior to the Record Date for distributions payable for the Quarter ending June 30, 2009, the Partnership shall deposit, or cause to be deposited in accordance with Section 5.2(a)(ii)(D), into the Distribution Reserve Account an amount equal to the Distribution Reserve Amount in respect of the Common Units so issued and General Partner Units issued pursuant to Section 5.2(b) in connection therewith. Except as provided in Section 5.11(d), all amounts held in the Distribution Reserve Account shall be segregated from all other assets of the Partnership and may only be used by the General Partner to pay the Distribution Reserve Amount.
(c) If the Distribution Reserve Amount is deposited in cash, the General Partner shall cause the Distribution Reserve Amount to be invested only in Eligible Investments. During the period in which the Distribution Reserve Amount is retained in the Distribution Reserve Account, all interest or other income earned from the investment (and reinvestment) of such Distribution Reserve Amount shall be retained in the Distribution Reserve Account and added to the Distribution Reserve Amount, subject to Section 5.11(d).
(d) The General Partner may, at any time and from time to time, distribute amounts from the Distribution Reserve Account to Cheniere LNG Holdings pursuant to the terms of the Contribution Agreement if the General Partner determines, with Special Approval, that such amounts are in excess of the amount required to fund Initial Quarterly Distributions for any Quarter ending on or prior to June 30, 2009; provided that if the net proceeds to the Partnership from the Initial Public Offering would allow the Partnership to purchase more than the
A-36
Distribution Treasury Securities required to fund the Distribution Reserve Amount, the Partnership shall distribute such excess amounts to Cheniere LNG Holdings on the date of the purchase without Special Approval.
(e) Promptly following the Distribution Reserve Termination Date, the General Partner shall cause remaining amounts, if any, held in the Distribution Reserve Account to be distributed to Cheniere LNG Holdings pursuant to the terms of the Contribution Agreement.
Section 6.1 Allocations for Capital Account Purposes.
For purposes of maintaining the Capital Accounts and in determining the rights of the Partners among themselves, the Partnership’s items of income, gain, loss and deduction (computed in accordance with Section 5.5(b)) shall be allocated among the Partners in each taxable year (or portion thereof) as provided herein below.
(a) Net Income. After giving effect to the special allocations set forth in Section 6.1(d), Net Income for each taxable year and all items of income, gain, loss and deduction taken into account in computing Net Income for such taxable year shall be allocated as follows:
(i) First, 100% to the General Partner, in an amount equal to the aggregate Net Losses allocated to the General Partner pursuant to Section 6.1(b)(iii) for all previous taxable years until the aggregate Net Income allocated to the General Partner pursuant to this Section 6.1(a)(i) for the current taxable year and all previous taxable years is equal to the aggregate Net Losses allocated to the General Partner pursuant to Section 6.1(b)(iii) for all previous taxable years;
(ii) Second, 100% to the General Partner and the Unitholders, in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests, until the aggregate Net Income allocated to such Partners pursuant to this Section 6.1(a)(ii) for the current taxable year and all previous taxable years is equal to the aggregate Net Losses allocated to such Partners pursuant to Section 6.1(b)(ii) for all previous taxable years; and
(iii) Third, the balance, if any, 100% to the General Partner and the Unitholders, in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests.
(b) Net Losses. After giving effect to the special allocations set forth in Section 6.1(d), Net Losses for each taxable period and all items of income, gain, loss and deduction taken into account in computing Net Losses for such taxable period shall be allocated as follows:
(i) First, 100% to the General Partner and the Unitholders, in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests, until the aggregate Net Losses allocated pursuant to this Section 6.1(b)(i) for the current taxable year and all previous taxable years is equal to the aggregate Net Income allocated to such Partners pursuant to Section 6.1(a)(iii) for all previous taxable years, provided that the Net Losses shall not be allocated pursuant to this Section 6.1(b)(i) to the extent that such allocation would cause any Unitholder to have a deficit balance in its Adjusted Capital Account at the end of such taxable year (or increase any existing deficit balance in its Adjusted Capital Account);
(ii) Second, 100% to the General Partner and the Unitholders, in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests; provided, that Net Losses shall not be allocated pursuant to this Section 6.1(b)(ii) to the extent that such allocation would cause any Unitholder to have a deficit balance in its Adjusted Capital Account at the end of such taxable year (or increase any existing deficit balance in its Adjusted Capital Account); and
(iii) Third, the balance, if any, 100% to the General Partner.
A-37
(c) Net Termination Gains and Losses. After giving effect to the special allocations set forth in Section 6.1(d), all items of income, gain, loss and deduction taken into account in computing Net Termination Gain or Net Termination Loss for such taxable period shall be allocated in the same manner as such Net Termination Gain or Net Termination Loss is allocated hereunder. All allocations under this Section 6.1(c) shall be made after Capital Account balances have been adjusted by all other allocations provided under this Section 6.1 and after all distributions of Available Cash provided under Sections 6.4 and 6.5 have been made; provided, however, that solely for purposes of this Section 6.1(c), Capital Accounts shall not be adjusted for distributions made pursuant to Section 12.4.
(i) If a Net Termination Gain is recognized (or deemed recognized pursuant to Section 5.5(d)), such Net Termination Gain shall be allocated among the Partners in the following manner (and the Capital Accounts of the Partners shall be increased by the amount so allocated in each of the following subclauses, in the order listed, before an allocation is made pursuant to the next succeeding subclause):
(A) First, to each Partner having a deficit balance in its Capital Account, in the proportion that such deficit balance bears to the total deficit balances in the Capital Accounts of all Partners, until each such Partner has been allocated Net Termination Gain equal to any such deficit balance in its Capital Account;
(B) Second, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest and (y) to all Unitholders holding Common Units, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest, until the Capital Account in respect of each Common Unit then Outstanding is equal to the sum of (1) its Unrecovered Initial Unit Price, (2) the Initial Quarterly Distribution for the Quarter during which the Liquidation Date occurs, reduced by any distribution pursuant to Section 6.4(a)(i) or (b)(i) with respect to such Common Unit for such Quarter (the amount determined pursuant to this clause (2) is hereinafter defined as the “Unpaid IQD”) and (3) any then existing Cumulative Common Unit Arrearage;
(C) Third, if such Net Termination Gain is recognized (or is deemed to be recognized) prior to the conversion of the last Outstanding Subordinated Unit, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest and (y) all Unitholders holding Subordinated Units, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest, until the Capital Account in respect of each Subordinated Unit then Outstanding equals the sum of (1) its Unrecovered Initial Unit Price, determined for the taxable year (or portion thereof) to which this allocation of gain relates, and (2) the Initial Quarterly Distribution for the Quarter during which the Liquidation Date occurs, reduced by any distribution pursuant to Section 6.4(a)(iii) with respect to such Subordinated Unit for such Quarter;
(D) Fourth, 100% to the General Partner and all Unitholders in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests, until the Capital Account in respect of each Common Unit then Outstanding is equal to the sum of (1) its Unrecovered Initial Unit Price, (2) the Unpaid IQD, (3) any then existing Cumulative Common Unit Arrearage, and (4) the excess of (aa) the First Target Distribution less the Initial Quarterly Distribution for each Quarter of the Partnership’s existence over (bb) the cumulative per Unit amount of any distributions of Available Cash that is deemed to be Operating Surplus made pursuant to Sections 6.4(a)(iv) and 6.4(b)(ii) (the sum of (1), (2), (3) and (4) is hereinafter defined as the “First Liquidation Target Amount”);
(E) Fifth, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest, (y) 13% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata, and (z) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to subclause (x) and (y) of this clause (E), until the Capital Account in respect of each Common Unit then Outstanding is equal to the sum of (1) the First Liquidation Target Amount, and (2) the excess of (aa) the Second Target Distribution less the First Target Distribution for each Quarter of the Partnership’s existence over (bb) the cumulative per Unit amount of any distributions of Available Cash that is deemed to be Operating Surplus made pursuant to Sections 6.4(a)(v) and 6.4(b)(iii) (the sum of (1) and (2) is hereinafter defined as the “Second Liquidation Target Amount”);
A-38
(F) Sixth, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest, (y) 23% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata, and (z) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to subclause (x) and (y) of this clause (F), until the Capital Account in respect of each Common Unit then Outstanding is equal to the sum of (1) the Second Liquidation Target Amount, and (2) the excess of (aa) the Third Target Distribution less the Second Target Distribution for each Quarter of the Partnership’s existence over (bb) the cumulative per Unit amount of any distributions of Available Cash that is deemed to be Operating Surplus made pursuant to Sections 6.4(a)(vi) and 6.4(b)(iv) (the sum of (1) and (2) is hereinafter defined as the “Third Liquidation Target Amount”); and
(G) Finally, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest, (y) 48% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata, and (z) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to subclause (x) and (y) of this clause (G).
(ii) If a Net Termination Loss is recognized (or deemed recognized pursuant to Section 5.5(d)), such Net Termination Loss shall be allocated among the Partners in the following manner:
(A) First, if such Net Termination Loss is recognized (or is deemed to be recognized) prior to the conversion of the last Outstanding Subordinated Unit, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest and (y) to all Unitholders holding Subordinated Units, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest, until the Capital Account in respect of each Subordinated Unit then Outstanding has been reduced to zero;
(B) Second, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest and (y) to all Unitholders holding Common Units, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest, until the Capital Account in respect of each Common Unit then Outstanding has been reduced to zero; and
(C) Finally, the balance, if any, 100% to the General Partner.
(d) Special Allocations. Notwithstanding any other provision of this Section 6.1, the following special allocations shall be made for such taxable period:
(i) Partnership Minimum Gain Chargeback. Notwithstanding any other provision of this Section 6.1, if there is a net decrease in Partnership Minimum Gain during any Partnership taxable period, each Partner shall be allocated items of Partnership income and gain for such period (and, if necessary, subsequent periods) in the manner and amounts provided in Treasury Regulation Sections 1.704-2(f)(6), 1.704-2(g)(2) and 1.704-2(j)(2)(i), or any successor provision. For purposes of this Section 6.1(d), each Partner’s Adjusted Capital Account balance shall be determined, and the allocation of income or gain required hereunder shall be effected, prior to the application of any other allocations pursuant to this Section 6.1(d) with respect to such taxable period (other than an allocation pursuant to Sections 6.1(d)(vi) and 6.1(d)(vii)). This Section 6.1(d)(i) is intended to comply with the Partnership Minimum Gain chargeback requirement in Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(f) and shall be interpreted consistently therewith.
(ii) Chargeback of Partner Nonrecourse Debt Minimum Gain. Notwithstanding the other provisions of this Section 6.1 (other than Section 6.1(d)(i)), except as provided in Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(i)(4), if there is a net decrease in Partner Nonrecourse Debt Minimum Gain during any Partnership taxable period, any Partner with a share of Partner Nonrecourse Debt Minimum Gain at the beginning of such taxable period shall be allocated items of Partnership income and gain for such period (and, if necessary, subsequent periods) in the manner and amounts provided in Treasury Regulation Sections 1.704-2(i)(4) and 1.704-2(j)(2)(ii), or any successor provisions. For purposes of this Section 6.1(d), each Partner’s Adjusted Capital Account balance shall be determined, and the allocation of income or gain required hereunder shall be effected, prior to the application of any other allocations pursuant to this Section 6.1(d), other than Section 6.1(d)(i) and other than an allocation pursuant to Sections 6.1(d)(vi) and 6.1(d)(vii), with respect to such taxable period. This Section 6.1(d)(ii) is intended to comply with the chargeback of items of income and gain requirement in Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(i)(4) and shall be interpreted consistently therewith.
A-39
(iii) Priority Allocations.
(A) At any time following the Distribution Reserve Period, if the amount of cash or the Net Agreed Value of any property distributed (except cash or property distributed pursuant to Section 12.4) to any Unitholder with respect to its Units for a taxable year is greater (on a per Unit basis) than the amount of cash or the Net Agreed Value of property distributed to the other Unitholders with respect to their Units (on a per Unit basis), then (1) each Unitholder receiving such greater cash or property distribution shall be allocated gross income in an amount equal to the product of (aa) the amount by which the distribution (on a per Unit basis) to such Unitholder exceeds the distribution (on a per Unit basis) to the Unitholders receiving the smallest distribution and (bb) the number of Units owned by the Unitholder receiving the greater distribution; and (2) the General Partner shall be allocated gross income in an aggregate amount equal to the product obtained by multiplying (aa) the quotient determined by dividing (x) the General Partner’s Percentage Interest at the time in which the greater cash or property distribution occurs by (y) the sum of 100 less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest at the time in which the greater cash or property distribution occurs times (bb) the sum of the amounts allocated in clause (1) above.
(B) After the application of Section 6.1(d)(iii)(A), all or any portion of the remaining items of Partnership gross income or gain for the taxable period, if any, shall be allocated (1) to the holders of Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata, until the aggregate amount of such items allocated to the holders of Incentive Distribution Rights pursuant to this paragraph 6.1(d)(iii)(B) for the current taxable year and all previous taxable years is equal to the cumulative amount of all Incentive Distributions made to the holders of Incentive Distribution Rights from the Closing Date to a date 60 days after the end of the current taxable year; and (2) to the General Partner an amount equal to the product of (aa) an amount equal to the quotient determined by dividing (x) the General Partner’s Percentage Interest by (y) the sum of 100 less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest times (bb) the sum of the amounts allocated in clause (1) above.
(iv) Qualified Income Offset. In the event any Partner unexpectedly receives any adjustments, allocations or distributions described in Treasury Regulation Sections 1.704-1(b)(2)(ii)(d)(4), 1.704-1(b)(2)(ii)(d)(5), or 1.704-1(b)(2)(ii)(d)(6), items of Partnership income and gain shall be specially allocated to such Partner in an amount and manner sufficient to eliminate, to the extent required by the Treasury Regulations promulgated under Section 704(b) of the Code, the deficit balance, if any, in its Adjusted Capital Account created by such adjustments, allocations or distributions as quickly as possible unless such deficit balance is otherwise eliminated pursuant to Section 6.1(d)(i) or (ii).
(v) Gross Income Allocations. In the event any Partner has a deficit balance in its Capital Account at the end of any Partnership taxable period in excess of the sum of (A) the amount such Partner is required to restore pursuant to the provisions of this Agreement and (B) the amount such Partner is deemed obligated to restore pursuant to Treasury Regulation Sections 1.704-2(g) and 1.704-2(i)(5), such Partner shall be specially allocated items of Partnership gross income and gain in the amount of such excess as quickly as possible; provided, that an allocation pursuant to this Section 6.1(d)(v) shall be made only if and to the extent that such Partner would have a deficit balance in its Capital Account as adjusted after all other allocations provided for in this Section 6.1 have been tentatively made as if this Section 6.1(d)(v) were not in this Agreement.
(vi) Nonrecourse Deductions. Nonrecourse Deductions for any taxable period shall be allocated to the Partners in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests. If the General Partner determines that the Partnership’s Nonrecourse Deductions should be allocated in a different ratio to satisfy the safe harbor requirements of the Treasury Regulations promulgated under Section 704(b) of the Code, the General Partner is authorized, upon notice to the other Partners, to revise the prescribed ratio to the numerically closest ratio that does satisfy such requirements.
(vii) Partner Nonrecourse Deductions. Partner Nonrecourse Deductions for any taxable period shall be allocated 100% to the Partner that bears the Economic Risk of Loss with respect to the Partner Nonrecourse
A-40
Debt to which such Partner Nonrecourse Deductions are attributable in accordance with Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-2(i). If more than one Partner bears the Economic Risk of Loss with respect to a Partner Nonrecourse Debt, such Partner Nonrecourse Deductions attributable thereto shall be allocated between or among such Partners in accordance with the ratios in which they share such Economic Risk of Loss.
(viii) Nonrecourse Liabilities. For purposes of Treasury Regulation Section 1.752-3(a)(3), the Partners agree that Nonrecourse Liabilities of the Partnership in excess of the sum of (A) the amount of Partnership Minimum Gain and (B) the total amount of Nonrecourse Built-in Gain shall be allocated among the Partners in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests.
(ix) Code Section 754 Adjustments. To the extent an adjustment to the adjusted tax basis of any Partnership asset pursuant to Section 734(b) or 743(b) of the Code is required, pursuant to Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(iv)(m), to be taken into account in determining Capital Accounts, the amount of such adjustment to the Capital Accounts shall be treated as an item of gain (if the adjustment increases the basis of the asset) or loss (if the adjustment decreases such basis), and such item of gain or loss shall be specially allocated to the Partners in a manner consistent with the manner in which their Capital Accounts are required to be adjusted pursuant to such Section of the Treasury Regulations.
(x) Economic Uniformity. At the election of the General Partner with respect to any taxable period ending upon, or after, the termination of the Subordination Period, all or a portion of the remaining items of Partnership gross income, gain, deduction or loss for such taxable period, after taking into account allocations pursuant to Section 6.1(d)(iii), shall be allocated 100% to each Partner with respect to such Partner’s Subordinated Units that are Outstanding as of the termination of the Subordination Period (“Final Subordinated Units”) or Common Units, as the case may be, in the proportion that the respective number of Common Units or Final Subordinated Units held by such Partner bears to the total number of Common Units or Final Subordinated Units then Outstanding, until each such Partner has been allocated the amount of gross income, gain, deduction or loss with respect to such Partner’s Common Units or Final Subordinated Units that causes the Capital Account maintained with respect to such Final Subordinated Units to equal an amount equal to the product of (A) the number of Final Subordinated Units held by such Partner and (B) the Per Unit Capital Amount for a Common Unit. The purpose of this allocation is to establish uniformity between the Capital Accounts underlying Final Subordinated Units and the Capital Accounts underlying Common Units held by Persons other than the General Partner and its Affiliates immediately prior to the conversion of such Final Subordinated Units into Common Units after giving effect to any allocations to holders of Common Units pursuant to this Section 6.1(d)(x). This allocation method for establishing such economic uniformity will be available to the General Partner only if the method for allocating the Capital Account maintained with respect to the Subordinated Units between the transferred and retained Subordinated Units pursuant to Section 5.5(c)(ii) does not otherwise provide such economic uniformity to the Final Subordinated Units.
(xi) Curative Allocation.
(A) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Section 6.1, other than the Required Allocations, the Required Allocations shall be taken into account in making the Agreed Allocations so that, to the extent possible, the net amount of items of income, gain, loss and deduction allocated to each Partner pursuant to the Required Allocations and the Agreed Allocations, together, shall be equal to the net amount of such items that would have been allocated to each such Partner under the Agreed Allocations had the Required Allocations and the related Curative Allocation not otherwise been provided in this Section 6.1. Notwithstanding the preceding sentence, Required Allocations relating to (1) Nonrecourse Deductions shall not be taken into account except to the extent that there has been a decrease in Partnership Minimum Gain and (2) Partner Nonrecourse Deductions shall not be taken into account except to the extent that there has been a decrease in Partner Nonrecourse Debt Minimum Gain. Allocations pursuant to this Section 6.1(d)(xi)(A) shall only be made with respect to Required Allocations to the extent the General Partner determines that such allocations will otherwise be inconsistent with the economic agreement among the Partners. Further, allocations pursuant to this Section 6.1(d)(xi)(A) shall be deferred with respect to allocations pursuant to clauses (1) and (2) hereof to the extent the General Partner determines that such allocations are likely to be offset by subsequent Required Allocations.
A-41
(B) The General Partner shall, with respect to each taxable period, (1) apply the provisions of Section 6.1(d)(xi)(A) in whatever order is most likely to minimize the economic distortions that might otherwise result from the Required Allocations, and (2) divide all allocations pursuant to Section 6.1(d)(xi)(A) among the Partners in a manner that is likely to minimize such economic distortions.
(xii) Corrective Allocations. In the event of any allocation of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items or any Book-Down Event or any recognition of a Net Termination Loss, the following rules shall apply:
(A) In the case of any allocation of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items (other than an allocation of Unrealized Gain or Unrealized Loss under Section 5.5(d) hereof), the General Partner shall allocate additional items of gross income and gain away from the holders of Incentive Distribution Rights to the Unitholders and the General Partner, or additional items of deduction and loss away from the Unitholders and the General Partner to the holders of Incentive Distribution Rights, to the extent that the Additional Book Basis Derivative Items allocated to the Unitholders or the General Partner exceed their Share of Additional Book Basis Derivative Items. For this purpose, the Unitholders and the General Partner shall be treated as being allocated Additional Book Basis Derivative Items to the extent that such Additional Book Basis Derivative Items have reduced the amount of income that would otherwise have been allocated to the Unitholders or the General Partner under the Partnership Agreement (e.g., Additional Book Basis Derivative Items taken into account in computing cost of goods sold would reduce the amount of book income otherwise available for allocation among the Partners). Any allocation made pursuant to this Section 6.1(d)(xii)(A) shall be made after all of the other Agreed Allocations have been made as if this Section 6.1(d)(xii)(A) were not in this Agreement and, to the extent necessary, shall require the reallocation of items that have been allocated pursuant to such other Agreed Allocations.
(B) In the case of any negative adjustments to the Capital Accounts of the Partners resulting from a Book-Down Event or from the recognition of a Net Termination Loss, such negative adjustment (1) shall first be allocated, to the extent of the Aggregate Remaining Net Positive Adjustments, in such a manner, as determined by the General Partner, that to the extent possible the aggregate Capital Accounts of the Partners will equal the amount that would have been the Capital Account balance of the Partners if no prior Book-Up Events had occurred, and (2) any negative adjustment in excess of the Aggregate Remaining Net Positive Adjustments shall be allocated pursuant to Section 6.1(c) hereof.
(C) In making the allocations required under this Section 6.1(d)(xii), the General Partner may apply whatever conventions or other methodology it determines will satisfy the purpose of this Section 6.1(d)(xii).
Section 6.2 Allocations for Tax Purposes.
(a) Except as otherwise provided herein, for federal income tax purposes, each item of income, gain, loss and deduction shall be allocated among the Partners in the same manner as its correlative item of “book” income, gain, loss or deduction is allocated pursuant to Section 6.1.
(b) In an attempt to eliminate Book-Tax Disparities attributable to a Contributed Property or Adjusted Property, items of income, gain, loss, depreciation, amortization and cost recovery deductions shall be allocated for federal income tax purposes among the Partners as follows:
(i)(A) In the case of a Contributed Property, such items attributable thereto shall be allocated among the Partners in the manner provided under Section 704(c) of the Code that takes into account the variation between the Agreed Value of such property and its adjusted basis at the time of contribution; and (B) any item of Residual Gain or Residual Loss attributable to a Contributed Property shall be allocated among the Partners in the same manner as its correlative item of “book” gain or loss is allocated pursuant to Section 6.1.
(ii)(A) In the case of an Adjusted Property, such items shall (1) first, be allocated among the Partners in a manner consistent with the principles of Section 704(c) of the Code to take into account the Unrealized
A-42
Gain or Unrealized Loss attributable to such property and the allocations thereof pursuant to Section 5.5(d)(i) or 5.5(d)(ii), and (2) second, in the event such property was originally a Contributed Property, be allocated among the Partners in a manner consistent with Section 6.2(b)(i)(A); and (B) any item of Residual Gain or Residual Loss attributable to an Adjusted Property shall be allocated among the Partners in the same manner as its correlative item of “book” gain or loss is allocated pursuant to Section 6.1.
(iii) The General Partner shall apply the principles of Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-3(d) to eliminate Book-Tax Disparities, except as otherwise determined by the General Partner with respect to goodwill, if any.
(c) For the proper administration of the Partnership and for the preservation of uniformity of the Limited Partner Interests (or any class or classes thereof), the General Partner shall (i) adopt such conventions as it deems appropriate in determining the amount of depreciation, amortization and cost recovery deductions; (ii) make special allocations for federal income tax purposes of income (including gross income) or deductions; and (iii) amend the provisions of this Agreement as appropriate (x) to reflect the proposal or promulgation of Treasury Regulations under Section 704(b) or Section 704(c) of the Code or (y) otherwise to preserve or achieve uniformity of the Limited Partner Interests (or any class or classes thereof). The General Partner may adopt such conventions, make such allocations and make such amendments to this Agreement as provided in this Section 6.2(c) only if such conventions, allocations or amendments would not have a material adverse effect on the Partners, the holders of any class or classes of Limited Partner Interests issued and Outstanding or the Partnership, and if such allocations are consistent with the principles of Section 704 of the Code.
(d) The General Partner may determine to depreciate or amortize the portion of an adjustment under Section 743(b) of the Code attributable to unrealized appreciation in any Adjusted Property (to the extent of the unamortized Book-Tax Disparity) using a predetermined rate derived from the depreciation or amortization method and useful life applied to the Partnership’s common basis of such property, despite any inconsistency of such approach with Treasury Regulation Section 1.167(c)-l(a)(6) or any successor regulations thereto. If the General Partner determines that such reporting position cannot reasonably be taken, the General Partner may adopt depreciation and amortization conventions under which all purchasers acquiring Limited Partner Interests in the same month would receive depreciation and amortization deductions, based upon the same applicable rate as if they had purchased a direct interest in the Partnership’s property. If the General Partner chooses not to utilize such aggregate method, the General Partner may use any other depreciation and amortization conventions to preserve the uniformity of the intrinsic tax characteristics of any Limited Partner Interests, so long as such conventions would not have a material adverse effect on the Limited Partners or the Record Holders of any class or classes of Limited Partner Interests.
(e) Any gain allocated to the Partners upon the sale or other taxable disposition of any Partnership asset shall, to the extent possible, after taking into account other required allocations of gain pursuant to this Section 6.2, be characterized as Recapture Income in the same proportions and to the same extent as such Partners (or their predecessors in interest) have been allocated any deductions directly or indirectly giving rise to the treatment of such gains as Recapture Income.
(f) All items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit recognized by the Partnership for federal income tax purposes and allocated to the Partners in accordance with the provisions hereof shall be determined without regard to any election under Section 754 of the Code that may be made by the Partnership; provided, however, that such allocations, once made, shall be adjusted (in the manner determined by the General Partner) to take into account those adjustments permitted or required by Sections 734 and 743 of the Code.
(g) Each item of Partnership income, gain, loss and deduction shall for federal income tax purposes be determined on an annual basis and prorated on a monthly basis and shall be allocated to the Partners as of the opening of the American Stock Exchange or such other National Securities Exchange on which the Common Units may then be listed or admitted for trading on the first Business Day of each month; provided, however, that gain or loss on a sale or other disposition of any assets of the Partnership or any other extraordinary item of income or loss realized and recognized other than in the ordinary course of business, as determined by the
A-43
General Partner, shall be allocated to the Partners as of the opening of the American Stock Exchange or such other National Securities Exchange on which the Common Units may then be listed or admitted for trading on the first Business Day of the month in which such gain or loss is recognized for federal income tax purposes. The General Partner may revise, alter or otherwise modify such methods of allocation to the extent permitted or required by Section 706 of the Code and the regulations or rulings promulgated thereunder.
(h) Allocations that would otherwise be made to a Limited Partner under the provisions of this Article VI shall instead be made to the beneficial owner of Limited Partner Interests held by a nominee in any case in which the nominee has furnished the identity of such owner to the Partnership in accordance with Section 6031(c) of the Code or any other method determined by the General Partner.
Section 6.3 Requirement and Characterization of Cash Distributions; Cash Distributions to Record Holders.
(a) Within 45 days following the end of each Quarter commencing with the Quarter ending on , 2007, an amount equal to 100% of Available Cash with respect to such Quarter shall, subject to the Delaware Act, be distributed in accordance with this Article VI by the Partnership to the Partners as of the Record Date selected by the General Partner. All amounts of Available Cash distributed by the Partnership on any date from any source shall be deemed to be Operating Surplus until the sum of all amounts of Available Cash theretofore distributed by the Partnership to the Partners pursuant to Section 6.4 equals the Operating Surplus from the Closing Date through the close of the immediately preceding Quarter. Any remaining amounts of Available Cash distributed on such date by the Partnership after giving effect to the two preceding sentences shall, except as otherwise provided in Section 6.5, be deemed to be “Capital Surplus.” Notwithstanding any provision to the contrary contained in this Agreement, the Partnership shall not make a distribution to any Partner on account of its interest in the Partnership if such distribution would violate the Delaware Act or any other applicable law.
(b) Notwithstanding Section 6.3(a), in the event of the dissolution and liquidation of the Partnership, all receipts received during or after the Quarter in which the Liquidation Date occurs, other than from borrowings determined to be Available Cash in accordance with (a)(ii) of the definition of Available Cash, shall be applied and distributed solely in accordance with, and subject to the terms and conditions of, Section 12.4.
(c) The General Partner may treat taxes paid by the Partnership on behalf of, or amounts withheld with respect to, all or less than all of the Partners, as a distribution of Available Cash to such Partners.
(d) Each distribution in respect of a Partnership Interest shall be paid by the Partnership, directly or through the Transfer Agent or through any other Person or agent, only to the Record Holder of such Partnership Interest as of the Record Date set for such distribution. Such payment shall constitute full payment and satisfaction of the Partnership’s liability in respect of such payment, regardless of any claim of any Person who may have an interest in such payment by reason of an assignment or otherwise.
Section 6.4 Distributions of Available Cash from Operating Surplus.
(a) During Subordination Period. Available Cash with respect to any Quarter within the Subordination Period that is deemed to be Operating Surplus pursuant to the provisions of Section 6.3 or 6.5 shall, subject to the Delaware Act, be distributed as follows, except as otherwise required by Section 5.6 in respect of other Partnership Securities issued pursuant thereto:
(i) First, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest and (y) to the Unitholders holding Common Units, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest, until there has been distributed in respect of each Common Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the Initial Quarterly Distribution for such Quarter;
(ii) Second, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest and (y) to the Unitholders holding Common Units, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest, until there has been distributed in respect of each Common Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the Cumulative Common Unit Arrearage existing with respect to such Quarter;
A-44
(iii) Third, (x) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest and (y) to the Unitholders holding Subordinated Units, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest, until there has been distributed in respect of each Subordinated Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the Initial Quarterly Distribution for such Quarter;
(iv) Fourth, to the General Partner and all Unitholders, in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests, until there has been distributed in respect of each Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the excess of the First Target Distribution over the Initial Quarterly Distribution for such Quarter;
(v) Fifth, (A) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest; (B) 13% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata; and (C) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to sub-clauses (A) and (B) of this clause (v) until there has been distributed in respect of each Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the excess of the Second Target Distribution over the First Target Distribution for such Quarter;
(vi) Sixth, (A) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest, (B) 23% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata; and (C) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to subclauses (A) and (B) of this subclause (vi), until there has been distributed in respect of each Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the excess of the Third Target Distribution over the Second Target Distribution for such Quarter; and
(vii) Thereafter, (A) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest; (B) 48% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata; and (C) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to subclauses (A) and (B) of this clause (vii);
provided, however, if the Initial Quarterly Distribution, the First Target Distribution, the Second Target Distribution and the Third Target Distribution have been reduced to zero pursuant to the second sentence of Section 6.6(a), the distribution of Available Cash that is deemed to be Operating Surplus with respect to any Quarter will be made solely in accordance with Section 6.4(a)(vii).
(b) After Subordination Period. Available Cash with respect to any Quarter after the Subordination Period that is deemed to be Operating Surplus pursuant to the provisions of Section 6.3 or 6.5, subject to the Delaware Act, shall be distributed as follows, except as otherwise required by Section 5.6(b) in respect of additional Partnership Securities issued pursuant thereto:
(i) First, 100% to the General Partner and the Unitholders in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests, until there has been distributed in respect of each Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the Initial Quarterly Distribution for such Quarter;
(ii) Second, 100% to the General Partner and the Unitholders in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests, until there has been distributed in respect of each Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the excess of the First Target Distribution over the Initial Quarterly Distribution for such Quarter;
(iii) Third, (A) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest; (B) 13% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata; and (C) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to subclauses (A) and (B) of this clause (iii), until there has been distributed in respect of each Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the excess of the Second Target Distribution over the First Target Distribution for such Quarter;
(iv) Fourth, (A) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest; (B) 23% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata; and (C) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to subclauses (A) and (B) of this clause (iv), until there has been distributed in respect of each Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the excess of the Third Target Distribution over the Second Target Distribution for such Quarter; and
(v) Thereafter, (A) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest; (B) 48% to the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights, Pro Rata; and (C) to all Unitholders, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the sum of the percentages applicable to subclauses (A) and (B) of this clause (v);
A-45
provided, however, if the Initial Quarterly Distribution, the First Target Distribution, the Second Target Distribution and the Third Target Distribution have been reduced to zero pursuant to the second sentence of Section 6.6(a), the distribution of Available Cash that is deemed to be Operating Surplus with respect to any Quarter will be made solely in accordance with Section 6.4(b)(v).
Section 6.5 Distributions of Available Cash from Capital Surplus.
Available Cash that is deemed to be Capital Surplus pursuant to the provisions of Section 6.3(a) shall, subject to the Delaware Act, be distributed, unless the provisions of Section 6.3 require otherwise, 100% to the General Partner and the Unitholders in accordance with their respective Percentage Interests, until a hypothetical holder of a Common Unit acquired in the Initial Public Offering has received with respect to such Common Unit during the period since the Closing Date through such date, distributions of Available Cash that are deemed to be Capital Surplus in an aggregate amount equal to the Initial Unit Price of such Common Unit. Available Cash that is deemed to be Capital Surplus shall then be distributed (A) to the General Partner in accordance with its Percentage Interest and (B) to all Unitholders holding Common Units, Pro Rata, a percentage equal to 100% less the General Partner’s Percentage Interest, until there has been distributed in respect of each Common Unit then Outstanding an amount equal to the Cumulative Common Unit Arrearage. Thereafter, all Available Cash shall be distributed as if it were Operating Surplus and shall be distributed in accordance with Section 6.4.
Section 6.6 Adjustment of Initial Quarterly Distribution and Target Distribution Levels.
(a) The Initial Quarterly Distribution, First Target Distribution, Second Target Distribution, Third Target Distribution, Common Unit Arrearages and Cumulative Common Unit Arrearages shall be proportionately adjusted in the event of any distribution, combination or subdivision (whether effected by a distribution payable in Units or otherwise) of Units or other Partnership Securities in accordance with Section 5.9. In the event of a distribution of Available Cash that is deemed to be from Capital Surplus, the then applicable Initial Quarterly Distribution, First Target Distribution, Second Target Distribution and Third Target Distribution, shall be adjusted proportionately downward to equal the product obtained by multiplying the otherwise applicable Initial Quarterly Distribution, First Target Distribution, Second Target Distribution and Third Target Distribution, as the case may be, by a fraction of which the numerator is the Unrecovered Initial Unit Price of the Common Units immediately after giving effect to such distribution and of which the denominator is the Unrecovered Initial Unit Price of the Common Units immediately prior to giving effect to such distribution.
(b) The Initial Quarterly Distribution, First Target Distribution, Second Target Distribution and Third Target Distribution, shall also be subject to adjustment pursuant to Section 6.9.
Section 6.7 Special Provisions Relating to the Holders of Subordinated Units.
(a) Except with respect to the right to vote on or approve matters requiring the vote or approval of a percentage of the holders of Outstanding Common Units and the right to participate in allocations of income, gain, loss and deduction and distributions made with respect to Common Units, the holder of a Subordinated Unit shall have all of the rights and obligations of a Unitholder holding Common Units hereunder; provided, however, that immediately upon the conversion of Subordinated Units into Common Units pursuant to Section 5.7, the Unitholder holding a Subordinated Unit shall possess all of the rights and obligations of a Unitholder holding Common Units hereunder, including the right to vote as a Common Unitholder and the right to participate in allocations of income, gain, loss and deduction and distributions made with respect to Common Units; provided, however, that such converted Subordinated Units shall remain subject to the provisions of Sections 5.5(c)(ii), 6.1(d)(x) and 6.7(c).
(b) A Unitholder shall not be permitted to transfer a Subordinated Unit or a Subordinated Unit that has converted into a Common Unit pursuant to Section 5.7 (other than a transfer to an Affiliate) if the remaining balance in the transferring Unitholder’s Capital Account with respect to the retained Subordinated Units or Retained Converted Subordinated Units would be negative after giving effect to the allocation under Section 5.5(c)(ii)(B).
A-46
(c) A Unitholder holding a Subordinated Unit that has converted into a Common Unit pursuant to Section 5.7 shall not be issued a Common Unit Certificate pursuant to Section 4.1, and shall not be permitted to transfer its converted Subordinated Units to a Person that is not an Affiliate of the holder until such time as the General Partner determines, based on advice of counsel, that a converted Subordinated Unit should have, as a substantive matter, like intrinsic economic and federal income tax characteristics, in all material respects, to the intrinsic economic and federal income tax characteristics of an Initial Common Unit. In connection with the condition imposed by this Section 6.7(c), the General Partner may take whatever steps are required to provide economic uniformity to the converted Subordinated Units in preparation for a transfer of such converted Subordinated Units, including the application of Sections 5.5(c)(ii), 6.1(d)(x) and 6.7(b), provided, however, that no such steps may be taken that would have a material adverse effect on the Unitholders holding Common Units represented by Common Unit certificates (for this purpose the allocation of income, gain, loss or deduction with respect to Subordinated Units or Common Units will be deemed not to have a material adverse effect on the Unitholders holding Common Units).
Section 6.8 Special Provisions Relating to the Holders of Incentive Distribution Rights.
Notwithstanding anything to the contrary set forth in this Agreement, the holders of the Incentive Distribution Rights (a) shall (i) possess the rights and obligations provided in this Agreement with respect to a Limited Partner pursuant to Articles III and VII and (ii) have a Capital Account as a Partner pursuant to Section 5.5 and all other provisions related thereto and (b) shall not (i) be entitled to vote on any matters requiring the approval or vote of the holders of Outstanding Units, except as provided by law, (ii) be entitled to any distributions other than as provided in Sections 6.4(a)(v), (vi) and (vii), 6.4(b)(iii), (iv) and (v), and 12.4 or (iii) be allocated items of income, gain, loss or deduction other than as specified in this Article VI.
Section 6.9 Entity-Level Taxation.
If legislation is enacted or the interpretation of existing language is modified by a court of competent jurisdiction so that a Group Member is treated as an association taxable as a corporation or is otherwise subject to an entity-level tax for federal, state or local income tax purposes, then the General Partner may reduce the Initial Quarterly Distribution, the First Target Distribution, the Second Target Distribution and the Third Target Distribution by the amount of income taxes that are payable by reason of any such new legislation or interpretation (the “Incremental Income Taxes”), or any portion thereof selected by the General Partner, in the manner provided in this Section 6.9. If the General Partner elects to reduce the Minimum Quarterly Distribution, the First Target Distribution, the Second Target Distribution and the Third Target Distribution for any Quarter with respect to all or a portion of any Incremental Income Taxes, the General Partner shall estimate for such Quarter the Partnership Group’s aggregate liability (the “Estimated Incremental Quarterly Tax Amount”) for all (or the relevant portion of) such Incremental Income Taxes; provided that any difference between such estimate and the actual tax liability for Incremental Income Taxes (or the relevant portion thereof) for such Quarter may, to the extent determined by the General Partner, be taken into account in determining the Estimated Incremental Quarterly Tax Amount with respect to each Quarter in which any such difference can be determined. For each such Quarter, the Initial Quarterly Distribution, First Target Distribution, Second Target Distribution and Third Target Distribution, shall be the product obtained by multiplying (a) the amounts therefor that are set out herein prior to the application of this Section 6.9 times (b) the quotient obtained by dividing (i) Available Cash with respect to such Quarter by (ii) the sum of Available Cash with respect to such Quarter and the Estimated Incremental Quarterly Tax Amount for such Quarter, as determined by the General Partner. For purposes of the foregoing, Available Cash with respect to a Quarter will be deemed reduced by the Estimated Incremental Quarterly Tax Amount for that Quarter.
A-47
MANAGEMENT AND OPERATION OF BUSINESS
(a) The General Partner shall conduct, direct and manage all activities of the Partnership. Except as otherwise expressly provided in this Agreement, all management powers over the business and affairs of the Partnership shall be exclusively vested in the General Partner, and no Limited Partner or Assignee shall have any management power over the business and affairs of the Partnership. In addition to the powers now or hereafter granted a general partner of a limited partnership under applicable law or that are granted to the General Partner under any other provision of this Agreement, the General Partner, subject to Section 7.3, shall have full power and authority to do all things and on such terms as it determines to be necessary or appropriate to conduct the business of the Partnership, to exercise all powers set forth in Section 2.5 and to effectuate the purposes set forth in Section 2.4, including the following:
(i) the making of any expenditures, the lending or borrowing of money, the assumption or guarantee of, or other contracting for, indebtedness and other liabilities, the issuance of evidences of indebtedness, including indebtedness that is convertible into Partnership Securities, and the incurring of any other obligations;
(ii) the making of tax, regulatory and other filings, or rendering of periodic or other reports to governmental or other agencies having jurisdiction over the business or assets of the Partnership;
(iii) the acquisition, disposition, mortgage, pledge, encumbrance, hypothecation or exchange of any or all of the assets of the Partnership or the merger or other combination of the Partnership with or into another Person (the matters described in this clause (iii) being subject, however, to any prior approval that may be required by Section 7.3 and Article XIV);
(iv) the use of the assets of the Partnership (including cash on hand) for any purpose consistent with the terms of this Agreement, including the financing of the conduct of the operations of the Partnership Group; subject to Section 7.6(a), the lending of funds to other Persons (including other Group Members); the repayment or guarantee of obligations of any Group Member; and the making of capital contributions to any Group Member;
(v) the negotiation, execution and performance of any contracts, conveyances or other instruments (including instruments that limit the liability of the Partnership under contractual arrangements to all or particular assets of the Partnership, with the other party to the contract to have no recourse against the General Partner or its assets other than its interest in the Partnership, even if same results in the terms of the transaction being less favorable to the Partnership than would otherwise be the case);
(vi) the distribution of Partnership cash;
(vii) the selection and dismissal of employees (including employees having titles such as “president,” “vice president,” “secretary” and “treasurer”) and agents, outside attorneys, accountants, consultants and contractors and the determination of their compensation and other terms of employment or hiring;
(viii) the maintenance of insurance for the benefit of the Partnership Group, the Partners and Indemnitees;
(ix) the formation of, or acquisition of an interest in, and the contribution of property and the making of loans to, any further limited or general partnerships, joint ventures, corporations, limited liability companies or other relationships (including the acquisition of interests in, and the contributions of property to, any Group Member from time to time) subject to the restrictions set forth in Section 2.4;
(x) the control of any matters affecting the rights and obligations of the Partnership, including the bringing and defending of actions at law or in equity and otherwise engaging in the conduct of litigation, arbitration or mediation and the incurring of legal expense and the settlement of claims and litigation;
(xi) the indemnification of any Person against liabilities and contingencies to the extent permitted by law;
A-48
(xii) the entering into of listing agreements with any National Securities Exchange and the delisting of some or all of the Limited Partner Interests from, or requesting that trading be suspended on, any such exchange (subject to any prior approval that may be required under Section 4.8);
(xiii) the purchase, sale or other acquisition or disposition of Partnership Securities, or the issuance of options, rights, warrants and appreciation rights relating to Partnership Securities;
(xiv) the undertaking of any action in connection with the Partnership’s participation in any Group Member; and
(xv) the entering into of agreements with any of its Affiliates to render services to a Group Member or to itself in the discharge of its duties as General Partner of the Partnership.
(b) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Agreement, any Group Member Agreement, the Delaware Act or any applicable law, rule or regulation, each of the Partners and the Assignees and each other Person who may acquire an interest in Partnership Securities hereby (i) approves, ratifies and confirms the execution, delivery and performance by the parties thereto of this Agreement, the Group Member Agreement of each other Group Member, and the Underwriting Agreement, Contribution Agreement, Letter Agreement, Management Services Agreements, Services Agreement, Secondment Agreement, O&M Agreement, Assignment Agreement, Crest Royalty Agreement, Tax Sharing Agreement and other agreements described in or filed as exhibits to the Registration Statement that are related to the transactions contemplated by the Registration Statement to which the Partnership or any of its Subsidiaries is a party as of the effective date of this Agreement; (ii) agrees that the General Partner (on its own or through any officer of the Partnership) is authorized to execute, deliver and perform the agreements referred to in clause (i) of this sentence and the other agreements, acts, transactions and matters described in or contemplated by the Registration Statement on behalf of the Partnership without any further act, approval or vote of the Partners or the Assignees or the other Persons who may acquire an interest in Partnership Securities; and (iii) agrees that the execution, delivery or performance by the General Partner, any Group Member or any Affiliate of any of them of this Agreement or any agreement authorized or permitted under this Agreement (including the exercise by the General Partner or any Affiliate of the General Partner of the rights accorded pursuant to Article XV) shall not constitute a breach by the General Partner of any duty that the General Partner may owe the Partnership or the Limited Partners or any other Persons under this Agreement (or any other agreements) or of any other duty existing at law, in equity or otherwise.
Section 7.2 Certificate of Limited Partnership.
The General Partner has caused the Certificate of Limited Partnership to be filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware as required by the Delaware Act. The General Partner shall use all reasonable efforts to cause to be filed such other certificates or documents that the General Partner determines to be necessary or appropriate for the formation, continuation, qualification and operation of a limited partnership (or a partnership in which the limited partners have limited liability) in the State of Delaware or any other state in which the Partnership may elect to do business or own property. To the extent the General Partner determines such action to be necessary or appropriate, the General Partner shall file amendments to and restatements of the Certificate of Limited Partnership and do all things to maintain the Partnership as a limited partnership (or a partnership or other entity in which the limited partners have limited liability) under the laws of the State of Delaware or of any other state in which the Partnership may elect to do business or own property. Subject to the terms of Section 3.4(a), the General Partner shall not be required, before or after filing, to deliver or mail a copy of the Certificate of Limited Partnership, any qualification document or any amendment thereto to any Limited Partner.
Section 7.3 Restrictions on the General Partner’s Authority.
(a) Except as otherwise provided in this Agreement, the General Partner may not, without written approval of the specific act by holders of all of the Outstanding Limited Partner Interests or by other written instrument executed and delivered by holders of all of the Outstanding Limited Partner Interests subsequent to the date of this Agreement, take any action in contravention of this Agreement.
A-49
(b) Except as provided in Articles XII and XIV, the General Partner may not sell, exchange or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of the assets of the Partnership Group, taken as a whole, in a single transaction or a series of related transactions (including by way of merger, consolidation, other combination or sale of ownership interests of the Partnership’s Subsidiaries) without the approval of holders of a Unit Majority; provided, however, that this provision shall not preclude or limit the General Partner’s ability to mortgage, pledge, hypothecate or grant a security interest in all or substantially all of the assets of the Partnership Group and shall not apply to any forced sale of any or all of the assets of the Partnership Group pursuant to the foreclosure of, or other realization upon, any such encumbrance. Without the approval of holders of a Unit Majority, the General Partner shall not, on behalf of the Partnership, except as permitted under Sections 4.6, 11.1 and 11.2, elect or cause the Partnership to elect a successor general partner of the Partnership.
Section 7.4 Reimbursement of the General Partner.
(a) Except as provided in this Section 7.4 and elsewhere in this Agreement, the General Partner shall not be compensated for its services as a general partner or managing member of any Group Member.
(b) The General Partner or Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc., without duplication, shall be reimbursed on a monthly basis, or such other basis as the General Partner may determine, for (i) all direct expenses it incurs or payments it makes on behalf of the Partnership Group (including salary, bonus, incentive compensation and other amounts paid to any Person, including Affiliates of the General Partner, to perform services for the Partnership Group or for the General Partner in the discharge of its duties to the Partnership Group and including overhead allocated to the Partnership by Affiliates of the General Partner consistent with then-applicable accounting and allocation methodologies generally permitted by FERC for rate-making purposes (or in the absence of then-applicable methodologies permitted by FERC, consistent with the most-recently applicable methodologies) and past business practices, and including the fees and expenses payable by the Partnership pursuant to the O&M Agreement and the Services Agreement), and (ii) all other expenses allocable to the Partnership Group or otherwise incurred in connection with operating the Partnership Group’s business (including expenses allocated to the General Partner by its Affiliates). The General Partner shall determine the expenses that are allocable to the Partnership Group. Reimbursements pursuant to this Section 7.4 shall be in addition to any reimbursement to the General Partner as a result of indemnification pursuant to Section 7.7. The allocation of overhead to the Partnership by Affiliates of the General Partner consistent with then-applicable accounting and allocation methodologies generally permitted by FERC for rate-making purposes (or in the absence of then-applicable methodologies permitted by FERC, consistent with the most-recently applicable methodologies) and past business practices shall be deemed to be fair and reasonable to the Partnership.
(c) The General Partner, without the approval of the Limited Partners (who shall have no right to vote in respect thereof), may propose and adopt on behalf of the Partnership Employee Benefit Plans, employee programs and employee practices (including plans, programs and practices involving the issuance of Partnership Securities or options to purchase or rights, warrants or appreciation rights relating to Partnership Securities), or cause the Partnership to issue Partnership Securities in connection with, or pursuant to, any Employee Benefit Plan, employee program or employee practice maintained or sponsored by the General Partner or any of its Affiliates, in each case for the benefit of employees of the General Partner or its Affiliates, or any Group Member or its Affiliates, or any of them, in respect of services performed, directly or indirectly, for the benefit of the Partnership Group. The Partnership agrees to issue and sell to the General Partner or any of its Affiliates any Partnership Securities that the General Partner or such Affiliates are obligated to provide to any employees pursuant to any such Employee Benefit Plans, employee programs or employee practices. Expenses incurred by the General Partner in connection with any such plans, programs and practices (including the net cost to the General Partner or such Affiliates of Partnership Securities purchased by the General Partner or such Affiliates from the Partnership to fulfill options or awards under such plans, programs and practices) shall be reimbursed in accordance with Section 7.4(b). Any and all obligations of the General Partner under any Employee Benefit Plans, employee programs or employee practices adopted by the General Partner as permitted by this Section 7.4(c) shall constitute obligations of the General Partner hereunder and shall be assumed by any successor General Partner approved pursuant to Section 11.1 or 11.2 or the transferee of or successor to all of the General Partner’s General Partner Interest pursuant to Section 4.6.
A-50
Section 7.5 Outside Activities.
(a) After the Closing Date, the General Partner, for so long as it is the General Partner of the Partnership (i) agrees that its sole business will be to act as a general partner or managing member, as the case may be, of the Partnership and any other partnership or limited liability company of which the Partnership is, directly or indirectly, a partner or member and to undertake activities that are ancillary or related thereto (including being a limited partner in the Partnership) and (ii) shall not engage in any business or activity or incur any debts or liabilities except in connection with or incidental to (A) its performance as general partner or managing member, if any, of one or more Group Members or as described in or contemplated by the Registration Statement or (B) the acquiring, owning or disposing of debt or equity securities in any Group Member.
(b) Subject to Section 7.5(c), each Indemnitee (other than the General Partner) shall have the right to engage in businesses of every type and description and other activities for profit and to engage in and possess an interest in other business ventures of any and every type or description, whether in businesses engaged in or anticipated to be engaged in by any Group Member, independently or with others, including business interests and activities in direct competition with the business and activities of any Group Member, and none of the same shall constitute a breach of this Agreement or any other duty existing at law, in equity or otherwise to any Group Member or any Partner or Assignee. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement or any duty existing at law, in equity or otherwise, but subject to Section 7.5(c) (i) the engaging in competitive activities by any Indemnitees (other than the General Partner) in accordance with the provisions of this Section 7.5 is hereby approved by the Partnership and all Partners, (ii) it shall be deemed not to be breach of any duty including any fiduciary duty or any other obligation of any type whatsoever of the General Partner or of any Indemnitee for the Indemnitees (other than the General Partner) to engage in such business interests and activities in preference to or to the exclusion of the Partnership.
(c) Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement or any duty existing at law, in equity or otherwise, the doctrine of corporate opportunity, or any analogous doctrine, shall not apply to an Indemnitee (including the General Partner). No Indemnitee (including the General Partner) who acquires knowledge of a potential transaction, agreement, arrangement or other matter that may be an opportunity for the Partnership shall have any duty to communicate or offer such opportunity to the Partnership, and it shall be deemed not to be breach of any duty including any fiduciary duty or any other obligation of any type whatsoever of the General Partner or of any Indemnitee for the Indemnitees (including the General Partner) to not communicate or offer such opportunity to the Partnership, and such Indemnitee (including the General Partner) shall not be liable to the Partnership, to any Limited Partner or any other Person for breach of any fiduciary or other duty by reason of the fact that such Indemnitee (including the General Partner) pursues or acquires for itself, directs such opportunity to another Person or does not communicate such opportunity or information to the Partnership; provided, however, that the preceding terms of this Section 7.5(c) shall not apply to any business opportunity (i) of which any Person who is an employee of any member of the Partnership Group or an officer, director or employee of the General Partner acquires knowledge while acting in his capacity as such officer, director or employee and not acting in his capacity as an officer, director or employee of an entity that is not a member of the Partnership Group or (ii) taken by an Indemnitee who is an individual for such Indemnitee’s personal benefit.
(d) The General Partner and each of its Affiliates may acquire Units or other Partnership Securities in addition to those acquired on the Closing Date and, except as otherwise provided in this Agreement, shall be entitled to exercise, at their option, all rights relating to all Units or other Partnership Securities acquired by them. The term “Affiliates” when used in this Section 7.5(d) with respect to the General Partner shall not include any Group Member.
Section 7.6 Loans from the General Partner; Loans or Contributions from the Partnership or Group Members.
(a) The General Partner or any of its Affiliates may lend to any Group Member, and any Group Member may borrow from the General Partner or any of its Affiliates, funds needed or desired by the Group Member for such periods of time and in such amounts as the General Partner may determine; provided, however, that in any such case the lending party may not charge the borrowing party interest at a rate greater than the rate that would
A-51
be charged the borrowing party or impose terms less favorable to the borrowing party than would be charged or imposed on the borrowing party by unrelated lenders on comparable loans made on an arm’s-length basis (without reference to the lending party’s financial abilities or guarantees), all as determined by the General Partner. The borrowing party shall reimburse the lending party for any costs (other than any additional interest costs) incurred by the lending party in connection with the borrowing of such funds. For purposes of this Section 7.6(a) and Section 7.6(b), the term “Group Member” shall include any Affiliate of a Group Member that is controlled by the Group Member.
(b) The Partnership may lend or contribute to any Group Member, and any Group Member may borrow from the Partnership, funds on terms and conditions determined by the General Partner. No Group Member may lend funds to the General Partner or any of its Affiliates (other than another Group Member).
(c) No borrowing by any Group Member or the approval thereof by the General Partner shall be deemed to constitute a breach of any duty of the General Partner or its Affiliates to the Partnership or the Limited Partners existing hereunder, or existing at law, in equity or otherwise by reason of the fact that the purpose or effect of such borrowing is directly or indirectly to (i) enable distributions to the General Partner or its Affiliates (including in their capacities as Limited Partners) to exceed the General Partner’s Percentage Interest of the total amount distributed to all partners or (ii) hasten the expiration of the Subordination Period or the conversion of any Subordinated Units into Common Units.
(a) To the fullest extent permitted by law but subject to the limitations expressly provided in this Agreement, all Indemnitees shall be indemnified and held harmless by the Partnership from and against any and all losses, claims, damages, liabilities, joint or several, expenses (including legal fees and expenses), judgments, fines, penalties, interest, settlements or other amounts arising from any and all claims, demands, actions, suits or proceedings, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative, in which any Indemnitee may be involved, or is threatened to be involved, as a party or otherwise, by reason of the Indemnitee’s serving or having served, or taking or having taken any action or inaction in, any capacity that causes or caused the Indemnitee to be, an Indemnitee; provided, that the Indemnitee shall not be indemnified and held harmless if there has been a final and non-appealable judgment entered by a court of competent jurisdiction determining that, in respect of the matter for which the Indemnitee is seeking indemnification pursuant to this Section 7.7, the Indemnitee acted in bad faith or engaged in fraud, willful misconduct or, in the case of a criminal matter, acted with knowledge that the Indemnitee’s conduct was unlawful; provided, further, no indemnification pursuant to this Section 7.7 shall be available to the General Partner or its Affiliates (other than a Group Member) with respect to its or their obligations incurred pursuant to the Underwriting Agreement or the Contribution Agreement (other than obligations incurred by the General Partner on behalf of the Partnership). Any indemnification pursuant to this Section 7.7 shall be made only out of the assets of the Partnership, it being agreed that the General Partner shall not be personally liable for such indemnification and shall have no obligation to contribute or loan any monies or property to the Partnership to enable it to effectuate such indemnification.
(b) To the fullest extent permitted by law, expenses (including legal fees and expenses) incurred by an Indemnitee who is indemnified pursuant to Section 7.7(a) in defending any claim, demand, action, suit or proceeding shall, from time to time, be advanced by the Partnership prior to a determination that the Indemnitee is not entitled to be indemnified upon receipt by the Partnership of any undertaking by or on behalf of the Indemnitee to repay such amount if it shall be determined that the Indemnitee is not entitled to be indemnified as authorized in this Section 7.7.
(c) The indemnification provided by this Section 7.7 shall be in addition to any other rights to which an Indemnitee may be entitled under any agreement, pursuant to any vote of the holders of Outstanding Limited Partner Interests, as a matter of law or otherwise, both as to actions in the Indemnitee’s capacity as an Indemnitee and as to actions in any other capacity (including any capacity under the Underwriting Agreement), and shall continue as to an Indemnitee who has ceased to serve in such capacity and shall inure to the benefit of the heirs, successors, assigns and administrators of the Indemnitee.
A-52
(d) The Partnership may purchase and maintain (or reimburse the General Partner or its Affiliates for the cost of) insurance, on behalf of the General Partner, its Affiliates and such other Persons as the General Partner shall determine, against any liability that may be asserted against, or expense that may be incurred by, such Person in connection with the Partnership’s activities or such Person’s activities on behalf of the Partnership, regardless of whether the Partnership would have the power to indemnify such Person against such liability under the provisions of this Agreement.
(e) For purposes of this Section 7.7, the Partnership shall be deemed to have requested an Indemnitee to serve as fiduciary of an Employee Benefit Plan whenever the performance by it of its duties to the Partnership also imposes duties on, or otherwise involves services by, it to the plan or participants or beneficiaries of the plan; excise taxes assessed on an Indemnitee with respect to an Employee Benefit Plan pursuant to applicable law shall constitute “fines” within the meaning of Section 7.7(a); and action taken or omitted by it with respect to any Employee Benefit Plan in the performance of its duties for a purpose reasonably believed by it to be in the best interest of the participants and beneficiaries of the plan shall be deemed to be for a purpose that is in the best interests of the Partnership.
(f) In no event may an Indemnitee subject the Limited Partners to personal liability by reason of the indemnification provisions set forth in this Agreement.
(g) An Indemnitee shall not be denied indemnification in whole or in part under this Section 7.7 because the Indemnitee had an interest in the transaction with respect to which the indemnification applies if the transaction was otherwise permitted by the terms of this Agreement.
(h) The provisions of this Section 7.7 are for the benefit of the Indemnitees, their heirs, successors, assigns and administrators and shall not be deemed to create any rights for the benefit of any other Persons.
(i) No amendment, modification or repeal of this Section 7.7 or any provision hereof shall in any manner terminate, reduce or impair the right of any past, present or future Indemnitee to be indemnified by the Partnership, nor the obligations of the Partnership to indemnify any such Indemnitee under and in accordance with the provisions of this Section 7.7 as in effect immediately prior to such amendment, modification or repeal with respect to claims arising from or relating to matters occurring, in whole or in part, prior to such amendment, modification or repeal, regardless of when such claims may arise or be asserted.
Section 7.8 Liability of Indemnitees.
(a) Notwithstanding anything to the contrary set forth in this Agreement, no Indemnitee shall be liable for monetary damages to the Partnership, the Limited Partners, the Assignees or any other Persons who have acquired interests in the Partnership Securities, for losses sustained or liabilities incurred as a result of any act or omission of an Indemnitee unless there has been a final and non-appealable judgment entered by a court of competent jurisdiction determining that, in respect of the matter in question, the Indemnitee acted in bad faith or engaged in fraud, willful misconduct or, in the case of a criminal matter, acted with knowledge that the Indemnitee’s conduct was criminal.
(b) Subject to its obligations and duties as General Partner set forth in Section 7.1(a), the General Partner may exercise any of the powers granted to it by this Agreement and perform any of the duties imposed upon it hereunder either directly or by or through its agents, and the General Partner shall not be responsible for any misconduct or negligence on the part of any such agent appointed by the General Partner in good faith.
(c) To the extent that, at law or in equity, an Indemnitee has duties (including fiduciary duties) and liabilities relating thereto to the Partnership or to the Partners, the General Partner and any other Indemnitee acting in connection with the Partnership’s business or affairs shall not be liable to the Partnership or to any Partner for its good faith reliance on the provisions of this Agreement.
A-53
(d) Any amendment, modification or repeal of this Section 7.8 or any provision hereof shall be prospective only and shall not in any way affect the limitations on the liability of the Indemnitees under this Section 7.8 as in effect immediately prior to such amendment, modification or repeal with respect to claims arising from or relating to matters occurring, in whole or in part, prior to such amendment, modification or repeal, regardless of when such claims may arise or be asserted.
(e) In exercising its authority under this Agreement, the General Partner is under no obligation to consider the separate interests of any Partner individually (including, without limitation, the particular tax consequences to any Partner individually) in deciding whether to cause the Partnership to take (or to decline to take) any action, and the General Partner shall not be liable for monetary damages for losses sustained, liabilities incurred or benefits not derived by Partners in connection with such decisions, provided that the General Partner has acted in good faith.
Section 7.9 Resolution of Conflicts of Interest; Standards of Conduct and Modification of Duties.
(a) Unless otherwise expressly provided in this Agreement or any Group Member Agreement, whenever any actual or potential conflict of interest exists or arises between the General Partner or any of its Affiliates, on the one hand, and the Partnership, any Group Member, any Partner or any Assignee, on the other, any resolution or course of action by the General Partner or its Affiliates in respect of such conflict of interest shall be permitted and deemed approved by all Partners, and shall not constitute a breach of this Agreement, of any Group Member Agreement, of any agreement contemplated herein or therein, or of any duty existing at law, in equity or otherwise, if the resolution or course of action in respect of such conflict of interest is (i) approved by Special Approval, (ii) approved by the vote of a majority of the Outstanding Common Units (excluding Common Units owned by the General Partner and its Affiliates), (iii) on terms no less favorable to the Partnership than those generally being provided to or available from unrelated third parties or (iv) fair and reasonable to the Partnership, taking into account the totality of the relationships between the parties involved (including other transactions that may be particularly favorable or advantageous to the Partnership). The General Partner shall be authorized but not required in connection with its resolution of such conflict of interest to seek Special Approval of such resolution, and the General Partner may also adopt a resolution or course of action that has not received Special Approval. If Special Approval is sought, then it shall be presumed that, in making its decision, the Conflicts Committee acted in good faith, and if Special Approval is not sought and the Board of Directors of the General Partner determines that the resolution or course of action taken with respect to a conflict of interest satisfies either of the standards set forth in clauses (iii) or (iv) above, then it shall be presumed that, in making its decision, the Board of Directors acted in good faith, and, in either case, in any proceeding brought by any Limited Partner or Assignee or by or on behalf of such Limited Partner or Assignee or any other Limited Partner or Assignee or the Partnership challenging such approval, the Person bringing or prosecuting such proceeding shall have the burden of overcoming such presumption. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement, the existence of the conflicts of interest described in the Registration Statement are hereby approved by all Partners and shall not constitute a breach of this Agreement or of any other duty existing at law, in equity or otherwise.
(b) Whenever the General Partner makes a determination or takes or declines to take any other action, or any of its Affiliates causes it to do so, in its capacity as the general partner of the Partnership as opposed to in its individual capacity, whether under this Agreement, any Group Member Agreement or any other agreement contemplated hereby or otherwise, then, unless another express standard is provided for in this Agreement, the General Partner, or such Affiliates causing it to do so, shall make such determination or take or decline to take such other action in good faith and shall not be subject to any other or different standards imposed by this Agreement, any Group Member Agreement, any other agreement contemplated hereby or under the Delaware Act or any other law, rule or regulation or at equity. In order for a determination or other action to be in “good faith” for purposes of this Agreement, the Person or Persons making such determination or taking or declining to take such other action must believe that the determination or other action is in the best interests of the Partnership.
A-54
(c) Whenever the General Partner makes a determination or takes or declines to take any other action, or any of its Affiliates causes it to do so, in its individual capacity as opposed to in its capacity as the general partner of the Partnership, whether under this Agreement, any Group Member Agreement or any other agreement contemplated hereby or otherwise, then the General Partner, or such Affiliates causing it to do so, are entitled, to the fullest extent permitted by law, to make such determination or to take or decline to take such other action free of any fiduciary or other duty or obligation whatsoever to the Partnership, any Limited Partner or Assignee; and the General Partner, or such Affiliates causing it to do so, shall not be required to act in good faith or pursuant to any other standard imposed by this Agreement, any Group Member Agreement, any other agreement contemplated hereby or under the Delaware Act or any other law, rule or regulation or at equity. By way of illustration and not of limitation, whenever the phrase, “at the option of the General Partner,” or some variation of that phrase, is used in this Agreement, it indicates that the General Partner is acting in its individual capacity. For the avoidance of doubt, but subject to Sections 4.6 and 4.7, whenever the General Partner votes or transfers its Units, General Partner Units or Incentive Distribution Rights, as appropriate, or refrains from voting or transferring its Units, General Partner Units or Incentive Distribution Rights, to the extent permitted under this Agreement, it shall be acting in its individual capacity. The General Partner’s organizational documents may provide that determinations to take or decline to take any action in its individual, rather than representative, capacity may or shall be determined by its members, if the General Partner is a limited liability company, stockholders, if the General Partner is a corporation, or the members or stockholders of the General Partner’s general partner, if the General Partner is a limited partnership.
(d) Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement, the General Partner and its Affiliates shall have no duty or obligation, express or implied, to (i) sell or otherwise dispose of any asset of the Partnership Group other than in the ordinary course of business or (ii) permit any Group Member to use any facilities or assets of the General Partner and its Affiliates, except as may be provided in contracts entered into from time to time specifically dealing with such use. Any determination by the General Partner or any of its Affiliates to enter into such contracts shall be at its option.
(e) Except as expressly set forth in this Agreement or required by the Delaware Act, neither the General Partner nor any other Indemnitee shall have any duties or liabilities, including fiduciary duties, to the Partnership or any Limited Partner or Assignee and the provisions of this Agreement, to the extent that they restrict, eliminate or otherwise modify the duties and liabilities, including fiduciary duties, of the General Partner or any other Indemnitee otherwise existing at law or in equity, are agreed by the Partners to replace such other duties and liabilities of the General Partner or such other Indemnitee.
(f) The Unitholders hereby authorize the General Partner, on behalf of the Partnership as a partner or member of a Group Member, to approve actions by the general partner or managing member of such Group Member similar to those actions permitted to be taken by the General Partner pursuant to this Section 7.9.
Section 7.10 Other Matters Concerning the General Partner.
(a) The General Partner may rely and shall be protected in acting or refraining from acting upon any resolution, certificate, statement, instrument, opinion, report, notice, request, consent, order, bond, debenture or other paper or document believed by it to be genuine and to have been signed or presented by the proper party or parties.
(b) The General Partner may consult with legal counsel, accountants, appraisers, management consultants, investment bankers and other consultants and advisers selected by it, and any act taken or omitted to be taken in reliance upon the advice or opinion (including an Opinion of Counsel) of such Persons as to matters that the General Partner reasonably believes to be within such Person’s professional or expert competence shall be conclusively presumed to have been done or omitted in good faith and in accordance with such advice or opinion. The General Partner shall be fully protected from liability to the Partnership, the Partners or other Persons bound to this Agreement for such reliance made in good faith.
A-55
(c) The General Partner shall have the right, in respect of any of its powers or obligations hereunder, to act through any of its duly authorized officers, a duly appointed attorney or attorneys-in-fact or the duly authorized officers of the Partnership.
Section 7.11 Purchase or Sale of Partnership Securities.
The General Partner may cause the Partnership to purchase or otherwise acquire Partnership Securities; provided that, except as may be required pursuant to Section 4.10, the General Partner may not cause any Group Member to purchase Subordinated Units during the Subordination Period. As long as Partnership Securities are held by any Group Member, such Partnership Securities shall not be considered Outstanding for any purpose, except as otherwise provided herein. The General Partner or any Affiliate of the General Partner may also purchase or otherwise acquire and sell or otherwise dispose of Partnership Securities for its own account, subject to the provisions of Articles IV and X.
Section 7.12 Registration Rights of the General Partner and its Affiliates.
(a) If, (i) the General Partner or any Affiliate of the General Partner (including for purposes of this Section 7.12, any Person that is an Affiliate of the General Partner at the date hereof notwithstanding that it may later cease to be an Affiliate of the General Partner) holds Partnership Securities that it desires to sell and (ii) Rule 144 of the Securities Act (or any successor rule or regulation to Rule 144) or another exemption from registration is not available to enable such holder of Partnership Securities (the “Holder”) to dispose of the number of Partnership Securities it desires to sell at the time it desires to do so without registration under the Securities Act, then at the option and upon the request of the Holder, the Partnership shall file with the Commission as promptly as practicable after receiving such request, and use all commercially reasonable efforts to cause to become effective and remain effective for a period of not less than six months following its effective date or such shorter period as shall terminate when all Partnership Securities covered by such registration statement have been sold, a registration statement under the Securities Act registering the offering and sale of the number of Partnership Securities specified by the Holder; provided, however, that the Partnership shall not be required to effect more than five registrations pursuant to Sections 7.12(a) and 7.12(b); and provided further, however, that if the Conflicts Committee determines in good faith that the requested registration would be materially detrimental to the Partnership and its Partners because such registration would (x) materially interfere with a significant acquisition, reorganization or other similar transaction involving the Partnership, (y) require premature disclosure of material information that the Partnership has a bona fide business purpose for preserving as confidential or (z) render the Partnership unable to comply with requirements under applicable securities laws, then the Partnership shall have the right to postpone such requested registration for a period of not more than six months after receipt of the Holder’s request, such right pursuant to this Section 7.12(a) or Section 7.12(b) not to be utilized more than once in any twelve-month period. Except as provided in the preceding sentence, the Partnership shall be deemed not to have used all commercially reasonable efforts to keep the registration statement effective during the applicable period if it voluntarily takes any action that would result in Holders of Partnership Securities covered thereby not being able to offer and sell such Partnership Securities at any time during such period, unless such action is required by applicable law. In connection with any registration pursuant to the immediately preceding sentence, the Partnership shall (i) promptly prepare and file (A) such documents as may be necessary to register or qualify the securities subject to such registration under the securities laws of such states as the Holder shall reasonably request; provided, however, that no such qualification shall be required in any jurisdiction where, as a result thereof, the Partnership would become subject to general service of process or to taxation or qualification to do business as a foreign corporation or partnership doing business in such jurisdiction solely as a result of such registration, and (B) such documents as may be necessary to apply for listing or to list the Partnership Securities subject to such registration on such National Securities Exchange as the Holder shall reasonably request, and (ii) do any and all other acts and things that may be necessary or appropriate to enable the Holder to consummate a public sale of such Partnership Securities in such states. Except as set forth in Section 7.12(d), all costs and expenses of any such registration and offering (other than the underwriting discounts and commissions) shall be paid by the Partnership, without reimbursement by the Holder.
A-56
(b) If, any Holder holds Partnership Securities that it desires to sell and Rule 144 of the Securities Act (or any successor rule or regulation to Rule 144) or another exemption from registration is not available to enable such Holder to dispose of the number of Partnership Securities it desires to sell at the time it desires to do so without registration under the Securities Act, then at the option and upon the request of the Holder, the Partnership shall file with the Commission as promptly as practicable after receiving such request, and use all commercially reasonable efforts to cause to become effective and remain effective for a period of not less than six months following its effective date or such shorter period as shall terminate when all Partnership Securities covered by such shelf registration statement have been sold, a “shelf” registration statement covering the Partnership Securities specified by the Holder on an appropriate form under Rule 415 under the Securities Act, or any similar rule that may be adopted by the Commission; provided, however, that the Partnership shall not be required to effect more than five registrations pursuant to Section 7.12(a) and this Section 7.12(b); and provided further, however, that if the Conflicts Committee determines in good faith that any offering under, or the use of any prospectus forming a part of, the shelf registration statement would be materially detrimental to the Partnership and its Partners because such offering or use would (x) materially interfere with a significant acquisition, reorganization or other similar transaction involving the Partnership, (y) require premature disclosure of material information that the Partnership has a bona fide business purpose for preserving as confidential or (z) render the Partnership unable to comply with requirements under applicable securities laws, then the Partnership shall have the right to suspend such offering or use for a period of not more than six months after receipt of the Holder’s request, such right pursuant to Section 7.12(a) or this Section 7.12(b) not to be utilized more than once in any twelve-month period. Except as provided in the preceding sentence, the Partnership shall be deemed not to have used all commercially reasonable efforts to keep the shelf registration statement effective during the applicable period if it voluntarily takes any action that would result in Holders of Partnership Securities covered thereby not being able to offer and sell such Partnership Securities at any time during such period, unless such action is required by applicable law. In connection with any shelf registration pursuant to this Section 7.12(b), the Partnership shall (i) promptly prepare and file (A) such documents as may be necessary to register or qualify the securities subject to such shelf registration under the securities laws of such states as the Holder shall reasonably request; provided, however, that no such qualification shall be required in any jurisdiction where, as a result thereof, the Partnership would become subject to general service of process or to taxation or qualification to do business as a foreign corporation or partnership doing business in such jurisdiction solely as a result of such shelf registration, and (B) such documents as may be necessary to apply for listing or to list the Partnership Securities subject to such shelf registration on such National Securities Exchange as the Holder shall reasonably request, and (ii) do any and all other acts and things that may be necessary or appropriate to enable the Holder to consummate a public sale of such Partnership Securities in such states. Except as set forth in Section 7.12(d), all costs and expenses of any such shelf registration and offering (other than the underwriting discounts and commissions) shall be paid by the Partnership, without reimbursement by the Holder.
(c) If the Partnership shall at any time propose to file a registration statement under the Securities Act for an offering of equity securities of the Partnership for cash (other than an offering relating solely to an Employee Benefit Plan), the Partnership shall use all commercially reasonable efforts to include such number or amount of securities held by any Holder in such registration statement as the Holder shall request; provided, that the Partnership is not required to make any effort or take any action to so include the securities of the Holder once the registration statement becomes or is declared effective by the Commission, including any registration statement providing for the offering from time to time of securities pursuant to Rule 415 of the Securities Act. If the proposed offering pursuant to this Section 7.12(c) shall be an underwritten offering, then, in the event that the managing underwriter or managing underwriters of such offering advise the Partnership and the Holder in writing that in their opinion the inclusion of all or some of the Holder’s Partnership Securities would adversely and materially affect the success of the offering, the Partnership shall include in such offering only that number or amount, if any, of securities held by the Holder that, in the opinion of the managing underwriter or managing underwriters, will not so adversely and materially affect the offering. Except as set forth in Section 7.12(d), all costs and expenses of any such registration and offering (other than the underwriting discounts and commissions) shall be paid by the Partnership, without reimbursement by the Holder.
A-57
(d) If underwriters are engaged in connection with any registration referred to in this Section 7.12, the Partnership shall provide indemnification, representations, covenants, opinions and other assurance to the underwriters in form and substance reasonably satisfactory to such underwriters. Further, in addition to and not in limitation of the Partnership’s obligation under Section 7.7, the Partnership shall, to the fullest extent permitted by law, indemnify and hold harmless the Holder, its officers, directors and each Person who controls the Holder (within the meaning of the Securities Act) and any agent thereof (collectively, “Indemnified Persons”) from and against any and all losses, claims, damages, liabilities, joint or several, expenses (including legal fees and expenses), judgments, fines, penalties, interest, settlements or other amounts arising from any and all claims, demands, actions, suits or proceedings, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative, in which any Indemnified Person may be involved, or is threatened to be involved, as a party or otherwise, under the Securities Act or otherwise (hereinafter referred to in this Section 7.12(d) as a “claim” and in the plural as “claims”) based upon, arising out of or resulting from any untrue statement or alleged untrue statement of any material fact contained in any registration statement under which any Partnership Securities were registered under the Securities Act or any state securities or Blue Sky laws, in any preliminary prospectus (if used prior to the effective date of such registration statement), or in any summary or final prospectus or in any amendment or supplement thereto (if used during the period the Partnership is required to keep the registration statement current), or arising out of, based upon or resulting from the omission or alleged omission to state therein a material fact required to be stated therein or necessary to make the statements made therein not misleading; provided, however, that the Partnership shall not be liable to any Indemnified Person to the extent that any such claim arises out of, is based upon or results from an untrue statement or alleged untrue statement or omission or alleged omission made in such registration statement, such preliminary, summary or final prospectus or such amendment or supplement, in reliance upon and in conformity with written information furnished to the Partnership by or on behalf of such Indemnified Person specifically for use in the preparation thereof.
(e) The provisions of Sections 7.12(a), 7.12(b) and 7.12(c) shall continue to be applicable with respect to the General Partner (and any of the General Partner’s Affiliates) after it ceases to be a general partner of the Partnership, during a period of two years subsequent to the effective date of such cessation and for so long thereafter as is required for the Holder to sell all of the Partnership Securities with respect to which it has requested during such two-year period inclusion in a registration statement otherwise filed or that a registration statement be filed; provided, however, that the Partnership shall not be required to file successive registration statements covering the same Partnership Securities for which registration was demanded during such two-year period. The provisions of Section 7.12(d) shall continue in effect thereafter.
(f) The rights to cause the Partnership to register Partnership Securities pursuant to this Section 7.12 may be assigned (but only with all related obligations) by a Holder to a transferee or assignee of such Partnership Securities, provided (i) the Partnership is, within a reasonable time after such transfer, furnished with written notice of the name and address of such transferee or assignee and the Partnership Securities with respect to which such registration rights are being assigned; and (ii) such transferee or assignee agrees in writing to be bound by and subject to the terms set forth in this Section 7.12.
(g) Any request to register Partnership Securities pursuant to this Section 7.12 shall (i) specify the Partnership Securities intended to be offered and sold by the Person making the request, (ii) express such Person’s present intent to offer such Partnership Securities for distribution, (iii) describe the nature or method of the proposed offer and sale of Partnership Securities, and (iv) contain the undertaking of such Person to provide all such information and materials and take all action as may be required in order to permit the Partnership to comply with all applicable requirements in connection with the registration of such Partnership Securities.
Section 7.13 Reliance by Third Parties.
Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Agreement, any Person dealing with the Partnership shall be entitled to assume that the General Partner and any officer of the General Partner authorized by the General Partner to act on behalf of and in the name of the Partnership has full power and authority to encumber, sell or otherwise use in any manner any and all assets of the Partnership and to enter into any authorized contracts on
A-58
behalf of the Partnership, and such Person shall be entitled to deal with the General Partner or any such officer as if it were the Partnership’s sole party in interest, both legally and beneficially. Each Limited Partner hereby waives, to the fullest extent permitted by law, any and all defenses or other remedies that may be available against such Person to contest, negate or disaffirm any action of the General Partner or any such officer in connection with any such dealing. In no event shall any Person dealing with the General Partner or any such officer or its representatives be obligated to ascertain that the terms of this Agreement have been complied with or to inquire into the necessity or expedience of any act or action of the General Partner or any such officer or its representatives. Each and every certificate, document or other instrument executed on behalf of the Partnership by the General Partner or its representatives shall be conclusive evidence in favor of any and every Person relying thereon or claiming thereunder that (a) at the time of the execution and delivery of such certificate, document or instrument, this Agreement was in full force and effect, (b) the Person executing and delivering such certificate, document or instrument was duly authorized and empowered to do so for and on behalf of the Partnership and (c) such certificate, document or instrument was duly executed and delivered in accordance with the terms and provisions of this Agreement and is binding upon the Partnership.
BOOKS, RECORDS, ACCOUNTING AND REPORTS
Section 8.1 Records and Accounting.
The General Partner shall keep or cause to be kept at the principal office of the Partnership appropriate books and records with respect to the Partnership’s business, including all books and records necessary to provide to the Limited Partners any information required to be provided pursuant to Section 3.4(a). Any books and records maintained by or on behalf of the Partnership in the regular course of its business, including the record of the Record Holders and Assignees of Units or other Partnership Securities, books of account and records of Partnership proceedings, may be kept on, or be in the form of, computer disks, hard drives, punch cards, magnetic tape, photographs, micrographics or any other information storage device; provided, that the books and records so maintained are convertible into clearly legible written form within a reasonable period of time. The books of the Partnership shall be maintained, for financial reporting purposes, on an accrual basis in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
The fiscal year of the Partnership shall be a fiscal year ending December 31.
(a) As soon as practicable, but in no event later than 120 days after the close of each fiscal year of the Partnership, the General Partner shall cause to be mailed or made available, by any reasonable means (including posting on the Partnership’s website), to each Record Holder of a Unit as of a date selected by the General Partner, an annual report containing financial statements of the Partnership for such fiscal year of the Partnership, presented in accordance with U.S. GAAP, including a balance sheet and statements of operations, Partnership equity and cash flows, such statements to be audited by a firm of independent public accountants selected by the General Partner.
(b) As soon as practicable, but in no event later than 90 days after the close of each Quarter except the last Quarter of each fiscal year, the General Partner shall cause to be mailed or made available, by any reasonable means (including posting on the Partnership’s website), to each Record Holder of a Unit, as of a date selected by the General Partner, a report containing unaudited financial statements of the Partnership and such other information as may be required by applicable law, regulation or rule of any National Securities Exchange on which the Units are listed or admitted to trading, or as the General Partner determines to be necessary or appropriate.
A-59
Section 9.1 Tax Returns and Information.
The Partnership shall timely file all returns of the Partnership that are required for federal, state and local income tax purposes on the basis of the accrual method and the taxable year or years that it is required by law to adopt, from time to time, as determined in good faith by the General Partner. The tax information reasonably required by Record Holders for federal and state income tax reporting purposes with respect to a taxable year shall be furnished to them within 90 days of the close of the calendar year in which the Partnership’s taxable year ends. The classification, realization and recognition of income, gain, losses and deductions and other items shall be on the accrual method of accounting for federal income tax purposes.
(a) The Partnership shall make the election under Section 754 of the Code in accordance with applicable regulations thereunder, subject to the reservation of the right to seek to revoke any such election upon the General Partner’s determination that such revocation is in the best interests of the Limited Partners. Notwithstanding any other provision herein contained, for the purposes of computing the adjustments under Section 743(b) of the Code, the General Partner shall be authorized (but not required) to adopt a convention whereby the price paid by a transferee of a Limited Partner Interest will be deemed to be the lowest quoted closing price of the Limited Partner Interests on any National Securities Exchange on which such Limited Partner Interests are listed or admitted to trading during the calendar month in which such transfer is deemed to occur pursuant to Section 6.2(g) without regard to the actual price paid by such transferee.
(b) Except as otherwise provided herein, the General Partner shall determine whether the Partnership should make any other elections permitted by the Code.
Section 9.3 Tax Controversies.
Subject to the provisions hereof, the General Partner is designated as the Tax Matters Partner (as defined in the Code) and is authorized and required to represent the Partnership (at the Partnership’s expense) in connection with all examinations of the Partnership’s affairs by tax authorities, including resulting administrative and judicial proceedings, and to expend Partnership funds for professional services and costs associated therewith. Each Partner agrees to cooperate with the General Partner and to do or refrain from doing any or all things reasonably required by the General Partner to conduct such proceedings.
Notwithstanding any other provision of this Agreement, the General Partner is authorized to take any action that may be required to cause the Partnership and other Group Members to comply with any withholding requirements established under the Code or any other federal, state or local law including pursuant to Sections 1441, 1442, 1445 and 1446 of the Code. To the extent that the Partnership is required or elects to withhold and pay over to any taxing authority any amount resulting from the allocation or distribution of income to any Partner or Assignee (including by reason of Section 1446 of the Code), the General Partner may treat the amount withheld as a distribution of cash pursuant to Section 6.3 in the amount of such withholding from such Partner.
Section 10.1 Admission of Initial Limited Partners.
Upon the issuance by the Partnership of Common Units, Subordinated Units and Incentive Distribution Rights to the General Partner, and the Underwriters as described in Section 5.2 and 5.3 in connection with the Initial Offering, the General Partner shall admit such parties to the Partnership as Initial Limited Partners in respect of the Common Units, Subordinated Units or Incentive Distribution Rights issued to them.
A-60
Section 10.2 Admission of Substituted Limited Partners.
By transfer of a Limited Partner Interest in accordance with Article IV, the transferor shall be deemed to have given the transferee the right to seek admission as a Substituted Limited Partner subject to the conditions of, and in the manner permitted under, this Agreement. A transferor of a Certificate representing a Limited Partner Interest shall, however, only have the authority to convey to a purchaser or other transferee who does not execute and deliver a Transfer Application (a) the right to negotiate such Certificate to a purchaser or other transferee and (b) the right to transfer the right to request admission as a Substituted Limited Partner to such purchaser or other transferee in respect of the transferred Limited Partner Interests. No transferor of a Limited Partner Interest or other Person shall have any obligation or responsibility to provide a Transfer Application or Tax Certificate to a transferee or assist or participate in any way with respect to the completion or delivery thereof. Each transferee of a Limited Partner Interest (including any nominee holder or an agent acquiring such Limited Partner Interest for the account of another Person) who executes and delivers a properly completed Transfer Application shall, by virtue of such execution and delivery, be an Assignee. Such Assignee shall automatically be admitted to the Partnership as a Substituted Limited Partner with respect to the Limited Partner Interests so transferred to such Person at such time as such transfer is recorded in the books and records of the Partnership, and until so recorded, such transferee shall be an Assignee. The General Partner shall periodically, but no less frequently than on the first Business Day of each Quarter, cause any unrecorded transfers of Limited Partner Interests with respect to which a properly completed, duly executed Transfer Application has been received to be recorded in the books and records of the Partnership. An Assignee shall have an interest in the Partnership equivalent to that of a Limited Partner with respect to allocations and distributions, including liquidating distributions, of the Partnership. With respect to voting rights attributable to Limited Partner Interests that are held by Assignees, the General Partner shall be deemed to be the Limited Partner with respect thereto and shall, in exercising the voting rights in respect of such Limited Partner Interests on any matter, vote such Limited Partner Interests at the written direction of the Assignee who is the Record Holder of such Limited Partner Interests. If no such written direction is received, such Limited Partner Interests will not be voted. An Assignee shall have no other rights of a Limited Partner.
Section 10.3 Admission of Successor General Partner.
A successor General Partner approved pursuant to Section 11.1 or 11.2 or the transferee of or successor to all of the General Partner Interest pursuant to Section 4.6 who is proposed to be admitted as a successor General Partner shall be admitted to the Partnership as the General Partner, effective immediately prior to the withdrawal or removal of the predecessor or transferring General Partner, pursuant to Section 11.1 or 11.2 or the transfer of the General Partner Interest pursuant to Section 4.6, provided, however, that no such successor shall be admitted to the Partnership until compliance with the terms of Section 4.6 has occurred and such successor has executed and delivered such other documents or instruments as may be required to effect such admission. Any such successor shall, subject to the terms hereof, carry on the business of the members of the Partnership Group without dissolution.
Section 10.4 Admission of Additional Limited Partners.
(a) A Person (other than the General Partner, an Initial Limited Partner or a Substituted Limited Partner) who makes a Capital Contribution to the Partnership in accordance with this Agreement shall be admitted to the Partnership as an Additional Limited Partner only upon furnishing to the General Partner:
(i) evidence of acceptance in form satisfactory to the General Partner of all of the terms and conditions of this Agreement, including the power of attorney granted in Section 2.6; and
(ii) such other documents or instruments as may be required by the General Partner to effect such Person’s admission as an Additional Limited Partner.
(b) Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Section 10.4, no Person shall be admitted as an Additional Limited Partner without the consent of the General Partner. The admission of any Person as an
A-61
Additional Limited Partner shall become effective on the date upon which the name of such Person is recorded as such in the books and records of the Partnership, following the consent of the General Partner to such admission.
Section 10.5 Amendment of Agreement and Certificate of Limited Partnership.
To effect the admission to the Partnership of any Partner, the General Partner shall take all steps necessary or appropriate under the Delaware Act to amend the records of the Partnership to reflect such admission and, if necessary, to prepare as soon as practicable an amendment to this Agreement and, if required by law, the General Partner shall prepare and file an amendment to the Certificate of Limited Partnership, and the General Partner may for this purpose, among others, exercise the power of attorney granted pursuant to Section 2.6.
WITHDRAWAL OR REMOVAL OF PARTNERS
Section 11.1 Withdrawal of the General Partner.
(a) The General Partner shall be deemed to have withdrawn from the Partnership upon the occurrence of any one of the following events (each such event herein referred to as an “Event of Withdrawal”);
(i) The General Partner voluntarily withdraws from the Partnership by giving written notice to the other Partners;
(ii) The General Partner transfers all of its General Partner Interest pursuant to Section 4.6;
(iii) The General Partner is removed pursuant to Section 11.2;
(iv) The General Partner (A) makes a general assignment for the benefit of creditors; (B) files a voluntary bankruptcy petition for relief under Chapter 7 of the United States Bankruptcy Code; (C) files a petition or answer seeking for itself a liquidation, dissolution or similar relief (but not a reorganization) under any law; (D) files an answer or other pleading admitting or failing to contest the material allegations of a petition filed against the General Partner in a proceeding of the type described in clauses (A)-(C) of this Section 11.1(a)(iv); or (E) seeks, consents to or acquiesces in the appointment of a trustee (but not a debtor-in-possession), receiver or liquidator of the General Partner or of all or any substantial part of its properties;
(v) A final and non-appealable order of relief under Chapter 7 of the United States Bankruptcy Code is entered by a court with appropriate jurisdiction pursuant to a voluntary or involuntary petition by or against the General Partner; or
(vi)(A) in the event the General Partner is a corporation, a certificate of dissolution or its equivalent is filed for the General Partner, or 90 days expire after the date of notice to the General Partner of revocation of its charter without a reinstatement of its charter, under the laws of its state of incorporation; (B) in the event the General Partner is a partnership or a limited liability company, the dissolution and commencement of winding up of the General Partner; (C) in the event the General Partner is acting in such capacity by virtue of being a trustee of a trust, the termination of the trust; (D) in the event the General Partner is a natural person, his death or adjudication of incompetency; and (E) otherwise in the event of the termination of the General Partner.
If an Event of Withdrawal specified in Section 11.1(a)(iv), (v) or (vi)(A), (B), (C) or (E) occurs, the withdrawing General Partner shall give notice to the Limited Partners within 30 days after such occurrence. The Partners hereby agree that only the Events of Withdrawal described in this Section 11.1 shall result in the withdrawal of the General Partner from the Partnership.
(b) Withdrawal of the General Partner from the Partnership upon the occurrence of an Event of Withdrawal shall not constitute a breach of this Agreement under the following circumstances: (i) at any time during the
A-62
period beginning on the Closing Date and ending at 12:00 midnight, Central Time, on March 31, 2017, the General Partner voluntarily withdraws by giving at least 90 days’ advance notice of its intention to withdraw to the Limited Partners; provided, that prior to the effective date of such withdrawal, the withdrawal is approved by Unitholders holding at least a majority of the Outstanding Common Units (excluding Common Units held by the General Partner and its Affiliates) and the General Partner delivers to the Partnership an Opinion of Counsel (“Withdrawal Opinion of Counsel”) that such withdrawal (following the selection of the successor General Partner) would not result in the loss of the limited liability of any Limited Partner or any Group Member or cause any Group Member to be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise to be taxed as an entity for federal income tax purposes (to the extent not already so treated or taxed); (ii) at any time after 12:00 midnight, Central Time, on March 31, 2017, the General Partner voluntarily withdraws by giving at least 90 days’ advance notice to the Unitholders, such withdrawal to take effect on the date specified in such notice; (iii) at any time that the General Partner ceases to be the General Partner pursuant to Section 11.1(a)(ii) or is removed pursuant to Section 11.2; or (iv) notwithstanding clause (i) of this sentence, at any time that the General Partner voluntarily withdraws by giving at least 90 days’ advance notice of its intention to withdraw to the Limited Partners, such withdrawal to take effect on the date specified in the notice, if at the time such notice is given one Person and its Affiliates (other than the General Partner and its Affiliates) own beneficially or of record or control at least 50% of the Outstanding Units. The withdrawal of the General Partner from the Partnership upon the occurrence of an Event of Withdrawal shall also constitute the withdrawal of the General Partner as general partner or managing member, if any, to the extent applicable, of the other Group Members. If the General Partner gives a notice of withdrawal pursuant to Section 11.1(a)(i), the holders of a Unit Majority, may, prior to the effective date of such withdrawal, elect a successor General Partner. The Person so elected as successor General Partner shall automatically become the successor general partner or managing member, to the extent applicable, of the other Group Members (to the extent permitted or required by their governing documents) of which the General Partner is a general partner or a managing member, and is hereby authorized to, and shall, continue the business of the Partnership and, to the extent applicable, the other Group Members, without dissolution. If, prior to the effective date of the General Partner’s withdrawal, a successor is not selected by the Unitholders as provided herein or the Partnership does not receive a Withdrawal Opinion of Counsel, the Partnership shall be dissolved in accordance with Section 12.1. Any successor General Partner elected in accordance with the terms of this Section 11.1 shall be subject to the provisions of Section 10.3.
Section 11.2 Removal of the General Partner.
The General Partner may be removed if such removal is approved by the Unitholders holding at least 66 2/3%, of the Outstanding Limited Partner Units (including Limited Partner Units held by the General Partner and its Affiliates) voting as a single class. Any such action by such holders for removal of the General Partner must also provide for the election of a successor General Partner by the Unitholders holding a majority of the outstanding Common Units voting as a class and a majority of the outstanding Subordinated Units voting as a class (including Units held by the General Partner and its Affiliates). Such removal shall be effective immediately following the admission of a successor General Partner pursuant to Section 10.3. The removal of the General Partner shall also automatically constitute the removal of the General Partner as general partner or managing member, to the extent applicable, of the other Group Members of which the General Partner is a general partner or a managing member. If a Person is elected as a successor General Partner in accordance with the terms of this Section 11.2, such Person shall, upon admission pursuant to Section 10.3, automatically become a successor general partner or managing member, to the extent applicable, of the other Group Members (to the extent permitted or required by their governing documents) of which the General Partner is a general partner or a managing member, and is hereby authorized to, and shall, continue the business of the Partnership and, to the extent applicable, the other Group Members, without dissolution. The right of the holders of Outstanding Units to remove the General Partner shall not exist or be exercised unless the Partnership has received an opinion opining as to the matters covered by a Withdrawal Opinion of Counsel. Any successor General Partner elected in accordance with the terms of this Section 11.2 shall be subject to the provisions of Section 10.3.
A-63
Section 11.3 Interest of Departing General Partner and Successor General Partner.
(a) In the event of (i) withdrawal of the General Partner under circumstances where such withdrawal does not violate this Agreement or (ii) removal of the General Partner by the holders of Outstanding Units under circumstances where Cause does not exist, if the successor General Partner is elected in accordance with the terms of Section 11.1 or 11.2, the Departing General Partner shall have the option, exercisable prior to the effective date of the departure of such Departing General Partner, to require its successor to purchase its General Partner Interest and its general partner interest (or equivalent interest), if any, in the other Group Members and all of the Incentive Distribution Rights (collectively, the “Combined Interest”) in exchange for an amount in cash equal to the fair market value of such Combined Interest, such amount to be determined and payable as of the effective date of its departure. If the General Partner is removed by the Unitholders under circumstances where Cause exists or if the General Partner withdraws under circumstances where such withdrawal violates this Agreement, and if a successor General Partner is elected in accordance with the terms of Section 11.1 or 11.2 (or if the business of the Partnership is continued pursuant to Section 12.2 and the successor General Partner is not the former General Partner), such successor shall have the option, exercisable prior to the effective date of the departure of such Departing General Partner (or, in the event the business of the Partnership is continued, prior to the date the business of the Partnership is continued), to purchase the Combined Interest for such fair market value of such Combined Interest of the Departing General Partner. In either event, the Departing General Partner shall be entitled to receive all reimbursements due such Departing General Partner pursuant to Section 7.4, including any employee-related liabilities (including severance liabilities), incurred in connection with the termination of any employees employed by the Departing General Partner or its Affiliates (other than any Group Member) for the benefit of the Partnership or the other Group Members.
For purposes of this Section 11.3(a), the fair market value of the Departing General Partner’s Combined Interest shall be determined by agreement between the Departing General Partner and its successor or, failing agreement within 30 days after the effective date of such Departing General Partner’s departure, by an independent investment banking firm or other independent expert selected by the Departing General Partner and its successor, which, in turn, may rely on other experts, and the determination of which shall be conclusive as to such matter. If such parties cannot agree upon one independent investment banking firm or other independent expert within 45 days after the effective date of such departure, then the Departing General Partner shall designate an independent investment banking firm or other independent expert, the Departing General Partner’s successor shall designate an independent investment banking firm or other independent expert, and such firms or experts shall mutually select a third independent investment banking firm or independent expert, which third independent investment banking firm or other independent expert shall determine the fair market value of the Combined Interest of the Departing General Partner. In making its determination, such third independent investment banking firm or other independent expert may consider the then current trading price of Units on any National Securities Exchange on which Units are then listed or admitted to trading, the value of the Partnership’s assets, the rights and obligations of the Departing General Partner and other factors it may deem relevant.
(b) If the Combined Interest is not purchased in the manner set forth in Section 11.3(a), the Departing General Partner (or its transferee) shall become a Limited Partner and its Combined Interest shall be converted into Common Units pursuant to a valuation made by an investment banking firm or other independent expert selected pursuant to Section 11.3(a), without reduction in such Partnership Interest (but subject to proportionate dilution by reason of the admission of its successor). Any successor General Partner shall indemnify the Departing General Partner (or its transferee) as to all debts and liabilities of the Partnership arising on or after the date on which the Departing General Partner (or its transferee) becomes a Limited Partner. For purposes of this Agreement, conversion of the Combined Interest of the Departing General Partner to Common Units will be characterized as if the Departing General Partner (or its transferee) contributed its Combined Interest to the Partnership in exchange for the newly issued Common Units.
(c) If a successor General Partner is elected in accordance with the terms of Section 11.1 or 11.2 (or if the business of the Partnership is continued pursuant to Section 12.2 and the successor General Partner is not the former General Partner) and the option described in Section 11.3(a) is not exercised by the party entitled to do so,
A-64
the successor General Partner shall, at the effective date of its admission to the Partnership, contribute to the Partnership cash in the amount equal to the product of (x) the quotient obtained by dividing (A) the Percentage Interest of the General Partner Interest of the Departing General Partner by (B) a percentage equal to 100% less the Percentage Interest of the General Partner Interest of the Departing General Partner and (y) the Net Agreed Value of the Partnership’s assets on such date. In such event, such successor General Partner shall, subject to the following sentence, be entitled to its Percentage Interest of all Partnership allocations and distributions to which the Departing General Partner was entitled in respect of its General Partner Interest. In addition, the successor General Partner shall cause this Agreement to be amended to reflect that, from and after the date of such successor General Partner’s admission, the successor General Partner’s interest in all Partnership distributions and allocations shall be its Percentage Interest.
Section 11.4 Termination of Subordination Period, Conversion of Subordinated Units and Extinguishment of Cumulative Common Unit Arrearages.
Notwithstanding any provision of this Agreement, if the General Partner is removed as general partner of the Partnership under circumstances where Cause does not exist and no Units held by the General Partner and its Affiliates are voted in favor of such removal, (i) the Subordination Period will end and all Outstanding Subordinated Units will immediately and automatically convert into Common Units on a one-for-one basis (provided, however, that such converted Subordinated Units shall remain subject to the provisions of Sections 5.5(c)(ii), 6.1(d)(x) and 6.7(c)), (ii) all Cumulative Common Unit Arrearages on the Common Units will be extinguished and (iii) the General Partner that is so removed will have the right to convert its General Partner Interest and its Incentive Distribution Rights into Common Units or to receive cash in exchange therefor, as provided in Section 11.3.
Section 11.5 Withdrawal of Limited Partners.
No Limited Partner shall have any right to withdraw from the Partnership; provided, however, that when a transferee of a Limited Partner’s Limited Partner Interest becomes a Record Holder of the Limited Partner Interest so transferred, such transferring Limited Partner shall cease to be a Limited Partner with respect to the Limited Partner Interest so transferred.
The Partnership shall not be dissolved by the admission of Substituted Limited Partners or Additional Limited Partners or by the admission of a successor General Partner in accordance with the terms of this Agreement. Upon the removal or other event of withdrawal of the General Partner, if a successor General Partner is elected pursuant to Sections 11.1, 11.2 or 12.2, the Partnership shall not be dissolved and such successor General Partner is hereby authorized to, and shall, continue the business of the Partnership. Subject to Section 12.2, the Partnership shall dissolve, and its affairs shall be wound up, upon:
(a) an Event of Withdrawal of the General Partner as provided in Section 11.1(a) (other than Section 11.1(a)(ii)), unless a successor is elected and an Opinion of Counsel is received as provided in Section 11.1(b) or 11.2 and such successor is admitted to the Partnership pursuant to this Agreement;
(b) an election to dissolve the Partnership by the General Partner that is approved by the holders of a Unit Majority;
(c) the entry of a decree of judicial dissolution of the Partnership pursuant to the provisions of the Delaware Act; or
(d) at any time there are no Limited Partners, unless the Partnership is continued without dissolution in accordance with the Delaware Act.
A-65
Section 12.2 Continuation of the Business of the Partnership.
Upon (a) an Event of Withdrawal caused by the withdrawal or removal of the General Partner as provided in Section 11.1(a)(i) or (iii) and the failure of the Partners to select a successor to such Departing General Partner pursuant to Section 11.1 or 11.2, then within 90 days thereafter, or (b) an event constituting an Event of Withdrawal as defined in Section 11.1(a)(iv), (v) or (vi), then, to the maximum extent permitted by law, within 180 days thereafter, the holders of a Unit Majority may elect to continue the business of the Partnership without dissolution on the same terms and conditions set forth in this Agreement by appointing as a successor General Partner a Person approved by the holders of a Unit Majority. Unless such an election is made within the applicable time period as set forth above, the Partnership shall dissolve and conduct only activities necessary to wind up its affairs. If such an election is so made, then:
(i) the Partnership shall continue without dissolution unless dissolved in accordance with this Article XII;
(ii) if the successor General Partner is not the former General Partner, then the interest of the former General Partner shall be treated in the manner provided in Section 11.3; and
(iii) the successor General Partner shall be admitted to the Partnership as General Partner, effective as of the Event of Withdrawal, by agreeing in writing to be bound by this Agreement; provided, that the right of the holders of a Unit Majority to approve a successor General Partner and to continue the business of the Partnership shall not exist and may not be exercised unless the Partnership has received an Opinion of Counsel that (x) the exercise of the right would not result in the loss of limited liability of any Limited Partner and (y) neither the Partnership nor any Group Member would be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise be taxable as an entity for federal income tax purposes upon the exercise of such right to continue (to the extent not already so treated or taxed).
Upon dissolution of the Partnership, the General Partner shall select one or more Persons to act as Liquidator. The Liquidator (if other than the General Partner) shall be entitled to receive such compensation for its services as may be approved by holders of at least a majority of the Outstanding Common Units, and Subordinated Units voting as a single class. The Liquidator (if other than the General Partner) shall agree not to resign at any time without 15 days’ prior notice and may be removed at any time, with or without cause, by notice of removal approved by holders of at least a majority of the Outstanding Common Units, and Subordinated Units voting as a single class. Upon dissolution, removal or resignation of the Liquidator, a successor and substitute Liquidator (who shall have and succeed to all rights, powers and duties of the original Liquidator) shall within 30 days thereafter be approved by holders of at least a majority of the Outstanding Common Units and Subordinated Units voting as a single class. The right to approve a successor or substitute Liquidator in the manner provided herein shall be deemed to refer also to any such successor or substitute Liquidator approved in the manner herein provided. Except as expressly provided in this Article XII, the Liquidator approved in the manner provided herein shall have and may exercise, without further authorization or consent of any of the parties hereto, all of the powers conferred upon the General Partner under the terms of this Agreement (but subject to all of the applicable limitations, contractual and otherwise, upon the exercise of such powers, other than the limitation on sale set forth in Section 7.3) necessary or appropriate to carry out the duties and functions of the Liquidator hereunder for and during the period of time required to complete the winding up and liquidation of the Partnership as provided for herein.
The Liquidator shall proceed to dispose of the assets of the Partnership, discharge its liabilities, and otherwise wind up its affairs in such manner and over such period as determined by the Liquidator, subject to Section 17-804 of the Delaware Act and the following:
(a) The assets may be disposed of by public or private sale or by distribution in kind to one or more Partners on such terms as the Liquidator and such Partner or Partners may agree. If any property is distributed in kind, the
A-66
Partner receiving the property shall be deemed for purposes of Section 12.4(c) to have received cash equal to its fair market value; and contemporaneously therewith, appropriate cash distributions must be made to the other Partners. The Liquidator may defer liquidation or distribution of the Partnership’s assets for a reasonable time if it determines that an immediate sale or distribution of all or some of the Partnership’s assets would be impractical or would cause undue loss to the Partners. The Liquidator may distribute the Partnership’s assets, in whole or in part, in kind if it determines that a sale would be impractical or would cause undue loss to the Partners.
(b) Liabilities of the Partnership include amounts owed to the Liquidator as compensation for serving in such capacity (subject to the terms of Section 12.3) and amounts to Partners otherwise than in respect of their distribution rights under Article VI. With respect to any liability that is contingent, conditional or unmatured or is otherwise not yet due and payable, the Liquidator shall either settle such claim for such amount as it thinks appropriate or establish a reserve of cash or other assets to provide for its payment.
(c) All property and all cash in excess of that required to discharge liabilities as provided in Section 12.4(b) shall be distributed to the Partners in accordance with, and to the extent of, the positive balances in their respective Capital Accounts, as determined after taking into account all Capital Account adjustments (other than those made by reason of distributions pursuant to this Section 12.4(c)) for the taxable year of the Partnership during which the liquidation of the Partnership occurs (with such date of occurrence being determined pursuant to Treasury Regulation Section 1.704-1(b)(2)(ii)(g)), and such distribution shall be made by the end of such taxable year (or, if later, within 90 days after said date of such occurrence).
Section 12.5 Cancellation of Certificate of Limited Partnership.
Upon the completion of the distribution of Partnership cash and property as provided in Section 12.4 in connection with the liquidation of the Partnership, the Certificate of Limited Partnership and all qualifications of the Partnership as a foreign limited partnership in jurisdictions other than the State of Delaware shall be canceled and such other actions as may be necessary to terminate the Partnership shall be taken.
Section 12.6 Return of Contributions.
The General Partner shall not be personally liable for, and shall have no obligation to contribute or loan any monies or property to the Partnership to enable it to effectuate, the return of the Capital Contributions of the Limited Partners or Unitholders, or any portion thereof, it being expressly understood that any such return shall be made solely from Partnership assets.
Section 12.7 Waiver of Partition.
To the maximum extent permitted by law, each Partner hereby waives any right to partition of the Partnership property.
Section 12.8 Capital Account Restoration.
No Limited Partner shall have any obligation to restore any negative balance in its Capital Account upon liquidation of the Partnership. The General Partner shall be obligated to restore any negative balance in its Capital Account upon liquidation of its interest in the Partnership by the end of the taxable year of the Partnership during which such liquidation occurs, or, if later, within 90 days after the date of such liquidation.
A-67
AMENDMENT OF PARTNERSHIP AGREEMENT;
MEETINGS; RECORD DATE
Section 13.1 Amendments to be Adopted Solely by the General Partner.
Each Partner agrees that the General Partner, without the approval of any other Partner or Assignee, may amend any provision of this Agreement and execute, swear to, acknowledge, deliver, file and record whatever documents may be required in connection therewith, to reflect:
(a) a change in the name of the Partnership, the location of the principal place of business of the Partnership, the registered agent of the Partnership or the registered office of the Partnership;
(b) the admission, substitution, withdrawal or removal of Partners in accordance with this Agreement;
(c) a change that the General Partner determines to be necessary or appropriate to qualify or continue the qualification of the Partnership as a limited partnership or a partnership in which the Limited Partners have limited liability under the laws of any state or to ensure that the Group Members will not be treated as associations taxable as corporations or otherwise taxed as entities for federal income tax purposes;
(d) a change that the General Partner determines, (i) does not adversely affect in any material respect the Limited Partners considered as a whole or any particular class of Partnership Interests as compared to other classes of Partnership Interests, (ii) to be necessary or appropriate to (A) satisfy any requirements, conditions or guidelines contained in any opinion, directive, order, ruling or regulation of any federal or state agency or judicial authority or contained in any federal or state statute (including the Delaware Act) or (B) facilitate the trading of the Units (including the division of any class or classes of Outstanding Units into different classes to facilitate uniformity of tax consequences within such classes of Units) or comply with any rule, regulation, guideline or requirement of any National Securities Exchange on which the Units are or will be listed or admitted to trading, (iii) to be necessary or appropriate in connection with action taken by the General Partner pursuant to Section 5.9 or (iv) is required to effect the intent expressed in the Registration Statement or the intent of the provisions of this Agreement or is otherwise contemplated by this Agreement;
(e) a change in the fiscal year or taxable year of the Partnership and any other changes that the General Partner determines to be necessary or appropriate as a result of a change in the fiscal year or taxable year of the Partnership including, if the General Partner shall so determine, a change in the definition of “Quarter” and the dates on which distributions are to be made by the Partnership;
(f) an amendment that is necessary, in the Opinion of Counsel, to prevent the Partnership, or the General Partner or its directors, officers, trustees or agents from in any manner being subjected to the provisions of the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended, or “plan asset” regulations adopted under ERISA, regardless of whether such are substantially similar to plan asset regulations currently applied or proposed by the United States Department of Labor;
(g) an amendment that the General Partner determines to be necessary or appropriate in connection with the creation or authorization or issuance of any class or series of Partnership Securities pursuant to Section 5.6;
(h) any amendment expressly permitted in this Agreement to be made by the General Partner acting alone;
(i) an amendment effected, necessitated or contemplated by a Merger Agreement approved in accordance with Section 14.3 including any amendment permitted by Section 14.5;
(j) an amendment that the General Partner determines to be necessary or appropriate to reflect and account for the formation by the Partnership of, or investment by the Partnership in, any corporation, partnership, joint venture, limited liability company or other entity, in connection with the conduct by the Partnership of activities permitted by the terms of Section 2.4;
A-68
(k) a merger or conveyance pursuant to Section 14.3(d); or
(l) any other amendments substantially similar to the foregoing.
Section 13.2 Amendment Procedures.
Except as provided in Sections 13.1 and 13.3, all amendments to this Agreement shall be made in accordance with the following requirements. Amendments to this Agreement may be proposed only by the General Partner; provided, however, that, to the full extent permitted by law, the General Partner shall have no duty or obligation to propose any amendment to this Agreement and may decline to do so free of any fiduciary duty or obligation whatsoever to the Partnership, any Limited Partner or Assignee and, in declining to propose an amendment, to the fullest extent permitted by law shall not be required to act in good faith or pursuant to any other standard imposed by this Agreement, any Group Member Agreement, any other agreement contemplated hereby or under the Delaware Act or any other law, rule or regulation or at equity. A proposed amendment shall be effective upon its approval by the General Partner and the holders of a Unit Majority, unless a greater or different percentage is required under this Agreement or by Delaware law. The General Partner shall notify all Record Holders upon final adoption of any such proposed amendments.
Section 13.3 Amendment Requirements.
(a) Notwithstanding the provisions of Sections 13.1 and 13.2, no provision of this Agreement that requires the vote, consent or approval of holders of a percentage of Outstanding Units (including Units deemed owned by the General Partner) required to take any action shall be amended, altered, changed, repealed or rescinded in any respect that would have the effect of reducing such voting percentage unless such amendment is approved by the written consent or the affirmative vote of holders of Outstanding Units whose aggregate Outstanding Units constitute not less than the voting requirement sought to be reduced.
(b) Notwithstanding the provisions of Sections 13.1 and 13.2, no amendment to this Agreement may (i) enlarge the obligations of any Limited Partner without its consent, unless such shall be deemed to have occurred as a result of an amendment approved pursuant to Section 13.3(c) or (ii) enlarge the obligations of, restrict in any way any action by or rights of, or reduce in any way the amounts distributable, reimbursable or otherwise payable to, the General Partner or any of its Affiliates without its consent, which consent may be given or withheld at its option.
(c) Except as provided in Section 14.3, and without limitation of the General Partner’s authority to adopt amendments to this Agreement without the approval of any Partners or Assignees as contemplated in Section 13.1, any amendment that would have a material adverse effect on the rights or preferences of any class of Partnership Interests in relation to other classes of Partnership Interests must be approved by the holders of not less than a majority of the Outstanding Partnership Interests of the class affected.
(d) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Agreement, except for amendments pursuant to Section 13.1 and except as otherwise provided by Section 14.3(b), no amendments shall become effective without the approval of the holders of at least 90% of the Outstanding Limited Partner Units voting as a single class unless the Partnership obtains an Opinion of Counsel to the effect that such amendment will not affect the limited liability of any Limited Partner under applicable law.
(e) Except as provided in Section 13.1, this Section 13.3 shall only be amended with the approval of the holders of at least 90% of the Outstanding Limited Partner Units.
Section 13.4 Special Meetings.
All acts of Limited Partners to be taken pursuant to this Agreement shall be taken in the manner provided in this Article XIII. Special meetings of the Limited Partners may be called by the General Partner or by Limited
A-69
Partners owning 20% or more of the Outstanding Limited Partner Units of the class or classes for which a meeting is proposed. Limited Partners shall call a special meeting by delivering to the General Partner one or more requests in writing stating that the signing Limited Partners wish to call a special meeting and indicating the general or specific purposes for which the special meeting is to be called. Within 60 days after receipt of such a call from Limited Partners or within such greater time as may be reasonably necessary for the Partnership to comply with any statutes, rules, regulations, listing agreements or similar requirements governing the holding of a meeting or the solicitation of proxies for use at such a meeting, the General Partner shall send a notice of the meeting to the Limited Partners either directly or indirectly through the Transfer Agent. A meeting shall be held at a time and place determined by the General Partner on a date not less than 10 days nor more than 60 days after the mailing of notice of the meeting. Limited Partners shall not vote on matters that would cause the Limited Partners to be deemed to be taking part in the management and control of the business and affairs of the Partnership so as to jeopardize the Limited Partners’ limited liability under the Delaware Act or the law of any other state in which the Partnership is qualified to do business.
Section 13.5 Notice of a Meeting.
Notice of a meeting called pursuant to Section 13.4 shall be given to the Record Holders of the class or classes of Units for which a meeting is proposed in writing by mail or other means of written communication in accordance with Section 16.1 at least 10 days in advance of such meeting. The notice shall be deemed to have been given at the time when deposited in the mail or sent by other means of written communication.
For purposes of determining the Limited Partners entitled to notice of or to vote at a meeting of the Limited Partners or to give approvals without a meeting as provided in Section 13.11 the General Partner may set a Record Date, which shall not be less than 10 nor more than 60 days before (a) the date of the meeting (unless such requirement conflicts with any rule, regulation, guideline or requirement of any National Securities Exchange on which the Units are listed or admitted to trading, in which case the rule, regulation, guideline or requirement of such National Securities Exchange shall govern) or (b) in the event that approvals are sought without a meeting, the date by which Limited Partners are requested in writing by the General Partner to give such approvals. If the General Partner does not set a Record Date, then (a) the Record Date for determining the Limited Partners entitled to notice of or to vote at a meeting of the Limited Partners shall be the close of business on the day next preceding the day on which notice is given, and (b) the Record Date for determining the Limited Partners entitled to give approvals without a meeting shall be the date the first written approval is deposited with the Partnership in care of the General Partner in accordance with Section 13.11.
When a meeting is adjourned to another time or place, notice need not be given of the adjourned meeting and a new Record Date need not be fixed, if the time and place thereof are announced at the meeting at which the adjournment is taken, unless such adjournment shall be for more than 45 days. At the adjourned meeting, the Partnership may transact any business which might have been transacted at the original meeting. If the adjournment is for more than 45 days or if a new Record Date is fixed for the adjourned meeting, a notice of the adjourned meeting shall be given in accordance with this Article XIII.
Section 13.8 Waiver of Notice; Approval of Meeting; Approval of Minutes.
The transactions of any meeting of Limited Partners, however called and noticed, and whenever held, shall be as valid as if it had occurred at a meeting duly held after regular call and notice, if a quorum is present either in person or by proxy. Attendance of a Limited Partner at a meeting shall constitute a waiver of notice of the meeting, except when the Limited Partner attends the meeting for the express purpose of objecting, at the beginning of the meeting, to the transaction of any business because the meeting is not lawfully called or
A-70
convened; and except that attendance at a meeting is not a waiver of any right to disapprove the consideration of matters required to be included in the notice of the meeting, but not so included, if the disapproval is expressly made at the meeting.
Section 13.9 Quorum and Voting.
The holders of a majority of the Outstanding Units of the class or classes for which a meeting has been called (including Outstanding Units of such class or classes deemed owned by the General Partner) represented in person or by proxy shall constitute a quorum at a meeting of Limited Partners of such class or classes unless any such action by the Limited Partners requires approval by holders of a greater percentage of such Units, in which case the quorum shall be such greater percentage. At any meeting of the Limited Partners duly called and held in accordance with this Agreement at which a quorum is present, the act of Limited Partners holding Outstanding Units that in the aggregate represent a majority of the Outstanding Units entitled to vote and be present in person or by proxy at such meeting shall be deemed to constitute the act of all Limited Partners, unless a greater or different percentage is required with respect to such action under the provisions of this Agreement, in which case the act of the Limited Partners holding Outstanding Units that in the aggregate represent at least such greater or different percentage shall be required. The Limited Partners present at a duly called or held meeting at which a quorum is present may continue to transact business until adjournment, notwithstanding the withdrawal of enough Limited Partners to leave less than a quorum, if any action taken (other than adjournment) is approved by the required percentage of Outstanding Units specified in this Agreement (including Outstanding Units deemed owned by the General Partner). In the absence of a quorum, any meeting of Limited Partners may be adjourned from time to time by the affirmative vote of holders of at least a majority of the Outstanding Units entitled to vote at such meeting (including Outstanding Units deemed owned by the General Partner) represented either in person or by proxy, but no other business may be transacted, except as provided in Section 13.7.
Section 13.10 Conduct of a Meeting.
The General Partner shall have full power and authority concerning the manner of conducting any meeting of the Limited Partners or solicitation of approvals in writing, including the determination of Persons entitled to vote, the existence of a quorum, the satisfaction of the requirements of Section 13.4, the conduct of voting, the validity and effect of any proxies and the determination of any controversies, votes or challenges arising in connection with or during the meeting or voting. The General Partner shall designate a Person to serve as chairman of any meeting and shall further designate a Person to take the minutes of any meeting. All minutes shall be kept with the records of the Partnership maintained by the General Partner. The General Partner may make such other regulations consistent with applicable law and this Agreement as it may deem advisable concerning the conduct of any meeting of the Limited Partners or solicitation of approvals in writing, including regulations in regard to the appointment of proxies, the appointment and duties of inspectors of votes and approvals, the submission and examination of proxies and other evidence of the right to vote, and the revocation of approvals in writing.
Section 13.11 Action Without a Meeting.
If authorized by the General Partner, any action that may be taken at a meeting of the Limited Partners may be taken without a meeting, without a vote and without prior notice if an approval in writing setting forth the action so taken is signed by Limited Partners owning not less than the minimum percentage of the Outstanding Units (including Units deemed owned by the General Partner) that would be necessary to authorize or take such action at a meeting at which all the Limited Partners were present and voted (unless such provision conflicts with any rule, regulation, guideline or requirement of any National Securities Exchange on which the Units are listed or admitted to trading, in which case the rule, regulation, guideline or requirement of such National Securities Exchange shall govern). Prompt notice of the taking of action without a meeting shall be given to the Limited Partners who have not approved in writing. The General Partner may specify that any written ballot submitted to Limited Partners for the purpose of taking any action without a meeting shall be returned to the Partnership within the time period, which shall be not less than 20 days, specified by the General Partner. If a ballot returned
A-71
to the Partnership does not vote all of the Units held by the Limited Partners, the Partnership shall be deemed to have failed to receive a ballot for the Units that were not voted. If approval of the taking of any action by the Limited Partners is solicited by any Person other than by or on behalf of the General Partner, the written approvals shall have no force and effect unless and until (a) they are deposited with the Partnership in care of the General Partner, (b) approvals sufficient to take the action proposed are dated as of a date not more than 90 days prior to the date sufficient approvals are deposited with the Partnership and (c) an Opinion of Counsel is delivered to the General Partner to the effect that the exercise of such right and the action proposed to be taken with respect to any particular matter (i) will not cause the Limited Partners to be deemed to be taking part in the management and control of the business and affairs of the Partnership so as to jeopardize the Limited Partners’ limited liability, and (ii) is otherwise permissible under the state statutes then governing the rights, duties and liabilities of the Partnership and the Partners.
Section 13.12 Right to Vote and Related Matters.
(a) Only those Record Holders of the Units on the Record Date set pursuant to Section 13.6 (and also subject to the limitations contained in the definition of “Outstanding”) shall be entitled to notice of, and to vote at, a meeting of Limited Partners or to act with respect to matters as to which the holders of the Outstanding Units have the right to vote or to act. All references in this Agreement to votes of, or other acts that may be taken by, the Outstanding Units shall be deemed to be references to the votes or acts of the Record Holders of such Outstanding Units.
(b) With respect to Units that are held for a Person’s account by another Person (such as a broker, dealer, bank, trust company or clearing corporation, or an agent of any of the foregoing), in whose name such Units are registered, such other Person shall, in exercising the voting rights in respect of such Units on any matter, and unless the arrangement between such Persons provides otherwise, vote such Units in favor of, and at the direction of, the Person who is the beneficial owner, and the Partnership shall be entitled to assume it is so acting without further inquiry. The provisions of this Section 13.12(b) (as well as all other provisions of this Agreement) are subject to the provisions of Section 4.3.
MERGER, CONSOLIDATION OR CONVERSION
The Partnership may merge or consolidate with or into one or more corporations, limited liability companies, statutory trusts or associations, real estate investment trusts, common law trusts or unincorporated businesses, including a partnership (whether general or limited (including a limited liability partnership or a limited liability limited partnership)) or convert into any such entity, formed under the laws of the State of Delaware or any other state of the United States of America, pursuant to a written agreement of merger or consolidation (“Merger Agreement”) or plan of conversion (“Plan of Conversion”) in accordance with this Article XIV.
Section 14.2 Procedure for Merger, Consolidation or Conversion.
(a) Merger, consolidation or conversion of the Partnership pursuant to this Article XIV requires the prior consent of the General Partner; provided, however, that, to the fullest extent permitted by law, the General Partner shall have no duty or obligation to consent to any merger, consolidation or conversion of the Partnership and, to the fullest extent permitted by law, may decline to do so free of any duty (including fiduciary duty) or obligation whatsoever to the Partnership, any Limited Partner or Assignee and, in declining to consent to a merger, consolidation or conversion, shall not be required to act in good faith or pursuant to any other standard imposed by this Agreement, any Group Member Agreement, any other agreement contemplated hereby or under the Delaware Act or any other law, rule or regulation or at equity.
A-72
(b) If the General Partner shall determine to consent to the merger or consolidation, the General Partner shall approve the Merger Agreement, which shall set forth:
(i) the names and jurisdictions of formation or organization of each of the business entities proposing to merge or consolidate;
(ii) the name and jurisdiction of formation or organization of the business entity that is to survive the proposed merger or consolidation (the “Surviving Business Entity”);
(iii) the terms and conditions of the proposed merger or consolidation;
(iv) the manner and basis of exchanging or converting the equity securities of each constituent business entity for, or into, cash, property or interests, rights, securities or obligations of the Surviving Business Entity; and (i) if any general or limited partner interests, securities or rights of any constituent business entity are not to be exchanged or converted solely for, or into, cash, property or interests, rights, securities or obligations of the Surviving Business Entity, the cash, property or general or limited partner interests, rights, securities or obligations of any general or limited partnership, corporation, trust, limited liability company, unincorporated business or other entity (other than the Surviving Business Entity) which the holders of such interests, securities or rights are to receive in exchange for, or upon conversion of, their interests, securities or rights, and (ii) in the case of securities represented by certificates, upon the surrender of such certificates, which cash, property or interests, rights, securities or obligations of the Surviving Business Entity or any general or limited partnership, corporation, trust, limited liability company, unincorporated business or other entity (other than the Surviving Business Entity), or evidences thereof, are to be delivered;
(v) a statement of any changes in the constituent documents or the adoption of new constituent documents (the articles or certificate of incorporation, articles of trust, declaration of trust, certificate or agreement of limited partnership, certificate of formation, limited liability company agreement or other similar charter or governing document) of the Surviving Business Entity to be effected by such merger or consolidation;
(vi) the effective time of the merger, which may be the date of the filing of the certificate of merger pursuant to Section 14.4 or a later date specified in or determinable in accordance with the Merger Agreement (provided, that if the effective time of the merger is to be later than the date of the filing of such certificate of merger, the effective time shall be fixed at a date or time certain at or prior to the time of the filing of such certificate of merger and stated therein); and
(vii) such other provisions with respect to the proposed merger or consolidation that the General Partner determines to be necessary or appropriate.
(c) If the General Partner shall determine to consent to conversion of the Partnership, the General Partner shall approve the Plan of Conversion, which shall set forth:
(i) the name of the converting entity and the converted entity;
(ii) a statement that the Partnership is continuing its existence in the organizational form of the converted entity;
(iii) a statement as to the type of entity that the converted entity is to be and the state or country under the laws of which the converted entity is to be incorporated, formed or organized;
(iv) the manner and basis of exchanging or converting the equity securities of the converting entity for, or into, cash, property or interests, rights, securities or obligations of the converted entity;
(v) in an attachment or exhibit, the articles or certificate of incorporation, articles of trust, declaration of trust, certificate or agreement of limited partnership, certificate of formation, limited liability company agreement or other similar charter or governing documents of the converted entity;
(vi) the effective time of the conversion, which may be the date of the filing of the certificate of conversion pursuant to Section 14.4 or a later date specified in or determinable in accordance with the Plan
A-73
of Conversion (provided, that if the effective time of the conversion is to be later than the date of the filing of such certificate of conversion, the effective time shall be fixed at a date or time certain at or prior to the time of the filing of such certificate of conversion and stated therein); and
(vii) such other provisions with respect to the proposed conversion that the General Partner determines to be necessary or appropriate.
Section 14.3 Approval by Limited Partners of Merger, Consolidation or Conversion.
(a) Except as provided in Sections 14.3(d) and 14.3(e), the General Partner, upon its approval of the Merger Agreement or the Plan of Conversion and the merger, consolidation or conversion contemplated thereby, as the case may be, shall direct that the Merger Agreement or the Plan of Conversion and the merger, consolidation or conversion contemplated thereby, as the case may be, be submitted to a vote of Limited Partners, whether at a special meeting or by written consent, in either case in accordance with the requirements of Article XIII. A copy or a summary of the Merger Agreement or the Plan of Conversion, as the case may be, shall be included in or enclosed with the notice of a special meeting or the written consent.
(b) Except as provided in Sections 14.3(d) and 14.3(e), the Merger Agreement or the Plan of Conversion, as the case may be, and the merger, consolidation or conversion contemplated thereby, shall be approved upon receiving the affirmative vote or consent of the holders of a Unit Majority.
(c) Except as provided in Sections 14.3(d) and 14.3(e), after such approval by vote or consent of the Limited Partners, and at any time prior to the filing of the certificate of merger or certificate of conversion pursuant to Section 14.4, the merger, consolidation or conversion may be abandoned pursuant to provisions therefor, if any, set forth in the Merger Agreement or the Plan of Conversion, as the case may be.
(d) Notwithstanding anything else contained in this Article XIV or in this Agreement, the General Partner is permitted, without Limited Partner approval, to convert the Partnership or any Group Member into a new limited liability entity, to merge the Partnership or any Group Member into, or convey all of the Partnership’s assets to, another limited liability entity which shall be newly formed and shall have no assets, liabilities or operations at the time of such conversion, merger or conveyance other than those it receives from the Partnership or other Group Member if (i) the General Partner has received an Opinion of Counsel that the conversion, merger or conveyance, as the case may be, would not result in the loss of the limited liability of any Limited Partner or cause the Partnership to be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise to be taxed as an entity for federal income tax purposes (to the extent not previously treated as such), (ii) the sole purpose of such conversion, merger or conveyance is to effect a mere change in the legal form of the Partnership into another limited liability entity and (iii) the governing instruments of the new entity provide the Limited Partners and the General Partner with substantially the same rights and obligations as are herein contained.
(e) Additionally, notwithstanding anything else contained in this Article XIV or in this Agreement, the General Partner is permitted, without Limited Partner approval, to merge or consolidate the Partnership with or into another entity if (A) the General Partner has received an Opinion of Counsel that the merger or consolidation, as the case may be, would not result in the loss of the limited liability of any Limited Partner or cause the Partnership to be treated as an association taxable as a corporation or otherwise to be taxed as an entity for federal income tax purposes (to the extent not previously treated as such), (B) the merger or consolidation would not result in an amendment to the Partnership Agreement, other than any amendments that could be adopted pursuant to Section 13.1, (C) the Partnership is the Surviving Business Entity in such merger or consolidation, (D) each Unit outstanding immediately prior to the effective date of the merger or consolidation is to be an identical Unit of the Partnership after the effective date of the merger or consolidation, and (E) the number of Partnership Securities to be issued by the Partnership in such merger or consolidation do not exceed 20% of the Partnership Securities Outstanding immediately prior to the effective date of such merger or consolidation.
A-74
Section 14.4 Certificate of Merger; Certificate of Conversion.
Upon the required approval by the General Partner and the Unitholders of a Merger Agreement or the Plan of Conversion, as the case may be, and the merger, consolidation or conversion contemplated thereby, a certificate of merger or certificate of conversion shall be executed and filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware in conformity with the requirements of the Delaware Act.
Section 14.5 Amendment of Partnership Agreement.
Pursuant to Section 17-211(g) of the Delaware Act, an agreement of merger or consolidation approved in accordance with this Article XIV may (a) effect any amendment to this Agreement or (b) effect the adoption of a new partnership agreement for the Partnership if it is the Surviving Business Entity. Any such amendment or adoption made pursuant to this Section 14.5 shall be effective at the effective time or date of the merger or consolidation.
Section 14.6 Effect of Merger, Consolidation or Conversion.
(a) At the effective time of the certificate of merger:
(i) all of the rights, privileges and powers of each of the business entities that has merged or consolidated, and all property, real, personal and mixed, and all debts due to any of those business entities and all other things and causes of action belonging to each of those business entities, shall be vested in the Surviving Business Entity and after the merger or consolidation shall be the property of the Surviving Business Entity to the extent they were of each constituent business entity;
(ii) the title to any real property vested by deed or otherwise in any of those constituent business entities shall not revert and is not in any way impaired because of the merger or consolidation;
(iii) all rights of creditors and all liens on or security interests in property of any of those constituent business entities shall be preserved unimpaired; and
(iv) all debts, liabilities and duties of those constituent business entities shall attach to the Surviving Business Entity and may be enforced against it to the same extent as if the debts, liabilities and duties had been incurred or contracted by it.
(b) At the effective time of the certificate of conversion, the nature and characteristics of the converted entity will be determined by the Plan of Conversion, applicable laws of the State of Delaware and the laws of the jurisdiction to which the Partnership is converted.
(c) A merger, consolidation or conversion effected pursuant to this Article shall not be deemed to result in a transfer or assignment of assets or liabilities from one entity to another.
Section 14.7 Business Combination Limitations.
(a) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Agreement, with respect to any “Business Combination” (as such term is defined in Section 203 of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware, 8 Del. C. Section 101, et seq. (the “DGCL”), the provisions of Section 203 of the DGCL shall be applied with respect to the Partnership as though (i) the Partnership is a Delaware corporation subject to Section 203 of the DGCL, (ii) the General Partner is the board of directors of such corporation, and (iii) the holders of Limited Partner Interests are stockholders of such corporation and the Limited Partner Interests are shares of stock and voting stock in such corporation.
(b) Amendments to, or actions to repeal or adopt provisions inconsistent with, Section 14.7(a) shall require the approval of the Unitholders holding at least 66 2/3% of the Outstanding Limited Partner Units (including Limited Partner Units held by the General Partner and its Affiliates).
(c) Neither the General Partner nor any of its Affiliates shall be considered an “interested stockholder” under Section 203 of the DGCL for purposes of this Section 14.7.
A-75
RIGHT TO ACQUIRE LIMITED PARTNER INTERESTS
Section 15.1 Right to Acquire Limited Partner Interests.
(a) Notwithstanding any other provision of this Agreement, if at any time the General Partner and its Affiliates hold more than 80% of the total Limited Partner Interests of any class then Outstanding, the General Partner shall then have the right, which right it may assign and transfer in whole or in part to the Partnership or any Affiliate of the General Partner, exercisable at its option, to purchase all, but not less than all, of such Limited Partner Interests of such class then Outstanding held by Persons other than the General Partner and its Affiliates, at the greater of (x) the Current Market Price as of the date three days prior to the date that the notice described in Section 15.1(b) is mailed and (y) the highest price paid by the General Partner or any of its Affiliates for any such Limited Partner Interest of such class purchased during the 90-day period preceding the date that the notice described in Section 15.1(b) is mailed.
(b) If the General Partner, any Affiliate of the General Partner or the Partnership elects to exercise the right to purchase Limited Partner Interests granted pursuant to Section 15.1(a), the General Partner shall deliver to the Transfer Agent notice of such election to purchase (the “Notice of Election to Purchase”) and shall cause the Transfer Agent to mail a copy of such Notice of Election to Purchase to the Record Holders of Limited Partner Interests of such class or classes (as of a Record Date selected by the General Partner) at least 10, but not more than 60, days prior to the Purchase Date. Such Notice of Election to Purchase shall also be published for a period of at least three consecutive days in at least two daily newspapers of general circulation printed in the English language and published in the Borough of Manhattan, New York. The Notice of Election to Purchase shall specify the Purchase Date and the price (determined in accordance with Section 15.1(a)) at which Limited Partner Interests will be purchased and state that the General Partner, its Affiliate or the Partnership, as the case may be, elects to purchase such Limited Partner Interests, upon surrender of Certificates representing such Limited Partner Interests in exchange for payment, at such office or offices of the Transfer Agent as the Transfer Agent may specify, or as may be required by any National Securities Exchange on which such Limited Partner Interests are listed. Any such Notice of Election to Purchase mailed to a Record Holder of Limited Partner Interests at his address as reflected in the records of the Transfer Agent shall be conclusively presumed to have been given regardless of whether the owner receives such notice. On or prior to the Purchase Date, the General Partner, its Affiliate or the Partnership, as the case may be, shall deposit with the Transfer Agent cash in an amount sufficient to pay the aggregate purchase price of all of such Limited Partner Interests to be purchased in accordance with this Section 15.1. If the Notice of Election to Purchase shall have been duly given as aforesaid at least 10 days prior to the Purchase Date, and if on or prior to the Purchase Date the deposit described in the preceding sentence has been made for the benefit of the holders of Limited Partner Interests subject to purchase as provided herein, then from and after the Purchase Date, notwithstanding that any Certificate shall not have been surrendered for purchase, all rights of the holders of such Limited Partner Interests (including any rights pursuant to Articles IV, V, VI, and XII) shall thereupon cease, except the right to receive the purchase price (determined in accordance with Section 15.1(a)) for Limited Partner Interests therefor, without interest, upon surrender to the Transfer Agent of the Certificates representing such Limited Partner Interests, and such Limited Partner Interests shall thereupon be deemed to be transferred to the General Partner, its Affiliate or the Partnership, as the case may be, on the record books of the Transfer Agent and the Partnership, and the General Partner or any Affiliate of the General Partner, or the Partnership, as the case may be, shall be deemed to be the owner of all such Limited Partner Interests from and after the Purchase Date and shall have all rights as the owner of such Limited Partner Interests (including all rights as owner of such Limited Partner Interests pursuant to Articles IV, V, VI and XII).
(c) At any time from and after the Purchase Date, a holder of an Outstanding Limited Partner Interest subject to purchase as provided in this Section 15.1 may surrender his Certificate evidencing such Limited Partner Interest to the Transfer Agent in exchange for payment of the amount described in Section 15.1(a) therefor without interest thereon.
A-76
Section 16.1 Addresses and Notices.
Any notice, demand, request, report or proxy materials required or permitted to be given or made to a Partner or Assignee under this Agreement shall be in writing and shall be deemed given or made when delivered in person or when sent by first class United States mail or by other means of written communication to the Partner or Assignee at the address described below. Any notice, payment or report to be given or made to a Partner or Assignee hereunder shall be deemed conclusively to have been given or made, and the obligation to give such notice or report or to make such payment shall be deemed conclusively to have been fully satisfied, upon sending of such notice, payment or report to the Record Holder of such Partnership Securities at his address as shown on the records of the Transfer Agent or as otherwise shown on the records of the Partnership, regardless of any claim of any Person who may have an interest in such Partnership Securities by reason of any assignment or otherwise. An affidavit or certificate of making of any notice, payment or report in accordance with the provisions of this Section 16.1 executed by the General Partner, the Transfer Agent or the mailing organization shall be prima facie evidence of the giving or making of such notice, payment or report. If any notice, payment or report addressed to a Record Holder at the address of such Record Holder appearing on the books and records of the Transfer Agent or the Partnership is returned by the United States Postal Service marked to indicate that the United States Postal Service is unable to deliver it, such notice, payment or report and any subsequent notices, payments and reports shall be deemed to have been duly given or made without further mailing (until such time as such Record Holder or another Person notifies the Transfer Agent or the Partnership of a change in his address) if they are available for the Partner or Assignee at the principal office of the Partnership for a period of one year from the date of the giving or making of such notice, payment or report to the other Partners and Assignees. Any notice to the Partnership shall be deemed given if received by the General Partner at the principal office of the Partnership designated pursuant to Section 2.3. The General Partner may rely and shall be protected in relying on any notice or other document from a Partner, Assignee or other Person if believed by it to be genuine.
The parties shall execute and deliver all documents, provide all information and take or refrain from taking action as may be necessary or appropriate to achieve the purposes of this Agreement.
This Agreement shall be binding upon and inure to the benefit of the parties hereto and their heirs, executors, administrators, successors, legal representatives and permitted assigns.
This Agreement constitutes the entire agreement among the parties hereto pertaining to the subject matter hereof and supersedes all prior agreements and understandings pertaining thereto.
None of the provisions of this Agreement shall be for the benefit of, or shall be enforceable by, any creditor of the Partnership.
No failure by any party to insist upon the strict performance of any covenant, duty, agreement or condition of this Agreement or to exercise any right or remedy consequent upon a breach thereof shall constitute waiver of any such breach of any other covenant, duty, agreement or condition.
A-77
This Agreement may be executed in counterparts, all of which together shall constitute an agreement binding on all the parties hereto, notwithstanding that all such parties are not signatories to the original or the same counterpart. Each party shall become bound by this Agreement immediately upon affixing its signature hereto or, in the case of a Person acquiring a Unit, upon accepting the certificate evidencing such Unit or executing and delivering a Transfer Application as herein described, independently of the signature of any other party.
This Agreement shall be construed in accordance with and governed by the laws of the State of Delaware, without regard to the principles of conflicts of law.
Section 16.9 Invalidity of Provisions.
If any provision of this Agreement is or becomes invalid, illegal or unenforceable in any respect, the validity, legality and enforceability of the remaining provisions contained herein shall not be affected thereby.
Section 16.10 Consent of Partners.
Each Partner hereby expressly consents and agrees that, whenever in this Agreement it is specified that an action may be taken upon the affirmative vote or consent of less than all of the Partners, such action may be so taken upon the concurrence of less than all of the Partners and each Partner shall be bound by the results of such action.
Section 16.11 Facsimile Signatures.
The use of facsimile signatures affixed in the name and on behalf of the transfer agent and registrar of the Partnership on certificates representing Common Units is expressly permitted by this Agreement.
Section 16.12 Third Party Beneficiaries.
Each Partner agrees that any Indemnitee shall be entitled to assert rights and remedies hereunder as a third-party beneficiary hereto with respect to those provisions of this Agreement affording a right, benefit or privilege to such Indemnitee.
[REMAINDER OF THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK.]
A-78
IN WITNESS WHEREOF, the parties hereto have executed this Agreement as of the date first written above.
| GENERAL PARTNER: | ||
| CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS GP, LLC | ||
| By: |
| |
| Name: |
| |
| Title: |
| |
| ORGANIZATIONAL LIMITED PARTNER: | ||
| CHENIERE LNG HOLDINGS, LLC | ||
| By: |
| |
| Name: |
| |
| Title: |
| |
| LIMITED PARTNERS: | ||
| All Limited Partners now and hereafter admitted as Limited Partners of the Partnership, pursuant to powers of attorney now and hereafter executed in favor of, and granted and delivered to the General Partner. | ||
| CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS GP, LLC | ||
| By: |
| |
| Name: |
| |
| Title: |
| |
A-79
EXHIBIT A
to the First Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
Certificate Evidencing Common Units
Representing Limited Partner Interests in
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
| No. |
Common Units |
In accordance with Section 4.1 of the First Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P., as amended, supplemented or restated from time to time (the “Partnership Agreement”), Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P., a Delaware limited partnership (the “Partnership”), hereby certifies that (the “Holder”) is the registered owner of Common Units representing limited partner interests in the Partnership (the “Common Units”) transferable on the books of the Partnership, in person or by duly authorized attorney, upon surrender of this Certificate properly endorsed and accompanied by a properly executed application for transfer of the Common Units represented by this Certificate. The rights, preferences and limitations of the Common Units are set forth in, and this Certificate and the Common Units represented hereby are issued and shall in all respects be subject to the terms and provisions of, the Partnership Agreement. Copies of the Partnership Agreement are on file at, and will be furnished without charge on delivery of written request to the Partnership at, the principal office of the Partnership located at 717 Texas Avenue, Suite 3100, Houston, Texas 77002. Capitalized terms used herein but not defined shall have the meanings given them in the Partnership Agreement.
The Holder, by accepting this Certificate, is deemed to have (i) requested admission as, and agreed to become, a Limited Partner and to have agreed to comply with and be bound by and to have executed the Partnership Agreement, (ii) represented and warranted that the Holder has all right, power and authority and, if an individual, the capacity necessary to enter into the Partnership Agreement, (iii) granted the powers of attorney provided for in the Partnership Agreement and (iv) made the waivers and given the consents and approvals contained in the Partnership Agreement.
THE HOLDER OF THIS SECURITY ACKNOWLEDGES FOR THE BENEFIT OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. THAT THIS SECURITY MAY NOT BE SOLD, OFFERED, RESOLD, PLEDGED OR OTHERWISE TRANSFERRED IF SUCH TRANSFER WOULD (A) VIOLATE THE THEN APPLICABLE FEDERAL OR STATE SECURITIES LAWS OR RULES AND REGULATIONS OF THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION, ANY STATE SECURITIES COMMISSION OR ANY OTHER GOVERNMENTAL AUTHORITY WITH JURISDICTION OVER SUCH TRANSFER, (B) TERMINATE THE EXISTENCE OR QUALIFICATION OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. UNDER THE LAWS OF THE STATE OF DELAWARE, OR (C) CAUSE CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. TO BE TREATED AS AN ASSOCIATION TAXABLE AS A CORPORATION OR OTHERWISE TO BE TAXED AS AN ENTITY FOR FEDERAL INCOME TAX PURPOSES (TO THE EXTENT NOT ALREADY SO TREATED OR TAXED). CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS GP, LLC, THE GENERAL PARTNER OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P., MAY IMPOSE ADDITIONAL RESTRICTIONS ON THE TRANSFER OF THIS SECURITY IF IT RECEIVES AN OPINION OF COUNSEL THAT SUCH RESTRICTIONS ARE NECESSARY TO AVOID A SIGNIFICANT RISK OF CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. BECOMING TAXABLE AS A CORPORATION OR OTHERWISE BECOMING TAXABLE AS AN ENTITY FOR FEDERAL INCOME TAX PURPOSES. THE RESTRICTIONS SET FORTH ABOVE SHALL NOT PRECLUDE THE SETTLEMENT OF ANY TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING THIS SECURITY ENTERED INTO THROUGH THE FACILITIES OF ANY NATIONAL SECURITIES EXCHANGE ON WHICH THIS SECURITY IS LISTED OR ADMITTED TO TRADING.
Exhibit A-1
This Certificate shall not be valid for any purpose unless it has been countersigned and registered by the Transfer Agent and Registrar.
| Dated: | CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. | |||||
| Countersigned and Registered by: | By: | Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC, its General Partner | ||||
|
as Transfer Agent and Registrar |
By: |
| ||||
| Name: |
| |||||
| By: |
|
By: |
| |||
| Authorized Signature | Secretary | |||||
[Reverse of Certificate]
ABBREVIATIONS
The following abbreviations, when used in the inscription on the face of this Certificate, shall be construed as follows according to applicable laws or regulations:
| TEN COM - | as tenants in common | UNIF GIFT/TRANSFERS MIN ACT | ||
| TEN ENT -
JT TEN - |
as tenants by the entireties
as joint tenants with right of survivorship and not as tenants in common |
Custodian (Cust) (Minor)
under Uniform Gifts/Transfers to CD Minors Act (State) | ||
|
FOR VALUE RECEIVED, hereby assigns, conveys, sells and transfers unto | ||||
Additional abbreviations, though not in the above list, may also be used.
|
|
| |
| (Please print or typewrite name and address of Assignee) |
(Please insert Social Security or other identifying number of Assignee) |
Exhibit A-2
Common Units representing limited partner interests evidenced by this Certificate, subject to the Partnership Agreement, and does hereby irrevocably constitute and appoint as its attorney-in-fact with full power of substitution to transfer the same on the books of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
| Date: | NOTE: | The signature to any endorsement hereon must correspond with the name as written upon the face of this Certificate in every particular, without alteration, enlargement or change. | ||
| THE SIGNATURE(S) MUST BE GUARANTEED BY AN ELIGIBLE GUARANTOR INSTITUTION (BANKS, STOCKBROKERS, SAVINGS AND LOAN ASSOCIATIONS AND CREDIT UNIONS WITH MEMBERSHIP IN AN APPROVED SIGNATURE GUARANTEE MEDALLION PROGRAM), PURSUANT TO S.E.C. RULE 17Ad-15 | (Signature)
(Signature) | |||
No transfer of the Common Units evidenced hereby will be registered on the books of the Partnership, unless the Certificate evidencing the Common Units to be transferred is surrendered for registration or transfer and an Application for Transfer of Common Units has been properly completed and executed by a transferee either (a) on the form set forth below or (b) on a separate application that the Partnership will furnish on request without charge. A transferor of the Common Units shall have no duty to the transferee with respect to execution of the Application for Transfer of Common Units in order for such transferee to obtain registration of the transfer of the Common Units.
Exhibit A-3
APPLICATION FOR TRANSFER OF COMMON UNITS
Transferees of Common Units must execute and deliver this application to Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P., c/o Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC, 717 Texas Avenue, Houston, Texas 77002; Attn: CFO, to be admitted as limited partners to Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.
The Assignee (a) requests admission as a Substituted Limited Partner and agrees to comply with and be bound by, and hereby executes, the First Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P., as amended, supplemented or restated to the date hereof (the “Partnership Agreement”), (b) represents and warrants that the Assignee has all right, power and authority and, if an individual, the capacity necessary to enter into the Partnership Agreement, (c) appoints the General Partner of the Partnership and, if a Liquidator shall be appointed, the Liquidator of the Partnership as the Assignee’s attorney-in-fact to execute, swear to, acknowledge and file any document, including the Partnership Agreement and any amendment thereto and the Certificate of Limited Partnership of the Partnership and any amendment thereto, necessary or appropriate for the Assignee’s admission as a Substituted Limited Partner and as a party to the Partnership Agreement, (d) gives the powers of attorney provided for in the Partnership Agreement, and (e) makes the waivers and gives the consents and approvals contained in the Partnership Agreement. Capitalized terms not defined herein have the meanings assigned to such terms in the Partnership Agreement.
Date:
|
Social Security or other identifying number |
Signature of Assignee | |
|
Purchase Price including commissions, if any |
Name and Address of Assignee | |
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this certification and to the best of my knowledge and belief it is true, correct and complete and, if applicable, I further declare that I have authority to sign this document on behalf of:
| Name of Interestholder |
|
Signature and Date |
|
Title (if applicable) |
Note: If the Assignee is a broker, dealer, bank, trust company, clearing corporation, other nominee holder or an agent of any of the foregoing, and is holding for the account of any other person, this application should be completed by an officer thereof or, in the case of a broker or dealer, by a registered representative who is a member of a registered national securities exchange or a member of the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc., or, in the case of any other nominee holder, a person performing a similar function. If the Assignee is a broker, dealer, bank, trust company, clearing corporation, other nominee owner or an agent of any of the foregoing, the above certification as to any person for whom the Assignee will hold the Common Units shall be made to the best of the Assignee’s knowledge.
Exhibit A-4

LEGAL NOTICE
This document was prepared by Stone & Webster Management Consultants, Inc. (“Stone & Webster Consultants”) solely for the benefit of Cheniere Energy Inc. (“Cheniere”). Neither Stone & Webster Consultants, Cheniere nor their parent corporations or affiliates, nor any person acting in their behalf (a) makes any warranty, expressed or implied, with respect to the use of any information or methods disclosed in this document; or (b) assumes any liability with respect to the use of any information or methods disclosed in this document.
Any recipient of this document, by their acceptance or use of this document, releases Stone & Webster Consultants, Cheniere, their parent corporations and affiliates from any liability for direct, indirect, consequential, or special loss or damage whether arising in contract, warranty, express or implied, tort or otherwise, and irrespective of fault, negligence, and strict liability.
E-MAIL NOTICE
E-mail copies of this report are not official unless authenticated and signed by Stone & Webster Consultants and are not to be modified in any manner without Stone & Webster Consultants’ expressed written consent.
 |
B-2 | |||||
NOMENCLATURE
| ACI | American Concrete Institute | |
| AISC | American Institute of Steel Construction | |
| ANSI | American National Standards Institute | |
| API | American Petroleum Institute | |
| AQCR | Air Quality Control Region | |
| ASCE | American Society of Civil Engineers | |
| ASME | American Society of Mechanical Engineers | |
| ASNT | American Society for Non-Destructive Testing | |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing and Materials | |
| AWS | American Welding Society | |
| BACT | Best Available Control Technology | |
| bcf | Billion Cubic Feet | |
| bscfd | Billion Standard Cubic Feet per Day | |
| Btu | British Thermal Unit | |
| bpd | Barrels per Day | |
| CAER | Community Awareness and Emergency Response | |
| CATOX | Catalytic Oxidation Units | |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide | |
| COE | Corp of Engineers | |
| CPI | Corrugated Plate Interceptor | |
| CFR | Code of Federal Regulations | |
| DCS | Distributed Control System | |
| DSCR | Debt Service Coverage Ratio | |
| DLE | Dry Low Emissions | |
| DOT | Department of Transportation | |
| DSAW | Double Submerged-Arc Welded | |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency | |
| EPC | Engineering, Procurement and Construction | |
| FAA | Federal Aviation Administration | |
| FEED | Front End Engineering Design | |
| FERC | Federal Energy Regulatory Commission | |
| FWS | Fish and Wildlife Service | |
| HAZOP | Hazards and Operability | |
| hp | Horsepower | |
| IBC | International Building Code | |
| IDC | Interest During Construction | |
| IEC | International Electrotechnical Commission | |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers | |
| IMO | International Maritime Organization | |
| IRR | Internal Rate of Return | |
| ISA | Instrument Society of America | |
| ISO | International Standards Organization | |
| ITS | Interruptible Transportation Service | |
| JV | Joint Venture | |
| kV | Kilovolt | |
| kW | Kilowatt | |
| LDEQ | Louisiana Department of Environmental Quality |
 |
B-3 |
|||||
| LNG | Liquefied Natural Gas | |
| LS | Lump Sum | |
| MMscfd | Million Standard Cubic Feet per Day | |
| MP | Mile Post | |
| MSS | Manufacturer Standardization Society | |
| MW | Megawatt | |
| NAAQS | National Ambient Air Quality Standards | |
| NACE | National Association of Corrosion Engineers | |
| NDE | Non-Destructive Examination | |
| NEMA | National Electric Manufacturers Association | |
| NFPA | National Fire Protection Association | |
| NOx | Nitrogen Oxides | |
| NOI | Notice of Intent | |
| NOT | Notice of Termination | |
| NPV | Net Present Value | |
| O&M | Operations and Maintenance | |
| OBE | Operating Basis Earthquake | |
| OC | Operations Center | |
| OCIMF | Oil Companies International Marine Forum | |
| OSHA | Occupational Safety and Health Administration | |
| OSRP | Oil Spill Response Plan | |
| P&I | Protection and Indemnity | |
| PLC | Programmable Logic Controller | |
| PO | Purchase Order | |
| PPE | Personal Protective Equipment | |
| PSD | Prevention of Significant Deterioration | |
| psia | pounds per square inch (absolute) | |
| psig | pounds per square inch (gauge) | |
| QA | Quality Assurance | |
| QC | Quality Control | |
| RAM | Reliability, Availability and Maintainability | |
| SCR | Selective Catalytic Reduction | |
| SIGTTO | Society of International Gas Tanker and Terminal Operations | |
| SPCC | Spill Prevention and Containment Control | |
| SQG | Small Quantity Generator | |
| SSE | Safe Shutdown Earthquake | |
| SSPC | Steel Structures Painting Council | |
| TEMA | Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers’ Association | |
| USCG | United States Coast Guard | |
| V | Volt | |
| VOC | Volatile Organic Compounds |
 |
B-4 | |||||
Independent Technical Review Report
Sabine Pass LNG Terminal
| 1.0 | Background | B-6 | ||
| 2.0 | Summary of Risks | B-7 | ||
| 3.0 | Project Description | B-13 | ||
| 4.0 | Project Status | B-15 | ||
| 5.0 | Project Implementation | B-16 | ||
| 6.0 | Construction Budget | B-18 | ||
| 7.0 | Construction Schedule | B-18 | ||
| 8.0 | Environmental Risks | B-20 | ||
| 9.0 | Operations and Maintenance Programs | B-20 | ||
| 10.0 | Contracts | B-21 | ||
| 11.0 | Conclusions | B-23 | ||
| 12.0 | Site Visit Photographs | B-24 | ||
 |
B-5 | |||||
Cheniere Energy, Inc., the Sponsor, is based in Houston, Texas, USA. It originally established a fully owned subsidiary, Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (“Sabine”) to develop, own and operate the Sabine Pass LNG Terminal Project (“Project”). The Project is located alongside the navigable Sabine River Channel in Cameron Parrish, Louisiana, directly across the river from Sabine Pass, Texas. It comprises a receiving and regasification terminal that will receive, store, and vaporize imported liquefied natural gas (“LNG”). Vaporized natural gas will be exported via natural gas pipeline to U.S. consumers. The Project will operate as a tolling terminal, processing LNG on behalf of two initial Terminal Use Agreement (“TUA”) Customers, Total LNG USA, Inc. and Chevron USA, Inc., who will own the imported LNG and the exported natural gas. The two TUA Customers have each reserved a LNG import and a regasification export capacity of approximately 1,000 million standard cubic feet of gas per day (“MMscfd”). A third TUA Customer, Cheniere Marketing, Inc. (“Cheniere”) has reserved a maximum capacity of approximately 2,000 MMscfd. At this time Cheniere has not yet executed a LNG Off-take Agreement with any LNG liquefaction facility to secure an LNG supply to process through the Project. The terminal was originally designed to import sufficient LNG to produce a maximum peak natural gas export capacity of approximately 2,600 MMscfd. This is termed the Phase I Project. In mid-2006, the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion Project (the “Phase 2 Project”) was implemented. Upon completion, this will increase the maximum peak export capacity to approximately 4,000 MMscfd.
The Phase 1 Project is being implemented under a lump sum turnkey EPC Contract by Bechtel Corporation, (“Bechtel” or the “EPC Contractor”). Principal subcontractors include Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Ltd. (“MHI”) with Matrix Services (jointly “MHI/Matrix”) for the LNG tanks, Weeks Marine Inc. (“Weeks”) for the marine terminal, and Remedial Construction Services, L.P. (“Recon”) for site preparation and soil improvement. Bechtel is also the general EPC Contractor for Phase 2 under a reimbursable form of contract. In addition, Bechtel is providing construction management services to assist Sabine with managing the other principal fixed-price Phase 2 EPC Contractors, a joint venture of Diamond LNG (an MHI company) and Zachry (“Diamond/Zachry”) for the two additional LNG Tanks, and Recon for site preparation and soil improvement.
The U.S. Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (“FERC”) issued approval for the Phase 1 Project on December 21, 2004. Limited Notice to Proceed was issued under the Phase 1 EPC Contract on January 4, 2005. Subsequently, the full Notice to Proceed was issued on April 4, 2005. The Guaranteed Substantial Completion Date was originally September 2, 2008; however, a hurricane Force Majeure Change Order has revised the date to December 20, 2008. Full utilization of the terminal by the two TUA Customers is to commence by April 1, 2009 for Total and by July 1, 2009 for Chevron.
In July 2005 Sabine submitted a permit application to FERC for the Sabine Pass LNG Terminal Phase 2 Expansion Project. Approval was granted on June 15, 2006. Stage 1 of the Phase 2 Expansion Project will increase the peak terminal throughput capacity by 1,400 MMscfd to the ultimate peak capacity of 4,000 MMscfd. Change orders were issued during the construction of the Phase 1 Project to provide tie-ins and other pre-investment work necessary to minimize potential construction and operations interferences to Phase 1 activities during the execution of the Phase 2 Expansion Project. Cheniere undertook a substantial engineering effort and committed pre-investment expenditure to identify and mitigate potential interferences by Phase 2 on the timely completion and operation of Phase 1. In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion of Sabine Pass poses negligible risk to the timely completion and operation of the Phase 1 Project.
 |
B-6 | |||||
Aerial View from the North During Site Preparation

Stone & Webster Management Consultants, Inc. (“Stone & Webster Consultants”) was retained by Cheniere Energy, Inc. to conduct an independent technical assessment of the Project on behalf of the potential investors. Stone & Webster Consultants’ independent technical review report (“Report”), including the observations and conclusions presented herein, is based on, among other things, our review of the available technical, performance, schedule and cost data, visits to terminal site, and interviews with Cheniere personnel. The Report presents our findings and conclusions regarding the following:
| • | Plant design and technology; |
| • | Project execution plans and implementation schedule; |
| • | Capital costs; |
| • | Expected plant performance and operating parameters; |
| • | Operations and maintenance programs and budgets; and |
| • | Environmental permitting and regulatory issues. |
As indicated above, the Terminal is being implemented in two phases under different contracting strategies. The primary revenue for the Project is derived from the Total and Chevron TUAs. Accordingly, Stone & Webster Consultants has considered areas where there is perceived technical risk to the implementation of the Phase 1 Project and areas where the Phase 2 Expansion Project and its operation could impact the Phase I Project. Particular focus has been placed on circumstances where the risk component could materially impact the projected cash flows. Tables 2.0-1 and 2.0-2 present a summary of our assessment of these risks.
 |
B-7 | |||||
Table 2.0-1
Phase 1 Project Risks
| Risk Component | Comment | |
| LNG Supply Low Risk |
This is a Terminal User obligation under the terms of the TUAs with Total and Chevron. | |
| Technology Low Risk |
In general, the Project is using established and suitable technology for the Project. Stone & Webster Consultants is of the opinion that the process facilities to be installed at the terminal are robust and should provide for a long and useful service life. Likewise Stone & Webster Consultants confirms that there are no unusual risks regarding the technology proposed for LNG receipt, LNG storage, or regasification. | |
| Scale Up Low Risk |
In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, there is no scale-up risk associated with the Project. All major equipment is proven at the proposed size and capacity levels. Furthermore, the combined LNG export capacity of the two initial TUA Customers is 2,000 MMscfd versus a nameplate export rating of 2,600 MMscfd, thus providing ample excess capacity to service the two primary TUAs.. | |
| Environmental Issues Low Risk |
Stone & Webster Consultants’ review has not identified any environmental issues that would have an undue effect upon either the Project construction schedule or budget, and compliance with local, state and federal requirements will result in full compliance with the Equator Principles. | |
| Regulatory Issues Low Risk |
The Sponsor has identified the appropriate permits and other regulatory approvals required for this Project, including the LNG carrier transit, berths and unloading facilities; the LNG storage and regasification units; power generation; and other infrastructure and auxiliary facilities. In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, the Sponsor is making satisfactory progress towards obtaining the requisite approvals in a timely manner that supports the proposed construction schedule. Total and Chevron will jointly, but separately apply for a send-out pipeline permit to export their gas from the Terminal.
On December 21, 2004, FERC issued the Order Granting Authorization under Section 3 of the Natural Gas Act (“FERC Order”) to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., authorizing Sabine to construct an LNG terminal and send-out pipeline. The Louisiana LDEQ has issued Sabine a PSD air emissions permit. Sabine received its final construction permit from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. | |
| Contracting Strategy and Project Execution Low to Medium Risk |
The EPC Contractor is Bechtel Corporation, a skilled and experienced contractor with a long proven track record in the engineering, procurement and construction of energy-related projects, including LNG liquefaction and regasification facilities. The LNG storage tanks will be subcontracted to a consortium of MHI and Matrix Services. The marine terminal and associated dredging have been subcontracted to Weeks Marine, an experienced and reputable marine contractor. Site preparation and pile installation has been subcontracted to Recon, a skilled and experienced civil engineering contractor. In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, each of these firms has the requisite experience and capability to undertake the assigned role for the implementation of the Project. |
 |
B-8 | |||||
| Risk Component | Comment | |
| Cheniere is a start-up company and does not have sufficient permanent in-house personnel to properly and fully staff the Project Management Team, during Project execution. Therefore the Sponsor will hire temporary contract personnel and consultants to fill the open PMT positions. This organizational structure is typical for projects of this size and complexity, even by well-established major oil and gas corporations, due to previous downsizing. The PMT personnel have not previously worked together as a team and therefore have gone through a learning curve period. | ||
| Capital Cost Low to Medium Risk |
The EPC Contract portion of the Phase 1 Project cost is being implemented under a LSTK contract with Bechtel. In our opinion, the Owner’s Costs properly reflect the responsibilities and risks carried by the Owner. The Total Phase 1 Project Costs is currently budgeted to fall in the range of US$900 to US$950 million. Stone & Webster Consultants has reviewed the detailed build-up of both the EPC Contract Cost and the Owner’s Costs. In our opinion, based upon our benchmarking of this Capital Expenditure (“CAPEX”) against that of comparable projects, the budget is reasonable. | |
| Operating Cost Low Risk |
Operations, maintenance and contract labor costs total US$10.0 million per annum. Other fixed operating costs amount to US$15.1 million per annum in the aggregate. Apportioned Cheniere G&A costs carried by the Project add $8.3 million, and the GE power generation maintenance expenses add a further US$3.2 million, bringing the total annual (Phase 1) O&M costs for year 2010 to US$36.6 million.
Based on Stone & Webster Consultants’ experience with similar LNG receiving and regasification terminals world-wide, these O&M expenses fall well within industry benchmarks for similar facilities.
Based upon the benchmark comparison, the O&M Budget estimate is reasonable. Moreover, the OPEX reimbursement provisions provided by the two primary TUAs cover any reasonable overage above the current O&M cost estimate. | |
| Operating Performance Low Risk |
In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, the proposed facilities pose no unusual operating risks for a facility of this nature.
The Sponsor has not commissioned a Reliability, Availability, and Maintainability (“RAM”) Analysis for the Project, but the expected availability of the individual tandem vaporization units is expected to be approximately 96 percent. Based on Stone & Webster Consultants’ experience, the re-gasification and export availability for all sixteen of the Phase 1 vaporizers should be approximately 81.5 percent. This means at least thirteen vaporizers should be fully available at all times. This results in a minimum continuous export availability of approximately 2,340 MMscfd versus the export capacity under the two primary TUAs of 2,000 MMscfd.
The required export capacity of 2,000 MMscfd is equivalent to 90,500 cubic meters per day of LNG in liquid form. The available Phase 1 LNG storage capacity is 480,000 cubic meters, resulting in a storage-to-export ratio of 5.3:1 The industry norm is approximately 4:1, so the terminal has ample storage capacity to service the two primary TUAs. | |
 |
B-9 | |||||
| Risk Component | Comment | |
| Operating Performance Low Risk |
The required LNG reception quantity including retainage is approximately 90,500 cubic meters per day, which can be supplied on average by one 140,000 cubic meter LNG carrier every 36 hours.
Given the availability of two independent unloading berths, Stone & Webster Consultants has no significant concerns regarding LNG receiving capacity, even accounting for unavailability due to inclement weather. | |
| Interfaces Low to Medium Risk |
The respective Customers of the Terminal are responsible for providing pipeline interconnections between the Terminal and the existing export natural gas pipeline grid connections. The main export line should be approximately 16 miles long to the principal connections tie-in points.
Marine support facilities, e.g., tugs and line handling boats are the responsibility of the Terminal Users; however, Sabine will assist in securing and managing these services.
Drinking water will be supplied in bottled form by local suppliers. Utility water will be provided via pipeline from a local supplier. Power will be supplied internally by three LM2500+ simple-cycle gas turbine-driven generators. Only two of the turbines are required for the export capacity required by the two primary TUAs. There will be no external power supply. | |
| Geography Low to Medium Risk |
Meteorological conditions for the site and the Gulf of Mexico are well understood. The site is within the hurricane belt. The design applies appropriate criteria to mitigate the impact of hurricanes. |
Table 2.0-2
Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion
| Risk Component | Comment | |
| Supply Low Risk |
A third TUA has been executed with another Cheniere affiliate, Cheniere Marketing, Inc, but per Stone &Webster Consultants’ understanding, Cheniere has not yet contracted with any LNG liquefaction facility to supply Cheniere with LNG for processing through the Terminal. | |
| Technology Low Risk |
The Expansion Project is using proven technology for the tanks and vaporizers. The LNG Berths are being extended using open cell bulkhead technology to accommodate LNG carriers larger than 250,000 cubic meters. Open cell technology has been demonstrated to be effective in over 140 projects in Alaska and the Contiguous 48 States. | |
| Scale Up Low Risk |
The Project is using established equipment sizes. Equipment is identical to that used for Phase 1. | |
| Regulatory Issues Low Risk |
The Project is governed by established federal, state and local regulations. FERC issued its Authorization Order for the Phase 2 Expansion Project on June 15, 2006. | |
 |
B-10 | |||||
| Risk Component | Comment | |
| Environmental Issues Low Risk |
Stone & Webster Consultants’ review did not identify any environmental issues that would have an adverse effect on the Project cost, schedule or operation. | |
| Equator Principles Issues Low Risk |
The EA complies with the requirements of the Equator Principles. In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, compliance with State and Federal requirements will result in full compliance with the Equator Principles. | |
| Impact of Expansion on Phase 1 Low Risk |
There are no unmanageable potential impacts or conflicts between Phase 1 and the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion Project.
The Phase 2 Stage 1 expansion can be constructed, commissioned and operated without detriment to the Phase 1 facilities.
Significant care has been given to ensuring that the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion of Sabine Pass poses negligible risk to the timely completion and operation of the Phase 1 Project. | |
| Contracting Strategy and Project Execution Low to Medium Risk |
In general, Sabine has opted to contract with the same contractors and principal suppliers as used for the Phase 1 Project. Bechtel serves as the main EPCCm Contractor, Diamond-Zachry for the construction of the two new LNG storage tanks, and Recon for soils remediation.
In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, each of these firms has the requisite experience and capability to undertake the assigned role for the implementation of the Project. In addition, Stone & Webster Consultants confirms that this contracting strategy should minimize any conflict between like contractors on the two phases of the Project.
Sabine has selected a cost-reimbursable contracting philosophy for the majority of the Phase 2 Expansion Project that is designed to maximize its flexibility. A lump sum contract has been selected for the LNG tanks albeit with a labor escalation clause. Material costs were fixed following execution of the contract. These tanks are essentially identical to the three Phase 1 tanks. Zachry rather than Matrix is partnering with Diamond as the tank constructor.
In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, the contracting strategy is designed to ensure that the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion Project poses negligible risk to the timely completion and operation of the Phase 1 Project.
Sabine has established a dedicated Project Management Team. Sabine will also use Bureau Veritas and other contract personnel, term contract personnel, and possibly personnel from other EPC contractors to supplement the Project Management Team. These positions will be filled as needed as the Project execution progresses.
This organizational structure is typical for projects of this size and complexity, even by well-established major oil and gas corporations, due to previous downsizing. However, these PMT personnel have not previously worked together and will require a learning curve period before the team can efficiently and effectively oversee the various EPC Contractors and facilitate resolution of the detailed technical and execution queries that inevitably arise during execution of such a Project. This represents a medium risk to the Sponsors. | |
 |
B-11 | |||||
| Risk Component | Comment | |
| Project Schedule Low Risk |
Completion of the Phase-2 Expansion is not schedule-critical for Sabine’s debt holders. The 36-month schedule for Phase 2 is challenging but achievable. | |
| Capital Cost Low to Medium Risk |
The EPC Contract portion of the Phase 2 Project cost is being implemented under a reimbursable EPCCm contract with Bechtel and under fixed-price EPC Contracts with other contractors. In our opinion, the Owner’s Costs properly reflect the responsibilities and risks carried by the Owner. The Total Phase 2 Stage 1 Project Cost is currently budgeted to fall in the range of US$500 to US$550 million. Stone & Webster Consultants has reviewed the detailed build-up of both the EPC Contract Cost and the Owner’s Costs. In our opinion, based upon our benchmarking of this Capital Expenditure (“CAPEX”) against that of comparable projects, including the Phase 1 Project, the budget is reasonable. | |
| Operating Cost Low to Medium Risk |
Operations, maintenance and contract labor costs total US$10.0 million per annum. Other fixed operating costs amount to US$15.8 million per annum in the aggregate. Apportioned Cheniere G&A costs carried by the Project add $8.3 million, and the GE power generation maintenance expenses add a further US$4.6 million, bringing the total annual (Phase 1) O&M costs for year 2010 to US$38.7 million, a US$2.1 million increase over Phase 1. Note: fuel for regasification is provided by the Terminal Users. | |
| Interface with Existing Infrastructure Low Risk |
Tie-ins to the existing Phase 1 Project have been provided to minimize/eliminate tie-in issues. Expansion of the LNG Berths to accommodate larger LNG carriers is not on the critical path. It will be undertaken before mid-2007 and will not impact operation of the berths during Phase 1. | |
| Interface with Existing Infrastructure Low Risk |
Total and Chevron have contracted with the proposed Kinder Morgan LP (“KMLP”) pipeline for the transportation of their natural gas. Sabine will have unhindered access to the Cheniere Sabine Pass Pipeline, L.P. (“CSPP”) pipeline for export of gas from the facilities to service the Cheniere LNG Marketing TUA and for Phase 1 commissioning and performance testing, which will occur before the KMLP is commissioned. | |
| Logistics Low to Medium Risk |
The Expansion site has been provided with separate ingress and egress and separate laydown areas from the Phase 1 Project.
The Phase 1 Project and Phase 2 Expansion Project will share use of the common Construction Dock. Detailed planning will facilitate coordination of the use of this facility, but Phase 1 will always have priority access. A dedicated crane and crew will be provided at the Construction Dock to expedite access to all parties.
The Phase 1 Project is proving to be a preferred work location for local craft labor due to the duration of the combined Projects.
The time-lag between phases should facilitate Bechtel Home Office and construction labor moving from Phase 1 to the Phase 2 Project. | |
| Geography Medium Risk |
The site is located on the US Gulf coast in an area that is prone to hurricanes. The Phase 1 Project was affected by Hurricane Katrina and Rita during 2005. Primary risk pertains to the construction period when facilities are incomplete. |
 |
B-12 | |||||
3.0 PROJECT DESCRIPTION
3.1 Site
The Sabine Pass LNG plant site is situated on an area once utilized by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers as a depository for Sabine/Neches Waterway dredging spoils; hence the soils at the site require substantial remediation and enhancement.
3.2 Facilities
The Phase 1 Project consists of the following principal components:
| • | Marine receiving terminal capable of unloading two LNG carriers simultaneously. The marine terminal consists of two LNG carrier unloading docks, each capable of unloading an LNG carrier with cargo capacity in the range from 87,600 cubic meters to 250,000 cubic meters of LNG. The Sponsor anticipates that a 250,000 cubic meter LNG carrier will have a draft of 39.4 feet. The US Coast Guard (the “USCG”) states that the shipping channel is currently maintained at 40 feet of depth which is adequate to accommodate current LNG carriers, which have a maximum draft of approximately 37.4 feet. However, recent soundings tabulated by NOAA and data contained in the Vessel Maneuvering Simulation Study indicate channel depths of 42 feet, and that areas of the pass channel have depths of 45 feet. Sponsor will dredge the berth/terminal area to a depth of 45 feet below mean low water line plus two feet of over dredge. The deeper depth of the berths will permit Sabine to better monitor the rate of sedimentation accumulation to better plan future dredging operations.; |
| • | Three 160,000 cubic meter single containment LNG storage tanks. Each tank is designed for a working tank volume of 160,000 cubic meters, or approximately 1,006,400 barrels. This type of tank comprises an inner LNG containment tank fabricated from nine-percent nickel steel, suitable for the cryogenic storage temperature of approximately (-)260°F. The inner tank is then surrounded by an outer carbon steel tank, which retains the perlite insulation material, which is poured into the annular area between the two tank walls. Each LNG storage tank is enclosed within an individual earthen dike or berm designed to contain 110 percent of the maximum tank volume in the event of a tank rupture. In the U.S., this diked volume is a requirement of federal regulation 49CFR193, which is followed rigorously by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (“FERC”); |
| • | LNG circulation system to keep unloading systems cold between LNG shipments; |
| • | LNG tank and LNG carrier vapor handling systems ; |
| • | Storage tank boil-off gas compressors and re-condenser systems; |
| • | Three LNG in-tank transfer pumps in each tank. The sendout pumps will be multi-stage, seal-less vertical centrifugal pumps, with the entire pump and motor submerged in, in accordance with accepted industry practice; |
| • | Sixteen LNG high pressure export pumps submerged in a pumpout vessel supplied with the pump and Submerged Combustion Vaporizers (“SCV”). Each SCV is designed with an absorbed heat duty of approximately 116.0 MMBtu per hour, a well-proven capacity level. Vaporizers are essentially self-contained package units, complete with fully integrated burner management systems and safety interlocks. The SCV package also includes the electric motor-driven combustion air blower, which compresses air up to the submerged combustion pressure. SCVs are robust units, currently employed in approximately 75 percent of the world’s LNG regasification terminals, and thus represent very little risk; |
 |
B-13 | |||||
| • | Natural gas metering stations and export pipeline header; |
| • | Electric power generation and distribution. This comprises three LM 2500+ aeroderivative gas turbine driven generator sets, which are well-proven in the industry: |
| • | Utilities, infrastructure, and support facilities. |
The Phase 1 marine terminal consists of two LNG carrier unloading docks, each capable of unloading LNG carriers of between 87,600 cubic meters and 250,000 cubic meters of LNG storage capacity.
Phase 2 comprises the addition of:
| • | Modifications to the original berth design by adding approximately 100 feet of additional clearance at the stern of docked LNG carriers by replacing the rock rip-rap covered, sloped underwater shore with vertical bulkhead constructed using open-cell technology developed and patented by PND Incorporated (“PND”), headquartered in Anchorage, Alaska. |
| • | eight tandem vaporization units, each consisting of a high pressure send-out pump coupled to a SCV designed to vaporize approximately 180 MMscfd; |
| • | two additional 160,000 cubic meter LNG storage tanks; |
| • | a fourth GE (LM-2500+) gas turbine power generation unit; |
| • | a partial Ambient Air Vaporizer (“AAV”) train, consisting of 11 cells, to serve as a pilot testing facility. The use of AAV technology has potential operating cost reduction benefits in the summer months. A full AAV train comprises 33 cells and has a design vaporization capacity of 180 MMscfd. |
| • | a new Auxiliary Control Building; |
| • | a new electric power Substation; |
| • | a fourth instrument and utility air compression unit; |
| • | additional utilities and infrastructure facilities to support the overall expansion program; |
| • | additional tie-ins and other pre-investment work required to minimize potential construction and operations interferences due to the addition of the subsequent Phase 2 expansion stages. |
3.3 Operation
Pumps onboard an LNG carrier are used to unload LNG and transfer it to the storage tanks. As the LNG enters a storage tank, vapor in the tank is displaced. This cold vapor is returned to the LNG carrier to replace the equal volume of unloaded LNG and maintain constant pressure in both the tank and the carrier. This vapor is returned to the carrier via cryogenic blowers. Similarly, between LNG deliveries, a small amount of LNG will be circulated from the storage tanks through the carrier unloading lines to keep them at cryogenic unloading temperature. LNG is pumped from each storage tank by in-tank submerged transfer pumps. These discharge LNG from the tank at approximately 85 psig. Excess tank vapor is compressed to 85 psig. Vapor re-condensers then condense and re-absorb the compressed vapor into the pressurized LNG pumped from the tanks. Multi-stage export pumps boost the pressure of the LNG to 1550 psig. This high-pressure LNG is fed to submerged combustion vaporizers (“SCV”). Each pump feeds one SCV. A total of sixteen pump/vaporizer tandem sets are provided under Phase 1, each with a design export capacity of approximately 180 MMscfd. Achieved capacity depends on the LNG composition. A small amount of the vaporized export gas, less than two percent of the total capacity, will be consumed internally as fuel gas for the terminal. Export gas will be routed through a metering station into the main export pipeline header, which is connected to numerous natural gas distribution pipelines. All export pipeline infrastructure downstream of the metering station is to be supplied by others.
 |
B-14 | |||||
The Phase 1 Sabine Pass LNG Terminal will generate its own electric power from two operating General Electric (LM-2500+) gas turbine-driven generators plus one spare unit. Maximum expected power consumption is approximately 50 MW, compared to an installed capacity of 75 MW. Under Phase 2 a fourth LM-2500+ turbine-generator unit will be added. At the maximum peak export capacity of 4,000 MMscfd, three of the four generators will be required for full Terminal operations, with the fourth unit available as a stand-by spare.
4.1 Basis of Opinion
Stone & Webster Consultants’ evaluation of the current status of the Project is based on our review of the Phase 1 and Phase 2, December 2006 Monthly Progress Reports issued by Bechtel, and a site visit on January 18, 2007. Photographs taken during this site visit are included in Section 12 of this report.
4.2 Phase 1
Cumulative aggregate progress of the Phase 1 Project through the end of December 2006 was 68.2 percent compared to with planned progress of 69.3 percent. The Project has two near parallel critical paths, one relating to the LNG Tanks which has three days of float for LNG Tank 2 and the other relating to the power generation facilities which has nine days float. Progress on these two critical paths is such that Bechtel is expected to achieve the Target Bonus Date of April 3, 2008, which corresponds to completion of the main terminal and two of the three LNG Tanks and to a demonstrated export capacity of 2,000 MMscfd. The Base Milestone Schedule is based on the Target Bonus Date, which by definition began with zero days of float, where it currently remains. The Scheduled Substantial Completion Date which corresponds to completion of the entire terminal and demonstration of the maximum peak export capacity of 2,730 MMscfd, is currently scheduled for November 8, 2008, versus the Guaranteed Substantial Completion Date of December 20, 2008, which corresponds to 34 days of float. Therefore, the Project is currently proceeding in accordance with the Construction Budget and Schedule.
At the end of December 2006, engineering progress was 97.6 percent versus the baseline plan of 97.6 percent. Engineering will be completed once Substantial Completion is achieved and as-built drawings are developed. Procurement progress was 93.0 percent versus the plan of 93.0 percent. Construction progress was reported as 53.8 percent versus the plan of 55.6 percent. Construction progress during the last quarter of 2006 was adversely impacted by an unusual amount of rain which resulted in six lost work days. The lost work days could not be recovered by the end of December due to reduced manning during the Holiday Season. Stone & Webster Consultants notes that early January 2007 was also unusually wet, further impacting progress.
The full impacts of the 2005 hurricane season on Bechtel, the primary EPC Contractor, and the LNG tank and the marine terminal subcontractors were fully integrated into the schedule during November 2006. The Target Bonus Completion Date still remains as April 3, 2008, with zero days of float as noted above. The Guaranteed Substantial Completion Date has 34 days of positive float, indicating that this date will likely be achieved. Schedule Delay Liquidated Damages are associated with missing this contractual Milestone Date.
4.3 Phase 2 Stage 1
The Engineering teams are focused upon preparations for the first Phase 2 HAZOP Review to commence in mid-January, which will include all major facilities. However, there have been some delays in issuing piling construction drawings due to P&ID delays. The Procurement team issued commitments for large-bore welded stainless pipe and fittings, the Submerged Combustion Vaporizers, and Ambient Vaporizers in December. Purchase orders for the cryogenic LNG pumps will be awarded in January. The Phase 2 Project is currently undergoing soil stabilization and enhancement, and Bechtel and other Phase 2 contractors will be mobilizing to
 |
B-15 | |||||
the site over the next two months. The early construction management team has also mobilized to the site to oversee Recon’s Phase 2 site preparation work. Recon turned over the LNG Tank 4 site for pile driving and plans to turn over the LNG Tank 5 site in January. Pile driving has begun in one piperack area.
The overall Project Control Schedule has not yet been finalized so baseline progress curves have not yet been developed. Stone & Webster Consultants is somewhat concerned about this, since this was to have been finalized and accepted by all parties by the end of November 2006, in accordance with the Bechtel EPC Contract for Phase 2. According to the December Progress Report, the Project Control Schedule will be issued in January and the Control Estimate will be presented to Sabine by late February 2007.
5.1 Codes and Standards
In the Project documentation, the Sponsor required that all Project facilities are to be specified, engineered, procured, constructed, operated and maintained in accordance with all applicable Federal and state regulations and accepted industry practices and guidelines. The primary requirements for this federally regulated Project are mandated by the United States Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (“FERC”), which principally refer to 49 CFR 193 and NFPA 59A. These regulations are further augmented by the International Maritime Organization, Society of International Gas Tanker & Terminal Operators Ltd. (“SIGTTO”), and other applicable industry standards and codes which are required and incorporated by reference in the regulations and documents promulgated by these entities. The industry guideline adopted by SIGTTO is specifically referenced in the two Terminal Use Agreements (“TUA”) between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P and the Project’s anchor Customers, Total LNG USA, Inc. and Chevron USA Inc. Equipment provided under both Phase 1 and Phase 2 incorporates the latest technology updates with respect to high efficiency performance and low emissions. Thus the Project will represent little risk from an equipment performance and reliability perspective. Based on the foregoing requirements, in Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, the design is consistent with that of similar facilities within the United States and abroad and should result in an LNG terminal facility capable of fulfilling the commitments made under the TUAs.
5.2 Phase 1 Contracting Strategy
Cheniere contracted Bechtel to undertake the FEED for the Project. It pre-selected MHI/Matrix as the LNG Tank Subcontractor, Weeks Marine as the Marine Subcontractor, and Recon as the Soils Improvement Subcontractor. In addition, Cheniere limited bidding and negotiation on certain long-lead equipment to one or two vendors, including T-Thermal for the submerged combustion vaporizers, IHI for the boil-off gas compressor, and FMC and Connex SVT for the unloading arms. It then negotiated with Bechtel on an open-book estimate basis to provide a lump sum price for turnkey EPC Contract for the Project. Stone & Webster confirms that the selected subcontractors and equipment suppliers have the expertise and experience to perform the specified work or provide the equipment.
5.3 Phase 2 Contracting Strategy
Sponsor provided the following draft contracts and agreements for our review and comment:
| • | Reimbursable Bechtel EPCCm Contract,; |
| • | Fixed Price Diamond/Zachry EPC LNG Tank Contract; |
| • | Unit Rate Recon EPC Contract for Soils Improvement; |
All of these contracts were subsequently executed on July 21, 2006.
 |
B-16 | |||||
In addition, we reviewed the executed Willbros/CSPC EPC Contract for Cheniere Sabine Pass Pipeline Project, dated February 1, 2006.
Sabine executed a reimbursable EPCCm Contract with Bechtel that will provide engineering, procurement and construction management services together with direct hire construction services for those activities not provided by other contractors.
The reimbursable form of contract requires additional diligence and oversight by Sabine, especially when Phase 1 and Phase 2 work is being undertaken concurrently by the same contractor but paid under different compensation arrangements. Sabine issued its “Notice to Proceed” to Bechtel on July 26, 2006
The Phase 1 scope of work is proceeding under a fixed price, lump-sum turn key contract format. In contrast, the Phase 2 Project is being executed using a combination of individual reimbursable or unit rate contracts between Sabine and selected contractors and a reimbursable time and material contract with Bechtel responsible for all work not directly contracted by Sabine including detailed engineering, procurement and construction services. Bechtel will also serve as Sabine’s overall Construction Manager, in overseeing all contractors for the Phase 2 Expansion project. Under this arrangement Sabine retains total responsibility for risks associated with project scope and also assumes the risk for cost increases associated with labor productivity.
In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, Sabine has selected a contracting scheme that facilitates and complements its goal to minimize any interference between Phase 1 and Phase 2 activities. The contracting strategy recognizes the changes in the EPC contracting environment over the past two years, in particular the reluctance of contractors to bid large lump sum EPC contracts on the US Gulf Coast. Moreover, the contracting strategy also recognizes the benefits afforded under the Phase 1 lump sum contract by utilizing the same key contractors and vendors. The contracts reflect generally acceptable provisions and terms that do not impinge upon the Phase 1 Project. Overall, the Phase 2 contracting strategy provides Sabine with flexibility should it be necessary to change the mode or order in which the work is executed.
5.4 Foundations
The Sabine Pass LNG plant site is situated on an area once utilized by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers as a depository for Sabine River Channel dredging spoils. Dredged soils in the tank areas have been stabilized to a depth of 12 feet below grade. All foundations for major equipment and structures, including the LNG storage tanks, LNG process equipment, pipe racks and marine terminal equipment, are piled. Project specifications required field testing of at least four piles per tank that support the LNG storage tank foundation. Final pile design for the tank foundation piles was determined from these test results.
5.5 Implications of Phase 2 on the Phase 1 Project
Management and co-ordination of the Phase 1 Project and the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion Project present challenges that can be met by careful early planning and diligent attention to execution. Accordingly, Sabine and Bechtel have developed procedures and execution plans that address potential interferences or conflicts between the two projects. The potential adverse effect of the Phase 2 Expansion on the Phase 1 Project is mitigated substantially by the one-year lag between the two Project schedules. Essentially all Phase 1 engineering, procurement, and initial construction activities will be completed before those for Phase 2 commence. Sabine has performed a comprehensive scheduling analysis of the common utilization of the full-time crew and crane at the Construction Dock. This analysis indicates no unmanageable conflicts. Sabine represents that it will provide an experienced and adequately staffed Project Management Team and supporting Owner’s Engineer personnel to properly oversee Bechtel and the other Expansion Project contractors. Sabine and Bechtel will provide a user-friendly, logic-linked Critical Path Method (“CPM”) control schedule as quickly as practical to allow detailed
 |
B-17 | |||||
planning especially of tie-ins to the Phase 1 facilities, as well as common use of the Construction Dock and public access roads by all parties, including the two export pipeline projects. Stone & Webster Consultants confirms that this is consistent with good industry practice.
Sabine and Bechtel have implemented enhanced compensation programs to attract and retain skilled construction craft labor for both Projects. Should competition with outside projects drawing on the same labor resource create overall labor shortages at the Sabine site, Phase 1 will have absolute priority to available labor resources. Sabine plans to hire extra operations personnel on a term-contract basis to satisfy operations requirements of both Phases. The term-contract personnel will be released upon achievement of full operational status for the entire expanded facility. Total and Chevron have contracted to use the proposed KMLP pipeline for the transportation of their natural gas, thus completely freeing up the CSPP pipeline for unhindered access by Sabine for commissioning, performance testing of both Phase 1 and Phase 2, and for normal operation of the Phase 2 Stage 1 facilities in servicing the Cheniere TUA export volumes.
Given these scenarios and the overall Phase 2 Stage 1 Project Execution Plan, in Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, there are no unmanageable potential impacts, interferences or conflicts between the Phase 1 Project and the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion Project in terms of engineering, procurement, construction, commissioning, and performance testing, nor in terms of the achievement and continuation of normal operational status.
6.1 Phase 1 Budget
The EPC Contract portion of the Phase 1 Project cost is being implemented under a LSTK contract with Bechtel. In our opinion, the Owner’s Costs properly reflect the responsibilities and risks carried by the Owner. The Total Phase 1 Project Costs is currently budgeted to fall in the range of US$900 to US$950 million. Stone & Webster Consultants has reviewed the detailed build-up of both the EPC Contract Cost and the Owner’s Costs. In our opinion, based upon our benchmarking of this CAPEX budget against comparable projects, the budget is reasonable.
6.2 Phase 2 Budget
The EPC Contract portion of the Phase 2 Project cost is being implemented under a reimbursable EPCCm contract with Bechtel and under fixed-price EPC Contracts with other contractors. In our opinion, the Owner’s Costs properly reflect the responsibilities and risks carried by the Owner. The Total Phase 2 Stage 1 Project Cost is currently budgeted to fall in the range of US$500 to US$550 million. Stone & Webster Consultants has reviewed the detailed build-up of both the EPC Contract Cost and the Owner’s Costs. In our opinion, based upon our benchmarking of this CAPEX budget against comparable projects, including the Phase 1 Project, the budget is reasonable.
7.1 Phase 1
The Force Majeure impacts from the hurricanes, resulting in extension of the Guaranteed Substantial Completion Date from September 2, 2008 to December 20, 2008, have been incorporated into the updated Level III CPM Schedule. The revised key contractual Project Milestone dates are summarized below in Table 7.1-1.
Bechtel’s primary critical path runs through the LNG Storage tanks, with RFCD of LNG Tank 2 scheduled for March 21, 2008, with zero float. A near parallel secondary critical path runs through startup of the power generation facilities, which is scheduled for September 13, 2007. This activity currently has nine days of positive float. This means that the actual startup of these facilities can still slip 9 working days without impacting
 |
B-18 | |||||
achievement of the Target Bonus Date. Timely startup of the power generation facilities is essential to Bechtel being able to pre-commission and commission the entire terminal. The scheduled Target Bonus Date of April 3, 2008 continues to indicate zero days of float, as this was the original reference point for the development of the Milestone Schedule. However, the days of float for this reference Milestone Date can change as other milestones experience acceleration or deceleration. In Stone & Webster Consultants opinion, field construction is being undertaken in a well-managed and proactive manner. Once engineering and procurement constraints are removed, Stone & Webster Consultants expects actual construction progress to generate float and achieve the Target Bonus Date of April 3, 2008
Table 7.1-1
Scheduled Key Milestone Dates
| Milestone Description | EPC Contract Basis | Early Finish | Late Finish | |||
| FERC Approval | Condition Precedent | Dec 21, 2004 | Completed | |||
| Limited Notice to Proceed (LNTP) | On or Before Jan 4, 2005 | Jan 4, 2005 | Completed | |||
| Notice to Proceed (NTP) | Min 90 days after LNTP | April 4, 2005 | Completed | |||
| Approved Perf. Test Procedures | By 24 Months after NTP | April 4, 2007 | April 4, 2007 | |||
| Submit Target Bonus Test Procedures | Jan. 7, 2008 | Jan. 18, 2008 | ||||
| Ready For Cool Down System #1 | Terminal plus Tank No.1 | Feb 18, 2008 | Feb 28, 2008 | |||
| Ready For Cool Down System #2 | LNG Tank No.2 | March 21, 2008 | March 25, 2008 | |||
| Target Bonus Date (2000 MMscfd) | 1095 days after NTP | April 3, 2008 | April 3, 2008 | |||
| Ready For Cool Down System #3 | LNG Tank No.3 | July 1, 2008 | Sept. 5, 2008 | |||
| Ready For Performance Testing | July 18, 2008 | July 18, 2008 | ||||
| Substantial Completion | Sept 2, 2008 | Nov. 8, 2008 | ||||
| Guaranteed Substantial Completion | 1355 days after NTP | Nov. 8, 2008 | Dec. 20, 2008 | |||
| Final Completion (EPC Contract) | Max 90 days after SC | Dec. 10, 2008 | Feb. 12, 2009 | |||
| Total TUA Commences | Total TUA Agreement | April 1, 2009 | April 1, 2009 | |||
| Chevron TUA Commences | Chevron TUA | February 1, 2009 | July 1, 2009 |
7.2 Phase 2
Start-up and commissioning of the Phase 2 Expansion facilities are scheduled for the second quarter of 2009 based on an overall construction duration of 36 months from an Effective Date of July 26, 2006. While this duration would be considered overly optimistic for a new grass-roots facility, in Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, it is aggressive but achievable for the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion Project, recognizing that the commercial negotiations and design for the major equipment has already been concluded. This notwithstanding, the construction period for the LNG tanks does not contain excessive float and is not overly generous. Sabine and Bechtel will develop a rigorous, logic-linked, Critical Path Method (“CPM”) control schedule within 120 days after NTP. The CPM schedule will allow detailed planning of tie-ins to the Phase 1 facilities and evaluation of access to the site by all parties, including the two export pipeline projects.
 |
B-19 | |||||
Stone & Webster Consultants has reviewed the environmental and regulatory information provided to us by Sabine pertaining to the Phase 2 Expansion, most of which is contained in Sabine’s FERC application. FERC has issued its permit to construct the Phase 2 Expansion. In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, Sabine should be able to obtain the requisite supplementary permits and other regulatory authorizations for the Phase 2 Expansion Project without significant impacts upon either the Phase 1 Project or to the Phase 2 Expansion Project costs or schedule. The expanded facilities will comply with the Equator Principles.
9.0 OPERATIONS & MAINTENANCE PROGRAMS
9.1 Expanded Terminal O&M Costs
During the Phase 2 due diligence, Stone & Webster Consultants and Sabine mutually agreed on an operations and maintenance budget for the expanded, Phase 1 plus Phase 2 LNG Terminal, which is summarized in Table 9.1-1. These O&M Expenses were duplicated in the original due diligence Financial Models. The entries reflect those costs and expenses expected during the first full TUA Contract Year of operations, 2010.
Table 9.1-1
LNG Terminal O&M Expenses
Contract Year 2010
| O&M Expense Description | 2,000 MMscfd US$ Million |
4,000 MMscfd US$ Million | ||
| Operations, Maintenance & Contract Labor Costs |
10.0 | 10.0 | ||
| Other Fixed Operations and Maintenance Costs |
14.5 | 15.2 | ||
| Subtotal Fixed O&M Costs |
24.5 | 25.2 | ||
| Fixed Opex Contingency Allowance @ 2.5 percent |
0.6 | 0.6 | ||
| Total Annual Fixed O&M Costs |
25.1 | 25.8 | ||
| Annual G&A Costs (Sabine Management & O&M Agreements) |
8.3 | 8.3 | ||
| Annual GE Power Generation Long-term Maintenance Expenses |
3.2 | 4.6 | ||
| Total Operations & Maintenance Expenses for Year 2010 |
36.6 | 38.7 |
9.2 Terminal Operational Issues
Based upon all information available, Lanier, an outside marine consultant, concluded in its Marine Traffic Study that the infrastructure of the Sabine-Neches Waterway, coupled with projected staffing increases by the Sabine Pilots Association, would be adequate to handle all of the ship traffic increases projected over the next ten years, including the addition of the three new LNG terminals currently planned by other developers along the Sabine-Neches Waterway. Stone & Webster Consultants concurs with this assessment.
The Phase 1 due diligence effort and the two primary TUAs were based on the assumption that Sabine would receive LNG deliveries by carriers averaging 140,000 cubic meters in size. In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, an average unloading time of 30 hours per LNG carrier is sufficient. This unloading time is supported by shipping simulation study results obtained from software provided to Sabine by an outside shipping consultant. This unloading time results in a total unloading time of 14,160 hours shared between the two berths, which in turn results in 2,880 hours of slack time between the two berths. This is quite reasonable, assuming the average LNG carrier size is 140,000 cubic meters. However, the bulk of the current LNG carrier fleet ranges between 125,000 and 140,000 cubic meters in size. Assuming half of the deliveries were to arrive by 125,000
 |
B-20 | |||||
cubic meter carriers and half by 140,000 carriers, the total number of deliveries would be approximately 500. Assuming the same unloading time of 30 hours each results in a cumulative unloading time of 15,000 hours. The available slack time for this scenario would be 2,040 hours for a utilization percentage of 88 percent, which is also acceptable. Therefore, in Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, the marine unloading facilities as currently designed are more than adequate to support the 2,000 MMscfd of capacity held by the two primary TUA Customers. The facilities also appear to be adequate to support the Sabine Pass LNG Terminal expansion to its peak export capacity 4,000 MMscfd, given that a number of recently ordered LNG carriers are around the 250,000 cubic meter capacity for which the marine terminal is designed.
Sabine’s plan calls for up to fifteen of the pump/vaporizer tandem units to operate at peak capacity, with at least one unit remaining idle as a spare. However, only twelve SCVs are required to meet the combined average demand of the two primary TUA Customers, or 2,000 MMscfd.
In Stone & Webster Consultant’s opinion, one single spare vaporization tandem unit is insufficient to claim a continuous vaporization capacity of 4,000 MMscfd of gas for the expanded facilities. Sabine has not yet commissioned a comprehensive RAM analysis to determine the expected overall availability of the expanded facilities. Therefore, Stone & Webster Consultants determined its own estimate of the availability of the expanded facilities to be a sustained export capacity of approximately 3,500 to 3,600 MMscfd, corresponding to 20 of 24 installed SCVs in operation. Therefore, in Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, Sabine will be able to demonstrate the necessary performance level to service the two primary TUA Customers.
Stone & Webster Consultants is of the opinion that the addition of the fourth power generation unit will cover the power consumption requirements of the Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion Project, such that three units will cover operations with the fourth unit as a stand-by spare. In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, the proposed power generation facilities for the Phase 2 Expansion Project will provide a reliable system that will meet all potential Project performance expectations.
The responsibility for providing pipeline interconnections between the terminal and the existing export natural gas pipeline grid system rests solely with each of the respective Customers of the Sabine Pass LNG Terminal. CSPP has received FERC authorization to construct the CSPP pipeline with an authorized capacity of 2,600 MMscfd. However, Total and Chevron both have indicated that they instead plan to export gas via a new KMLP pipeline, and they are responsible for ensuring that the KMLP will be operational when the two primary TUAs commence operations. CSPP has executed a contract with Willbros Group, Inc. to have the CSPP installed and ready for service by the end of July, 2007. Timely completion of this pipeline is essential to achievement of the Target Bonus Date as this pipeline will deliver the natural gas fuel for the power generation units, which must be fully operational in early September. The scheduled Target Bonus Date for the Phase 1 Sabine Pass LNG Terminal Project is April 3, 2008, so the CSPP should be available to the Project in sufficient time for commissioning and testing under the Bechtel EPC Contract for EPC Contract completion and testing of the Phase 1 Project.
Stone & Webster Consultants has reviewed the proposed OPEX for the combined Phase 1 and Phase 2 Stage 1 facilities. In our opinion, a reasonable level of OPEX has been established by Sabine for the expanded terminal.
10.1 TUAs
Stone & Webster Consultants has reviewed the Total and Chevron TUAs that form the financial foundation of the Project, the respective executed TUA-associated Omnibus Agreements and the executed EPC Contract for Phase 1, dated December 18, 2004.
 |
B-21 | |||||
Under each of the TUAs, the fees to be paid to Sabine include a Fixed Component Fee, set at US$0.28 per MMBtu of LNG received and is fixed for the 20-year term of the TUA. The FOC Component Fee, designed to partially reimburse Sabine for fixed operating costs, is set initially at US$0.04 per MMBtu, but it is subject to escalation according to the U.S. Consumer Price Index. Also, Sabine is entitled to 2.0 percent of the LNG received for internal terminal energy consumption, primarily for vaporizer and power generation fuel. Stone & Webster Consultants confirms that this should be ample to cover the anticipated consumption. All third-party marine terminal expenses (tug boats and line service boats, etc.) can be passed through 100 percent to the Customers, and the Customers are also obligated to pay a portion of the terminal taxes in addition to the fixed fees. Overall, in Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion, the TUA fee structure is favorable to the Sponsor, in that payment is due in general terms regardless of terminal throughput, with little risk in terms of Force Majeure and Termination. .
An Omnibus Agreement forms an addendum to each TUA, and provides in each case for early payments, termed Capacity Reservation Fees, of the Fixed Component of the Reservation Fee. These provisions call for Total and Chevron to make US$20.0 million payments to the Sponsor that will be recouped through a monthly reduction in the Fixed Component Fee equal to US$166,667 per month (US$2 million per annum for each) for the first ten years of primary TUA operations.
10.2 Phase 1 EPC Contract
Stone & Webster Consultants reviewed the executed EPC Contract, including the Attachments and Schedules. In our opinion, the EPC Contract generally conforms to the structure, format, and content of basic engineering, procurement and construction contracts utilized for the design and construction of facilities of this type.
The Contractor must maintain a Letter of Credit, valued at ten percent of the Contract Price. Upon achievement of Substantial Completion, the value is reduced to five percent, and the LOC is retired completely at the end of the Defects Correction Period, which ends eighteen months following Substantial Completion. These provisions, in general, provide favorable protection against EPC Contractor non-performance during the construction and warranty periods.
As noted previously, the current EPC Contract schedule is based on a 44-month duration, which Stone & Webster Consultants considered to be reasonable. Most schedules for similar facilities range from 37 to 45 months. Even though the Contract provides for Delay Liquidated Damages of up to 10 percent of the Contract Price, robust for a facility of this type, Stone & Webster Consultants sees little likelihood that Delay Liquidated Damages will require enforcement. Performance Liquidated Damages are specified with a maximum liability of up to 10 percent of the Contract Price for Sendout Rate Performance deficiency and up to two percent for Ship Unloading Time deficiency. The aggregate Performance Liquidated Damages are limited to 10 percent. Thus the Contactor is obligated for a maximum Liquidated Damages liability of 20 percent of the Contract Price.
Total Phase 1 EPC Contract maximum liability is limited to 30 percent; however, the Contractor is obligated for much higher liability in the requirement to demonstrate operational capability of all facilities prior to formal Performance Testing, all of which, taken together, constitute favorable protection. Overall, Stone & Webster considers that the terms of the EPC Contract are reasonable and properly place the responsibility for the timely completion and technical performance of the Project on the general EPC Contractor.
 |
B-22 | |||||
In Stone & Webster Consultants’ opinion:
| • | The Phase 1 Project is technically viable; |
| • | The Phase 1 Project Budget is reasonable; |
| • | The Phase 1 Schedule is reasonable; |
| • | The Phase 1 Project has been approved by FERC, indicating compliance with environmental regulations and that environmental risks are low; |
| • | The Phase 1 Project contracting strategy is reasonable and minimizes the strain on a start-up company; |
| • | The Phase 1 EPC contract provides a suitable basis for contracting the required services; |
| • | The Phase 1 Project will provide ample availability to service the required 2,000 MMscfd export capacity requirements of the two primary TUA customers; |
| • | The Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion of Sabine Pass poses negligible risk to the timely completion and operation of the Phase 1 Project; |
| • | The Phase 2 Stage 1 Expansion is technically feasible and viable; |
| • | The Phase 2 Stage 1 Budget is reasonable and generally consistent with that for the Phase 1 Project; |
| • | The Phase 2 Stage 1 Schedule is reasonable; |
| • | The Phase 2 Project has been approved by FERC, indicating compliance with environmental regulations and that environmental risks are low; |
| • | The Phase 2 Stage 1 Project contracting strategy provides the Company with maximum flexibility in Phase 2 Project execution; |
| • | The Phase 2 Stage 1 construction contracts provide a suitable basis for contracting the required services without impinging on the Phase 1 Project interests; and |
| • | The Phase 2 Stage 1 Project will in effect increase the overall export capacity to a maximum peak rate of 4,000 MMscfd and a long-term sustainable capacity of at least 3,500 MMscfd. |
 |
B-23 | |||||
Stone & Webster Consultants took the following site photographs during a site visit to the Terminal on January 18, 2007.
East Marine Berth

 |
B-24 | |||||
LNG Tanks Nos 1 through 3

 |
B-25 | |||||
LNG Tank No. 1

 |
B-26 | |||||
LNG Tank No. 1 Roof

 |
B-27 | |||||
Submerged Combustion Vaporizers

 |
B-28 | |||||
SCV Area Piperack

 |
B-29 | |||||
Pipeway from Marine Terminal

 |
B-30 | |||||
West Marine Berth

 |
B-31 | |||||
Administration Building

 |
B-32 | |||||
12,500,000 Common Units
Representing Limited Partner Interests
Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P.

P R O S P E C T U S
, 2007
Citigroup
Merrill Lynch & Co.
Credit Suisse
Until , 2007 (25 days after the date of this prospectus), all dealers that buy, sell or trade our common units, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This is in addition to the dealers’ obligation to deliver a prospectus when acting as underwriters and with respect to their unsold allotments or subscriptions.
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Set forth below are the expenses (other than underwriting discounts and commissions) expected to be incurred in connection with the issuance and distribution of the securities registered hereby. With the exception of the Securities and Exchange Commission registration fee, the NASD filing fee, the amounts set forth below are estimates.
| SEC registration fee |
$ | 32,301 | |
| NASD filing fee |
30,688 | ||
| American Stock Exchange listing fee |
70,000 | ||
| Printing and engraving expenses |
585,000 | ||
| Fees and expenses of legal counsel |
2,250,000 | ||
| Accounting fees and expenses |
140,000 | ||
| Transfer agent and registrar fees |
2,500 | ||
| Miscellaneous |
200,000 | ||
| Total |
$ | 3,310,489 | |
| * | To be provided by amendment. |
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers
The section of the prospectus entitled “The Partnership Agreement—Indemnification” discloses that we will generally indemnify officers, directors and affiliates of our general partner to the fullest extent permitted by the law against all losses, claims, damages or similar events and is incorporated herein by this reference. Reference is also made to Section 8 of the form of Underwriting Agreement to be filed as an exhibit to this registration statement in which we and our affiliates will agree to indemnify the underwriters against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and to contribute to payments that may be required to be made in respect of these liabilities. Subject to any terms, conditions or restrictions set forth in the partnership agreement, Section 17-108 of the Delaware Revised Uniform Limited Partnership Act empowers a Delaware limited partnership to indemnify and hold harmless any partner or other person from and against all claims and demands whatsoever.
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities.
On November 21, 2006, in connection with the formation of the partnership, Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. issued (1) to Cheniere LNG Holdings, LLC the 98% limited partner interest in the partnership for $980 and (2) to Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC the 2% general partner interest in an offering exempt from registration under Section 4(2) of the Securities Act. There have been no other sales of unregistered securities within the past three years.
Item 16. Exhibit and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) The following documents are filed as exhibits to this registration statement.
| Exhibit No. |
Description | ||
| 1.1 | ** | Form of Underwriting Agreement. | |
| 3.1 | + | Certificate of Limited Partnership of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. | |
| 3.2 | * | Form of First Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. (included as Appendix A to the Prospectus). | |
II-1
| Exhibit No. |
Description | ||
| 3.3 | + | Certificate of Formation of Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC. | |
| 3.4 | * | Form of Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC. | |
| 4.1 | Indenture, dated as of November 9, 2006, by and between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., as issuer, and The Bank of New York, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 4.2 | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of November 9, 2006, by and among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC, as representative of the several initial purchasers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 4.3 | Form of 7.25% Senior Secured Note due 2013 (included as Exhibit A1 to Exhibit 4.1 above). | ||
| 4.4 | Form of 7.50% Senior Secured Note due 2016 (included as Exhibit A1 to Exhibit 4.1 above). | ||
| 4.5 | * | Form of common unit certificate (attached as Exhibit A to the Partnership Agreement included as Appendix A to the Prospectus). | |
| 5.1 | * | Form of Opinion of Andrews Kurth LLP as to the legality of the securities being registered. | |
| 8.1 | * | Form of Opinion of Andrews Kurth LLP relating to tax matters. | |
| 10.1 | Collateral Trust Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee, Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.2 | Amended and Restated Parity Lien Security Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.3 | Third Amended and Restated Multiple Indebtedness Mortgage, Assignment of Rents and Leases and Security Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, between the Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.4 | Amended and Restated Parity Lien Pledge Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc., Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC and The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.5 | Security Deposit Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee, and The Bank of New York, as depositary agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.6 | State Tax Sharing Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and between Cheniere Energy, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.7 | Amended and Restated Terminal Use Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and between Cheniere Marketing, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
II-2
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 10.8 | Guarantee Agreement, dated as of November 9, 2006, by Cheniere Energy, Inc. in favor of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | |
| 10.9 | Letter Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and among Cheniere Marketing, Inc., Cheniere LNG, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. in favor of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | |
| 10.10 | LNG Terminal Use Agreement, dated November 8, 2004, by and between Chevron U.S.A. Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.11 | Omnibus Agreement, dated November 8, 2004, by and between Chevron U.S.A. Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.12 | Guaranty Agreement, dated December 15, 2004, from ChevronTexaco Corporation to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (SEC File No. 333-138916), filed on November 22, 2006). | |
| 10.13 | Amendment to LNG Terminal Use Agreement, dated December 1, 2005, by and between Chevron USA, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (SEC File No. 333-138916), filed on November 22, 2006). | |
| 10.14 | LNG Terminal Use Agreement, dated September 2, 2004, by and between Total LNG USA, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.15 | Amendment of LNG Terminal Use Agreement, dated January 24, 2005, by and between Total LNG USA, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.40 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on March 10, 2005). | |
| 10.16 | Omnibus Agreement, dated September 2, 2004, by and between Total LNG USA, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.17 | Guaranty, dated as of November 9, 2004, by Total S.A. in favor of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.18 | Operation and Maintenance Agreement, dated February 25, 2005, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on March 2, 2005). | |
| 10.19 | Management Services Agreement, dated February 25, 2005, between Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on March 2, 2005). | |
| 10.20 | Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement, dated December 18, 2004, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on December 20, 2004). | |
| 10.21 | Change Orders 1 through 27 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004 between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on March 3, 2006). | |
II-3
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 10.22 | Change Orders 28, 29 and 31 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004 between Sabine Pass LNG, L. P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on May 5, 2006). | |
| 10.23 | Change Orders 30, 32 and 33 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004 between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on August 4, 2006). | |
| 10.24 | Change Orders 34, 35, 36, 37 and 38 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 6, 2006). | |
| 10.25 | Agreement for Engineering, Procurement, Construction and Management of Construction Services for the Sabine Phase 2 Receiving, Storage and Regasification Terminal Expansion, dated July 21, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on August 4, 2006). | |
| 10.26 | Change Order 1 to Agreement for Engineering, Procurement, Construction and Management of Construction Services for the Sabine Phase 2 Receiving, Storage and Regasification Terminal Expansion, dated July 21, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 6, 2006). | |
| 10.27 | Engineer, Procure and Construct (EPC) LNG Tank Contract, dated July 21, 2006, among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., Zachry Construction Corporation and Diamond LNG LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on August 4, 2006). | |
| 10.28 | Engineer, Procure and Construct (EPC) LNG Unit Rate Soil Contract, dated July 21, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Remedial Construction Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on August 4, 2006). | |
| 10.29* | Management Services Agreement, dated September 1, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc. | |
| 10.30* | Form of Services Agreement between Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. and Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc. | |
| 10.31* | Form of Services and Secondment Agreement between Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P. and Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC. | |
| 10.32* | Form of Contribution and Conveyance Agreement. | |
| 10.33* | Form of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan. | |
| 10.34+ | Change Order 39 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation. | |
| 10.35 | Change Order 40 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 11, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.31 to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.’s Registration Statement on Form S-4/A (SEC File No. 333-138916), filed on January 10, 2007). | |
II-4
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 10.36+ | Change Order 41 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 11, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation. | |
| 10.37+ | Settlement and Purchase Agreement dated as of June 14, 2001, by and among Cheniere Energy, Inc., CXY Corporation, Crest Energy, L.L.C., Crest Investment Company and Freeport LNG Terminal, LLC, and two related letter agreements, each dated February 27, 2003. | |
| 10.38 | Letter regarding Assumption and Adoption of Obligations under Settlement and Purchase Agreement, dated May 9, 2005, and Indemnification Agreement, dated May 9, 2005, by Cheniere Energy, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.29 to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.’s Registration Statement on Form S-4/A (SEC File No. 333-138916), filed on January 10, 2007). | |
| 10.39* | Form of Restricted Units Agreement for employees, consultants and directors (three-year). | |
| 10.40* | Form of Restricted Units Agreement for employees, consultants and directors (four-year). | |
| 10.41* | Form of Director Units Option Agreement for employees and consultants (four-year). | |
| 10.42* | Form of Units Option Agreement for employees and consultants (three-year). | |
| 10.43* | Form of Units Option Agreement for employees and consultants (four-year). | |
| 21.1+ | List of Subsidiaries of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. | |
| 23.1* | Consent of UHY LLP. | |
| 23.2* | Consents of Andrews Kurth LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1 and Exhibit 8.1). | |
| 23.3* | Consent of Stone & Webster Management Consultants, Inc. | |
| 23.4+ | Consent of Lon McCain to be named as a director. | |
| 23.5* | Consent of Robert J. Sutcliffe to be named as a director. | |
| 24.1+ | Powers of Attorney (included in signature pages). | |
| 24.2+ | Power of Attorney of Meg Gentle. | |
| + | Previously filed |
| * | Filed herewith |
| ** | To be filed by amendment. |
Item 17. Undertakings
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes to provide to the underwriters at the closing specified in the underwriting agreement certificates in such denominations and registered in such names as required by the underwriters to permit prompt delivery to each purchaser.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Registrant pursuant to the provisions described in Item 14 above, or otherwise, the Registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the Registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the Registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the Registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
II-5
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes that:
(1) For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this Registration Statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the Registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this Registration Statement as of the time it was declared effective; and
(2) For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at the time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
The registrant undertakes to send to each limited partner at least on an annual basis a detailed statement of any transactions with Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC or its affiliates, and of fees, commissions, compensation and other benefits paid, or accrued to Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC or its affiliates for the fiscal year completed, showing the amount paid or accrued to each recipient and the services performed.
The registrant undertakes to provide to the limited partners the financial statements required by Form 10-K for the first full fiscal year of operations of the partnership.
II-6
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, the Registrant has duly caused this Registration Statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Houston, State of Texas, on February 14, 2007.
| CHENIERE ENERGY PARTNERS, L.P. | ||
| By: |
Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC, its general partner | |
| By: |
/S/ DON A. TURKLESON | |
| Name: | Don A. Turkleson | |
| Title: | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this Registration Statement has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the general partner of the Registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| * Charif Souki |
Director, Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
February 14, 2007 | ||
| * Stanley C. Horton |
Director, President and Chief Operating Officer |
February 14, 2007 | ||
| /S/ DON A. TURKLESON Don A. Turkleson |
Director, Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
February 14, 2007 | ||
| * Meg Gentle |
Director |
February 14, 2007 | ||
| * Keith M. Meyer |
Director |
February 14, 2007 | ||
| *By: | /s/ DON A. TURKLESON | |
| Don A. Turkleson Attorney-in-Fact | ||
II-7
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit No. |
Description | ||
| 1.1 | ** | Form of Underwriting Agreement. | |
| 3.1 | + | Certificate of Limited Partnership of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. | |
| 3.2 | * | Form of First Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. (included as Appendix A to the Prospectus). | |
| 3.3 | + | Certificate of Formation of Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC. | |
| 3.4 | * | Form of Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC. | |
| 4.1 | Indenture, dated as of November 9, 2006, by and between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., as issuer, and The Bank of New York, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 4.2 | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of November 9, 2006, by and among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC, as representative of the several initial purchasers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 4.3 | Form of 7.25% Senior Secured Note due 2013 (included as Exhibit A1 to Exhibit 4.1 above). | ||
| 4.4 | Form of 7.50% Senior Secured Note due 2016 (included as Exhibit A1 to Exhibit 4.1 above). | ||
| 4.5 | * | Form of common unit certificate (attached as Exhibit A to the Partnership Agreement included as Appendix A to the Prospectus). | |
| 5.1 | * | Form of Opinion of Andrews Kurth LLP as to the legality of the securities being registered. | |
| 8.1 | * | Form of Opinion of Andrews Kurth LLP relating to tax matters. | |
| 10.1 | Collateral Trust Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee, Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.2 | Amended and Restated Parity Lien Security Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.3 | Third Amended and Restated Multiple Indebtedness Mortgage, Assignment of Rents and Leases and Security Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, between the Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.4 | Amended and Restated Parity Lien Pledge Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc., Sabine Pass LNG-LP, LLC and The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.5 | Security Deposit Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., The Bank of New York, as collateral trustee, and The Bank of New York, as depositary agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| 10.6 | State Tax Sharing Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and between Cheniere Energy, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | ||
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 10.7 | Amended and Restated Terminal Use Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and between Cheniere Marketing, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | |
| 10.8 | Guarantee Agreement, dated as of November 9, 2006, by Cheniere Energy, Inc. in favor of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | |
| 10.9 | Letter Agreement, dated November 9, 2006, by and among Cheniere Marketing, Inc., Cheniere LNG, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. in favor of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 16, 2006). | |
| 10.10 | LNG Terminal Use Agreement, dated November 8, 2004, by and between Chevron U.S.A. Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.11 | Omnibus Agreement, dated November 8, 2004, by and between Chevron U.S.A. Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.12 | Guaranty Agreement, dated December 15, 2004, from ChevronTexaco Corporation to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (SEC File No. 333-138916), filed on November 22, 2006). | |
| 10.13 | Amendment to LNG Terminal Use Agreement, dated December 1, 2005, by and between Chevron USA, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (SEC File No. 333-138916), filed on November 22, 2006). | |
| 10.14 | LNG Terminal Use Agreement, dated September 2, 2004, by and between Total LNG USA, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.15 | Amendment of LNG Terminal Use Agreement, dated January 24, 2005, by and between Total LNG USA, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.40 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on March 10, 2005). | |
| 10.16 | Omnibus Agreement, dated September 2, 2004, by and between Total LNG USA, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.17 | Guaranty, dated as of November 9, 2004, by Total S.A. in favor of Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 15, 2004). | |
| 10.18 | Operation and Maintenance Agreement, dated February 25, 2005, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on March 2, 2005). | |
| 10.19 | Management Services Agreement, dated February 25, 2005, between Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on March 2, 2005). | |
| 10.20 | Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement, dated December 18, 2004, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on December 20, 2004). | |
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 10.21 | Change Orders 1 through 27 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004 between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on March 3, 2006). | |
| 10.22 | Change Orders 28, 29 and 31 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004 between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on May 5, 2006). | |
| 10.23 | Change Orders 30, 32 and 33 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004 between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on August 4, 2006). | |
| 10.24 | Change Orders 34, 35, 36, 37 and 38 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 6, 2006). | |
| 10.25 | Agreement for Engineering, Procurement, Construction and Management of Construction Services for the Sabine Phase 2 Receiving, Storage and Regasification Terminal Expansion, dated July 21, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on August 4, 2006). | |
| 10.26 | Change Order 1 to Agreement for Engineering, Procurement, Construction and Management of Construction Services for the Sabine Phase 2 Receiving, Storage and Regasification Terminal Expansion, dated July 21, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on November 6, 2006). | |
| 10.27 | Engineer, Procure and Construct (EPC) LNG Tank Contract, dated July 21, 2006, among Sabine Pass LNG, L.P., Zachry Construction Corporation and Diamond LNG LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on August 4, 2006). | |
| 10.28 | Engineer, Procure and Construct (EPC) LNG Unit Rate Soil Contract, dated July 21, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Remedial Construction Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Cheniere Energy, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (SEC File No. 001-16383), filed on August 4, 2006). | |
| 10.29* | Management Services Agreement, dated September 1, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG-GP, Inc. and Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc. | |
| 10.30* | Form of Services Agreement between Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. and Cheniere LNG Terminals, Inc. | |
| 10.31* | Form of Services and Secondment Agreement between Cheniere LNG O&M Services, L.P. and Cheniere Energy Partners GP, LLC. | |
| 10.32* | Form of Contribution and Conveyance Agreement. | |
| 10.33* | Form of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan. | |
| 10.34+ | Change Order 39 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 18, 2004, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation. | |
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 10.35 | Change Order 40 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 11, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.31 to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.’s Registration Statement on Form S-4/A (SEC File No. 333-138916), filed on January 10, 2007). | |
| 10.36+ | Change Order 41 to Lump Sum Turnkey Engineering, Procurement and Construction Agreement dated December 11, 2006, between Sabine Pass LNG, L.P. and Bechtel Corporation. | |
| 10.37+ | Settlement and Purchase Agreement dated as of June 14, 2001, by and among Cheniere Energy, Inc., CXY Corporation, Crest Energy, L.L.C., Crest Investment Company and Freeport LNG Terminal, LLC, and two related letter agreements, each dated February 27, 2003. | |
| 10.38 | Letter regarding Assumption and Adoption of Obligations under Settlement and Purchase Agreement, dated May 9, 2005, and Indemnification Agreement, dated May 9, 2005, by Cheniere Energy, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.29 to Sabine Pass LNG, L.P.’s Registration Statement on Form S-4/A (SEC File No. 333-138916), filed on January 10, 2007). | |
| 10.39* | Form of Restricted Units Agreement for employees, consultants and directors (three-year). | |
| 10.40* | Form of Restricted Units Agreement for employees, consultants and directors (four-year). | |
| 10.41* | Form of Director Units Option Agreement for employees and consultants (four-year). | |
| 10.42* | Form of Units Option Agreement for employees and consultants (three-year). | |
| 10.43* | Form of Units Option Agreement for employees and consultants (four-year). | |
| 21.1+ | List of Subsidiaries of Cheniere Energy Partners, L.P. | |
| 23.1* | Consent of UHY LLP. | |
| 23.2* | Consents of Andrews Kurth LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1 and Exhibit 8.1). | |
| 23.3* | Consent of Stone & Webster Management Consultants, Inc. | |
| 23.4+ | Consent of Lon McCain to be named as a director. | |
| 23.5* | Consent of Robert J. Sutcliffe to be named as a director. | |
| 24.1+ | Powers of Attorney (included in signature pages). | |
| 24.2+ | Power of Attorney of Meg Gentle. | |
| + | Previously filed |
| * | Filed herewith |
| ** | To be filed by amendment. |